

DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.04.035
考虑轮轨周期性磨耗因素的滚动接触动态特性研究
吴丹,丁旺才,王鹏
(兰州交通大学 机电工程学院,甘肃 兰州,730070)
摘要:为探究轮轨周期性磨耗综合作用对轮轨动态相互作用力和接触蠕滑特性的影响,建立柔性轮轨下的车辆-轨道耦合动力学模型,通过现场实测车轮谐波磨耗和钢轨波磨,将轨道不平顺和3种钢轨波磨分别叠加得到3种轨道激励;以车轮谐波磨耗分别与3种轨道激励组合作为轮轨周期性磨耗工况,对比分析低速和高速下3种轮轨周期性磨耗工况作用下的滚动接触动态特性。研究结果表明:无论是在低速还是在高速下,轮轨垂向力最大值均出现在轮轨周期性磨耗工况一的钢轨波磨段,且在工况一作用下,垂向力相较于工况三的最大增幅达76.16%;而钢轨波磨对轮轨横向力的影响较小。在工况一作用下出现了2个高频振动峰值,且由钢轨波磨引起的振动频率比车轮谐波磨耗触发的激振频率大;轮轨周期性磨耗对纵向蠕滑力受速度的影响比较显著,对横向蠕滑力的影响不起主导作用;在工况一作用下,无论是低速还是高速,轮轨间接触斑面积均在钢轨波磨段出现最大值,且随速度增大,相较于工况三其增幅也随之增大;轮轨周期性磨耗中的残余波磨无论对轮轨动态相互作用力还是对轮轨间蠕滑特性的影响均较小。
关键词:车辆-轨道耦合动力学;车轮谐波磨耗;钢轨波磨;残余波磨;蠕滑力
中图分类号:U270.1 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
文章编号:1672-7207(2021)04-1389-10
Research on dynamic characteristics of rolling contact considering wheel-rail periodic wear
WU Dan, DING Wangcai, WANG Peng
(School of Mechanical Engineering, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, Lanzhou 730070, China)
Abstract: To investigate the influence of wheel-rail periodic wear on the dynamic interaction force and contact creep characteristics, a vehicles-track coupled dynamics model was established for the flexible wheel-rail. Through the field measured harmonic wear of wheel and rail corrugation, three kinds of orbital incentives were obtained by the superposition of orbit uneven and three kinds of rail track, respectively. The wheel harmonic wear separately combined with three kinds of orbit excitations was taken as wheel-rail periodic wear condition. The dynamic characteristics of rolling contact for three kinds of wheel-rail periodic wear under low-speed and high-speed corrugating condition were compared and analyzed. The results show that no matter at low-speed or high-speed, the maximum wheel-rail vertical force appears in the rail corrugation section under wheel-rail periodic wear condition 1, and the maximum increase of vertical force under operating condition 1 is up to 76.16% compared with operating condition 3. However, the rail corrugation has little effect on wheel-rail lateral force. During the operation of condition 1, there are two peaks of high frequency vibration, and the vibration frequency caused by rail corrugation is higher than that caused by wheel harmonic abrasion. The influence of wheel-rail periodic wear on longitudinal creep effort is significant, but it has no dominant influence on lateral creep effort. During the operation of condition 1, the contact spot area maximized in rail corrugation section at both low speed and high speed, and its increasing rate increases with the increase of speed compared with that in condition 3. The residual corrugation in the wheel-rail periodic wear has little effect on the dynamic interaction between wheel and rail and the creep characteristics between wheel and rail.
Key words: vehicle-track coupled dynamics; harmonic wear of wheel; rail corrugation; residual corrugation; creep effort
车辆-轨道耦合系统的振动特性直接影响动态轮轨力,使轮轨接触表面出现非均匀磨耗,进而出现车轮谐波磨耗以及钢轨波磨。同时,轮轨表面形成的钢轨波磨和车轮谐波磨耗又反作用于车辆-轨道系统,进一步加剧车辆-轨道系统的振动及疲劳损伤,威胁列车的行车安全[1]。1998年德国ICE高速列车发生脱轨事故,经调查研究,其原因是多边形橡胶弹性轮的接触载荷过大,使车轮轮辋断裂[2]。近几年,国内外动车组和地铁中普遍发现存在车轮谐波磨耗现象[3-4],国内外学者对此进行了大量科研工作,并取得了许多研究成果。周新建等[5]通过UM和ANSYS软件建立了刚性轮柔性轨下的车辆-轨道耦合动力学模型,分析了车轮谐波磨耗对轮轨蠕滑特性的影响。肖乾等[6]通过UM软件建立车辆-轨道耦合动力学模型,分析了轮轨振动行为下的轮轨接触特性,并研究了车轮谐波磨耗阶数和波深幅值对轮轨蠕滑力/率的影响。罗仁等[7]基于车辆-轨道耦合动力学模型分析了车轮谐波磨耗对车辆动力学性能的影响,发现车轮谐波磨耗阶数、波深幅值以及速度对轮轨作用力的影响显著。BOGACZ等[8]通过研究车轮谐波磨耗对轮轨间动力作用的影响,分析了刚性轮轨和柔性轮轨下的计算结果,认为柔性轮轨模型能更真实地反映轮轨振动关系,并发现考虑车轮谐波磨耗因素时速度对轮轨动态特性的影响最大。JOHANSSON等[9]根据轮轨接触FASTSIM算法,建立了多体系统轮轨耦合模型,通过数值迭代模拟时域内的轮轨动态相互作用,并以某地铁为例,分析了车轮谐波磨耗对轮轨动态特性的影响。刘国云等[10]通过建立刚柔耦合的车辆-轨道动力学模型,分析了钢轨波磨对轮轨的相互作用以及车辆系统振动响应的影响。宋小林等[11]以实测钢轨波磨作为轨道激励,基于车辆-轨道耦合动力学模型,分析了钢轨波磨对轮轨系统动力特性的影响。WANG等[12]基于车辆-轨道耦合动力学理论,分析了钢轨波磨的波长和波深幅值对轮轨动力相互作用的影响。宋志坤等[13]通过建立柔性轮轨下的车辆-轨道耦合动力学模型,研究了轮轨波磨综合作用下的轮轨振动特性。目前多是研究车轮谐波磨耗对轮轨间动力作用以及车辆动力学性能的影响,或钢轨波磨对轮轨动力相互作用的影响,而综合考虑车轮谐波磨耗和钢轨波磨因素对轮轨动态特性影响的研究较少,并且就轮轨周期性磨耗共同作用对轮轨蠕滑特性的影响研究很少,而轮轨周期性磨耗作用必然会造成轮轨接触斑内蠕滑特性发生改变,由于轮轨蠕滑特性不仅对列车的牵引及制动性能起决定作用,而且影响列车的横向稳定性和脱轨安全性。因此,研究考虑轮轨周期性磨耗因素对轮轨动力响应以及轮轨间接触蠕滑特性的影响具有重要的理论意义和工程应用价值。基于此,本文作者结合线路实测和动力学仿真计算,分析3种轮轨周期性磨耗工况下的车辆振动响应以及轮轨间蠕滑特性,为后续研究轮轨周期性磨耗的发生机理提供参考。
1 钢轨波磨和车轮谐波磨耗的测试及分析
1.1 钢轨波磨
钢轨波磨表现为沿钢轨纵向具有1个或多个特征波长的轨道不平顺,呈多处非连续性地分布于钢轨轨头表面。高速铁路钢轨波磨波长较短,在高速区,其波长一般为120~150 mm,波深幅值为0.04~0.08 mm;在低速区,其波长一般为60~80 mm,波深幅值一般大于0.1 mm[14-15]。根据现场勘查发现,线路钢轨波磨主要发生在站点附近的低速区,主要原因是列车的频繁加速、减速以及站点附近线路多表现为曲线半径小和坡度大,导致轮轨接触斑内黏着区和滑动区异常增大或减小。图1所示为现场实测徐兰高速上行线低速区K1 638+600―K1 636+640区段钢轨波磨特征,采用电子平直尺测量该区段的钢轨波磨,测量区段的曲线半径为1 200 m,缓和曲线长为130 mm,超高为100 mm,波磨表现为短波长准周期形态,经数据处理得到钢轨实测波磨图(见图2)。为对比分析钢轨波磨打磨前、后的轮轨振动响应以及蠕滑特性,测量了该路段刚打磨后的残余波磨。由GMC-96X钢轨打磨车打磨后的轨面状态如图3所示,实测残余波磨图如图4所示。

图1 上行某处钢轨下股纵向打磨前波磨
Fig. 1 Corrugation before longitudinal corrugating under rail somewhere uplink
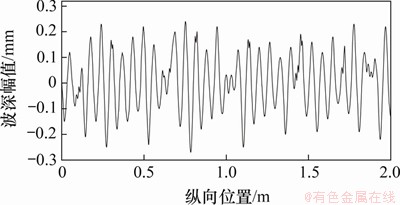
图2 实测钢轨波磨图
Fig. 2 Corrugation diagram of measured rail

图3 上行某处钢轨下股纵向打磨后轨面状态
Fig. 3 Rail surface state after longitudinal corrugating under rail somewhere uplink
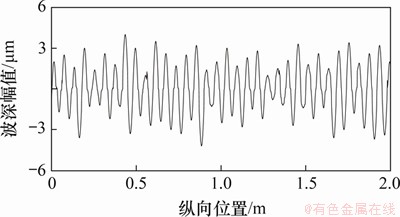
图4 实测钢轨残余波磨图
Fig. 4 Residual corrugation diagram of measured rail
1.2 车轮谐波磨耗
采用中德合资NSH-CTI公司生产的U2000-G400型不落轮机床对车轮进行谐波磨耗测试。测量时,由轮缘顶部自内向外测量,在车轮廓形上滑移的同时,保持磨耗测量头始终与轮对接触。测试现场如图5所示。

图5 车轮谐波磨耗测试现场
Fig. 5 Harmonic wear of wheel test site
图6所示为镟后15.8万km的车轮谐波磨耗实测结果。由图6可以看出:头车1位轮对的左轮和右轮在第20阶粗糙度幅值均明显增大,可知车轮谐波磨耗主要是由第20阶次主导。因此,在实际仿真计算中,可以将实际谐波磨耗处理成由20阶次主导的单一谐波激励。
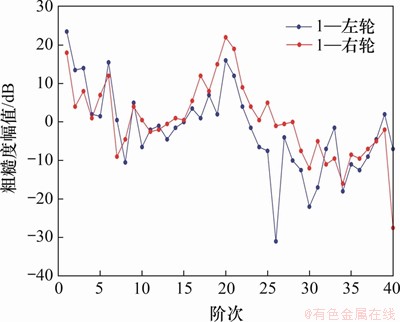
图6 车轮谐波磨耗阶次图
Fig. 6 Harmonic wear of wheel order diagram
2 车辆-轨道耦合动力学模型的建立
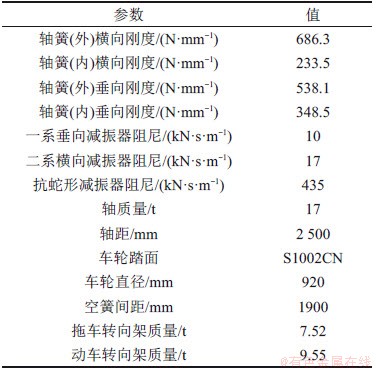
随动车组运行速度不断提高,轮轨间的激励频率由低频区逐渐向中高频区扩展,且轮轨间多因素耦合导致的车轮谐波磨耗以及钢轨波磨等不利因素存在,使列车在运营周期内不可避免地出现中高频振动响应,而多刚体系统动力学模型只适用于分析低频区响应。由于在车辆-轨道耦合系统中,车体振动通常处于低频区(5 Hz以下),转向架振动通常处于中低频区(40 Hz以下),悬挂系统振动主要集中于3 Hz以内,而轮轨振动主要集中在中高频区(30~120 Hz),当考虑轮轨不利因素造成的轮轨冲击时,由接触刚度引起的振动频率达400~1 200 Hz。因此,对车辆-轨道耦合振动主要分析轮轨之间的动态相互作用。基于刚柔耦合系统动力学理论[16],分析考虑轮轨系统弹性振动的影响,建立图7所示柔性轮轨下车辆-轨道耦合系统的动力学模型,其中车辆动力学模型主要参数如表1所示。

图7 柔性轮轨下车辆-轨道耦合动力学模型
Fig. 7 Dynamic model of vehicle-track coupled under flexible wheel and rail
表1 车辆动力学模型主要参数
Table 1 Main parameters of vehicle dynamics model
对轮对进行柔性化处理时,采用的方法是将轮对模型进行有限元离散,利用模态综合法获得轮对的主要振型。轨道结构柔性化时,钢轨视为离散弹性点支承基础上的无限长铁木辛柯梁,考虑垂向、横向以及扭转自由度,该梁模型能在高频区内求得更接近实际的振动特性。扣件被模拟成Bushing力元类型的特殊力,轨道板视为两端无约束的有限长自由梁,支承在连续分布的线性弹簧和阻尼上,其柔性轨道模型如图8所示。图8中:mr为钢轨的单位长度质量;mtb为轨道板的质量;Kph和Cph分别为轨下垫层及扣件对应的横向刚度和阻尼;Kpv和Cpv分别为轨下垫层及扣件对应的垂向刚度和阻尼;Ksh和Csh分别为轨道板与CA砂浆层间的横向刚度和阻尼;Ksv和Csv分别为轨道板与CA砂浆层间的垂向刚度和阻尼;φLr和φRr分别为左、右钢轨侧滚角;YLr和YRr分别为左、右钢轨横移量;ZLr和ZRr分别为左、右钢轨浮沉量。
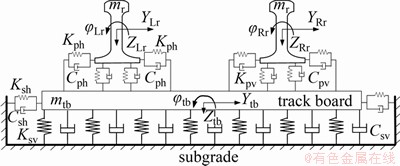
图8 柔性轨道模型
Fig. 8 Model of flexible track
3 轮轨周期性磨耗对车辆-轨道系统振动响应的影响
车轮谐波磨耗和钢轨波磨是轮轨关系众多不利因素中最为普遍和严重的激扰源,对列车运行稳定性、平稳性以及可靠性产生重大影响。为研究车轮谐波磨耗和钢轨波磨共同作用下即轮轨周期性磨耗下的轮轨动态相互作用力以及蠕滑特性,将轨道不平顺和3种钢轨波磨(实测波磨、实测残余波磨、无波磨)分别叠加得到3种轨道激励工况,以实测车轮谐波磨耗的主导阶次和幅值作为车轮谐波磨耗激励,分析不同轨道激励工况和车轮谐波磨耗综合作用下的轮轨动力响应。
3.1 轨道不平顺激励
经现场勘测发现,该线路区段主要表现出上股侧磨和下股波磨的情况,小曲线半径造成的钢轨侧磨对车辆系统动力学横向指标产生一定的影响,但考虑到该段线路的上股侧磨量很小,故重点考虑下股波磨以及轨道高低、轨向、轨距和水平不平顺对轮轨系统动态相互作用的影响。将实测徐兰高速线路轨道高低不平顺和钢轨波磨以及残余波磨数据分别进行拟合叠加,其中左股高低不平顺与钢轨波磨叠加后的不平顺激励如图9所示。
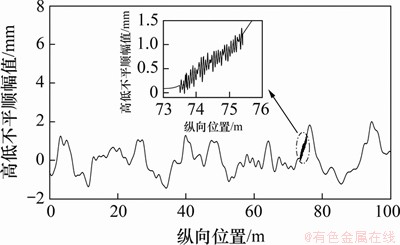
图9 轨道不平顺激励
Fig. 9 Irregularity excitation of track
3.2 轮轨动力响应分析
根据实测区段运营车辆的特征参数,在高速区,取车速为300 km/h;在低速区,取车速为150 km/h。基于车轮谐波磨耗的实测结果,取车轮谐波磨耗阶次为20阶,波深幅值为0.02 mm。以3种叠加合成的轨道不平顺(实测钢轨波磨与轨道不平顺的合成,实测残余波磨与轨道不平顺的合成,无波磨仅考虑轨道不平顺)作为轨道激励输入。以车轮谐波磨耗分别与3种轨道激励组合作为轮轨周期性磨耗工况,共3种工况。其中实测钢轨波磨段和残余波磨段出现在线路73.5~75.5 m处。通过计算得到1位轮对左轮在3种轮轨周期性磨耗工况下的轮轨垂向力时域图(图10)以及轮轨垂向力频域图(图11),其中最大轮轨垂向力见表2。
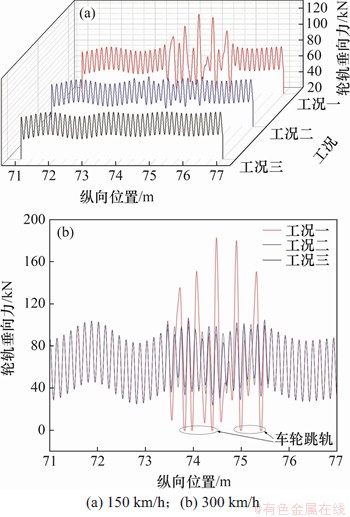
图10 轮轨垂向力时域图
Fig. 10 Time domain diagrams of vertical force
表2 轮轨周期性磨耗下的最大轮轨垂向力
Table 2 Maximum vertical force of wheel-rail periodic wear

由图10和表2可知:当速度为150 km/h时,在轮轨周期性磨耗工况一作用下的轮轨垂向力在钢轨波磨段明显比工况三的高,其增幅达51.03%,且整个区间内轮轨垂向力的最大值120.63 kN出现在钢轨波磨段,这表明钢轨波磨对轮轨垂向力的影响起主导作用;在工况二作用下引起的轮轨垂向力与工况三下的轮轨垂向力相差较小,增幅仅3.97%,表明残余波磨对轮轨垂向力的影响很小;当速度为300 km/h时,轮轨周期性磨耗对轮轨垂向力的影响规律与上述规律相似;但当速度为150 km/h时,3种工况下均未出现瞬时跳轨现象,而当速度为300 km/h时,在工况一下,纵向位置73.81,73.97,74.38,74.98和75.40 m处出现了跳轨现象,同时,该工况下的最大轮轨垂向力182.89 kN出现在钢轨波磨段,相较于工况三增幅达76.16%,而工况二下轮轨垂向力的最大值相较于工况三的增幅仅为2.68%。由此表明,当考虑轮轨周期性磨耗时,钢轨波磨随列车运行速度的提高对轮轨垂向力的影响明显增强,但无论是在低速还是高速下,残余波磨对轮轨垂向力的影响均较小。这表明经打磨车打磨合格(GQI指标达到优良)的钢轨,其表面的残余波磨对轮轨垂向力的影响可忽略不计。
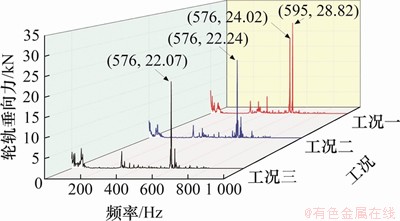
图11 300 km/h速度下的轮轨垂向力频域图
Fig. 11 Frequency domain diagram of vertical force at a speed of 300 km/h
图11所示为300 km/h速度下的轮轨垂向力频域图。由图11可知:当速度为300 km/h时,在轮轨周期性磨耗工况一作用下出现了2个高频振动峰值,分别由钢轨波磨和车轮谐波磨耗引起。其中车轮谐波磨耗引起的轮轨垂向力幅值在3种工况下均出现在576 Hz处,且最大幅值相差较小。在工况一作用下,由钢轨波磨引起的振动频率595 Hz比车轮谐波磨耗触发的激振频率576 Hz大,且轮轨垂向力幅值也表现出这一规律,其原因是钢轨波磨的波深幅值比车轮谐波磨耗的波深幅值大。而在工况二和工况三作用下,没有表现出明显的双高频振动分量,单一高频是由20阶车轮谐波磨耗产生的轮轨激励频率,该频率f也可通过下式进行计算:
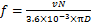 (1)
(1)
式中:N为车轮谐波磨耗阶数;v为车速;D为车轮滚动圆直径。
当v=300 km/h,D=920 mm时,20阶车轮谐波磨耗产生的轮轨激励频率为576.94 Hz。车轮谐波磨耗引起的轮轨垂向力的主频为576 Hz,与采用式(1)计算得到的激扰频率一致。
钢轨垂向振动加速度的时域图的动态响应特征与轮轨垂向力的类似。
通过计算得到1位轮对左轮在3种轮轨周期性磨耗工况下的轮轨横向力时域图,如图12所示。由图12可知:当速度为150 km/h时,在3种轮轨周期性磨耗工况作用下,轮轨横向力绝对值的最大值未出现在钢轨波磨段和残余波磨段,并且在钢轨波磨段工况一较工况三没有明显的增大,工况二在钢轨残余波磨段的轮轨横向力绝对值的最大值较工况三增幅更小,仅为0.91%;当速度为300 km/h时,在3种轮轨周期性磨耗工况作用下,轮轨横向力绝对值的最大值也未出现在钢轨波磨段和残余波磨段,这表明钢轨波磨和残余波磨对轮轨横向力的影响较小,该值主要由轨道不平顺主导。但在钢轨波磨段,轮轨横向力仍表现出考虑钢轨波磨时其值最大,无波磨时其值最小的特征。同时,随速度增大,钢轨波磨段的增幅也随之增大,并出现了跳轨现象。
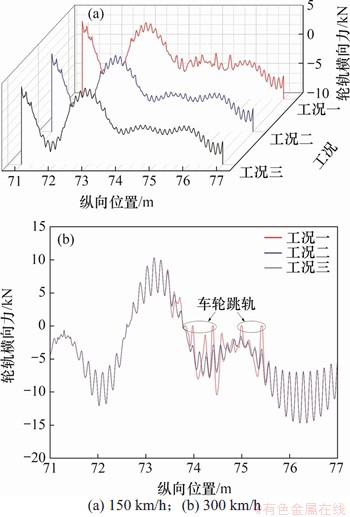
图12 轮轨横向力时域图
Fig. 12 Time domain diagrams of transverse forces
4 轮轨周期性磨耗对蠕滑特性的影响
动车组在运行过程中,其轮轨接触条件对轮轨间蠕滑特性影响较大。由上述分析可知,考虑轮轨周期性磨耗的轮轨动态响应明显增强,从而使轮轨接触条件复杂不利,进而影响轮轨间的蠕滑特性。因此,有必要分析考虑轮轨周期性磨耗下的轮轨蠕滑特性。
基于Kalker提出的轮轨滚动接触模型,采用FASTSIM算法计算得到了轮轨周期性磨耗作用下的轮轨纵向蠕滑力(图13)和横向蠕滑力(图14)。其中,各工况下的最大纵向蠕滑力和最大横向蠕滑力分别见表3和表4。
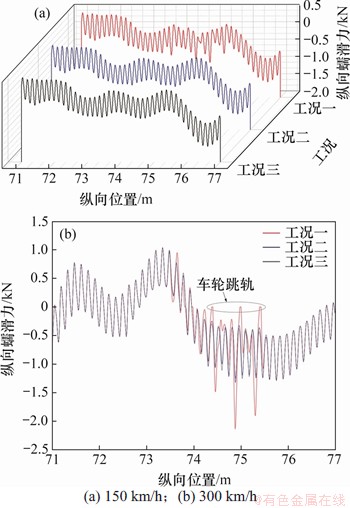
图13 轮轨周期性磨耗下的纵向蠕滑力
Fig. 13 Longitudinal creep force of wheel-rail periodic wear
表3 轮轨周期性磨耗下的最大纵向蠕滑力
Table 3 Maximum longitudinal creep force of wheel-rail periodic wear
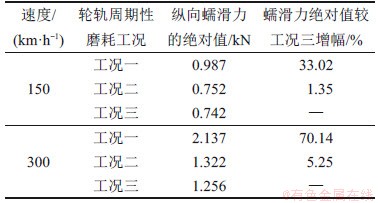
由图13和表3可知:当速度为150 km/h时,在轮轨周期性磨耗工况一作用下,钢轨波磨段的纵向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值较其余2种工况有明显增大,最大增幅达33.02%,但在整个区间内,轮轨纵向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值1.551 kN并未出现在钢轨波磨段。这表明钢轨波磨对轮轨纵向蠕滑力会产生影响,但不是主导因素;在工况二作用下,钢轨残余波磨段的纵向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值较工况三下的增幅较小,仅为1.35%,表明经打磨合格后的钢轨残余波磨对轮轨纵向蠕滑力的影响可忽略不计;当速度为300 km/h时,在工况一作用下,钢轨波磨段的纵向蠕滑力增幅明显增大,并且在整个区间内轮轨纵向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值2.137 kN出现在钢轨波磨段,相较于工况三其最大增幅达70.14%,并且出现了跳轨现象。这表明在高速下,钢轨波磨对纵向蠕滑力的影响很大;在工况二作用下,钢轨残余波磨段的纵向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值较工况三增幅较小,仅为5.25%,但仍表现出幅值随速度增大而增大的规律。由此可见,随速度增大,钢轨波磨对纵向蠕滑力的影响较大,而无论在高速区还是在低速区,残余波磨对纵向蠕滑力的影响都很小。
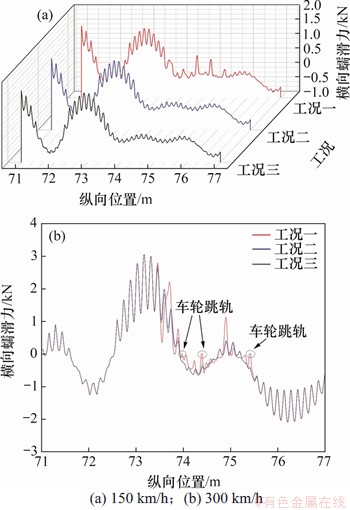
图14 轮轨周期性磨耗下的横向蠕滑力
Fig. 14 Transverse creep force of wheel-rail periodic wear
表4 轮轨周期性磨耗下的最大横向蠕滑力
Table 4 Maximum transverse creep force of wheel-rail periodic wear
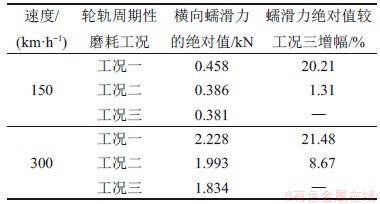
由图14和表4可知:当速度为150 km/h时,在轮轨周期性磨耗工况一作用下,钢轨波磨段横向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值为0.458 kN,相较于工况三增幅为20.21%。在工况二作用下,钢轨残余波磨段的横向蠕滑力与工况三下的横向蠕滑力相差不大,增幅仅1.31%。同时,整个区间上横向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值1.478 kN并未出现在钢轨波磨段和残余波磨段;当速度为300 km/h时,3种工况下的横向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值3.056 kN也未出现在钢轨波磨段和残余波磨段,但相较150 km/h时,3种工况下的幅值均出现明显增大;在工况一钢轨波磨段,横向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值为2.228 kN,相较于工况三增幅为21.48%,并且出现了跳轨现象;在工况二下,钢轨残余波磨段上横向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值相较于工况三增幅为8.67%。
综合分析3种轮轨周期性磨耗工况对横向蠕滑力的影响可知:无论在高速还是低速,横向蠕滑力绝对值的最大值均未出现在钢轨波磨段和残余波磨段,这表明钢轨波磨和残余波磨对横向蠕滑力会产生影响,但不起主导作用;同时,随速度增大,横向蠕滑力的增幅非常明显。
轮轨接触斑面积的计算结果如图15和表5所示。由图15和表5可知:在轮轨周期性磨耗工况一作用下,钢轨波磨段轮轨接触斑面积的最大值较工况三增幅明显,且呈现包络现象,其产生机理是轮轨周期性磨耗作用下车轮谐波磨耗在滚动若干个波长后,车轮谐波磨耗的波峰同钢轨波磨的波谷重合所致。在轮轨周期性磨耗工况一作用下,整个区间内的轮轨接触斑面积的最大值151.218 mm2出现在钢轨波磨段。工况二在钢轨残余波磨段的接触斑面积较工况三无明显变化,最大增幅仅1.99%;当速度为300 km/h时,随速度增大,3种轮轨周期性磨耗工况下轮轨接触斑面积较低速时均出现较大增幅。在工况一作用下的轮轨接触斑面积较工况三增幅达47.27%,且整个区间内接触斑面积的最大值201.170 mm2出现在钢轨波磨段,在轮轨周期性磨耗下车轮出现跳轨现象。在工况二作用下,钢轨残余波磨段相较于工况三的增幅不大,仅为3.98%,但高于低速时的增幅。
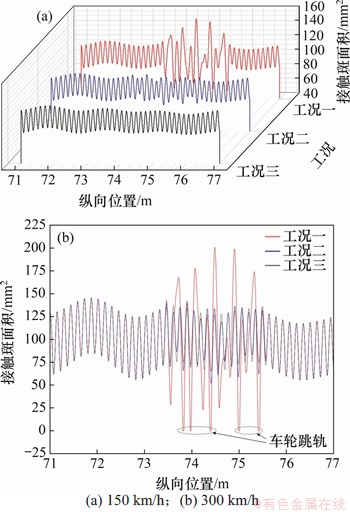
图15 轮轨周期性磨耗下的轮轨接触斑面积
Fig. 15 Wheel-rail contact areas of wheel-rail periodic wear
表5 轮轨周期性磨耗下的最大轮轨接触斑面积
Table 5 Maximum wheel-rail contact areas of wheel-rail periodic wear
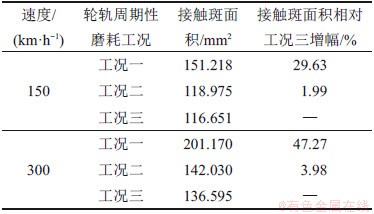
综合分析3种轮轨周期性磨耗工况对接触斑面积的影响可知:无论是在低速还是高速下,轮轨接触斑面积的最大值均发生在钢轨波磨段,这表明钢轨波磨对轮轨接触斑面积的影响非常显著,起主导作用。而残余波磨对接触斑面积的影响不大,但随速度增大,其增幅也出现增大的趋势。
5 结论
1) 无论是低速还是高速,轮轨动态相互作用力和轮轨滚动接触蠕滑特性均表现出随速度增大而增大的特征。并且在高速时,由于轮轨周期性磨耗的作用导致车轮出现了跳轨现象。
2) 相较于无波磨情况,轮轨垂向力受钢轨波磨的影响较大,且在低速和高速时,轮轨垂向力最大值均出现在钢轨波磨段,而钢轨波磨对轮轨横向力的影响较小。由钢轨波磨引起的振动频率595 Hz比车轮谐波磨耗触发的激振频率576 Hz大,且轮轨垂向力幅值也呈现出这一规律,其原因是钢轨波磨的波深幅值比车轮谐波磨耗的波深幅值大。
3) 相较于无波磨情况,在低速时,轮轨周期性磨耗引起的纵向蠕滑力的增幅为33.02%,而高速时,其增幅达70.14%,轮轨周期性磨耗对纵向蠕滑力受速度的影响比较显著。相对于纵向蠕滑力,无论在高速还是低速,横向蠕滑力的最大值均未出现在钢轨波磨段,钢轨波磨对横向蠕滑力的影响不起主导作用。钢轨波磨对轮轨接触斑面积的影响非常显著,起主导作用,且随速度增大,其增幅也随之增大。
4) 残余波磨无论对轮轨动态相互作用力还是轮轨间蠕滑特性的影响均很小。这表明钢轨经打磨合格后其残余波磨对行车安全没有影响。
参考文献:
[1] WU Xingwen, RAKHEJA S, QU Sheng, et al. Dynamic responses of a high-speed railway car due to wheel polygonalisation[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2018, 56(12): 1817-1837.
[2] LIU Xiaoyuan, ZHAI Wanming. Analysis of vertical dynamic wheel/rail interaction caused by polygonal wheels on high-speed trains[J]. Wear, 2014, 314(1/2): 282-290.
[3] WU Hao, WU Pingbo, LI Fansong, et al. Fatigue analysis of the gearbox housing in high-speed trains under wheel polygonization using a multibody dynamics algorithm[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2019, 100: 351-364.
[4] JIN Xuesong, WU Lei, FANG Jianying, et al. An investigation into the mechanism of the polygonal wear of metro train wheels and its effect on the dynamic behaviour of a wheel/rail system[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2012, 50(12): 1817-1834.
[5] 周新建, 肖乾, 程树, 等. 柔性轨道下高速列车车轮谐波磨耗对轮轨滚动接触蠕滑特性的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2017, 38(4): 84-91.
ZHOU Xinjian, XIAO Qian, CHENG Shu, et al. Influence of wheel harmonic wear of high speed train on creep characteristics of wheel-rail rolling contact under flexible track[J]. China Railway Science, 2017, 38(4): 84-91.
[6] 肖乾, 程树, 张海, 等. 车轮谐波磨耗对直线线路上高速轮轨接触蠕滑特性的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2016, 37(6): 60-68.
XIAO Qian, CHENG Shu, ZHANG Hai, et al. Influence of wheel harmonic wear on creep characteristics of high speed wheel-rail contact on straight line[J]. China Railway Science, 2016, 37(6): 60-68.
[7] 罗仁, 曾京, 邬平波, 等. 高速列车车轮不圆顺磨耗仿真及分析[J]. 铁道学报, 2010, 32(5): 30-35.
LUO Ren, ZENG Jing, WU Pingbo, et al. Simulation and analysis of wheel out-of-roundness wear of high-speed train[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2010, 32(5): 30-35.
[8] BOGACZ R, FRISCHMUTH K. On dynamic effects of wheel-rail interaction in the case of polygonalisation[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 79: 166-173.
[9] JOHANSSON A, ANDERSSON C. Out-of-round railway wheels-a study of wheel polygonalization through simulation of three-dimensional wheel-rail interaction and wear[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2005, 43(8): 539-559.
[10] 刘国云, 曾京, 张波. 钢轨波磨对高速车辆振动特性的影响[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(6): 137-143.
LIU Guoyun, ZENG Jing, ZHANG Bo. Influence of rail corrugation on high-speed vehicle vibration performances[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(6): 137-143.
[11] 宋小林, 翟婉明, 王开云. 波磨对轮轨系统动力特性的影响分析[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2018, 39(5): 42-50.
SONG Xiaolin, ZHAI Wanming, WANG Kaiyun. Effect of rail corrugation on dynamic properties of wheel-rail system[J]. China Railway Science, 2018, 39(5): 42-50.
[12] WANG Kaiyun, LIU Pengfei, ZHAI Wanming, et al. Wheel/rail dynamic interaction due to excitation of rail corrugation in high-speed railway[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2015, 58(2): 226-235.
[13] 宋志坤, 侯银庆, 胡晓依, 等. 柔性轮轨下轮轨波磨综合作用的振动特性研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2018, 40(11): 33-40.
SONG Zhikun, HOU Yinqing, HU Xiaoyi, et al. Research on vibration characteristics of wheel-rail corrugation under flexible wheel and rail[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(11): 33-40.
[14] 谷永磊, 赵国堂, 金学松, 等. 高速铁路钢轨波磨对车辆-轨道动态响应的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2015, 36(4): 27-31.
GU Yonglei, ZHAO Guotang, JIN Xuesong, et al. Effects of rail corrugation of high speed railway on vehicle-track coupling dynamic response[J]. China Railway Science, 2015, 36(4): 27-31.
[15] 姜子清, 司道林, 李伟, 等. 高速铁路钢轨波磨研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2014, 35(4): 9-14.
JIANG Ziqing, SI Daolin, LI Wei, et al. On rail corrugation of high speed railway[J]. China Railway Science, 2014, 35(4): 9-14.
[16] 金学松. 轮轨蠕滑理论及其试验研究[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2006: 16-43.
JIN Xuesong. Theory and experimental study of wheel and rail creep[M]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University Press, 2006: 16-43.
(编辑 刘锦伟)
收稿日期: 2020 -06 -07; 修回日期: 2020 -08 -18
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(11962013, 11732014);甘肃省高等学校创新基金资助项目(2020B-110);兰州交通大学青年科学基金资助项目(2017011) (Projects(11962013, 11732014) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2020B-110) supported by the University Innovation Fund of Gansu Province; Project(2017011) supported by the Young Scholars Science Foundation of Lanzhou Jiaotong University)
通信作者:丁旺才,博士,教授,从事车辆系统动力学和非线性动力学研究;E-mail:dingwc@mail.lzjtu.cn
引用格式: 吴丹, 丁旺才, 王鹏. 考虑轮轨周期性磨耗因素的滚动接触动态特性研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(4): 1389-1398.
Citation: WU Dan, DING Wangcai, WANG Peng. Research on dynamic characteristics of rolling contact considering wheel-rail periodic wear[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2021, 52(4): 1389-1398.