青藏铁路多年冻土斜坡路基失稳变形特性
苏谦,钟彪,王迅,黄俊杰,白皓
(西南交通大学 土木工程学院,四川 成都,610031)
摘 要:从力学相似性角度对处于最大融化深度时的冻土斜坡路基进行离心模型试验,获得冻土斜坡路基的失稳变形特性、影响因素及失稳原因。通过天然冻土斜坡的现场试验结果验证基于力学相似性的离心模型试验方案的合理性及试验结果的可靠性。试验结果表明:冻土斜坡路基发生失稳的根本原因是软弱带的抗剪强度不足,致使路基发生较大变形;冻土斜坡路基的变形主要集中在冻融交界面之上的浅层土体,变形骤变点在冻融交界面附近;滑裂面贯穿活动层后沿着冻融交界面;在本试验条件下,合理的路堤中心高度为4.0~5.0 m。
关键词:冻土斜坡路基;离心模型试验;稳定性;变形特性
中图分类号:U213.1;TU445 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2010)05-1938-07
Instable deformation characteristics of sloping subgrade in permafrost region for Qinghai-Tibet railway
SU Qian, ZHONG Biao, WANG Xun, HUANG Jun-jie, BAI Hao
(School of Civil Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, China)
Abstract: A centrifuge model test of sloping subgrade was conducted using the mechanical similarity when the freezing-thawing depth reaches the greatest. The deformation characteristics, influence factors as well as failure causes were researched. Compared with the in-situ test achievement of the natural slope in the permafrost region, the feasibility of the test scheme as well as the reliability of the results based on the mechanical similarity was verified. The results show that the root cause of the instability is the deficiency of shear resistance strength of the weak belt, resulting in the large deformation. Meanwhile, the deformation mainly concentrates on the shallow soil layer above the freezing-thawing interface, and the deformation mutation point takes place near the freezing-thawing interface. The crack slips along the freezing-thawing interface after cutting through the active layer. Under the experimental conditions, the reasonable height of embankment is 4.0-5.0 m.
Key words: sloping subgrade; centrifuge model test; stability; deformation characteristics
青藏铁路虽然已建成通车2 a多,但发现沿线冻土地区路基仍然存在一些问题,如冻胀融沉产生一些病害,尤其是冻土斜坡路基,病率更高。这些病害不仅在青藏铁路有,其他国家冻土地区的铁路线路也存在类似的问题,一些国家的冻土地区铁路病害率甚至在30%以上。这些病害给线路的运营和维修带来较大的困难。在冻土斜坡稳定性研究方面,早在1897年,国外就有学者进行了初步描述。McRobert等[1]对Mackenzie河流域的冻土滑坡失稳进行了研究,并对冻土斜坡失稳现象进行了划分。Weeks等[2-3]在冻土斜坡稳定性机理及评价方法上进行了研究。在我国,张长庆等[4]在南水北调西线工程前期科学考察青藏公路沿线工程地质研究中指出融冻泥流频繁发生,冻土区边坡开挖及斜坡稳定性是工程活动中必须解决的问题。近年来,Niu等[5-7]对青藏高原多年冻土区斜坡稳定性进行了研究,得出了斜坡失稳的主要类型、斜坡稳定性的评价方法等。在斜坡冻土变形观测和计算方面,郭东信等[8]对青藏公路风火山垭口盆地融冻泥流阶地进行了研究,在不同方向布置了变形观测点,观测了不同方向泥流推进速度,并对泥流阶地地貌形态进行了完整的描述。王绍令[9]对青藏公路风火山地区以东大沟为中心的8个热融滑塌体的类型、形态、动态变化、防治措施等进行了归纳总结。Wang等[10]在20世纪90年代以青藏高原风火山西大沟为研究基地,对冻土斜坡在自然状态下的蠕变现象进行历时3 a的原位蠕变观测,初步描述了冻土斜坡原位蠕变规律。Zhu等[11]对中天山地区斜坡岩块覆盖层的变形进行了分析、计算。在冻土斜坡模型试验研究方面,国内外研究较少。Harris等[12]利用离心模型试验研究了冰土层融化过程中斜坡运动的机制,试验结果很好地解释了冻土层浅层滑坡问题和寒冷地区由冷转暖期间的斜坡运动机理。靳德武等[13]对斜坡模型试验进行了相似分析,建立了冻土斜坡模型试验的相似指标和相似判据,并进行了相似模型设计和冻融模型试验。但以上研究主要是针对天然冻土斜坡,涉及冻土斜坡路基的研究较少,与青藏铁路通车以来沿线产生的路基问题十分不符,这些研究对青藏铁路的运营维护还不足以提供充分的依据,因此,开展冻土区斜坡路基的稳定性和变形特性研究十分必要。在此,本文作者通过离心模型试验对青藏铁路冻土斜坡路基的失稳原因、变形特性及影响因素进行分析。
1 试验方案
1.1 试验模型
考虑到设备等原因,模拟冻土斜坡路基的冻融过程有一定困难,因此,着重从力学相似性角度对冻土斜坡路基失稳原因及其变形特性进行分析。研究表明,冻土斜坡路基达到最大融化深度的季节是在暖季,且降雨也主要集中在暖季,此时,冻土斜坡路基的稳定性最差,模拟此状态下的失稳及变形特性具有针对性。路基的最大融化深度及各土层力学参数通过现场试验数据选取,并考虑路基经过7~10次冻融循环下冻融土强度降低的特性[14]。
试验中冻土斜坡路基选在具有典型性和代表性的风火山试验段,该试验段年平均气温为-6.24 ℃,气温年差达26.2 ℃,且对气候变化的响应敏感,热稳定性较差。同时,试验段有较充分的过余冻结能力,能使填筑的一定高度的路堤与多年冻土衔接。当路堤填筑地区的气候存在过余冻结能力时,若路堤高度人为上限小于路堤高度和基底天然上限之和,即hT<H+h0,则基底天然上限将上升;若hT<H,则高度人为上限将伸入堤身中,形成冻土核。其路堤中心高度和路基面中心融深满足如下经验公式[15]:
hT=1.90+0.092H (1)
其中:hT为路基基面中心高度人为上限;H为路堤中心高度(H<7 m)。
路基坡面的朝向、当地风向及降雨对融深的影响,主要体现在冻土斜坡路基人为上限的选取上。朝阳边坡坡面以下的土层,由于同时受到强烈的垂直热流与水平热流传导作用,融深最大,比基面中心大20%~30%;相反,背阴边坡面中心融深最小,阴坡路肩与基面中心融深相近,两者比值为0.9~1.0。同时,暖季以东北风和东风为主,降雨量也主要集中在暖季,因而风向有利于阴坡路肩的散热,致使阴坡路肩处有较大的融深比。
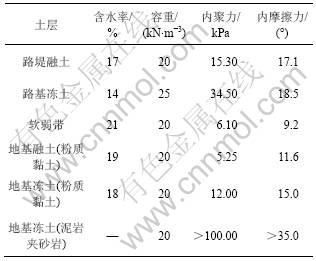
暖季冻土融化后,水分下渗,水分沿深度分布的不均匀,使得冻土斜坡路基各土层的力学性质差异巨大。在冻融交界面附近的土体,受到多年冻土的阻水作用,水分在其附近富集,形成相对软弱带。根据路基各土层的冻融状态及力学性质的明显差异,将其分为路堤融土、软弱带、路堤冻土、地基融土(粉质黏土)和地基冻土(粉质黏土)、地基冻土(泥岩夹砂岩)6层(见图1)。各土层力学参数如表1所示。本文采用离心模型试验,试验的模型相似比为1:40。
路堤高度和地基坡度是影响冻土斜坡路基稳定性

图1 冻土斜坡路基的试验模型
Fig.1 Testing model of sloping subgrade
表1 冻土路基各土层力学参数
Table 1 Mechanical parameters of soil layers
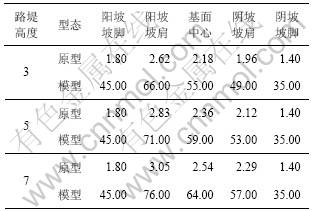
的2个主要影响因素。为单独分析其影响规律,试验设计了3种路堤中心高度和3种地基坡度的模型。其中3种路堤中心高度分别为3,5和7 m,地基坡度固定为1:6,根据式(1)及坡面朝向影响特性,3种路堤中心高度对应的人为上限如表2所示。分析地基坡度的影响规律时,保持路堤中心高度为5 m,各模型按路堤中心高度为5 m对应的人为上限选取,地基坡度分别为1:8,1:6到1:4。
表2 冻土斜坡路基中心高度的人为上限
Table 2 Artificial limit of sloping subgrade m
1.2 试验测点布置
为研究冻土斜坡路基发生失稳的原因及失稳后在不同部位和不同深度的变形差异,沿阳坡顺向分别选取路基表面、软弱带表面、软弱带底面(冻融交界面)、基面中心剖面、阳坡路肩剖面、阳坡坡脚剖面和阳坡坡脚外4 m剖面共7处关键测试带进行分析,如图2所示。
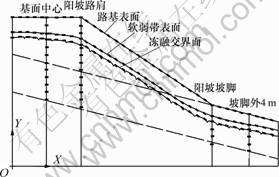
图2 试验测试点布置
Fig.2 Distribution of testing position
2 变形及稳定性分析
2.1 变形及失稳特性
冻土斜坡路基的变形具有显著的特征,以路堤高度为5 m、地基坡度为1:4的冻土斜坡路基为例,试验后模型侧面变形示意图如图3所示。由于受地基不对称、坡面朝向及风向的影响,路基变形呈现明显的不对称,且变形主要集中在阳坡一侧。从图3可以看出:滑裂面的特征具有显著性和特殊性。冻土斜坡路基的水平位移曲线如图4所示。从图4可以看出:裂缝始于靠近阳坡一侧的荷载板边缘附近的路基面上,裂缝贯穿路堤融通后,沿着冻融交界面。裂缝开裂位置在靠近阳坡坡肩一侧的荷载板边缘附近,路基表面水平位移出现突增现象,裂缝宽度达到0.12~0.22 m。冻土斜坡路基的滑裂面形状与一般路基的滑弧裂面具有明显区别,其主要原因是冻融土性质差异以及靠近冻融交界面附近的水分富集形成了相对软弱土层。
另外,除了路基面存在裂缝外,大约在阳坡中心附近还存在坡面裂缝,该裂缝的存在说明滑塌体不是
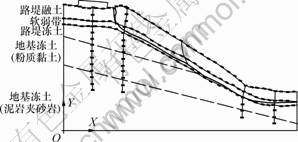
图3 试验后模型侧面变形图
Fig.3 Lateral deformation after experiment
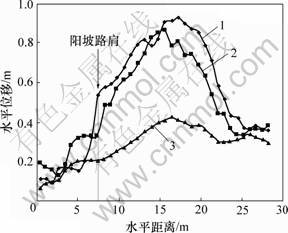
1—路基表面;2—软弱带表面;3—软弱带底面
图4 冻土斜坡路基的水平位移曲线图
Fig.4 Curves of horizontal displacement
一次性整体滑动,而是分块有序的运动。首先,坡脚处的土体尤其是软弱带受到较大的挤压力作用,因抗剪强度不足,而使一部分土体沿冻融交界面发生滑移,从而产生坡面裂缝,此时前一部分土体临空而失去支撑,导致土体塌落下滑从而产生基面的拉裂缝。同时,不同部位和不同深度的土层对路基失稳的贡献程度也不同。
从图4还可以看出:路基表面和软弱带表面的水平位移分布曲线比较陡,而软弱带底面的水平位移分布曲线比较平缓。沿深度方向,软弱带的变形速率最快,路基变形的骤变点在软弱带底面即冻融交界面附近,软弱带对冻土斜坡路基的稳定性起控制作用。冻土斜坡路基的沉降曲线如图5所示,可见:冻土斜坡路基在列车荷载扰动下,易在路基面产生较大沉降。图6和7所示为各剖面的水平位移曲线。从图6和7可知:路基失稳后,整体向阳坡外侧运动,但各部分的变形速率及变形幅度差异较大,沿深度方向,路基的水平变形主要集中在路基表面到冻融交界面的浅层土体范围内,且软弱带的水平变形速率最快,骤变点在冻融交界面附近;顺坡方向,滑坡体后缘即阳坡附近的土体水平位移最大,顺坡向外,水平位移逐渐 减少。
2.2 离心试验与天然冻土斜坡现场试验结果对比
冻土斜坡稳定性及变形研究是斜坡研究领域的一项独特内容,已有学者做过相关方面的研究。但具体针对青藏线冻土斜坡路基稳定性及变形特性的现场试验研究还正在进行。在失稳原因及变形机制研究方面,冻土斜坡路基与天然冻土斜坡具有一定的相似之处。因此,天然冻土斜坡的研究成果可以对离心试验方案的可行性及试验结果的可靠性起到一定验证作用。将本文结果与文献[6-7]试验结果进行对比。牛富俊 等[6-7]所研究的试验段为青藏高原风火山北侧北麓河地区,属于青藏高原干旱气候区,寒冷干旱,四季不明,年平均气温为-5.2 ℃。按冻土含冰量、冻土构造,该处冻土类型自上而下划分为:0~2.0 m为季节融化层;2.0~4.0 m为含土冰层;4.0 m以下为多冰冻土。该试验段与离心模型试验所选取的试验段距离接近,
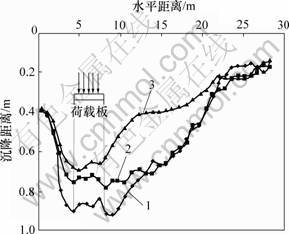
1—路基表面;2—软弱带表面;3—软弱带底面
图5 冻土斜坡路基的沉降曲线图
Fig.5 Curves of settlement
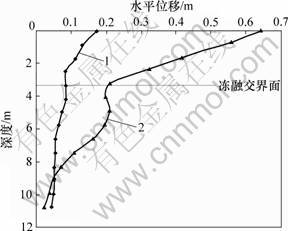
1—路基面中心剖面;2—阳坡坡肩
图6 路基基面中心和阳坡坡肩剖面的水平位移曲线
Fig.6 Curves of horizontal displacement at profile of center face and sunny slope shoulder
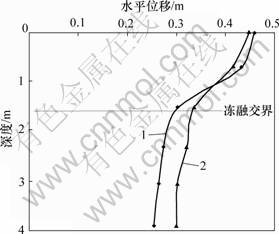
1—坡脚;2—坡脚外4 m
图7 阳坡坡脚和坡脚外4 m剖面的水平位移曲线
Fig.7 Curves of horizontal displacement at profile of toe of slope and 4 m outside of it
气候条件及地质情况相似,因此,可比性较好。本试验结果表明:斜坡变形主要集中在2 m内的浅层土体,土体的聚变点在2 m左右,即冻土斜坡的冻融交界面附近。其变形范围、骤变点位置以及不同部位的变形特征与文献[6-7]中的结果是一致的,但两者破坏的形态有些差异:天然斜坡的破坏常表现为表面的褶皱和土体叠片,且滑裂面表现为滑弧形,而本试验冻土斜坡路基所得到的破坏形态没有褶皱和叠片现象,且滑裂面沿着冻融交界面。其原因主要与铁路路基与天然斜坡土质的差异、排水条件、工程处理、滑坡体的规模等有关。
2.3 变形及稳定性影响因素分析
2.3.1 路堤高度
路堤高度主要影响冻土斜坡路基的人为上限。从热学稳定性角度来说,如果考虑青藏铁路运营50 a,只有在年平均气温低于临界值-3.5 ℃的地段,路堤的临界高度才存在,才能够维持冻土上限在铁路运营 50 a内不会下移[16]。并且在一定路堤高度范围内,路堤高度增大,意味着从上界面流向地中的热量传递过程中受到的热阻增大,有利于热稳定[17]。但从力学稳定性角度,增大路堤高度意味着冻土斜坡路基的稳定性减弱。因此,在满足热稳定及力学稳定之间,必定存在一个合理的路堤高度。
图8所示为路基表面水平位移随路堤中心高度的变化规律。裂缝宽度随着路堤中心高度增大而增大,当路堤中心高度不大于5 m时,各模型的路基表面水平位移随路堤中心高度的增加而缓慢增大;当路堤中心高度大于5 m时,其水平位移随路堤中心高度的增加而迅速增大。从热学稳定的角度分析,路基存在上、下临界高度,且与地区的气候条件紧密相关,不同年平均气温下的临界路堤高度如图9所示[16]。考虑到青藏铁路运营50 a后大气温度将上升2.2~2.6 ℃[18],对应的下临界路堤高度约为4.0 m。因此,在该气候条件下,建议合理路堤中心高度为4.0~5.0 m。
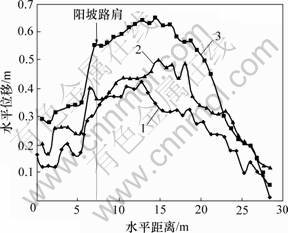
路堤中心高度/m: 1—3; 2—5; 3—7
图8 不同路堤中心高度下路基表面水平位移曲线
Fig.8 Curves of horizontal displacement with different embankment heights
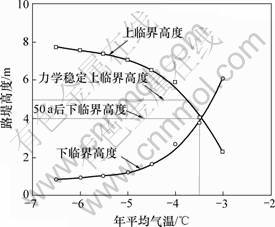
图9 临界路堤高度与年平均气温关系曲线[16]
Fig.9 Curves of critical embankment height vs mean annual air temperature[16]
2.3.2 地基坡度
地基坡度影响冻土斜坡路基的整体稳定。图10所示为路基表面水平位移随地基坡度的变化曲线。从图10可以得到:3种地基坡度的模型在靠近阳坡一侧荷载板边缘处的路基面上均出现不同程度的突增现象,说明三者均有裂缝,且随着地基坡度的增大,裂缝宽度也随着增大;当地基坡度不大于1:6时,地基坡度对路基的变形影响很小,但当地基坡度大于1:6时,路基表面的水平位移迅速增大。因此,建议在坡度大于1:6的地基上修筑路堤时,应采取必要的工程措施。
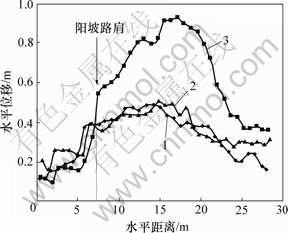
地基坡度:1—1:8;2—1:6;3—1:4
图10 地基坡度不同时路基表面的水平位移曲线
Fig.10 Curves of horizontal displacement with different ground gradients
3 结论
(1) 冻土融化后在冻融交界面附近富集水分形成的相对软弱带,是导致冻土斜坡路基发生失稳的根本原因。
(2) 冻土斜坡路基在不同部位及不同深度土体的变形具有明显的差异,路基的水平变形主要集中在冻融交界面之上的浅层土体,骤变点发生在冻融交界面附近。滑坡体后缘的土体变形速率比前缘的土体变 形快。
(3) 在本试验条件下,冻土斜坡路基的变形随路堤中心高度及地基坡度的增大而增大。满足热稳定和力学稳定的合理路堤中心高度为4~5 m。
(4) 通过对比天然冻土斜坡现场试验结果,得出了普通冻土斜坡路基的变形特性与天然冻土斜坡异同点,同时也验证了基于力学相似条件下离心模型试验方案的可行性以及试验结果的可靠性。
参考文献:
[1] McRobert E C, Morgenstern N R. The stability of thawing slopes[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1974, 11(4): 447-469.
[2] Weeks A G. The stability of natural slope in south-east England as affected by periglacial acticity[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology, 1969, 2(1): 49-63.
[3] Hutchinson J N. Periglacial solifluction: An approximate mechanism for clay soil[J]. Geotecnique, 1974, 24: 438-443.
[4] 张长庆, 朱林楠, 张健明, 等. 中国南水北调西线工程地区的冻土与工程问题[J]. 冰川冻土, 1993, 15(1): 90-95.
ZHANG Chang-qing, ZHU Lin-nan, ZHANG Jian-ming, et al. The problem between frozen ground and engineering in western line engineering of trans-water from south to north, China[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 1993, 15(1): 90-95.
[5] NIU Fu-jun, CHENG Guo-dong, XIE Qun. Study on instability of slopes in permafrost regions of Qinghai-Tibet High Plateau[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Permafrost Engineering. Yakutsk: Permafrost Inst.S8 RAS Press, 2002: 192-197.
[6] 牛富俊, 程国栋, 赖远明, 等. 青藏高原多年冻土区热融滑塌型斜坡失稳研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2004, 26(3): 402-406.
NIU Fu-jun, CHENG Guo-dong, LAI Yuan-ming, et al. Instability study on thaw slumping in permafrost regions of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2004, 26(3): 402-406.
[7] 靳德武, 牛富俊, 陈志新, 等. 青藏高原融冻泥流型滑坡灾害及其稳定性评价方法[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2004, 32(3): 49-51.
JIN De-wu, NIU Fu-jun, CHEN Zhi-xin, et al. Landslide hazard from gelifluction in Qinghai-Tibet plateau and stability analysis method[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2004, 32(3): 49-51.
[8] 郭东信, 黄以职, 赵秀峰. 青藏公路风火山娅口盆地融冻泥流阶地初步研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 1993, 15(l): 58-62.
GUO Dong-xin, HUANG Yi-zhi, ZHAO Xiu-feng. A preliminary research of soliflution terraees in fenghuoshan pass basin on Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 1993, 15(1): 58-62.
[9] 王绍令. 青藏公路风火山地区的热融滑塌[J]. 冰川冻土, 1990, 12(l): 63-70.
WANG Shao-ling. Thaw slumping in Fenghuo-Mountain area along Qinghai-Xizang Highway[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 1990, 12(1): 63-70.
[10] Wang B L, Freneh H M. In situ creep of frozen soil, Fenghuo-Shan, Tibet Plateau, China[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1995, 32(3): 545-552.
[11] ZHU Cheng, ZHANG Jian-xin, CHENG Peng. Rock glaciers in the central Tianshan Mountain, China[J]. Permafrost and Periglaeial Proeesses, 1996, 7(1): 69-78.
[12] Harris C, Rea B, Davies M. Scaled physical modelling of mass movement processes on thawing slopes[J]. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 2001, 12(1): 125-135.
[13] 靳德武, 牛富俊, 陈志新, 等. 冻土斜坡模型试验相似分析[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2004, 26(1): 29-32.
JIN De-wu, NIU Fu-jun, CHEN Zhi-xin, et al. Simulation analysis for model experiment of frozen soil slope[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2004, 26(1): 29-32.
[14] 苏谦, 唐第甲, 刘深. 青藏斜坡黏土冻融循环物理力学性质试验[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(增1): 2990-2994.
SU Qian, TANG Di-jia, LIU Shen. Test on physico-mechanical properties of Qinghai-Tibet slope clay under freezing-thawing cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 247(supple 1): 2990-2994.
[15] 黄小铭, 张国卿. 青藏高原多年冻土地区路堤人为上限的变化规律[C]//青藏铁路多年冻土科研成果论文集. 兰州: 西北科学研究院, 2003: 254-255.
HUANG Xiao-ming, ZHANG Guo-qing. Variation laws of the artificial permafrost table of the roadbed on Qinghai-Tibet Platean[C]//Professional Papers on Permafrost studies of Qinghai-Xizang Railway. Lanzhou: Northwest Research Institute, 2003: 254-255.
[16] 张明义, 张建明, 赖远明. 青藏高原多年冻土区铁路路堤临界高度数值计算分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2004, 26(3): 600-606.
ZHANG Ming-yi, ZHANG Jian-ming, LAI Yuan-ming. Numerical analysis of the critical height of railway subgrade in permafrost regions of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2004, 26(3): 600-606.
[17] 章金钊, 李祝龙, 武名. 冻土路基稳定性主要影响因素探讨[C]//第一届全国公路科技创新高层论坛. 北京: 外文出版社, 2000: 229-232.
ZHAGN Jin-zhao, LI Zhu-long, WU Ming. Exploration on the main factors of the stability for the frozen soil roadbed[C]// Professional Papers on Road Science and Technology at the First Innovational High-level Forum. Beijing: Foreign Languages Press, 2000: 229-232.
[18] 程国栋, 杨成松. 青藏铁路建设中的冻土力学问题[J]. 力学与实践, 2006, 28(3): 1-8.
CHENG Guo-dong, YANG Cheng-song. Mechanics related with frozen ground in construction of Qinghai-Tibet Railway[J]. Mechanics In Engineering, 2006, 28(3): 1-8.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2009-10-27;修回日期:2010-02-29
基金项目:国家“十一五”科技支撑计划项目 (2006BAC07b02)
通信作者:苏谦(1972-),男,山西运城人,教授,从事土木设计理论与新结构研究;电话:13688018729;E-mail: suqian@126.com