J. Cent. South Univ. (2016) 23: 1015-1022
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3150-9
Reduction of Panzhihua titanium-bearing oxidized pellets by CO-N2-H2 gas
ZHANG Jian-liang(张建良), ZHENG Chang-le(郑常乐), TANG Yun-teng(汤云腾), CHAI Yi-fan(柴轶凡)
School of Metallurgical and Ecological Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Abstract: The effect of H2 gas content on the reduction of Panzhihua titanomagnetite concentrate pellets by carbon monoxide was investigated by isothermal reduction experiment using CO-N2-H2 gas mixtures in a vertical electric resistance furnace. The morphology and phase transformation of reduced samples obtained were detected by scanning electron microscopy, energy disperse spectroscopy analysis and X-ray diffractometry respectively. The results show that increasing H2 content will enhance the initial stage of reduction rate apparently. There are two reasons responsible for this effect, one is that H2 accelerates the chemical reaction, and the other is that the addition of H2 gas can improve the porosity of pellet intensively. It is noteworthy that this effect is more obvious when the reduction temperature reaches 1473 K with sticking phenomenon happening. There are no crystalline phases which can be found such as ulvospinle, ilmenite, ferrous-pseudobrookite and any titanium oxide except titanomagnetite (TTM). The reduction progress is suggested as follows: 1) Fe2O3→Fe3O4→FeO→Fe; 2) Fe2TiO5→Fe2TiO4+Fe3O4→TTM. Element Al migrates and gets enriched in high titanium content iron ores, and eventually Al to Ti molar ratio is 1:3. Al is likely to dissolve in titanium iron oxides to form a kind of composite iron compound, which results in the restrain of reduction.
Key words: titanomagnetite pellet; carbon monoxide; hydrogen; reduction; blast furnace
1 Introduction
Iron ores titanium containing, which are found throughout the world in large deposits, are becoming alternative resources for ironmaking [1-4]. There is a special and huge iron ore deposit called vanadium titanomagnetite (TTM), about 10 billion tonnage storage in Panzhihua area, southwest of China. By the beneficiation process, titanomagnetite concentrates and ilmenite concentrates can be produced. Currently, most of the TTM concentrates are used as the main materials for the blast furnace process in Panzhihua area [5]. However, it has been known that the reduction rate of Panzhihua titanomagnetite concentrates (PTC) is slower than that of magnetite due to its special crystal structure of the ore with the existence of titanium, which results in a higher thermodynamic stability of TTM [1, 6-9]. This implies a longer residence time in BF than that with the common iron ore, thereby involving more energy and reductant consumption. Therefore, it is important to enhance the reduction rate of PTC. Measurements for increasing the reduction rate of PTC have been extensively studied, which refer to the addition of alkali metal salt such as sodium sulfate, sodium carbonate and borax and the addition of ferrosilicon when using direct reduction [5, 7]. It is found that the reduction rate of PTC is accelerated by means of aforementioned methods. However, there are still some disadvantages for these methods, which pose the negative effects on the refractory lining for the introduction of alkali metal and extra cost due to the investment for ferrosilicon.
It was reported that the complete reduction of iron oxides in TTM by carbon monoxide required temperatures above 1273 K and high reducing potential [8]. Understanding of limitations in the reduction of titania-ferrous ore requires a detailed investigation into the ore particle structure and phase transformation in the course of reduction. Many studies [1, 6, 8, 10] have been carried out under the pure CO or H2 atmosphere when TTM is reduced. H2 has been proven with many advantages including better reducing capabilities, significant potential to reduce energy consumption and to decrease corresponding greenhouse gases compared with CO in iron ore reduction [11]. However, actual atmosphere in blast furnace is CO-N2 gas mixture, therefore experiments with CO-N2 gas mixture are necessary. In recent years, for the development of oxygen enrichment technology to enhance iron ore reduction, H2 content is increased in blast furnace (BF).
However, few attentions have been taken to study the effect of H2 content on reduction of titania-ferrous ore by carbon monoxide. Therefore, it is necessary to clarify the mechanism of the reduction of titania-ferrous ore by carbon oxide mixed with hydrogen for the base application. This work presents results of reduction of Panzhihua titanium-bearing pellets. In comparison with the previous data, carbon monoxide mixed with various H2 gas contents was used to simulate the gas composition in BF shaft and the reduction mechanism was also discussed by the examination of the phase transformation during the reduction.
2 Experimental
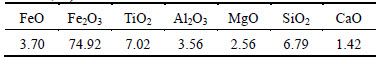
The titanium-bearing oxidized pellets used in this work were supplied by Panzhihua steel, in Sichuan province of China. The chemical composition of PTC pellets in this work is given in Table 1.
Table 1 Chemical composition of PTC pellet (mass fraction, %)
The isothermal reduction experiment of the PTC pellets at 1173, 1273, 1373 and 1473 K in different gas contents was carried out in a vertical electric resistance furnace, which is schematically demonstrated in Fig. 1.
Reduction experiments were conducted using a thermal balance and it was heated up to each experiment temperature in N2 gas stream. Then, a sample was hung on the thermal balance when the reducing gas mixture was introduced to the reactor. The carbon monoxide, hydrogen and nitrogen used in the experiments were of super high purity, super high purity and high purity, respectively. The volume ratio of N2 and CO was kept at 7:3, and the volume fraction of H2 in total gas flow was set as 0, 4%, 8% and 12%, respectively (to simulate the reduction circumstance in oxygen-enriched BF). The total gas flow rate was maintained at 6 L/min. It was noted that the influence of the gas flow rate on the reduction rate used in this experiment was negligible as the reduction rate was almost identical when the gas flow rate was changed from 5 L/min to 8 L/min with an increment of 1 L/min. During the reduction process, the mass change of reacting samples was monitored by electronic balance (Mettler Toledo AL204-IC electronic balance) and recorded in real-time by computer. After a certain period of reaction, samples were taken out from the furnace and quenched in water for analysis. The extent of reduction was calculated as a mass fraction of oxygen in iron oxides removed in the course of reduction and it was calculated by
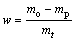 (1)
(1)
where mo is the starting mass of the sample, mt is the mass of the removed oxygen from the sample after reduction time t, and mp is the maximum possible mass loss of oxygen from iron oxides in pellet sample. The mineralogical morphology of sample was examined by XRD (Nikkaku D/max-RB, using Cu Kα), scanning electron microscope (SEM, JEOL JSM-6510A) and EDS (Noran System six).
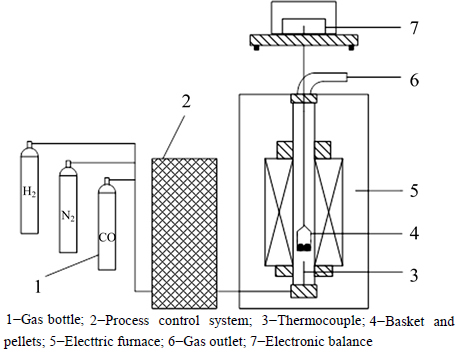
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of experimental setup:
3 Experimental results and discussion
3.1 Effect of H2 content
Figure 2 shows the degree of reduction as a function of time for PTC pellets at 1173, 1273, 1373, and 1473 K, respectively, under different H2 partial pressures. It can be seen that the reduction rate can be considerably enhanced when the temperature is raised to 1373 K at certain H2 content. However, the reduction rate decreases dramatically when the temperature reaches 1473 K. This can be explained as follows. In this work, it is consistent with the study conducted by PARK and OSTROVSKI [6], which indicates that the sticking phenomenon does not happen in the particles even after 120 min when the temperature is below 1373 K. It has been known that the sintering and sticking among particles are due to the mass transfer from the inside of the particle or from the grain boundary between particles [12]. Besides, the non-sticking behavior of the TTM during reduction probably results from the titanium oxides dispersed in the pellets. PARK and OSTROVSKI showed that titanium in the form of titanium oxides [1] was distributed uniformly in the particles before and after reduction. The titanium oxides in the pellets might act as a barrier against the mass transfer of metallic iron from the interior of the particle to the interface, thus resulting in the non-sticking during the high-temperature reduction process. However, there is sticking phenomenon when the temperature reaches 1473 K. This means that titanium oxides in the pellets are incapable of restricting the mass transfer of metallic iron from the interior of the particles to the interface when the temperature surpasses 1473 K. Moreover, the melted metallic iron forms a protective layer, which inhabits the mass transfer of the gaseous phase into the inner area of PTC pellets.
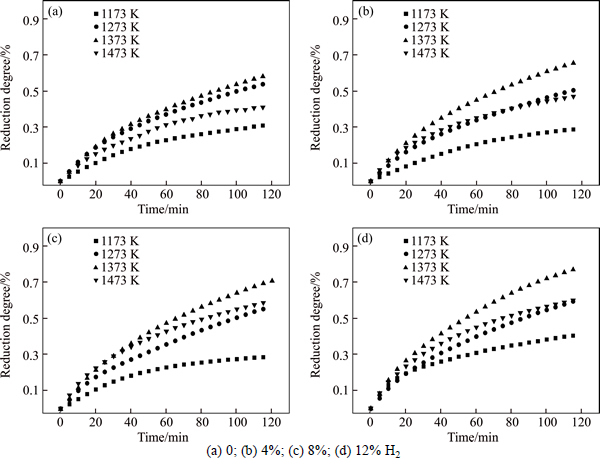
Fig. 2 Degree of reduction as a function of time for PTC pellets:
It is worth noting that, with the increase of H2 content from 0 to 12% at 1473 K, the reduction rate gradually surpasses the value at 1273 K, as shown in Figs. 2(c) and (d). The reasons perhaps can be explained as follows. As to the initial reduction stage, there is not enough metallic iron generated to form a protective layer. As a result, the increase of H2 content gives rise to a significantly enhanced reduction rate. In addition, the existence of H2 in reducing gas considerably decreases the sticking index due to the formation of porous and fibrous iron precipitating on the interface, which can be used as an effective inhibition of sticking in iron ore reduction process [9]. Therefore, the formation of porous structure in ore particles should be clarified during the reduction process.
To get a detailed knowledge about the influence of the H2 content on the formation of porous structure, the cross-section morphology of pellets is displayed in Fig. 3. It can be seen that there is a large quantity of porosity generated in ore particles when the H2 content is increased to 4% and becomes more when H2 content is increased to 8%. It is not only because the smaller molecule size of H2 relative to CO provides more efficient diffusion to the inner parts of the pellet but also because the product H2O/H2 molecule size ratio is larger than that of CO2/CO, which means that greater pressure is generated to make the pores expand, thus permitting more gas exchange at the oxide/metal interface. It was reported that the reduction degree was enhanced a lot with the porosity increasing since H2 accelerated the reduction process and the product H2O reacted with CO to create H2, which took part in the reduction again [13], and the regenerated H2 would further promote the porosity expansion. It has been proposed that part of H2 did not participate in the reduction but acted as something like catalyst which speeded up the reduction greatly [14]. And it can be found that the metallic iron nucleus is prior to grow at the pore or ore particle edge. It is implied in this work that H2 can not only accelerate the reaction itself but also improve the dynamic conditions.
3.2 Phase transformation during reduction of PTC pellets
Samples in the process of reduction by N2 -CO mixed with 8% H2 at 1373 K were analyzed by XRD and the result is shown in Fig. 4. The major crystalline phases in the raw PTC pellets are hematite and pseudobrookite. At the beginning 5 min of reduction, pseudobrookite is reduced and magnetite and TTM are observed. Ulvospinle as the intermediate product is not detected. The possible reason may be due to the rapid reaction between ulvospinle and magnetite to form TTM. The intensity for hematite phase gradually decreases and disappears when the reduction time proceeds after 15 min while wuestite has been found at the same time with relatively weak XRD peak. The reduced magnetite is also found to react with titanium oxide to form more TTM. After 30 min, when the reduction degree achieves 40%, the hematite peak disappears and the peak for wuestite becomes dominant in the XRD pattern. It can be seen that the amount of wuestite decreases from 30 min to 60 min and disappears eventually at the end of experiment. However, the TTM peak maintains a constant intensity from 30 min to 60 min and decreases slightly when the experiment is over, which means that the dominant reaction is wuestite to metallic iron during this time and the reaction magnetite to wuestite is probably carried on at the same time, however, the TTM reduction is almost stopped. It may be due to the fact that magnetite is prior to being reduced compared with TTM and it seems that TTM fails to be reduced under the experiment condition even after 120 min since no other iron titanium oxide has been detected. The above- mentioned facts show that the two main iron oxides in the PTC pellet, hematite and pseudobrookite, are carriedon in accordance with two ways to restore step by step in the process of reduction. It has been known that hematite is reduced in this sequence: Fe2O3→Fe3O4→FeO→Fe and it was reported by HE [15] that pseudobrookite was reduced in this way: Fe2TiO5→Fe2TiO4→FeTiO3→FeTi2O5→Ti2O3. However, no ulvospinle, ilmenite, ferrous-pseudobrookite or any titanium oxide except TTM has been detected. Therefore, the reduction process can be suggested as follows: 1) Fe2O3→Fe3O4→FeO→Fe; 2) Fe2TiO5→Fe2TiO4+Fe3O4→TTM. This is different with the work by SUN et al [16] which showed that the easiest step during the reduction was TTM to wuestite starting with the reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+ and wuestite to Fe accompanied by the removal of oxygen. Besides, the further reduction of TTM would be mainly carried out below the BF shaft by direct reduction, which needs to be studied in the next work.
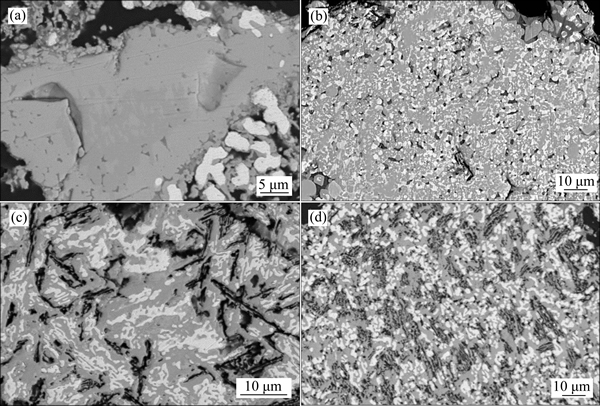
Fig. 3 Cross-section SEM images of reduction pellets by addition of 0% (a), 4% (b), 8% (c), 12% (d) H2 gas, respectively, at 1100 °C after 120 min
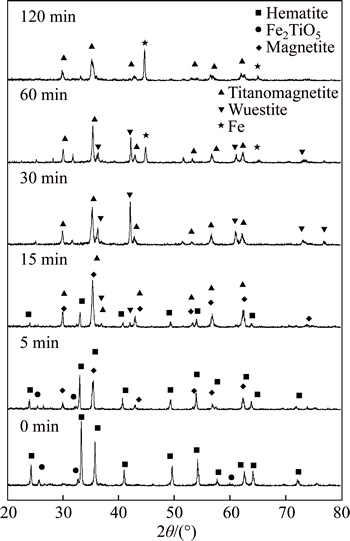
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of samples reduced by N2 -CO mixed with 8% H2 at 1373 K in process of reduction
3.3 Morphology and energy disperse spectroscopy analysis
To investigate the reduction process in detail, the cross-section morphology of samples in the process of PTC pellet reduction by N2-CO mixed with 8% hydrogen gas at 1373 K was examined by BES and the results are shown in Fig. 5. It can be seen from Fig. 5(a) that the raw ore of PTC pellet is mainly homogeneous particals segmented by oxides phase. According to XRD analysis above and the EDS analysis given in Table 2, the homogeneous partide is a solid solution between hematite and pseudobrookite as the atom ratio of iron, titanium to oxygen elements is 5:1:10. Wuestite is firstly found after 5 min reduction (Fig. 5(b)), which shows that there is some difference between EDS analysis and XRD analysis. It is probably caused by the fact that the reduction time is too short and the trace product cannot be detected by XRD analysis. As seen from Fig. 5(c), the raw ore particle almost has completed the first step reduction and started to generate a large amount of wuestite. Metallic iron is first found in Fig. 5(d) and gets accumulated after 60 min as the white phase shown in Fig. 5(e). It is noteworthy that a new dark gray phase derived from TTM is generated in Fig. 5(e), and it is kept until the experiment is over, as shown in Fig. 5(f) (the gray region), which is consistent with the XRD detection. There are two other morphological regions identified in Fig. 5(f). White one is metallic iron which have got together to form a sheet shape and the dark gray one is slag phase with high Si, Mg or Al content. The two phases tightly surround TTM, and this is also the reason discussed above why TTM cannot get completely reduced, which restricts the reduction degree. In addition, TTM has higher thermodynamic stability. In spite of this, this work is not consistent with the previous work which indicated that TTM was easy to be reduced to generate wuestite and ulvospinel in carbon monoxide or hydrogen gas. Further studies need to be conducted on direct reduction in PTC pellet simulating reduction under BF shaft.

Fig. 5 Morphology changes of sample particle in N2 -CO mixed with 8% hydrogen gas at 1373 K:
Table 2 Compositions of samples during reduction by N2 -CO mixed with 8% hydrogen gas at 1373 K (mass fraction, %)
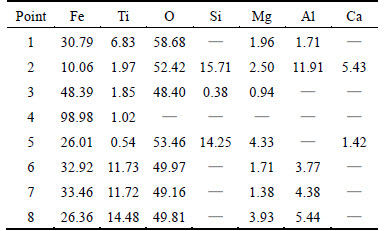
EDS analysis results of points marked in Fig. 5 are shown in Table 2. Points 1-2 show that iron ore does not contain Si-Ca component, which mainly exists in gangue. Moreover, no Si-Ca component in iron ores is detected in the reduction process, which indicates that iron and slag separate well with each other. However, the behavior of element Al is not the same in the reduction process. Points 1-2 show that Al is mainly in gangue, and only a small amount of Al exists in the raw iron ore. Points 3-5 show that there is no element Al in the precipitated wustite, metallic iron and slags containing a high content of Si, however, it is found that high content of Al at Points 6-8 is enriched in high titanium-ferrous ore. In addition, it is very easy to see that Al content increases with content of element titanium. This means that element Al may be separated from gangue into titanium-ferrous ore and the atom ratio of element Al to Ti is close to 1:3. Studies [12-13] have suggested that MgO could form a solid solution with TiO2 to generate complex compounds and enriched progressively in the unreduced titanium-ferrous ore with the reduction progressing. However, this phenomenon does not happened in this work, and element Al is likely to be enriched due to Al2O3 solid solution with titanium- ferrous to form some kinds of complex compounds. And this may be one of the reasons hindering the reduction of titanium-ferrous. This phenomenon will be further explained in the subsequent experiments.
3.4 Kinetic analysis
According to the above-mentioned discussion, it can be concluded that the reduction of PTC pellets proceeds topochemically. Based on the study by GUO [17], this kind of reaction conforms to the unreacted shrinking core model (URCM) including the processes of gaseous species diffusion and intrinsic chemical reaction. The total reduction time is expressed as Eq. (2) which is applied to the condition in which solid sphere reacts with gas phase and the effect of gas external diffusion can be negligible. Therefore, the reduction rate would mainly be dependent upon the internal diffusion of reductant across the solid product layer and interfacial chemical reaction.
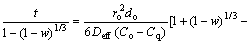
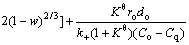 (2)
(2)
where t is reduction time (s), C0 and Cq are reduction gas concentrations at granule surface and in equilibrium (mol/m3), respectively, k+ is positive reaction rate constant (m/s), Deff is effective diffusion coefficient (m2/s), r0 is characteristic initial radius of pellet (m), d0 is initial oxygen concentration in the pellet (mol/m3), and w is fraction reaction.
Considering that the reduction of TTM concentrate pellets is a multi-step complex process without a single reaction throughout the whole reduction process, Cq is difficult to be determined exactly which is related to the equilibrium constant determined by the dominant reaction. Reduction of FeO is the most difficult step in the whole reduction process. Therefore, only the reduction of FeO is considered when calculating Kθ and equilibrium gas concentration which have no effect on relative comparison. It can be seen from Eq. (2) thatthere is a linear relationship between 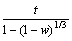 and 1+(1-w)1/3-2(1-w)2/3. By plotting the linear regression relationship between them, Deff and k+ can be obtained from slope and intercept, respectively. And the resistances of internal diffusion Ri and interfacial chemical reaction Rc can be calculated as
and 1+(1-w)1/3-2(1-w)2/3. By plotting the linear regression relationship between them, Deff and k+ can be obtained from slope and intercept, respectively. And the resistances of internal diffusion Ri and interfacial chemical reaction Rc can be calculated as
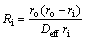 (3)
(3)
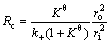 (4)
(4)
where ri is the radius of unreacted core (m) during the reduction process.
Assuming the densities of solid reactant and its product are equal, ri can be expressed by r0 and w as follows:
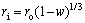 (5)
(5)
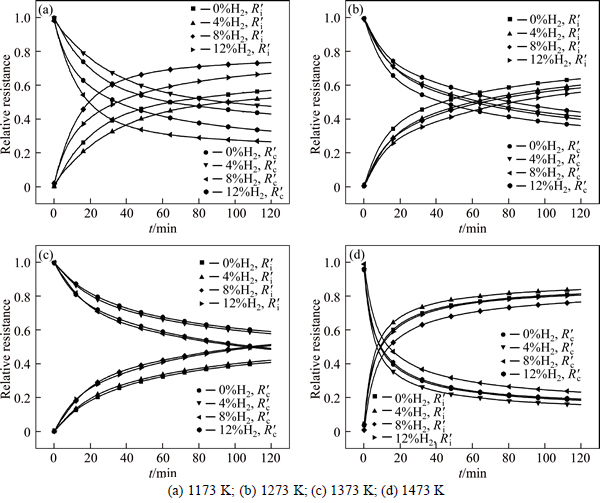
Fig. 6 Relative resistance of internal diffusion and interfacial chemical reaction with reduction progressing:
According to the above equations, the relative resistance of internal diffusion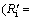 Ri/(Ri+Rc)) and interfacial chemical reaction
Ri/(Ri+Rc)) and interfacial chemical reaction 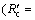 Rc/(Ri+Rc)) can be calculated and the results are shown in Fig. 6. It can be seen that the reaction is controlled by interfacial chemical reaction at the beginning of reduction and then
Rc/(Ri+Rc)) can be calculated and the results are shown in Fig. 6. It can be seen that the reaction is controlled by interfacial chemical reaction at the beginning of reduction and then 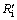 surpasses
surpasses 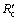 gradually with reduction, which means that the internal diffusion is dominant. With the experimental temperature rising from 1173 K to 1373 K, the interfacial chemical reaction controlling time is prolonged and even last to the end of experiment at 1173 K, which means that the reductant gas mass transfer condition is improved more than interfacial chemical reaction dynamics. It is the same with above results of increasing H2 content that the porosity of pellet is improved significantly. At 1473 K, the reduction is mainly controlled by internal diffusion after 15 min reaction, which is consistent with the above analysis that sticking phenomenon has occurred. It can also be confirmed from Fig. 6 that internal diffusion relative resistance effect is weakened first and then is intensified when H2 content increases from 0 to 12% above 1173 K, which means that increasing H2 content can improve internal diffusion condition more first and then less than enhance interfacial chemical reaction dynamics. There is no obvious regulation at 1173 K, however, in general, interfacial chemical reaction dynamics should be incentive to be improved more as H2 content increases.
gradually with reduction, which means that the internal diffusion is dominant. With the experimental temperature rising from 1173 K to 1373 K, the interfacial chemical reaction controlling time is prolonged and even last to the end of experiment at 1173 K, which means that the reductant gas mass transfer condition is improved more than interfacial chemical reaction dynamics. It is the same with above results of increasing H2 content that the porosity of pellet is improved significantly. At 1473 K, the reduction is mainly controlled by internal diffusion after 15 min reaction, which is consistent with the above analysis that sticking phenomenon has occurred. It can also be confirmed from Fig. 6 that internal diffusion relative resistance effect is weakened first and then is intensified when H2 content increases from 0 to 12% above 1173 K, which means that increasing H2 content can improve internal diffusion condition more first and then less than enhance interfacial chemical reaction dynamics. There is no obvious regulation at 1173 K, however, in general, interfacial chemical reaction dynamics should be incentive to be improved more as H2 content increases.
4 Conclusions
1) In the temperature range from 1173 to 1473 K, the addition of H2 in 30%CO-70%N2 (volume fraction) gas can considerably enhance the reduction degree. At 1373 K, the reduction degree reaches the maximum value and it is decreased when the temperature continues to increase because the sticking phenomenon restricts the gas-solid mass transfer. The reduction progress is carried out in two stages. And improving H2 content would mainly accelerate the first stage of reduction. The reasons are that H2 can not only enhance the chemical reaction but also weaken the sticking phenomenon before metallic iron is generated and it can promote the formation of porosity in ore particles.
2) During the reduction, Panzhihua titanomagnetite concentrate pellet is reduced to iron and iron-titanium oxides depending on the reduction temperature, time and H2 content. A simultaneous reduction progress can be suggested as follows: 1) Fe2O→Fe3O4→FeO→Fe; 2) Fe2TiO5→Fe2TiO4+Fe3O4→TTM. It is implied that further reduction of iron ore TTM would be carried out below BF shaft by direct reduction which needs to be studied in detail.
3) Even though increasing temperature can enhance interfacial chemical reaction, the relative resistance of interfacial chemical reaction is still increased and the reduction process is completely controlled by interfacial chemical reaction at 1373 K. This claims that raising temperature would improve more internal diffusion dynamics than interfacial chemical reaction dynamics. Above 1173 K, increasing H2 content gradually would improve internal diffusion condition more first and then less than enhance interfacial chemical reaction dynamics. There is no obvious regulation at 1173 K. However, in general, interfacial chemical reaction dynamics should be incentive to be improved more as H2 content increases.
References
[1] PARK Eungyeul, OSTROVSKI Oleg. Reduction of titania-ferrous ore by carbon monoxide [J]. ISIJ International, 2003, 43(9): 1316-1325.
[2] ZHENG Hai-yan, XUE Xun, WEI Guo. Thermodynamics analyses on the comprehensive utilization of vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite [C]// Proceedings of the 5th International Congress on the Science and Technology of Ironmaking. Shanghai: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009: 1208-1210.
[3] WANG Shu-lan, LI Guang-qiang, LOU Tai-ping. The conductivity and the crystallization of perovskite (CaTiO3) from Ti-bearing blast furnace slag studied by A.C. Impedance method [J]. ISIJ International, 1999, 39(11): 1116-1119.
[4] YANG Shao-li, SHENG Ji-fu. Technology of pig iron and titanium slag smelting [M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 2006: 19. (in Chinese)
[5] CHEN De-sheng, SONG Bo, WANG Li-na. Solid state reduction of Panzhihua titanomagnetite concentrates with pulverized coal [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24(8): 864-869.
[6] PARK Eungyeul, OSTROVSKI Oleg. Reduction of the mixtture of titanomagnetite ironsand and hematite iron ore fines by carbon monoxide [J]. ISIJ International, 2004, 44(1): 214-216.
[7] HU Tu, LV Xue-wei, BAI Chen-guang. Carbothermic reduction of titanomagnetite concentrates with ferrosillcon addition [J]. ISIJ International, 2013, 52(4): 557-563.
[8] PARK Eungyeul, OSTROVSKI Oleg. Reduction of titania-ferrous ore by hydrogen [J]. ISIJ International, 2004, 44(6): 999-1005.
[9] LONGBOTTOM R J, OSTROVSKI O, PARK Eungyeul. Formation of cementite from titanomagnetite ore [J]. ISIJ International, 2006, 46(5): 641-646.
[10] SUN Hao-yan, WANG Jing-song, HAN Yi-hua. Reduction mechanism of titanomagnetite concentrate by hydrogen [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2013, 125(11): 122-128.
[11] YI Ling-yun, HUANG Zhu-cheng, TAO Jiang. Sticking of iron ore pellets during reduction with hydrogen and carbon monoxide mixtures: Behavior and mechanism [J]. Powder Technology, 2013, 235(11): 1001-1007.
[12] KINGERY W D, BOWEN H K, UHLMANN D R. Introduction to ceramics [M]. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 1976: 474.
[13] KEMPPAINEN A, MATTILA O, HEIKKINEN E P, PAANANEN T, FABRITIUS T. Effect of H2–H2O on the reduction of olivine pellets in CO–CO2 gas [J]. ISIJ International, 2012(52): 1973-1978.
[14] HIDEKI O N, TOSHINARI Y, TATEO U. Effect of water-gas shift reaction on reduction of iron oxide powder packed bed with H2-CO mixtures [J]. ISIJ International, 2003, 43(10): 1502-1511.
[15] HE Qi-song. Thermodynamic analysis of titanium magnetite pellets in the reduction process [J]. Iron and Steel, 1983, 18(4): 1-6. (in Chinese)
[16] SUN Hao-yan, DONG Xiang-juan, SHE Xue-feng. Solid state reduction of titanomagnetite concentrate by graphite [J]. ISIJ International, 2013, 53(4): 564-569.
[17] GUO Han-jie. Physical chemistry of metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2010: 120-123. (in Chinese)
(Edited by YANG Bing)
Foundation item: Project(51134008) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2012CB720401) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Received date: 2015-03-04; Accepted date: 2015-07-22
Corresponding author: ZHANG Jian-liang; Tel: +86-10-62332095; E-mail: jl.zhang@126.ustb.edu.cn