J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (2010) 17: 413-418
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-010-0061-z 
Effects of different characteristic surfaces at initial stage of frost growth
CAI Liang(蔡亮)1, HOU Pu-xiu(侯普秀)2,WANG Rong-han(王荣汉)1, ZHANG Xiao-song(张小松)1
1. School of Energy and Environment, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China;
2. School of Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
? Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2010
Abstract: The effects of surface energy on phase change of water vapor at initial stage of frost growth were studied to find an effective method of restraining frost growth. The mechanism of restraining frost growth by low energy surface (bigger contact angle) was analyzed based on crystal growth theory. Then, the phase change of water vapor and the process of frost growth on the copper and wax energy surfaces were observed using microscope. The results indicate that it is difficult for wax surface (low energy surface), on which there are still water droplets at 100 s, to form critical embryo, so frost growth can be restrained in a way. Water formation, droplet growth, ice formation and dendritic ice growth processes happen on both surfaces, ordinally. But the ice beads, with larger average diameter and sparse distribution on the wax surface, form later (at about 300 s) than that on the copper surface, and the dendritic ice also appears later. All of these support that ice crystal formation and dendritic crystal growth at initial stage of frost growth can be retarded on the low energy surface.
Key words: frost growth; surface characteristic; contact angle; wax coat
1 Introduction
Frost on the evaporator surface brings many negative effects [1-2], and these problems have continued for a long time. As far as the air-breathing engine for aerospace transport systems is concerned, the efficiency of fan in the pro-cooler is decreased and the surging allowance is reduced due to frost formation [3]. Some defrosting methods are adopted to alleviate the effects of frost after it has grown for a time. But in the process of defrosting, heat is absorbed from room and indoor heat exchanger, and long time defrosting will badly influence indoor comfort degree. Besides, the residual droplets on the heat exchanger would freeze in the process of next heating, while it would take long time to wipe off the rudimental droplets completely. In order to avoid the above negative effects, some methods are used to restrain frost growth and to wipe off the rudimental droplets for prolonging the alternation between two defrosting processes to decrease defrosting time. Some literatures reported that contact angel could influence frost shape and distribution [4-8], as well as the shedding of frost [9]. Interiorly, WU and WEBB [5] investigated the frost formation on both hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. They find that the frosting pattern on the hydrophobic surface appeared to be “pock-marked”, as compared to a uniform pattern on the hydrophilic surface. WANG et al [9] supposed that low energy surface could be used as evaporator surface of heat pump. Overseas, LEE et al [6] found that frost structures were classified into feather-type, grass-type and plate-type for hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces. In this work, theoretical and experimental methods were used to research this problem.
2 Theoretical analysis
Thermodynamics indicates that when water vapor phase change happens, Gibbs free energy will decrease. In this process, when single vapor molecule phase changes, the change of Gibbs free energy is:
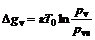 (1)
(1)
where 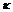 is Boltzmann constant, T0 is the temperature of system, pv is the pressure of vapor, and pvs is saturated vapor pressure at T0. Expression (1) indicates that phase change will happen only if pv/pvs>1, that is, vapor must be super-saturated.
is Boltzmann constant, T0 is the temperature of system, pv is the pressure of vapor, and pvs is saturated vapor pressure at T0. Expression (1) indicates that phase change will happen only if pv/pvs>1, that is, vapor must be super-saturated.
Water vapor condensation would experience two processes: at first, liquid nucleus (new phase) forms in the parent phase, which is called nucleus formation process; the second process is the growth of liquid nucleus. The nucleus formation on the evaporator surface is unsymmetrical nucleus formation [10]. Suppose evaporator surface is a smooth one, the shape of liquid nuclear is global crown, and the contact angle of liquid nuclear on the surface is θ, as shown in Fig.1.
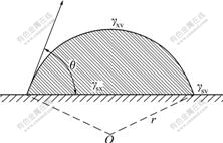
Fig.1 Global crown liquid nuclear on smooth surface
Global crown nuclear in Fig.1 must accord with mechanics balance [11], that is:
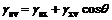 (2)
(2)
where γsv, γsx and γxv are surface tensions of each interface, respectively; subscripts s, x and v are fundus surface, nuclear surface and gaseous surface, respectively; and θ is the contact angle.
When phase change occurs, surface free energy must inevitably increase because new phase is formed in the parent phase. Total free energy of system consists of two parts, in which body free energy relates to volume of new phase, and surface free energy relates to surface area of new phase. When global crown nuclear forms on the fundus surface, the change of system Gibbs free energy is:
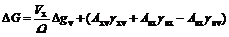 (3)
(3)
where Vx is the volume of nuclear; Ω is the volume of single water molecule; Axv is the interface area of nuclear surface and vapor surface; and Asx is the interface area of nuclear surface and fundus surface.
Combining Eq.(2) and Eq.(3), make out derivative, and let ΔG′=0, liquid nuclear critical radius of curvature can be gotten. After this, the work needed to form critical liquid nucleus is:
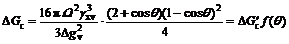
(4)
where 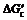 is the work needed to form symmetrical nucleus (θ=180?), and
is the work needed to form symmetrical nucleus (θ=180?), and
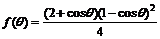 .
.
It can be seen from previous equation that free energy will increase when critical liquid nucleus forms. This energy is provided by energy fluctuating of total system, the probability of which relates to exp[-ΔGc/(κT)] based on statistical mechanics, so nucleation speed can be expressed as:
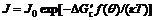 (5)
(5)
where J0 is the kinetics constant of nucleation speed.
It can be seen from Eq.(5) that nucleation speed decreases with the increase of ΔGc at the same temperature. When water vapor pressure and system temperature are invariable, only θ can influence ΔGc. The change of nucleation speed with θ is shown in Fig.2.
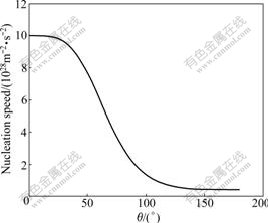
Fig.2 Change of nucleation speed with contact angle (T=268 K, pv/pvs=5)
From Fig.2 it can be gotten that J decreases with the increase of θ. When 50?<θ<100?, J decreases rapidly with the increase of θ. Based on phase change theory, the next vapor-liquid phase change will process focusing on the formed liquid nucleus, and the decrease of liquid nucleus must induce the decrease of liquid water on the bigger contact angle surface compared with that on the smaller one under the same conditions.
After liquid nucleus formation, vapor-liquid phase change occurs continuously based on these nuclei, and nearby droplets may unite [11]. If the water is super- cooled, ice nucleus will form and ice crystal will grow based on these nuclei. The speed of ice nucleus formation has the same format with Eq.(5). The only difference is nucleation speed constant. The probability of water frozen [12] is:
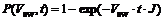 (6)
(6)
where Vsw is the volume of super-cooled water.
3 Experimental apparatus
Experimental apparatus is shown in Fig.3.
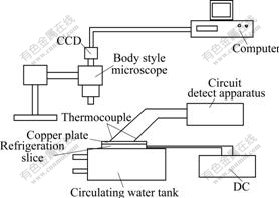
Fig.3 Experimental apparatus for frost growth
Semiconductor chilling plate was used as a refrigeration equipment. Its hot end was cooled by circular water. Frost growth surface was a copper plate (cold surface), the size of which was 40.0 mm×40.0 mm×1.5 mm. The frost growth surface and semiconductor chilling plate were felted by silicon gel. Eight copper-constantan couples were distributed equably on the copper plate. Measurement error of the copper-constantan couple was ±0.1 ℃. Cold surface temperature could wave in the range from -25 to -5 ℃.
Image magnifying and collection system was used to observe microcosmic structure of ice crystal. This system was constituted of a microscope, a change coupled device (CCD), a collection card and a computer. The amplification multiples of microscope objective, working distance of which was 45 mm (using bigger objective) or 110 mm (not using bigger objective), could be 2, 4 and 8. The total amplification multiple was 320.
The test was carried out in a consistent temperature and humidity room with hole-board ventilation. Room temperature (T∞) and humidity ( ) were measured by KANOMAX hydrothermoscope. Its temperature measurement error was ±0.5 ℃, relative humidity measurement error was less than 2%, and the wind velocity was about 0.25 m/s.
) were measured by KANOMAX hydrothermoscope. Its temperature measurement error was ±0.5 ℃, relative humidity measurement error was less than 2%, and the wind velocity was about 0.25 m/s.
Before experiment, four copper plates were polished by 400# sand paper to wipe off blot on the surfaces. Then, two copper plates were spread with wax on the surfaces. Wax’s main components were silicone and some grease. The contact angles of copper plate surface and wax surface were 58? and 98?, respectively. Experiments were carried out 5-10 times on the two surfaces, respectively.
Images got from experiment are shown in Figs.4 and 5.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Effects of surface contact angle on droplets formation
Droplet formation images on the two surfaces are shown in Fig.4.
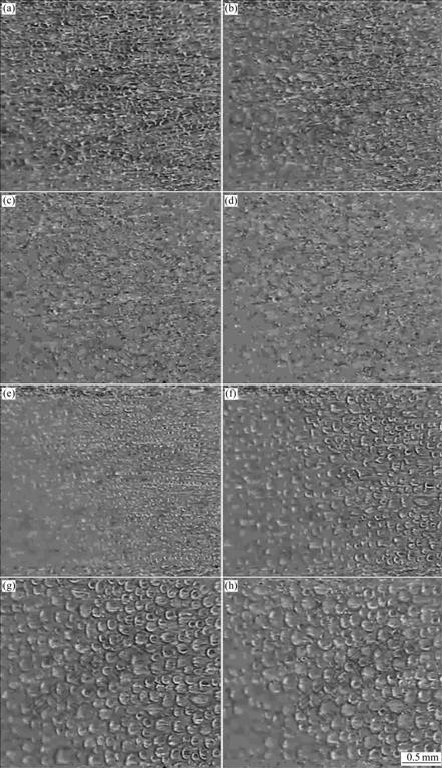
Fig.4 Droplet forming images on copper surface at 50 s (a), 100 s (b), 150 s (c) and 200 s (d), and on wax surface at 50 s (e), 100 s (f), 150 s (g) and 200 s (h)
The circumstance temperature was 25 ℃, relative humidity was 70%, wind velocity was 0.25 m/s, cold surface temperature was -5 ℃, and actual amplification multiple was 90.
Traditional viewpoints revealed that drop-wise condensation occurred only if contact angle was bigger than 90? [13]. But recently many experiments have indicated that drop-wise condensation could realize at the low contact angle [14]. In this work, the contact angle of copper surface was 58?, the condensation on this surface was not full film-wise condensation, but drop-film/ film-wise mixture. The area proportion of drop-wise condensation was about 40%.
It can be concluded from the experiment that droplets forming processes on the two surfaces have evident differences. It can be seen from Fig.4 and Fig.6 that in the initial stage, the liquid water area on the copper surface, as well as the droplet diameter, is bigger than that on the wax surface, but droplet diameter on the wax surface increases rapidly. The average diameter on the copper surface at 50 s is 44.6 μm, while 25.3 μm on the wax surface. However, droplet diameter on the copper surface almost does not increase after 100 s, and droplet diameter on the wax surface increases evidently: 56 μm at 100 s and 84.8 μm at 150 s.
The reason that droplets on the wax surface have smaller diameter and area at the initial stage is that nuclei formed on the wax surface are less than those on the copper surface in the same period, so the growth focused on liquid nucleus is more sufficient and the droplet diameter is bigger. Droplet diameter on the wax surface is bigger than that on the copper surface after 100 s. The phenomenon is caused by two reasons: firstly, water droplets on the copper surface have frozen after 100 s, and the subsequent process is dendritic crystal growth; secondly, Brown coagulation would occur on the hydrophobic surface [10]. This behavior makes droplet diameter on the wax surface increase rapidly. Furthermore, the coagulation of droplets makes the area covered by the water formerly contacting with air, and new water droplet would form in this area, so the distribution of droplet diameter is very asymmetric: droplets formed by Brown coagulation have bigger diameter, and others have smaller diameter.
Water droplets on the copper surface also freeze more quickly than those on the wax surface. Plentiful ice layers and ice droplets form on the copper surface at 100 s, while on the wax surface, only a few water droplets freeze at 150 s, and some water droplets still exist at 200 s. This phenomenon expresses that solid nuclei on the wax surface are less than those on the copper surface at the same time. So the freeze probability of super- cooled water is lower.
4.2 Effects of surface contact angle on frost growth
The experimental results indicate that wax coating not only restrains water from freezing, but also influences ice crystal distribution. Frost growth images at different time are shown in Fig.5.
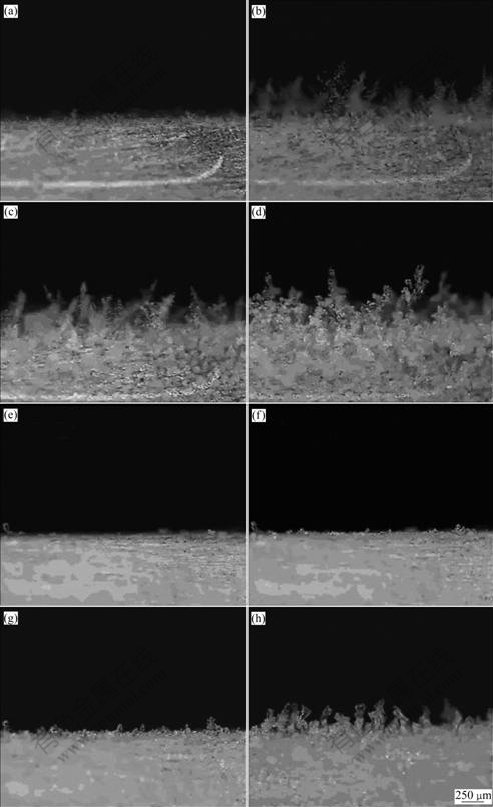
Fig.5 Frost growth images on copper surface at 100 s (a), 300 s (b), 500 s (c) and 900 s (d), and on wax surface at 100 s (e), 300 s (f), 500 s (g) and 900 s (h)
The circumstance temperature was 15 ℃, relative humidity was 65%, and cold surface temperature was -10 ℃. The angle between camera lens and cold surface was 45?.
As shown in Fig.5, much frost grows on the copper surface at 100 s, while there is no evident ice crystal on the wax surface. After 300 s, dendritic crystals appear on the copper surface, but on the wax surface, only a few ice crystals form and their height is very low. The circs is the same at 500 s. More crystals do not appear on the wax surface until 900 s, but their height and density are lower than those on the copper surface. From Eqs.(5) and (6) it can be seen that if contact angle of a surface is bigger, nucleation speed of liquid nucleus and ice nucleus on this surface will be less than that of other surfaces. When circumstance is the same, liquid water on this surface will be less, and super-cooled water freezes also much late, so this surface can restrain frost growth in some way.
It can also be seen form Fig.5 and Fig.7 that the end of dendritic crystal begins to thaw when frost grows for a while. The liquid water flows towards crystal root and freezes again, forming global end, which slows down the growth of the frost height and increases the density of the frost.
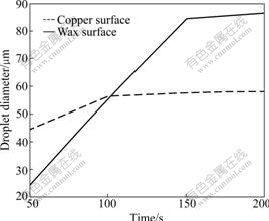
Fig.6 Curves of droplet diameters with time on two surfaces
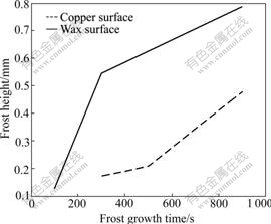
Fig.7 Frost height on two surfaces
5 Conclusions
(1) Nucleation speed relates to the surface contact angle. Nucleation speed and super-cooled water frozen speed on the surface of big contact angle are lower.
(2) Drop-wise condensation and film-wise condensation occur synchronously on the copper surface, which is different from traditional viewpoint.
(3) The water droplets on the wax surface distribute sparsely and cover less area than those on the copper surface. Furthermore, the droplets freeze late.
(4) The diameter of the water droplet on the wax surface distributes equably and is small at the beginning. But after a while, droplet diameter increases rapidly because of Brown coagulation, and the distribution is very asymmetric.
(5) Frost on the wax surface, with lower height and density, appears later than that on the copper surface. All indicate that wax coating does restrain frost growth.
References
[1] ZHANG Zhe, LI Yan-zhong, WANG Qiang. Study of factors governing the rate of frost accumulation on finned-tube heat exchangers of air-cooled heat pump [J]. Fluid Machinery, 2002, 30(11): 46-49. (in Chinese)
[2] O'NEAL D L, TREE D R. A review of frost formation in simple geometries [J]. ASHRAE Transactions, 1985, 91(2): 267-281.
[3] WANG Yong-shou. Study on restrain frost effect of condensed gas on air pre-cooler [J]. Winged Missiles Journal, 2005(4): 52-60. (in Chinese)
[4] OKOROAFOR E U, NEWBOROUGH M. Minimizing frost growth on cold surface exposed to humid air by means of cross-linked hydrophilic polymeric coatings [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2000, 20(8): 737-758.
[5] WU X M, WEBB R L. Investigation of the possibility of frost release from a cold surface [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2001, 24(3/4): 151-156.
[6] LEE H , SHIN J M, HA S, CHOI B, LEE J. Frost formation on a plate with different surface hydrophilicity [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2004, 47(22): 4881-4893.
[7] HOKE J L, GEORGIADIS J G, JACOBI A M. The interaction between the substrate and frost layer through condensate distribution [R]. Urbana Champaign: Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Center, College of Engineering, University of Illinois, 2000: 53-76.
[8] TAO Y X, BESANT R W, REZKALLAH K S. A mathematical model for prediction the densification and growth of frost on a flat plate [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1993, 36(2): 353-363.
[9] WANG Xian-lin, JIANG Shao-jian, AI Yuan-fang, CAO Zhi-jue. Discussion on hydrophobic surface for preventing frosting and speeding defrosting of heat pump [J]. Energy Construction Technology, 2004, 22(5): 37-38. (in Chinese)
[10] MIN Nai-ben. Physical fundamental of crystal growth [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishes, 1982. (in Chinese)
[11] CAO Zhi-jue. Dynamic description of the phenomena of drop-wise condensation and the optimal contact angle [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2002, 51(1): 25-30. (in Chinese)
[12] HOBBS P V. Ice physics [M]. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1974: 101-102.
[13] SONG Yong-ji, REN Xiao-guang, REN shao-mei, WANG Hong, JIANG Lei, ZHAI Jin. Condensation heat transfer of steam on super-hydrophobic surfaces [J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2007, 28(1): 95-97. (in Chinese)
[14] SONG Yong-ji, ZHANG Dong-chang, LIN Ji-fang. Effect of stream temperature on drop-wise condensation heat transfer [J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 1991, 42(1): 119-123. (in Chinese)
Foundation item: Project(50376052) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(307013) supported by the Key Project of Chinese Ministry of Education: Project(2008BAJ12B02) supported by the National Science and Technology Pillar Program in the 11th Five-Year Plan Period
Received date: 2009-05-18; Accepted date: 2009-09-06
Corresponding author: CAI Liang, PhD; Tel: +86-25-83792722; E-mail: cailiang@seu.edu.cn
(Edited by YANG You-ping)