镁基大块非晶合金在过冷液相区流变行为本构关系
程 明1, 张士宏1, J.A.Wert2
(1. 中国科学院 金属研究所, 沈阳 110016;
2. Ris国家实验室, Roskilde DK-4000, 丹麦)
摘 要: 研究了Mg60Cu30Y10大块非晶合金在过冷液相区的流变行为。 结果表明: 随着温度升高和应变速率增加, 平衡态的牛顿流转变为非平衡态的非牛顿流; 其流变行为对于温度和应变速率非常敏感。 由粘度与应变速率的关系, 根据Arrhenius型VFT方程, 确定了流动应力、 应变速率和温度的关系。 Mg60Cu30Y10大块非晶合金在过冷液相区的流变性能依赖于温度与变形速率, 其微观机制可由自由体积模型解释, 为大块非晶合金流变成形工艺的实现提供理论依据: 温度高于玻璃转变温度以后, 自由体积的增加使非晶合金变形过程中能够移动的原子数目随之增加, 自由体积周围的原子沿外力的作用方向移动, 即宏观上的塑性流变行为。 应变速率增加, 由热激活引起的自由体积增加不能满足更多原子流变所需的空间体积, 导致牛顿流向非牛顿流转变。
关键词: 镁基大块非晶; 过冷液相区; 流变行为; 本构关系 中图分类号: TG139.8
文献标识码: A
Constitutive equation for viscous flow behavior of Mg-based bulk metallic glass in supercooled liquid region
CHENG Ming1, ZHANG Shi-hong1, J.A.Wert2
(1. Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China;
2. Ris National Laboratory, Roskilde DK-4000, Denmark)
Abstract: Viscous flow behavior of Mg60Cu30Y10 bulk metallic glass in supercooled liquid region was investigated. The supercooled liquids exhibit that Newtonian viscosity in equilibrium state transforms to a non-Newtonian viscosity in non-equilibrium state with temperature and strain rate increasing. According to VFT (Vogel-Fulcher-Tammann) equation with the Arrhenius function, the relation between flow stress and viscosity and temperature was established. Viscous flow of Mg60Cu30Y10 bulk metallic glass depends on temperature and strain rate. It can be described with the free-volume model and used to interpret the implement of Mg-based bulk metallic glass viscous forming process. When the temperature is higher than glass transition temperature, the number of atoms which can jump during deformation of bulk metallic glass increases. Atomic jumps are biased in the direction of the external force. This forms the plastic flow showed in macroscopic. With strain rate increasing, free volume obtained from thermal fluctuations cant meet the need of more and more atomic jumps. It results in steady state Newtonian viscosity transfer to non-Newtonian viscosity.
Key words: Mg-based bulk metallic glass; supercooled liquid region; viscous flow behavior; constitutive equation
20世纪90年代以来人们发现并深入研究了一系列在结晶前具有宽过冷液相区的大块非晶合金, 如Mg 基、 Zr基、 La基、 Pd基和Cu基等。 其中大块非晶合金在过冷液相区的结构与力学性能受到广泛关注。 Chu等[1, 2]对Pd40Ni40P20和Zr55Al10Cu30-Ni5大块非晶合金在过冷液相区的变形行为进行了实验研究。 Reger-Leonhard等[3]研究了Zr55Cu30-Al10Ni5大块非晶合金在玻璃转变温度附近的牛顿粘性流动和变形后的组织变化。 Nieh等[4]研究了Zr52.5Al10Ti5Cu17.9Ni14.6大块非晶合金在过冷液相区的变形行为及非晶结构的变形机理。 Wei等[5]研究了Nd60Fe20Co10Al10大块非晶合金从室温直到723 K的变形行为。 Wang等[6]研究了完全非晶和部分晶化的Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5(Vit1)大块非晶合金的均匀塑性流动。 Kato等[7]提出恒速率变形条件下Pd40Ni40P20大块非晶合金的应力—应变曲线模型, 同时反映了线性与非线性粘塑性行为。 Perera等[8]研究了从热分析和力学实验得到的Zr42.1-Ti12.9Cu11.5Ni10.2Be23.3大块非晶合金的脆性指数, 并与其他两种热稳定性稍逊的Pd48Ni32P20和Pt60Ni15P25大块非晶合金的脆性指数进行比较, 3种合金显示出不同的动力学行为。 Kawamura等[9-12]研究了过冷液态La55Al25Ni20、 Zr65Al10Ni10-Cu15 、 Pd40Ni40P20 和Fe72Hf8Nb2B18大块非晶合金在宽的应变速率范围内的粘度、 变形行为等。 沈等[13]综述了大块非晶合金过冷液相区内流变力学及变形机制的研究状况, 指出大块非晶合金的粘滞流变是一种非晶相-晶化相复相结构的变形行为, 相关研究将会沿着结构转变与流变力学行为相结合的方向继续前进。
本文作者在研究了Mg60Cu30Y10大块非晶合金在过冷液相区的流变行为的基础上, 根据Arrhenius型VFT方程, 确定流动应力、 应变速率和温度的关系, 并用自由体积模型解释其微观机制。
1 镁基大块非晶合金在过冷液相区的流变行为及本构关系
过冷液相区是指从大块非晶合金的玻璃转变温度到结晶温度之间的温度区间。 在此温度区域内, 大块非晶合金具有特殊的结构状态和力学特性, 其流变行为对于温度和应变速率非常敏感。
图1所示为Mg60Cu30Y10大块非晶合金流动应力与应变速率和温度的关系[12]。 室温值表示压缩断裂强度, 用开环表示。 其它点表示流动应力。 图中三角形斜率表示的应变速率敏感指数(m), 在420K和430K实验应变速率范围内约为0.3; 在更高的温度区间m值趋近于1, 表明在440K以上为理想牛顿流。 这与文献[14]中DSC确定的437K的玻璃转变温度吻合得很好。

图1 Mg60Cu30Y10合金流动应力与应变速率和温度的关系[12]
Fig.1 Flow stress as function of strain rate and temperature for Mg60Cu30Y10 alloy
图2所示为不同温度下Mg60Cu30Y10合金粘度与应变速率的关系。 粘度η根据下式计算:
η=σflow/3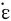 (1)
(1)
式中 σflow为流动应力; 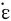 为应变速率。
为应变速率。
在低于437K时非晶合金处于玻璃固态, 随着应变速率增加, 粘度降低, 表现为非牛顿流。 在过冷液态区间, 低应变速率下表现为粘度与应变速率无关的牛顿流。 在较高的应变速率下, 粘度降低, 表现为牛顿流向非牛顿流的转变。 非晶合金在过冷液相区的粘度可以表示为一条通用曲线。 在每一个温度下, 粘度η先用牛顿粘度η0规格化。 规格化后的粘度再进行二次变换, 转变为靠近非晶合金Tg的一个参考温度的曲线。 应变速率的转换因子定义为αT=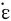 m/
m/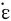 , 其中
, 其中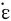 m为通用曲线上的应变速率。 平衡态粘度可以表示为Vogel-Fulcher-Tammann (VFT) 关系:
m为通用曲线上的应变速率。 平衡态粘度可以表示为Vogel-Fulcher-Tammann (VFT) 关系:

式中 η*0和A为拟合参数; T0为VFT温度。
在Tg临近温度区间的粘度与Arrhenius型方程符合得很好。 牛顿粘度可以近似表示为
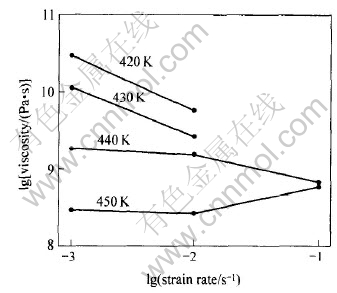
图2 Mg60Cu30Y10合金粘度与应变速率和温度的关系
Fig.2 Viscosity as function of strain rate and temperature for Mg60Cu30Y10 alloy
η0=Bexp[H/(RT)](3)
式中 B为拟合参数; H为激活能; R为摩尔气体常数。
转换因子可以近似表示为Arrhenius型方程:
αT=Cexp[H*/(RT)](4)
式中 C为拟合参数; H*为激活能。
通用曲线可以近似表示为扩展指数方程:

式中 D和β为拟合参数。
由此可以得到Tg临近温度范围内过冷液态流体粘度表达式:

综合式(1)和式(6), 确定流动应力、 应变速率和温度的关系为
2 镁基大块非晶合金在过冷液相区流变行为的微观机制
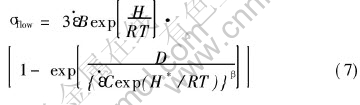
非晶相中不存在晶界和位错结构, 其原子排布中存在自由体积(free-volume)。 Spaepen认为稳态非均匀流的微观机理在于由应力驱动生成与扩散湮灭达到动态平衡的结构无序[15]。 图3所示为非晶合金变形过程中原子移动示意图。 其中, V为自由
图3 非晶合金变形过程原子移动示意图[13]
Fig.3 Illustration of individual atomic jump during viscous flow of metallic glass
体积; V*为原子体积, G为原子自由能, λ为原子的跃迁距离(约为1个原子半径)。
宏观流动的发生是一定数量单个原子跃迁的结果。 单个原子要实现跃迁, 首先在靠近它的临近环境必须存在一个足够大的空位来容纳它的原子体积V*(基于硬球模型)。 如果跃迁前后原子位于相对稳定的位置, 则局部自由能最小。 为了实现原子跃迁, 还必须提供足够的运动激活能ΔGm。 如果没有额外能量的存在, 它将通过热激活来获得。 越过能量壁垒的跃迁的数目在各个方向都相同。 这就是扩散(Diffusion)的基本微观机理。 在施加了一个额外的力, 如剪应力的情况下, 原子跃迁偏于施力方向。 穿过能量势垒向前跃迁的数目多于向后跃迁的数目, 这样导致向前原子的净通量, 形成流动(Flow)的基本机制。
在温度高于玻璃转变温度以后, 自由体积的增加使能够移动的原子数目随之增加。 外力τ的作用, 使自由体积周围的原子沿τ的作用方向移动, 故宏观上产生了常温时大块非晶合金所不能出现的塑性流变行为[16], 即过冷液态的Mg60Cu30Y10大块非晶合金在低应变速率下的牛顿粘性(平衡态)。
随着外力τ增加, 非晶相的变形速率随之增加, 这就需要更多数量的原子参与流变过程。 而由于热激活引起的自由体积增加已经不能满足更多原子流变所需的空间体积, 过冷液态的Mg60Cu30Y10大块非晶合金宏观表现为随应变速率增加导致的从牛顿流向非牛顿流的转变, 非牛顿流对应着非平衡状态。 一个原子要成为潜在的跃迁位置, 它的自由体积必须大于它的原子体积。 如图3(b)所示, 由于V〈V*, 外力τ作用于非晶相的能量τΩ不仅使原子移动后产生ΔG的自由能差, 而且还有一部分能量用于把更多的原子“挤入”原子间的空位内, 使自由体积周围的原子向外膨胀。 因此τΩ中的一部分能量转变为部分原子的弹性扭曲能ΔGe, 以产生新的自由体积来参与流变过程。
上述研究表明, 应用自由体积模型来考察大块非晶合金在过冷液相区内的结构状态和力学特性, 能够为大块非晶合金流变成形工艺的实现提供理论依据。
3 结论
1) 研究了Mg60Cu30Y10大块非晶合金在过冷液相区的流变行为: 随着温度升高和应变速率增加, 平衡态的牛顿流转变为非平衡态的非牛顿流, 其流变行为对于温度和应变速率非常敏感。
2) 根据Arrhenius型VFT方程, 确定流动应力、 应变速率和温度的关系。
3) Mg60Cu30Y10大块非晶合金在过冷液相区的流变性能依赖于温度与变形速率, 其微观机制可由自由体积模型解释, 这为大块非晶合金流变成形工艺的实现提供理论依据。
REFERENCES
[1]Chu J P, Chiang C L, Nieh T G, et al. Superplasticity in a bulk amorphous Pd-40Ni-20P alloy: a compression study[J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10: 1191-1195.
[2]Chu J P, Chiang C L, Mahalingam T et al. Plastic flow and tensile ductility of a bulk amorphous Zr55Al10-Cu30Ni5 alloy at 700K[J]. Scripta Mater, 2003, 49: 435-440.
[3]Reger-Leonhard A, Heilmaier M, Eckert J. Newtonian flow of Zr55Cu30Al10Ni5 bulk metallic glassy alloys[J]. Scripta Mater, 2000, 43: 459-464.
[4]Nieh T G, Wadsworth J, Liu C T, et al. Plasticity and structural instability in a bulk metallic glass deformed in the supercooled liquid region[J]. Acta Mater, 2001, 49: 2887-2896.
[5]Wei B C, Yu G S, Lser W, et al. Deformation behavior and dilatometric measurement of Nd-Fe based bulk metallic glass[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, A375-377: 1161-1164.
[6]Wang Q, Blandin J J, Suery M, et al. Homogeneous plastic flow of fully amorphous and partially crystallized Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 bulk metallic glass[J]. J Mater Sci Technol, 2003, 19(6): 557-560.
[7]Kato H, Kawamura Y, Inoue A, et al. Modeling of stree-strain curves for Pd40Ni10Cu30P20 glass alloy under constant strain-rate deformation[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, A304-306: 758-762.
[8]Perera D N, Tsai A P. Thermal and viscoelastic properties of a strong bulk metallic glass former[J]. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2000, 33: 1937-1946.
[9]Kawamura Y, Inoue A. Newtonian viscosity of supercooled liquid in a Pd40Ni40P20 metallic glass[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2000, 77(8): 1114-1116.
[10]Kawamura Y, Nakamura T, Inoue A, et al. High-strain-rate superplasticity due to Newtonian viscous flow in La55Al25Ni20 metallic glass[J]. Mater Trans JIM, 1999, 40(8): 794-803.
[11]Kawamura Y, Shibata T, Inoue A, et al. Superplastic deformation of Zr65Al10Ni10Cu15[J]. Scripta Mater, 1997, 37(4): 431-436.
[12]Kawamura Y, Itoi T, Nakamura T, et al. Superplasticity in Fe-based metallic glass with wide supercooled liquid region[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, A304-306: 735-739.
[13]沈军, 孙剑飞, 王刚, 等. 大块非晶合金过冷液相区的超塑性流变行为[J]. 材料导报, 2004, 18(7): 22-25.
SHEN Jun, SUN Jian-fei, WANG Gang, et al. Superplastic flow behavior of bulk metallic glasses in supercooled liquid region[J]. Materials Review, 2004, 18(7): 22-25.
[14]Wert J A, Pryds N, Zhang E. Rheological properties of a Mg60Cu30Y10 alloy in the supercooled liquid state[A]. Proceedings of the 22nd Ris International Symposium on Materials Science[C]. Roskilde, Denmark: Ris National Laboratory, 2001. 423.
[15]Spaepen F. A microscopic mechanism for study state inhomogeneous flow in metallic glasses[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1977, 25: 407-415.
[16]沈军, 王刚, 孙剑飞, 等. Zr基块体非晶合金在过冷液相区的超塑性流变行为[J]. 金属学报, 2004, 40(5): 518-522.
SHEN Jun, WANG Gang, SUN Jian-fei, et al. Superplastic flow behavior of Zr base bulk metallic glass in supercooled liquid region[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2004, 40(5): 518-522.
(编辑陈爱华)
收稿日期: 2005-07-15; 修订日期: 2005-08-20
作者简介: 程 明(1976-), 男, 博士研究生
通讯作者: 张士宏, 研究员; 电话: 024-83978266; E-mail: shzhang@imr.ac.cn