铜闪速炉内颗粒受热过程的数学建模与数值优化
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第5期
论文作者:高东波 彭小奇 宋彦坡 祝振宇 戴扬
文章页码:1506 - 1517
关键词:闪速熔炼过程;颗粒受热;数学模型;高速射流;数值模拟
Key words:flash smelting process; particle heating; mathematical model; high-speed jet; numerical simulation
摘 要:为了研究闪速炉冶炼颗粒着火延迟问题,建立反应塔内颗粒受热过程的数学模型,并进行计算。结果表明,在塔高0.6 m范围内,辐射换热对于颗粒的加热过程影响较大,而在反应塔0.6 m以下区域,对流换热占主导作用。鉴于强化对流换热过程对提高颗粒加热速度进而提高着火高度更有效,因此,建议采用高速热氧射流技术代替闪速炉内的天然气,使得颗粒周围的气相产生横向扰动,从而提高气-粒两相间的滑移速度和对流换热系数。同时,开展高速热氧射流和常规天然气燃烧工况下的数值模拟。结果表明,采用高速热氧射流技术能够提高颗粒的升温速度,进而使颗粒更快着火,特别是在塔径R=0.3~0.6 m范围内。这说明,在相同的操作条件下,采用高速热氧射流技术可以进一步提升熔炼效率。
Abstract: A mathematical model of the particle heating process in the reaction shaft of flash smelting furnace was established and the calculation was performed. The results indicate that radiation plays a significant role in the heat transfer process within the first 0.6 m in the upper part of the reaction shaft, whilst the convection is dominant in the area below 0.6 m for the particle heating. In order to accelerate the particle ignition, it is necessary to enhance the convection, thus to speed up the particle heating. A high-speed preheated oxygen jet technology was then suggested to replace the nature gas combustion in the flash furnace, aiming to create a lateral disturbance in the gaseous phase around the particles, so as to achieve a slip velocity between the two phases and a high convective heat transfer coefficient. Numerical simulation was carried out for the cases with the high-speed oxygen jet and the normal nature gas burners. The results show that with the high-speed jet technology, particles are heated up more rapidly and ignited much earlier, especially within the area of the radial range of R=0.3-0.6 m. As a result, a more efficient smelting process can be achieved under the same operational condition.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 1506-1517
Dong-bo GAO1, Xiao-qi PENG1,2, Yan-po SONG1, Zhen-yu ZHU1, Yang DAI1
1. School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Hunan First Normal University, Changsha 410205, China
Received 16 October 2020; accepted 10 March 2021
Abstract: A mathematical model of the particle heating process in the reaction shaft of flash smelting furnace was established and the calculation was performed. The results indicate that radiation plays a significant role in the heat transfer process within the first 0.6 m in the upper part of the reaction shaft, whilst the convection is dominant in the area below 0.6 m for the particle heating. In order to accelerate the particle ignition, it is necessary to enhance the convection, thus to speed up the particle heating. A high-speed preheated oxygen jet technology was then suggested to replace the nature gas combustion in the flash furnace, aiming to create a lateral disturbance in the gaseous phase around the particles, so as to achieve a slip velocity between the two phases and a high convective heat transfer coefficient. Numerical simulation was carried out for the cases with the high-speed oxygen jet and the normal nature gas burners. The results show that with the high-speed jet technology, particles are heated up more rapidly and ignited much earlier, especially within the area of the radial range of R=0.3-0.6 m. As a result, a more efficient smelting process can be achieved under the same operational condition.
Key words: flash smelting process; particle heating; mathematical model; high-speed jet; numerical simulation
1 Introduction
The flash smelting has been recognized as a highly efficient and environmentally benign process for extracting Cu or Ni metals from their sulfides. In the past decades, the flash furnaces have been widely used, producing more than 50% of copper and 70% of nickel in China. High productivity is one of the outstanding advantages of the flash smelting technology. However, when great efforts are committed to continuously increase the capacity of the flash furnace, similar technical problems are encountered in different smelters, such as the overheating in the lower part of the reaction shaft, the accelerated corrosion to the furnace walls, and high dust generation ratio of the process [1,2]. A number of studies including experiments [3-5], neural network [6], and numerical simulation [7-9] were conducted to investigate the root causes. Besides, thermodynamic simulation [10,11] was also applied to obtaining the phase equilibria in the flash smelting process [12].
THEMELIS et al [13] originally applied numerical simulation in the study of the flash smelting process. In 1995, JOKILAAKSO et al [14] used the CFD software Phoenics to study the fluid flow around the concentrate burner of a copper flash smelting furnace. Later in 1998, they simulated the temperature distributions in the reaction shaft with Phoenics again, by simplifying the 3D cylindrical structure into a 2D axial computational domain, but taking some basic chemical reactions into consideration [15]. After- wards, the numerical method was adopted for the study of the flash smelting process of nickel [16], zinc [17,18] and lead [19]. And simulation was also carried out for purposes of optimizing the furnace structures and operational parameters. In 2004, CHEN et al [20] performed numerical simulation of the flash smelting process with CFX, and the optimization of the concentrate burner operation was advanced. They also investigated the factors affecting the Fe3O4 formation inside the reaction shaft by changing the oxygen-enrichment and the flow rate of the process air in the numerical studies. As a result, the solution was concluded to reduce the copper loss in the slag [21]. Moreover, an in-depth analysis of the flow characteristics in the settler [22] was also reported by the same research group recently based on numerical simulations.
The concentrate combustion is an important topic in the numerical study of the flash smelting process, since it directly affects the completeness of reactions and the composition of final products of the process. It was believed that the concentrate particles completely reacted soon after they are fed into the reaction shaft. And this was proven in the simulation results of XIE [23] (Fig. 1(a)) and LI et al [24], which showed that most particles at the height (the vertical distance from the roof of the reaction shaft to the position where the sampling point locates, also referred to as the shaft height) of 2 m in the reaction shaft were fully reacted. However, for the same flash furnace, as its concentrate feed rate was doubled, a significant delay was found in the particle ignition [25], as shown in Fig. 1(b). In order to speed up the particle ignitions in the reaction shaft, many studies have then been carried out. CHEN et al [26] suggested to insert a nature gas lance through the center of the concentrate burner to supply heat to the ignition of particles. Instead of making improvement of the furnace structure, ZHOU et al [27] developed an indicator named the momentum ratio of the distribution air over the process air, and found that it has dramatic influence on the particle dispersion in the furnace. The indicator then has been widely accepted and used to optimize the operational parameters of the concentrate burner. Nevertheless, few theoretical analyses have been reported for the particle heating process in the reaction shaft. To further improve the efficiency and the capacity of the flash smelting process, it is crucial to investigate the causes of the ignition delay of particles. Therefore, a mathematical model was developed to analyze the heat transfer in the particle heating process inside the reaction shaft, to clarify the key factor that is helpful to accelerate the heating process and the ignition of particles. Numerical simulation was also carried out, to assess the effectiveness of the technical measure proposed in the study.

Fig. 1 Temperature increasing along reaction shaft
2 Theoretical modelling of heating process of concentrate particles
Since the concentrate particles are fed into the flash furnace at a temperature much lower than their ignition point, the particles must undergo a process of heating and temperature increasing before they reach their ignition point. This process is generally considered to be very fast, because the smelting reactions are completed in only a second or so in the furnace, but few detailed analyses have been reported how the particles are heated up inside the furnace. Hence, a mathematical model was established to investigate the heat transfer and the temperature change of the concentrate particles as they fall through the reaction shaft.
2.1 Mathematical model for analysis of particle heating process
The “concentrate cone” formed by the dispersed particles inside the furnace is approximated as a truncated cone in the model, extending from the exit of the process air to the bottom of the reaction shaft. The top diameter of the truncated cone takes the exit diameter of the pipe for the process air, and the bottom diameter is equal to the actual dispersion diameter of the concentrate cone measured in the industrial test [28].
An element of infinitesimal height Δh (as shown in Fig. 2) was taken for consideration. In order to simplify the analysis of heat transfer between the element and its surroundings, a few assumptions were made as follows.
(1) The element is approximated to be a cylinder because of its infinitesimal height, and the particles in the element are considered to be of the same size.
(2) By considering the element as a particle group, the heat received by the element is to heat up the particles inside.
(3) The heat transfer between the element and its surroundings includes the convection and radiation. For the radiation, only the radiative heat transfer Qr between the element and the shaft wall is considered, and the element is regarded as a gray body. Besides, the convective heat Qc is supposed to be received by the element only through the circumferential surface of the cyliner.

Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of element for particle heating process analysis
Hence, an equation of energy balance can be used to describe how the temperature of the element changes with the heat received:
 (1)
(1)
where cp is the specific heat capacity of concentrate particles, J/(kg·K). M is the total mass of particles in the element, kg. Tp is the particle temperature of the element, K. t is the residence time of particles through the element, s. Qc and Qr are the heat fluxes that the element receives by convection and radiation, respectively, W.
By replacing the variable Qc in Eq. (1) with Newton equation and Qr with Stephan-Boltzmann law, a differential equation of particle temperature changing with time can be obtained:
 (2)
(2)
where D denotes the diameter of the cylinder element, m. α is the convective heat transfer coefficient, W/(m2·K). Tg is the temperature of the hot gas around the element, K. ε denotes the emissivity of the element surface. σ0 is the Stephan- Boltzmann constant, and σ0=5.67×10-8 W/(m2·K4). Tw is the wall temperature of reaction shaft, K.
Then, the formula to calculate the temperature of the particle group can be obtained by integrating Eq. (2), that is

 (3)
(3)
where t1 is the time duration of the heating process, s. And T0 and T1 are the temperatures of the particle group at the beginning and the end of the time duration, K.
With Eq. (1), it can be found that, when the concentrate feed rate increases, more thermal energy is required to heat up the particles. In other words, if the heat flux remains the same, it will take longer, either in time or distance for the particle group to reach the same temperature. This then explains why the particles seem more difficult to be ignited in the reaction shaft at a higher concentrate feed rate. Also, if we wish to heat up the particles at the same rate as before, a higher heat flux must be provided, that is, the conditions of heat transfer must be improved so that the particles can receive much more heat in the same time duration.
The energy for the temperature rising of the particles is the sum of the convective heat from the hot gas and the radiative heat from the wall of the reaction shaft. In order to distinguish the role of radiation and convection in the heating process of particles, a program was developed to calculate the temperature of the particle group as it moves along the reaction shaft, to positions of different height, and the proportions of the convection and radiation in the total heat received by the element are summarized.
2.2 Effects of convection and radiation in particle heating process
A calculation was carried out for a case at a concentrate feed rate of 200 t/h. The proportions of convection and radiation in the total heat that particles receive within 3 m of the shaft height are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Proportions of convection and radiation in total heat received by particle group at different heights in reaction shaft
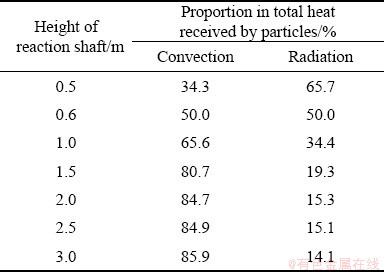
It was suggested that, in 0.5 m where the particles move along the reaction shaft, the radiation plays a major role in the heating process, providing 2/3 heat for the increasing of the particle temperature. However, by moving down just 0.1 m (to the height of 0.6 m), the effect of the convection increases significantly and its proportion becomes equivalent to that of the radiative heat. When the particles move down further, to the height of 1 m, the convective heat is dominant in the total heat. The proportion then keeps increasing, until exceeding 80% at the height of 1.5 m. Afterwards, the convective heat is changed slightly, increasing by 5% in the following 1.5 m.
As the results indicate, the radiation plays a greater role in the early stage of the particle heating process, while the convection is more important in the area below the height of 0.6 m in the reaction shaft. For the radiation, since the wall temperature is actually the temperature of the molten slag sticking to the shaft refractory linings, it is unlikely to change with the concentrate feed rate. Hence, the radiative heat flux can be hardly improved when the wall conditions are the same. Comparatively, the convection can be normally enhanced by increasing the convective heat transfer coefficient, and thus the focus of study is put on the convection heat transfer.
2.3 Suggestion for convection strengthening
The convection is a heat transfer process associated with fluid flow. The Dittus-Boelter equation gives the correlation of the Nusselt number with the Reynolds number (Re) and the Prandtl number (Pr) under the forced convection heat transfer [29]:
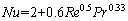 (4)
(4)
The convective heat transfer coefficient can be calculated by
 (5)
(5)
By substituting the definition of Re and Pr into Eq. (5), the convection coefficient can be related to the velocities of the gaseous and particle phases as
 (6)
(6)
where dp is the diameter of particles, and it usually takes the average of particle diameters in the group, m. up and ug denote the velocities of the particle and the gas, respectively, m/s. υg is the gaseous viscosity, m2/s. ρg is the gaseous density, kg/m3. cg is the specific heat capacity of the gas, J/(kg·K). λg denotes the gaseous thermal conductivity, W/(m·K).
The convective heat transfer coefficient between the particles and the gas is proportional to the square root of the velocity difference (i.e. slip velocity) of the two phases. Since it is unrealistic to change physical properties of either the gas or the particles, increasing the slip velocity is more practical to improve the convection inside the furnace. Based on above considerations, the high- speed preheated oxygen jet technology was recommended, aiming to enhance the convection heat transfer and thus to accelerate the particle heating process. Numerical simulation was then carried out to analyze the effectiveness of adopting this technical measure in the flash smelting process.
3 Numerical analysis of high-speed jet measure
The main air streams in the flash furnace include the process air, the distribution air and the central oxygen, which all come into the reaction shaft through the concentrate jet distributor (CJD) burner that locates in the center of the shaft roof. Besides, there are three combustion flows from the natural gas burner around the CJD burner. All these gaseous streams move axially along the reaction shaft, except that the distribution air exiting from the side of the distribution cone blows in the radial direction. The schematic diagrams of the flash furnace and the air streams through the CJD burner are shown in Figs. 3 and 4, respectively.

Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of flash furnace

Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of CJD burner and airflow through it
Dispersed through the curved surface of the distribution cone, the concentrate particles at 100 μm are susceptible to the gaseous flow, making their speed soon approach that of the gas. So, the slip velocity between the gaseous phase and the particles normally reduces quickly within a short distance below the CJD burner. Then, a more effective way to increase the slip velocity between the two phases is to create a lateral disturbance perpendicular to the vertical movement of the particles. As a result, the high-speed preheating oxygen jet is suggested to replace the natural gas combustion in the shaft roof. Specifically, the oxygen is injected at a high speed from three burners in the shaft roof at an angle of 15° to the vertical direction. Meanwhile, to compensate the heat loss by cancellation of the natural gas combustion, the oxygen is preheated to 1500 K as the supplement heat into the furnace.
3.1 Mathematical model for numerical simulation
Numerical simulation was carried out for the flash smelting process respectively with the standard natural gas burners and the high-speed preheated oxygen jet burners. The flash furnace is 7 m in diameter and 8 m in height. The gaseous passage of the settler is also included, which is 18.65 m long, 1.6 m high and 9.2 m wide inside (as shown in Fig. 3). A hybrid grid scheme was used for the discretization of the computation domain, of which the structured grids were adopted mainly in the gaseous passage of the settler, and the unstructured grids were applied to the domain of the reaction shaft. Meanwhile, the grids in the areas near the burners and in the center of the reaction shaft were locally refined. The total number of the grids is about 700000.
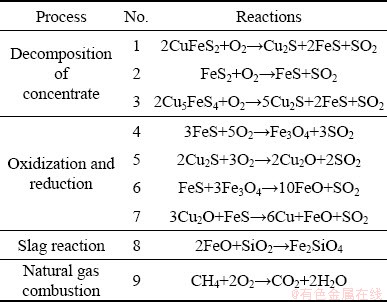
The flash smelting process involves complex interactions of the gaseous phase and the particles. The transfer processes of the gaseous phase are described and solved based on the Eulerian method, and those of the particle phase are based on the Lagrangian method. The governing equations to describe the transfer processes between the gaseous and the particle phases include the momentum equation, the energy equation and the species equation for each phase. All these equations can be referred to in literatures [27,28,30,31]. The chemical reactions involved in the smelting process and the natural gas combustion are given in Table 2.
Table 2 Chemical reactions included in numerical simulation
Numerical computation was performed for cases at a concentrate feed rate of 200 t/h, of which one is with the normal natural gas burner (named 200t-S) and the other with the high-speed preheated oxygen jet burner (named 200t-J). An industrial test was also carried out independently at the same concentrate feed rate (named 200t-T), to verify the accuracy of the numerical model. Operational parameters for all three cases are listed in Table 3.
Table 3 Production parameters of simulation cases

The gaseous temperature at three points of the flash furnace was measured by inserting the thermocouple into the furnace through the sampling holes. The positions of the sampling holes in the flash furnace are illustrated in Fig. 5.
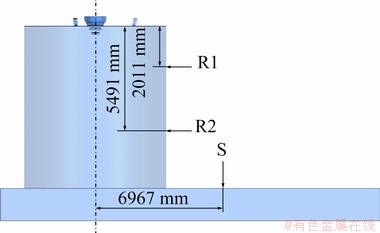
Fig. 5 Positions of sampling holes used for measurement of gaseous temperature
The temperatures measured in the industrial test were compared with the results of the numerical simulation (Case: 200t-T), as given in Table 4. The relative errors between the test data and the simulation results are all less than 5%. Therefore, the numerical models of the copper flash smelting process are considered to be accurate and reliable for following performance analysis of the high-speed preheated oxygen jet.
Table 4 Comparison of gaseous temperatures of industrial test and numerical results (200t-T)

3.2 Numerical results and discussion
The performance analysis of the high-speed preheated oxygen jet was made based on the comparison of simulation results in the cases of 200t-S and 200t-J, including the velocity field, the temperature field and the concentration field of the gaseous phase.
3.2.1 Comparison of velocity distribution in two cases
The velocity distribution in the central section along the X-axis (i.e. the direction along the furnace length) in the cases of 200t-J and 200t-S is shown in Fig. 6.
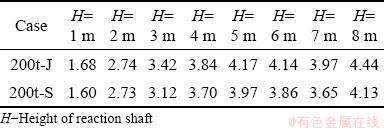
From Fig. 6(a), it is suggested that after being injected into the furnace at a high speed, the oxygen stream is guided into the main stream and merges in it at the height of about 2 m. Influenced by the high-speed jet at the top, the expansion of the central gas column to the right is slightly constrained, resulting in the whole column in the reaction shaft deflecting a bit to the left. In the case of 200t-J, the diameters of the gas column are a little larger than those in the normal condition (listed in Table 5), which is likely due to the hot oxygen injecting into the gas column.

Fig. 6 Velocity distribution in high-speed jet condition
Table 5 Comparison of gas column diameters in cases of 200t-J and 200t-S (m)
3.2.2 Comparison of temperature distribution in two cases
Figure 7 shows the temperature contour of the high-speed jet case and the normal natural gas combustion case. The adoption of the high-speed jet seems not to affect the temperature distribution significantly in the reaction shaft. However, by replacing the natural gas burner with the preheated high-speed oxygen jet, the local high temperature areas at the exit of the natural gas burner and around the central gas column disappear. Instead, the range of the central low temperature area reduces, and the temperature distribution inside the furnace tends to be more uniform.

Fig. 7 Temperature distribution in different conditions
Figure 8 shows the temperature changes along the height of the reaction shaft at different radial positions in the central section (the schematic diagram of the position is illustrated in Fig. 8(f)) in the cases of 200t-J and 200t-S. By preheating the oxygen to 1500 K, it is to compensate the heat loss caused by the cancellation of the natural gas combustion. However, since the enthalpy of the high-temperature oxygen is only half of the heat released by the natural gas combustion, and the high-speed jet can hardly penetrate the gas column to inject the heat into the center of the column, the temperature distribution in the case of 200t-J is not much different in the center of the reaction shaft from that in the case of 200t-S, as shown in Fig. 8(a). But at the position of R=0.3 m and R=0.6 m, the gaseous temperature increases much faster along the shaft height, which indicates a faster heating process for the particles.
By taking the melting point of the Cu-Fe-S-O solution as the ignition point of the particle group [32], the particles are found to be ignited earlier in the case of 200t-J, at the radial positions of R=0.3 m and R=0.6 m. Furthermore, the point of the highest gaseous temperature usually corresponds to the position where most particles are reacted. And in the case of 200t-J, these points are at the positions of R=0.3 m and R=0.6 m, indicating a faster smelting reaction. When extended to the area of R>1.2 m, the adoption of the high-speed jet seems to have no obvious impact on the temperature distribution, except that a local high temperature area can be found in the case of 200t-S due to the combustion of the natural gas.

Fig. 8 Comparison of temperature change in two cases of 200t-S and 200t-J
3.2.3 Comparison of SO2 concentration distribution in two cases
SO2 is an important product of the smelting process, so in the numerical studies, the distribution of the SO2 concentration field is often used to analyze the efficiency of the smelting process in the reaction shaft. The SO2 concentration changing with the shaft height in two cases is summarized in Fig. 9.

Fig. 9 Comparison of SO2 concentration in two cases of 200t-S and 200t-J
Similar to the temperature distribution, the adoption of the high-speed oxygen jet has limited impact on the central area of the furnace. But at the bottom of the reaction shaft, as indicated by the larger gaseous column diameter in the case of 200t-J, the particles are more dispersed, so the concentration of SO2 is lower than that in the case of 200t-S, due to a less dense particle distribution per unit area. While at the positions of R=0.3 m and R=0.6 m, the SO2 concentration increases more quickly and reaches the highest point much earlier in the case adopting the high-speed oxygen jet. In addition, the SO2 concentration is also higher at other radial positions in the case of 200t-J, indicating a more efficient smelting process in the case with the high-speed jet technology.
3.3 Performance analysis of high-speed jet technology
By introducing the high-speed preheated oxygen jet into the flash smelting process, a lateral disturbance is created in the gaseous flow, thus to increase the slip velocity between the gaseous phase and the particles in the upper part of the reaction shaft. Compared to the numerical results of the case with normal natural gas combustion (200t-S),the key findings in the smelting process with the high-speed preheated oxygen jet are summarized as follows.
(1) By preheating the oxygen to 1500 K, the heat loss caused by cancellation of the natural gas combustion is partly compensated. The local high temperature areas caused by natural gas combustion near the shaft roof disappear. In addition, the low temperature area below the CJD burner is smaller, and the temperature inside the shaft is more uniform, with no great temperature gradient forming around the central gas column, which will be beneficial to the particle heating process as well as the furnace maintenance.
(2) After adopting the high-speed preheated oxygen jet, the gaseous temperature in the center and the areas with the radius R>1.2 m changes slightly. However, in the area of the radius R=0.3-0.6 m, the particle heating is found to be significantly accelerated, and thus the particles are ignited earlier. Specifically, for the particles at the radial position of R=0.3 m and R=0.6 m, their ignition height rises 0.2 and 1.1 m, respectively.
(3) Similar characteristics can also be found in the gaseous SO2 concentration fields. But more importantly, the SO2 concentration in the gas column in the case of 200t-J is generally higher than that in the case of 200t-S, indicating that more sulfur is combusted in the reaction shaft, and thus a more efficient smelting reaction can be achieved.
4 Conclusions
(1) The radiation and convection are key heat transfer modes for particle heating in the reaction shaft. However, the radiation plays a greater role in the upper part of the furnace, specifically, within the shaft height of 0.6 m. Thereafter, the convection is dominant in the heating process of particles.
(2) The radiation heat flux inside the reaction shaft can be hardly improved due to the constant wall temperature. Comparatively, the convection can be enhanced, by increasing the slip velocity between the gaseous phase and the particle phase so as to achieve a higher convective heat transfer coefficient.
(3) The movement of the concentrate particles is easily impacted by the gaseous flow, with their velocity approaching to that of the gas. Thus, introducing a lateral gaseous disturbance perpendicular to the vertical movement of the particles will be effective to create a slip velocity between the particles and their surrounding gaseous phase.
(4) The high-speed preheated oxygen jet is suggested to replace the normal natural gas combustion in the flash smelting process. With pointing 15° to the vertical direction, the oxygen stream is injected into the main gas column, causing a lateral disturbance around the surface of the falling particles.
(5) The use of the high-speed preheated oxygen jet has no significant influence on the gaseous temperature in the center of the reaction shaft. However, within the area of R=0.3-0.6 m, particles are heated up more quickly and ignited earlier.
(6) The distribution of the SO2 concentration field also shows that the particles in the furnace are ignited and react faster when the high-speed oxygen jet is adopted. Moreover, the SO2 concentration in the gas column is generally higher, indicating a higher desulfurization rate, and thus a higher smelting efficiency can be achieved.
Acknowledgments
The project was funded by Jinguan Copper of Tongling Non-ferrous Metals Group Co., Ltd. Deep appreciations are given to persons providing technical supports in the research and the industrial tests. Special thanks are given to Prof. Jun ZHOU for his valuable suggestion to this research.
References
[1] AGRAWAL A, SAHU K K. Problems, prospects and current trends of copper recycling in India: An overview [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2010, 54(7): 401-416.
[2] KOJO I V, STORCH H. Copper production with Outokumpu flash smelting: An update [J]. Advanced Processing of Metals and Materials, 2006(8): 226-238.
[3] JORGENSEN F R A, KOH P T L. Combustion in flash smelting furnaces [J]. Journal of The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 2001, 53: 16-20.
[4] HAPP J V, JORGENSEN F R A. Experimental study of flash smelting of Broken Hill lead concentrate [C]//Flash Reaction Processes International Conference. Rolla, MO: University of Missouri-Rolla, 1988: 215-242.
[5] JORGENSEN F R A, MOYLE F J, WADSLEY M W. The ignition of chalcopyrite and pyrite during flash smelting [C]//Flash Reaction Processes International Conference. Rolla, MO: University of Missouri-Rolla, 1988: 167-189.
[6] GUI Wei-hua, WANG Ling-yun, YANG Chun-hua, XIE Yong-fang, PENG Xiao-bo. Intelligent prediction model of matte grade in copper flash smelting process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(5): 1075-1081.
[7] VAARNO J, JARVI J, AHOKAINEN T, LAURILA T, TASKINEN P. Development of a mathematical model of flash smelting and converting process [C]//Third International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries. Melbourne Australia: CSIRO, 2003: 147-154.
[8] LI Xin-feng, MEI Chi, ZHOU Ping, HAN Xiang-li, XIAO Tian-yuan. Mathematical model of multistage and multiphase chemical reactions in flash furnace [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2003, 13(1): 203-207.
[9] SWINBOURNE D R, KHO T S. Computational thermodynamics modeling of minor element distributions during copper flash converting [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2012, 43(4): 823-829.
[10] CHEN Lin, CHEN Peng, ZHANG Du-chao, LIU Wei-feng, YANG Tian-zu. Thermodynamic simulation of complex Pb-Bi concentrate oxidative bath smelting process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2021, 31(4): 1165-1174.
[11] WANG Qin-meng, GUO Xue-yi, WANG Song-song, LIAO Li-le, TIAN Qing-hua. Multiphase equilibrium modeling of oxygen bottom-blown copper smelting process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(11): 2503-2511.
[12] TASKINEN P, JOKILAAKSO A, LINDBERG D, XIA Ji-liang. Modelling copper smelting – The flash smelting plant, process and equipment [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2019, 129(7): 1-14.
[13] THEMELIS N J, MAKINEN J K, MUNROE N D H. Physical chemistry of extractive metallurgy [M]. Warrendale, PA: TMSAIME, 1985.
[14] JOKILAAKSO A, AHOKAINEN T, TEPPO O, YANG Y, LILIUS K. Experimental and computational-fluid-dynamics simulation of the Outokumpu flash smelting process [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 1995, 15(1-4): 217-234.
[15] AHOKAINEN T, JOKILAAKSO A. Numerical simulation of the Outokumpu flash smelting furnace reaction shaft [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1998, 37(3-4): 275-283.
[16] VARNAS S R, KEMORI N, KOH P T L. Evaluation of nickel flash smelting through piloting and simulation [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1998(29): 1329-1343.
[17] KOH P T L, NGUYEN T V, JORGENSEN F R A. Numerical modeling of combustion in a zinc flash smelter [J]. Applied Mathematical Modeling, 1998, 22: 941-948.
[18] SOLNORDAN C B, JORGENSEN F R A, KOH P T L, HUNT A. CFD modelling of the flow and reactions in the Olympic Dam flash smelter reaction shaft [J]. Applied Mathematical Modeling, 2006, 30: 1310-1325.
[19] CONSTANTINEAU J P, BOUFFARD S C, GRACE J R, RICHARDS G G. Pre-ignition behavior of lead sulfide in the flame of a flash smelter [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24: 845-851.
[20] CHEN Hong-rong, MEI Chi, XIE Kai, LI Xin-feng, ZHOU Jun, WANG Xiao-hua, GE Ze-ling. Operation optimization of concentrate burner in copper flash smelting furnace [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2004, 14(3): 631-636.
[21] CHEN Hong-rong, MEI Chi, XIE Kai, REN Hong-jiu, WANG Xiao-hua, ZHANG Yuan, LIU An-ming. Numerical simulation on flash smelting copper loss in slag [J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 60: 71-74. (in Chinese)
[22] ZHOU Jun, CHEN Zhuo, ZHOU Ping, YU Jian-ping, LIU An-ming. Numerical simulation of flow characteristics in settler of flash furnace [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(6): 1517-1525.
[23] XIE Kai. Several theory and operation optimization challenges in the development of modern copper flash smelters [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2005. (in Chinese)
[24] LI Xin-feng, MEI Chi, ZHANG Wei-hua. Simulation of copper flash smelter [J]. Journal of Central South University of Techndogy, 2001, 32(3): 262-266. (in Chinese)
[25] CHEN Zhuo, WANG Yun-xiao, SONG Xiu-ming, ZHAO Rong-sheng, YIN Shu-gui. Numerical simulation of smelting process in copper flash smelters at high loading rate [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(11): 2916-2921. (in Chinese)
[26] CHEN Zhuo, LONG Peng, SUN Zhi-qiang, ZHOU Jun, ZHOU Jie-min. CFD simulation and performance analysis of CJD burner for intensified flash smelting process [C]//ASME Heat Transfer Summer Conference Collocated with The ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting & The ASME International Conference on Nanochannels. Rio Grande, Puerto Rico: ASME, 2012: 1115-1120.
[27] ZHOU Jun, ZHOU Jie-min, CHEN Zhuo, MAO Yong-ning. Influence analysis of air flow momentum on concentrate dispersion and combustion in copper flash smelting furnace by CFD simulation [J]. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 2014, 66(9): 1629-1637.
[28] DAI Yang. Study of gas-particle transfer process enhancement in copper flash smelting with numerical simulations [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[29] CHEN Zhuo, ZHOU Ping, MEI Chi. Principle of transfer process [M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2011. (in Chinese)
[30] LI Jia-dong, ZHOU Ping, LIAO Zhou, CHAI Li-yuan, ZHOU Chenn Q, ZHANG Ling. CFD modelling and optimization of oxygen supply mode in KIVCET smelting process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(7): 1560-1568.
[31] MAO Yong-ning. Numerical simulation of copper flash smelting process and optimization of matching scheme for operational parameters [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012. (in Chinese)
[32] SASAKI Y, MORI Y, HATTORI Y, TANABE A. Prediction of combustion phenomena in flash smelting furnace for production enhancement using a mathematical model [C]//Sohn International Symposium Advanced Processing of Metals and Materials. San Diego: TMS, 2006: 545-559.
高东波1,彭小奇1,2,宋彦坡1,祝振宇1,戴 扬1
1. 中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 湖南第一师范学院,长沙 410205
摘 要:为了研究闪速炉冶炼颗粒着火延迟问题,建立反应塔内颗粒受热过程的数学模型,并进行计算。结果表明,在塔高0.6 m范围内,辐射换热对于颗粒的加热过程影响较大,而在反应塔0.6 m以下区域,对流换热占主导作用。鉴于强化对流换热过程对提高颗粒加热速度进而提高着火高度更有效,因此,建议采用高速热氧射流技术代替闪速炉内的天然气,使得颗粒周围的气相产生横向扰动,从而提高气-粒两相间的滑移速度和对流换热系数。同时,开展高速热氧射流和常规天然气燃烧工况下的数值模拟。结果表明,采用高速热氧射流技术能够提高颗粒的升温速度,进而使颗粒更快着火,特别是在塔径R=0.3~0.6 m范围内。这说明,在相同的操作条件下,采用高速热氧射流技术可以进一步提升熔炼效率。
关键词:闪速熔炼过程;颗粒受热;数学模型;高速射流;数值模拟
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Corresponding author: Yan-po SONG, E-mail: songyanpo@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65594-2
1003-6326/ 2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press

