文章编号:1004-0609(2013)S1-s0257-05
Ti60合金保载疲劳行为的准原位观察
杨丽娜,刘建荣,王清江,杨 锐
(中国科学院 金属研究所,沈阳 110016)
摘 要:利用激光共聚焦显微镜、扫描电子显微镜以及电子背散射衍射(EBSD)技术观察Ti60合金在高应力水平下的保载疲劳损伤行为。通过激光共聚焦显微镜观察发现,随着循环周次的增加,初生α相内产生的滑移线数量及滑移带宽度均有增加。EBSD分析结果表明,循环1 000周次后,观察到部分α晶粒发生偏转,材料的织构强度增加,织构类型发生变化。由于晶粒软硬取向不同,材料中发生应力重新分配现象,各晶粒之间产生协调作用,硬取向晶粒发生偏转,出现织构增强的特征。SEM观察到保载疲劳断口裂纹源处存在大量准解理小平面。
关键词:Ti60合金;保载疲劳;电子背散射衍射(EBSD);原位观察;显微组织
中图分类号:TF804.3 文献标志码:A
In-situ observation of dwell fatigue of Ti60 alloy
YANG Li-na, LIU Jian-rong, WANG Qing-jiang, YANG Rui
(Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China)
Abstract: The dwell fatigue damage behavior and deformation mechanism of Ti60 alloy were studied using laser scanning confocal microscope, SEM and EBSD. It is found that, with the increase of cycles, the amount and width of slip band in primary α phase increase. The EBSD results show that, after 1 000 cycles, partial α grains turn angles. The intensity and type of texture are changed. Because of different orientations of grains, the stress redistribution exists in materials. Strong grains turn angles and the textures are strengthened. The SEM observation exhibits that the quasi-cleavage facets form on the fracture surface.
Key words: Ti60 alloy; dwell fatigue; EBSD; in-situ observation; microstructure
钛合金由于具有密度小、比强度高、耐蚀、耐热等优点,在航空航天等领域得到广泛应用[1]。随着航空航天事业的发展,钛合金的使用温度逐步提高[2-4]。Ti60合金是中国科学院金属研究所设计的一种Ti-Al- Sn-Zr-Mo-Nb-Ta-Si系多元复合强化的高温钛合金,长时使用温度为600 ℃,它兼具α型钛合金优异的蠕变性能和α+β型钛合金的高强度,热强性、抗氧化性和热稳定性匹配良好[5]。该合金拟用于我国新型发动机叶片、轮盘等部位,以提高推重比[6]。
发动机盘件在服役过程中受与保载疲劳相似载荷,与传统三角波载荷相比,在相同峰值应力和应力比条件下,保载疲劳载荷下疲劳寿命明显偏低。提高飞行器的安全可靠性和耐久性是避免发生飞行事故的关键[7-9],研究高温钛合金材料的保载疲劳行为对发动机盘件安全可靠性具有重要意义。本文作者利用EBSD技术,对Ti60合金保载疲劳实验过程进行准原位观察,分析了显微组织中晶体取向的变化和保载疲劳载荷下Ti60合金疲劳寿命降低的损伤机理,为改善材料的保载疲劳性能提供基础依据。
1 实验
实验所用的材料为Ti60合金,名义成分为Ti-5.8Al-4.0Sn-3.5Zr-0.4Mo-0.4Si-0.4Nb-1.0Ta-0.05C。实验材料为钛合金锻件,相变点为(1 045±5) ℃,采用固溶+时效的双重热处理制度,即在两相区1 005 ℃固溶处理2 h后,再在700 ℃保温2 h后空冷到室温。金相试样经150号 SiC砂纸粗磨→精磨→机械抛光→化学腐蚀后,在MEF4A光学显微镜上进行金相观察,金相显微组织如图1所示,其特点是白色等轴初生α相颗粒镶嵌在β转变组织基体内,其体积分数为15%左右。
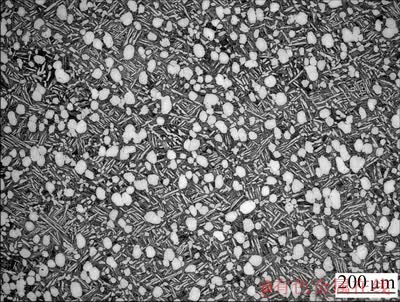
图1 Ti60合金的金相组织
Fig. 1 Microstructure of Ti60 alloy
疲劳实验在100 kN液压伺服MTS810疲劳试验机上进行,采用应力控制,并在室温大气条件下进行。图2所示为保载疲劳梯形波,加载和卸载时间均为2 s,峰值应力处保持2 min。对实验样品施加880 MPa载荷(材料的屈服强度为970 MPa),应力比R为0.1。当循环周次分别达到100、300、500、1 000周以及断裂失效时,将样品取下,利用EBSD技术对样品平行段上同一区域内晶体取向变化进行观测;利用激光共聚焦显微镜观察该区域内产生的滑移带特征及其与循环周次的关系。
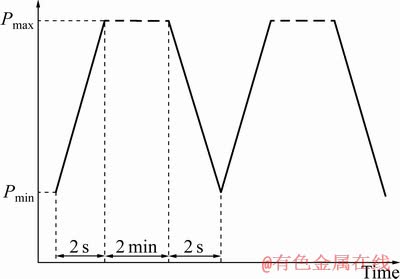
图2 保载疲劳梯形波形
Fig. 2 Waveform of dwell fatigue
2 结果与讨论
2.1 Ti60合金滑移变形观察
利用激光共聚焦显微镜观察Ti60合金试样中形成的滑移带随着保载疲劳循环的变化情况,如图3所示。由图3可见,当循环加载100周次时,初生α晶粒内可观察到滑移线,但数量较少。随着循环周次的增加,滑移线数量增多,滑移线变宽,表明形成滑移带,同一晶粒内可观察到多个滑移系启动;随着循环周次的进一步增加,累积塑性变形增加,滑移线数量增多,滑移带继续变宽,形成微裂纹。微裂纹的扩展和贯通导致了材料发生断裂失效。
2.2 Ti60合金晶体取向观察
利用EBSD技术观察试样在疲劳100、300、500和1 000周后显微组织中微织构的变化特征,如图4所示。对试样平行段上同一区域观察得到的反极图结果显示,保载试样在循环500周次以前,α晶粒的 (0001)基面与锻件弦向约成10°夹角以及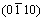 晶面与锻件弦向约成13°夹角,织构强度较弱,仅为4.5左右;当试样循环至1 000周次时,发现部分α晶粒发生偏转,经过10°左右的倾转,得到(0001)基面及
晶面与锻件弦向约成13°夹角,织构强度较弱,仅为4.5左右;当试样循环至1 000周次时,发现部分α晶粒发生偏转,经过10°左右的倾转,得到(0001)基面及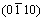 晶面与锻件弦向垂直的织构,且织构强度增加,达到8.22。这是由于Ti60合金中不同取向的晶粒具有不同的弹性模量,所以在变形过程中会发生软、硬取向晶粒应力重新分配的现象。材料协调变形使部分硬取向晶粒发生了偏转。
晶面与锻件弦向垂直的织构,且织构强度增加,达到8.22。这是由于Ti60合金中不同取向的晶粒具有不同的弹性模量,所以在变形过程中会发生软、硬取向晶粒应力重新分配的现象。材料协调变形使部分硬取向晶粒发生了偏转。
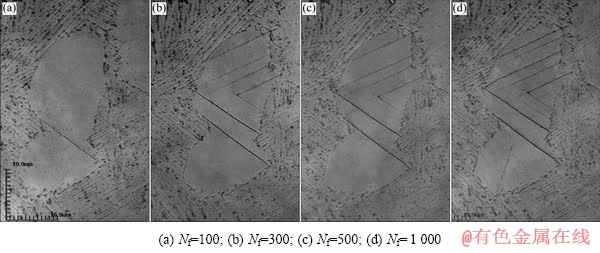
图3 保载疲劳过程中滑移带随循环周次的演变过程
Fig. 3 Observation of slip band under dwell fatigue waveform after different cycles
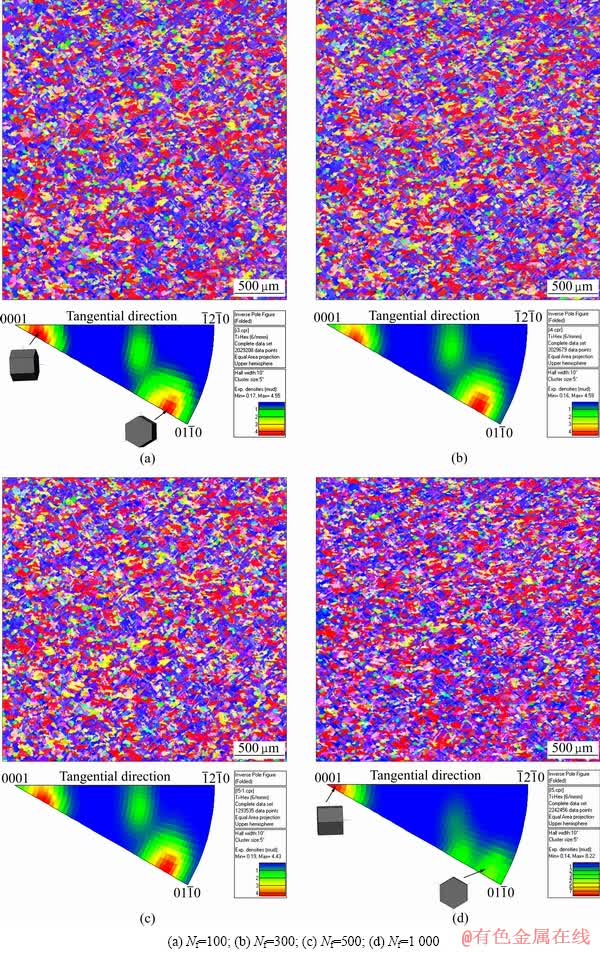
图4 保载疲劳过程中反极图观察
Fig. 4 Inverse pole figures during dwell fatigue after different cycles
2.3 断口特征
利用扫描电镜观察保载疲劳试样断口形貌,如图5所示。图5(a)所示为疲劳断口宏观形貌的SEM像,可以看出,疲劳裂纹源在试样内部。图5(b)所示为裂纹源区放大后观察到的准解理小平面,小平面尺寸与等轴初生α相的尺寸接近。类似的断口特征在IMI685[10]、Ti6242[11]、IMI834[12]、IMI829[13]等合金中也可以观察到。结合图3可知,准解理小平面的形成是由于滑移带处由于疲劳损伤使晶粒发生逐渐分离导致,而非脆性断裂。
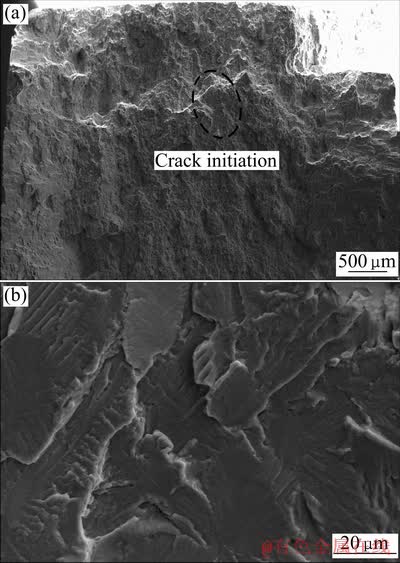

图5 保载疲劳裂纹源的SEM像
Fig. 5 SEM images crack initiation site under dwell fatigue
3 结论
1) 保载疲劳过程中,在初生α晶粒内产生滑移,且随着循环周次的增加,滑移线数量增多,滑移带宽度增加,且发生多滑移现象。
2) 保载疲劳循环在1 000周次以下时,材料的微织构类型以及强度无明显变化;当超过1 000周次,且接近疲劳断裂时,晶粒发生偏转,微织构强度增加。
3) 保载疲劳裂纹在样品内部萌生,断口表面可观察到准解理小平面。
REFERENCES
[1] 李 梁, 孙建科, 孟祥军. 钛合金超塑性研究及应用现状[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2004, 19(6): 34-38.
LI Liang, SUN Jian-ke, MENG Xiang-jun. Research progress and application of superplasticity of titanium alloys [J]. Development an Application of Materials, 2004, 19(6): 34-38.
[2] 许国栋, 王凤娥. 高温钛合金的发展和应用[J]. 稀有金属, 2008, 32(6): 774-780.
XU Guo-dong, WANG Feng-e. Development and application of high temperature titanium alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2008, 32(6): 774-780.
[3] 付艳艳, 宋月清, 惠松骁, 米绪军. 航空用钛合金的研究与应用进展[J]. 稀有金属, 2006, 30(6): 850-856.
FU Yan-yan, SONG Yue-qing, HUI Song-xiao, MI Xu-jun. Research and application of typical aerospace titanium alloy [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2006, 30(6): 850-856.
[4] 钱九红. 航空航天用新型钛合金的研究发展及应用[J]. 稀有金属, 2000, 24(3): 218-223.
QIAN Jiu-hong. Application and development of new titanium alloys for aerospace [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2000, 24(3): 218-223.
[5] 王清江, 刘建荣, 杨 锐, 魏寿庸, 刘羽寅, 陈占乾, 王鼎春, 高 颀. 一种高热强性、高热稳定性的高温钛合金: 中国, ZL200710011771.0[P]. 2008-01-16.
WANG Qing-jiang, LIU Jian-rong, YANG Rui, WEI Shou-yong, LIU Yu-yin, CHEN Zhan-qian, WANG Ding-chun, GAO Qi. A high temperature strength and high heat stability: CN, ZL200710011771. 0[P]. 2008-01-16.
[6] 刘建荣, 朱绍祥, 石卫民, 杨慧丽, 王清江, 刘羽寅, 杨 锐. 轧制工艺对Ti-60A棒材显微组织及拉伸性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2008, 37(3): 283-286.
LIU Jian-rong, ZHU Shao-xiang, SHI Wei-min, YANG Hui-li, WANG Qing-jiang, LIU Yu-yin, YANG Rui. Effect of rolling process on microstructure and tensile properties of Ti-60A alloy bars [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2008, 37(3): 283-286.
[7] HINES J A, PETERS J O. Fatigue behavior of titanium alloys [C]// Warrendal, Pennsylvanial, US: TMS Titanium Committee, 1998: 15.
[8] THOMPSON A W. Fatigue behavior of titanium alloys [C]// Warrendal, Pennsylvanial, US: TMS Titanium Committee, 1998: 23.
[9] PETERS J O, SAUER C. Fatigue behavior of titanium alloys [C]// Warrendal, Pennsylvanial, US: TMS Titanium Committee, 1998: 127.
[10] BACHE M R. A review of dwell sensitive fatigue in titanium alloys: The role of microstructure, texture and operating conditions [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2003, 25: 1079- 1087.
[11] SINHA V, MILLS M J, WILLIAMS J C. Determination of crystallographic orientation of dwell-fatigue fracture facets in Ti-6242 alloy [J]. J Mater Sci, 2007, 42: 8334-8341.
[12] BACHE M R, COPE M, DAVIES H M, EVANS W J. Dwell sensitive fatigue in a near alpha titanium alloy at ambient temperature [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 1998, 19(1): 83-88.
(编辑 李向群)
收稿日期:2013-07-28;修订日期:2013-10-10
通信作者:王清江,研究员;电话:024-83978830;E-mail: qjwang@imr.ac.cn