文章编号:1004-0609(2009)07-1294-06
脉冲电沉积制备电控离子分离NiHCF膜电极
马旭莉,郝晓刚,李永国,刘世斌,孙彦平
(太原理工大学 化学工程系,太原 030024)
摘 要:采用脉冲电沉积法在石墨基体上制备了铁氰化镍膜(NiHCF膜)。通过循环伏安法考察了不同脉冲参数(脉冲电压、脉冲周期、占空比、沉积次数)条件下制备的石墨基NiHCF膜电极的离子交换容量,并通过SEM和XPS分析了膜的表面形貌与组成。结果表明:脉冲电压0.3 V(vs SCE)、脉冲周期0.6 s、占空比为50%时沉积得到的NiHCF膜均匀致密,且具有较大的离子交换容量和良好的稳定性。脉冲电沉积法可用于制备性能优良的电化学控制离子分离膜电极。
关键词:脉冲电沉积;NiHCF膜;电化学控制离子分离;循环伏安
中图分类号:TQ 035 文献标识码:A
NiHCF film electrodes prepared by pulsed electrodeposition for electrochemically controlled ion separation
MA Xu-li, HAO Xiao-gang, LI Yong-guo, LIU Shi-bin, SUN Yan-ping
(Department of Chemical Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China)
Abstract: The electroactive nickel hexacyanoferrate (NiHCF) thin films were generated on graphite substrates by pulsed electrodeposition. The composition and morphology of the NiHCF thin film were investigated using XPS and SEM. In 1 mol/L KNO3 solution, the potential cycling in the range of 200?1 000 mV (vs SCE) is used to reversibly intercalate and deintercalate K+ from the matrix. The effects of the pulsed deposition parameters, such as pulse potential, duty cycle and deposition time (ton/toff) on the ion-exchange capacity of NiHCF film electrodes were investigated. The cycle life of the film electrodes was also investigated. The results show that the NiHCF thin films formed on graphite substrates are suitable for electrochemically controlled ion separation (ECIS) processes. The films display high ion exchange capacity for K+ and good stability, and the optimum pulse potential, pulse period and duty cycle are 0.3 V (vs SCE), 0.6s and 50%, respectively.
Key words: pulsed electrodeposition; NiHCF thin film; electrochemically controlled ion separation; cyclic voltammetry
电化学控制离子分离(Electrochemically controlled ion separation, ECIS)是一种环境友好的新型离子分离技术[1?2]。将电活性半导体离子交换材料沉积在导电基体表面制成膜电极,控制膜的氧化和还原状态可以从溶液中可逆地置入和释放离子,从而实现离子的分离,并使膜得到再生[3?4]。
铁氰化镍(NiHCF)由于其独特的化学计量关系和分子结构特征,以及对碱金属离子的选择性不同 (Cs+>Rb+>K+>Na+>Li+)而成为电化学控制分离碱金属离子的首选材料[5?6]。目前,制备NiHCF膜电极通常采用电化学方法,如阳极氧化[1, 7]与阴极循环伏安沉积法[8?9]。研究表明:NiHCF薄膜的电化学特性在很大程度上取决于其制备方法和成膜条件[10?11]。采用阳极氧化和循环伏安沉积法制备的NiHCF膜电极尽管对Cs离子具有优良的选择性,但沉积膜的离子交换容量偏低、循环寿命较差[12]。脉冲电沉积因其得到的膜具有晶粒 细化程度好以及膜沉积质量高等优点常用于制备金 属[13]、合金[14]或半导体薄膜材料[15]。研究表明,脉冲电沉积过程中通过调节脉冲参数(脉冲频率和脉冲电流等)可以很好地控制膜材料性能。NiHCF薄膜是一种半导体材料,在完全氧化或还原状态下为绝缘体,在氧化和还原态之间为导体。目前,采用脉冲电沉积法制备半导体NiHCF膜电极尚未见报道。本文作者在石墨基体上采用脉冲电沉积法制备半导体NiHCF膜,同时考察脉冲参数等制备条件对膜电极离子分离容量以及稳定性等电化学性能的影响。
1 实验
1.1 仪器与试剂
所用试剂均为分析纯或优级纯,水为纯水(Millipore 18.2 MΩ?cm)。所有电化学实验都采用VMP2型恒电位仪(Princeton USA),由EC-Lab软件控制。实验采用三电极体系,铂丝为对电极,饱和甘汞电极(SCE)为参比电极,石墨为工作电极。采用美国ESCALAB250型能谱仪和LEO 438VP型扫描电镜分别进行XPS和SEM分析。
1.2 电极制备
将直径为4 mm的石墨棒采用不同粗糙度的砂纸打磨至平整光滑,经纯水冲洗后晾干备用。将经过预处理的石墨基体做工作电极,于新配制的中性支持电解液(含2 mmol/L NiSO4、2 mmol/L K3Fe(CN)6和0.25 mol/L Na2SO4)中进行脉冲电沉积。在石墨电极基体有效接触面积为4 cm2,控制脉冲电压为0.2~0.7 V、脉冲时间为0.4~0.7 s、占空比ton/(ton+toff)为40%~75%等参数条件下,经脉冲一定次数(1 000~5 000次)制得NiHCF膜电极。脉冲波型采用控制一定时间(ton)脉冲电压后截断时间内(toff)控制电流为零。
为便于比较,将同样尺寸石墨电极基体浸入新配置好的相同中性支持电解液中,以25 mV/s的扫描速度在0.2~1.0 V之间扫描12 min,用循环伏安电沉积法制得NiHCF膜电极。
1.3 膜电极性能实验
将用脉冲电沉积法制得的NiHCF膜电极在 1 mol/L KNO3溶液中于0.2~1.0 V之间以25 mV/s的扫速循环扫描25次测定其离子交换容量和峰电流密度。取出后充分洗涤、晾干之后将试样进行SEM测定和XPS分析。NiHCF膜电极电量衰减实验在1 mol/L KNO3溶液中以50 mV/s扫描速度循环扫描250次。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 脉冲电沉积NiHCF膜电极的SEM像及XPS谱
图1所示为石墨基体脉冲电沉积NiHCF膜前后电极表面的形貌。由图1可见,石墨基体表面沉积膜前的形貌为典型的片层结构,脉冲电沉积后得到的薄膜表面均匀、致密但有许多缝隙,与循环伏安电沉积得到的粗燥不平且存在大量缺陷的膜有很大差异[16]。

图1 脉冲电沉积NiHCF膜前后表面的SEM像
Fig.1 SEM images of electrode surface before (a) and after (b) NiHCF film prepared on graphite substrate
脉冲沉积过程中(ton)脉冲电流瞬时增大使得电极表面吸附的原子数高,形成的晶核数也多;在截断时间(toff)内脉冲电流为零,晶核数不再增加但晶核继续成长。此时,电极界面处的镍离子得以迅速补充,减小了浓差极化的影响,使得再次导通脉冲时,在导通时间内可以利用高电流密度产生更高的电化学极化,从而利于成核率的提高,细化了晶粒,提高了沉积层的致密度。
图2所示为石墨基体脉冲电沉积NiHCF膜并在 1 mol/L KNO3溶液中循环伏安扫描25次后的XPS谱。图中710 eV和857 eV分别对应着Fe2p3和Ni2p,证明在石墨基体表面脉冲电沉积得到了NiHCF薄膜,293 eV对应着K2p,说明脉冲电沉积NiHCF膜在溶液中进行循环扫描时已置入K+。

图2 石墨基脉冲电沉积NiHCF膜的XPS谱
Fig.2 XPS pattern of NiHCF film on graphite
2.2 脉冲参数对NiHCF膜电极制备的影响
2.2.1 脉冲电压对膜性能的影响
脉冲电压是脉冲电沉积操作过程的一个主要参数,选择合适的脉冲电压对于制备高质量膜非常重要。在控制脉冲时间为0.6 s、占空比为50%,脉冲电压为0.3和0.5 V下脉冲沉积2 000次后得到的NiHCF膜电极在1 mol/L KNO3溶液中的CV曲线如图3所示。由图3可知,不同脉冲电压下制得的NiHCF膜电极循环伏安曲线有很大差异,膜的交换容量和阴阳极峰形都发生改变。

图3 不同脉冲电压的膜电极循环伏安曲线
Fig.3 Cyclic voltammograms of NiHCF films at different pulse potentials (scan rate 25 mV/s)
根据不同脉冲电压下沉积得到NiHCF膜的CV曲线计算其积分电量,可以更清晰地比较膜电极在氧化还原过程中的离子交换容量,如图4所示。由图4可明显看出,当脉冲电压为0.3 V时,得到的NiHCF膜电极离子交换容量优于其他电压下得到的膜。电沉积制备NiHCF膜首先需将Fe(CN)6?3还原为Fe(CN)6?4,再与Ni2+反应得到薄膜。脉冲电压太低则生成太多的还原态Fe(CN)6?4,电极附近的Ni离子很快消耗殆尽影响膜的生成速度;脉冲电压太高则生成的还原态Fe(CN)6?4浓度太低,同样会减小膜的生成速度。因此,在脉冲沉积过程中,NiHCF膜沉积的最佳条件要求电极表面Fe(CN)6?4浓度与Ni2+浓度达到合理的平衡,脉冲电压的大小对Fe(CN)6?4浓度与Ni2+浓度有很大的影响。
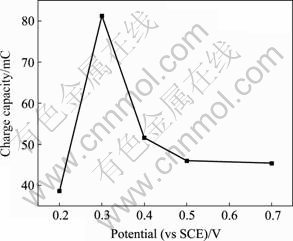
图4 不同脉冲电压下膜电极CV曲线的积分电量
Fig.4 Charge capacity of NiHCF film at different pulse potentials
2.2.2 脉冲截断时间toff对膜性能影响
图5所示为固定脉冲电压为0.3 V、导通时间(ton)为0.3 s时采用不同截断时间toff脉冲2 000次得到的 NiHCF膜电极在1 mol/L KNO3溶液中循环扫描25次后的CV曲线的积分电量。由图5可知,脉冲截断时间toff由0.1 s增加至0.3 s时,得到的膜电极循环伏安积分电量均逐渐增大;但当toff增大至0.4 s时,积分电量又突然减小。在toff截断时间内尽管控制电流为零,但由于双电层放电作用使得电极表面仍然存在着NiHCF膜的氧化与Fe(CN)63?/Fe(CN)64?的还原,以及Fe(CN)64?和Ni2+的成膜反应;toff不同使得溶液中Fe(CN)63?、Fe(CN)64?与Ni2+在电极表面有不同的浓度分布曲线。当toff较小(为0.1 s)时,toff小于双电层放电时间,此时溶液向电极表面提供的Fe(CN)63?和Ni2+不足,电极表面会发生析氢反应阻碍离子迁移,生成的膜较少;随着toff逐渐增大,Fe(CN)63?和Ni2+在电极表面能够迅速补充,扩散引起的Fe(CN)63?和Ni2+不足现象逐渐消失,膜的生成量也逐渐增大;但当toff继续增大至0.4 s后,截断时间内电极表面的NiHCF膜氧化程度加大,下一个导通时间内提供的电量一部分用于电极表面已氧化NiHCF膜的还原,NiHCF膜的实际生成量反而减小。因此脉冲电沉积过程也有一个最佳的截断时间。

图5 不同脉冲截断时间沉积NiHCF膜CV曲线的积分电量
Fig.5 Charge capacity of NiHCF film at different pulse times
2.2.3 脉冲沉积次数的影响
不同脉冲沉积次数对NiHCF膜电极离子交换容量的影响如图6所示。由图6可见,随着脉冲沉积次数的增加,NiHCF膜的交换容量逐渐增大,在前1 500次增长幅度明显,而1 500次后增长速度逐渐放缓。以“可溶性”结构NiHCF膜为例[17],根据循环伏安曲线积分电量可估算沉积膜的厚度[8],当脉冲次数为 3 500时,相应NiHCF膜的厚度达414 nm,因为膜较厚,导致电导率下降,同时由于反应物的不断消耗使膜的生成逐渐减少。

图6 不同脉冲沉积次数对膜电极CV曲线积分电量的影响
Fig.6 Effect of pulse deposition number on charge capacity of NiHCF films
2.3 脉冲电沉积瞬间电压和电流随时间的变化
图7所示为脉冲电压为0.3 V,导通时间ton与截断时间toff均为0.3 s时脉冲电沉积NiHCF膜过程前 10 s的瞬时电压与电流随时间的变化。由图7可知,脉冲沉积开始瞬间,电极表面还没有生成NiHCF膜,电极表面液/固界面双电层电容迅速充电,电解池两端的开路电压迅速上升到0.74 V。在第一个导通时间ton内,由于Fe(CN)63?还原为Fe(CN)64?产生电流,峰电流值瞬间增为最大值7.1 mA,NiHCF膜开始形成。之后,在第一个截断时间toff内,双电层电容放电,测得的开路电压从0.74 V迅速降低至0.57 V。此后随着膜的增长,开路电压逐渐缓慢地降低,峰电流值迅速减小。图8所示为0.3 V脉冲电压下脉冲电流—时间曲线。由图8可看出,峰电流随沉积时间呈现迅速减小的趋势。当脉冲沉积到最后阶段,截断时间toff内测得的开路电压下降趋于平缓。此时,双电层电容的充、放电过程趋于稳定,脉冲沉积的NiHCF膜的量逐渐减少但更加均匀。
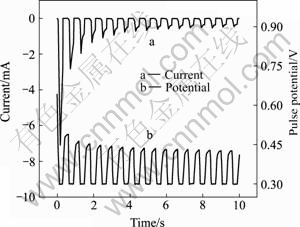
图7 脉冲电沉积NiHCF膜前10 s电流和脉冲电压随时间的变化
Fig.7 Changes of current(a) and pulse potential(b) with time during initial 10 s pulse deposition of NiHCF films
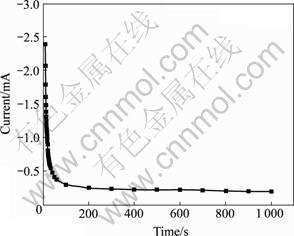
图8 0.3 V脉冲电压下脉冲电流—时间曲线
Fig.8 Current—time curve during pulse deposition of NiHCF films with pulse potential of 0.3 V
2.4 脉冲沉积NiHCF膜的电化学性能
图9所示为导通时间和截断时间均为0.3 s、占空比为50%和脉冲电压为0.3 V时脉冲电沉积2 000次得到的NiHCF膜电极与相同时间内循环伏安法制备得到的NiHCF膜电极分别在1 mol/L KNO3溶液中进行循环伏安扫描曲线。由图9可知,脉冲电沉积得到的膜电极交换容量大约是循环伏安法得到膜电极的3倍。

图9 脉冲电沉积与循环伏安法制备的NiHCF膜电极的循环伏安曲线
Fig.9 Cyclic voltammograms of NiHCF films prepared by pulse electrodeposition and CV electrodeposition
NiHCF薄膜的循环寿命是衡量其ECIS性能的又一个重要指标。在电势循环扫描过程中,膜的电活性会随循环次数的增加而降低,其寿命可通过考察其循环伏安曲线的离子交换容量随循环次数的衰减情况来定量分析。图10所示为脉冲沉积与循环伏安沉积法制备的NiHCF膜电极在1 mol/L KNO3溶液中以25 mV/s的扫速循环扫描250次的电量衰减图。由图10可知,脉冲电沉积法制备的NiHCF膜在经过250次循环扫描

图10 不同方法制备的NiHCF膜电极的电量衰减图
Fig.10 Normalized charge capacity of cycle number for NiHCF film prepared by pulsed electrodeposition (a) and CV electrodeposition (b)
后衰减不到3%,而循环伏安电沉积NiHCF膜在经历了250次循环扫描后衰减了约21%,说明脉冲电沉积法制备的NiHCF膜均匀致密,具有优良的稳定性。
3 结论
1) 通过脉冲电沉积法在石墨基体上可制备出均匀、致密的NiHCF膜。
2) 脉冲电沉积法操作简单,可控性强,仅需调节脉冲电沉积参数即可得到大离子交换容量和优良循环稳定性的NiHCF膜电极。
3) 脉冲电沉积法制备NiHCF膜的最优条件为:脉冲电压0.3 V(vs SCE),脉冲周期0.6 s,占空比50%。
REFERENCES
[1] RASSAT S D, SUKAMTO J H, ORTH R J, LILGA M A, HALLEN R T. Development of an electrically switched ion exchange process for selective ion separations[J]. Separation and Purification Technology ,1999, 15(3): 207?222.
[2] 郝晓刚, 张忠林, 刘世斌, 孙彦平. 电活性铁氰化镍离子交换膜的制备及应用. 中国专利, ZL200410012195.8[P]. 2006?07?05.
HAO Xiao-gang, ZHANG Zhong-lin, LIU Shi-bin, SUN Yan-ping. Preparation and application electroactive nickel hexacyanoferrate (NiHCF) ion exchange film. CN ZL200410012195.8[P]. 2006?07?05.
[3] JEERAGE K M, STEEN W A, SCHWARTZ D T. Correlating nanoscale structure with ion intercalation in electrodeposited nickel hexacyanoferrate thin films[J]. Chem Mater, 2002, 14(2): 530?535.
[4] 郝晓刚, 马旭莉. 电化学控制离子交换(分离)膜的制备、结构与性能[J]. 功能材料, 2007, 38(S): 2721?2726.
HAO Xiao-gang, MA Xu-li. Electrochemically controlled ion separation (ECIS) film: processing, structure and performance[J]. Functional Materials, 2007, 38(S): 2721?2726.
[5] JEERAGE K M, STEEN W A, SCHWARTZ D T. Charge-density-dependent partitioning of Cs+ and K+ into nickel hexacyanoferrate matrixes[J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18(9): 3620?3625.
[6] GUO J X, HAO X G, MA X L, ZHANG Z L, LIU S B. Electrochemical characterization of ion selectivity in electrodeposited nickel hexacyanoferrate thin films[J]. Mineral Metallurgy Materials, 2008, 15(1): 79?83.
[7] LILGA M A, ORTH R J, SUKAMTO J H, RASSAT S D, GENDERS J D, GOPAL R. Cesium separation using electrically switched ion exchange[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2001, 24(3): 451?466.
[8] JEERAGE K M, SCHWARTZ D T. Characterization of cathodically deposited nickel hexacyanoferrate for electrochemically switched ion exchange[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2000, 35(15): 2375?2392.
[9] STEEN W A, JERRAGE K M, SCHWARTZ D T. Raman spectroscopy of redox activity in cathodically electrodeposited nickel hexacyanoferrate thin films[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2002, 56(8): 1021?1029.
[10] ZAMPONIA S, BERRETTONI M, KULESZA P J, MIECZNIKOWSKI K, MALIK M A., MAKOWSKI O, MARASSI R. Influence of experimental conditions on electrochemical behavior of Prussian blue type nickel hexacyanoferrate film[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2003, 48(28): 4261?4269.
[11] HAO X G, SCHWARTZ D T. Tuning intercalation sites in nickel hexacyanoferrate using lattice nonstoichiometry[J]. Chem Mater, 2005, 17(23): 5831?5836.
[12] GOMEZ J R, MEDINA J A, JEERAGE K M, STEEN W A, SCHWARTZ D T. High capacity SiO2-graphite composite electrodes with chemically incorporated metal mhcfs for electrochemically switched alkaline cation exchange[J]. Electrochemical Society, 2004, 151(9): D87?D92.
[13] 王子涵, 杨 滨, 铁 军, 姜 涛, 杨玉国, 张济山. 脉冲频率对电沉积Ni镀层组织和性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(S3): 620?622.
WANG Zi-han, YANG Bin, TIE Jun, JIANG Tao, YANG Yu-guo, ZHANG Ji-shan. The effect of pulse frequency on the microstructure and tensile properties of Ni sheets[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(S3): 620?622.
[14] SUBRAMANIAN M, DHANIKAIVELU N, RAMA P R. Pulsed electrodeposition of cobalt and nickel alloy[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Metal Finishing, 2007, 85(5): 274?280.
[15] CHENG S Y, CHEN Y Q, HE Y J, CHEN G N. The structure and properties of SnS thin films prepared by pulse electro-deposition[J]. Materials Letters, 2007, 61(6): 1408?1412.
[16] 张 玫, 郝晓刚, 马旭莉, 刘世斌, 樊彩梅, 孙彦平. 石墨基体NiHCF薄膜的离子交换性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2006, 35(S2): 249?253.
ZHANG Mei, HAO Xiao-gang, MA Xu-li, LIU Shi-bin, FAN Cai-mei, SUN Yan-ping. Ion exchange performances of nickel hexacyanoferrate thin films on graphite substrate[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2006, 35(S2): 249?253.
[17] YU Q M, STEEN W A, JEERAGE K M, JIANG S Y, SCHWARTZ D T. Structure-dependent solvent and ion intercalation in reduced and oxidized nickel hexacyanoferrates[J]. Electrochemical Society, 2002, 149(6): E195?E203.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(20676089;20776091);山西省自然科学基金资助项目(2007011029)
收稿日期:2008-12-22;修订日期:2009-04-02
通讯作者:郝晓刚,教授,博士;电话:0351-6018554;E-mail: xghao@tyut.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)