一种由人类步行启发的半被动双足步行机器人
倪修华,陈维山,刘军考,石胜君
(哈尔滨工业大学 机器人技术与系统国家重点实验室,黑龙江 哈尔滨,150001)
摘要:针对半被动双足步行机器人所采用的控制方法大多较为复杂,并且缺乏控制参数对机器人性能影响的定量分析,从人类步行的生物力学研究得到启发,提出一种半被动双足步行机器人的控制方法,并定量分析该控制方法各参数对机器人性能的影响。在机器人摆动腿与地发生碰撞后开始于髋关节处施加方波力矩,作为动力输入。采用步态敏感范数衡量机器人的稳定性,采用无量纲步行能耗衡量机器人的步行效率。以稳定性、效率和步行速度作为机器人性能评价指标,通过仿真得到力矩、力矩作用时间和斜坡角度3个参数对机器人性能的影响。由于力矩在1个步行周期中没有做负功,该机器人具有与人类步行相似的高能量效率。该机器人能够实现沿上坡、下坡和平地步行。
关键词:半被动步行;机器人;稳定性;效率;速度
中图分类号:TP24 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)04-1028-07
A quasi-passive dynamic walker inspired by human walking
NI Xiu-hua, CHEN Wei-shan, LIU Jun-kao, SHI Sheng-jun
(State Key Laboratory of Robotics and System, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China)
Abstract: Since the present control methods for quasi-passive dynamic walkers are complex, and few quantitative study of the control parameters on the performance of quasi-passive dynamic walkers has been done, inspired by biomechanics in human walking, a control method for the quasi-passive dynamic walker and quantitative control parameters on the performance of the quasi-passive dynamic walker were studied. After the impact between swing leg and ground, a torque of square wave was applied at the hip as power supply. The gait sensitivity norm was used to quantify the stability, and the dimensionless cost of transport was used to quantify the walking efficiency. Stability, efficiency and velocity were used as three performance criteria. The effects of the amplitude of torque, the application time of torque and slope angle on the performance criteria were obtained by simulations. Since the torque does not do negative work during the whole walking period, the walker has a high efficiency as human walking. The robot can walk up a slope, walk down a slope and walk on flat ground.
Key words: quasi-passive dynamic walking; robot; stability; efficiency; velocity
McGeer[1]于1990年提出了被动步行的理论,并通过仿真和实验验证了无驱动与主动控制的被动步行机器人可以沿斜坡向下稳定行走。 根据被动步行的理论,许多学者在踝关节或者髋关节处加入主动驱动与控制[2-3],研制了多款可沿平地行走的半被动步行机器人。与基于零力矩点轨迹规划方法研制的以Asimo为代表的传统机器人相比,被动步行机器人具有更简单的结构和更高的能量效率[4-5],而且被动步行机器人的行走步态更加自然,与人的行走步态更加相似[6]。由于半被动步行机器人不采用轨迹规划与跟踪的控制方式,其控制方法是影响机器人性能的重要因素。Asano等[7]构造一个类似于纯被动步行的虚拟重力场,可以使机器人沿平地步行。Goswami等[8]通过控制施加在髋关节和踝关节的控制力矩来调节机器人的能量,可实现平地步行和上坡步行。李立国等[9]提出了虚拟斜坡行走方法,并进行了实验验证。Mao等[10]采用再励学习的方法实时计算控制力矩,Liu等[11]采用能量跟踪的方法计算控制力矩。这些半被动行走的控制方法或者需要检测机器人的行走状态,或者需要较为复杂的在线计算。对人类步行的生物力学研究结果表明,在摆动相初期髋关节力矩较大[12-13],随后力矩很小,其步行主要取决于自身的惯性参数,而不是高增益的反馈控制。以此为仿生学依据,付成龙等[14]提出一种于髋关节处施加间断的正弦力矩作为动力输入的控制方法,并给出了能够稳定行走的参数范围。但是该机器人所采用的正弦力矩,不利于模仿人类步行中力矩的突变特性,且只给出了能够稳定行走的参数范围,并没有研究各参数对稳定性等性能的影响。因此,本文提出一种在摆动足与地发生碰撞后开始,于髋关节处施加间断的方波力矩作为主动力输入的控制方法,并分析了各参数对机器人稳定性、效率和步行速度等性能的影响。
1 动力学模型与控制方法
1.1 动力学模型的建立
采用图1所示的2D纯被动步行机器人模型。设两腿具有完全相同的惯性参数和几何参数,重力加速度为g,斜坡角度为γ,γ<0表示机器人沿上坡步行,γ=0表示机器人平地步行,γ>0表示机器人沿下坡步行。单腿质量为m,腿长为l,绕质心转动惯量为I,沿腿轴线方向上髋关节到质心的距离为c,质心到腿轴线的距离为w,w又被称之为质心偏移,定义向前偏移为正,足是半径为r的圆弧。在髋关节处有弹簧刚度为k的扭簧。支撑腿和摆动腿与斜面法线所形成的夹角分别为θ和φ,定义逆时针方向为正。在每一个步行周期中于髋关节处施加方波力矩,作用于支撑腿和摆动腿的力矩分别U和-U,U的表达式为:
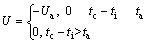 (1)
(1)
式中:Ua为施加于髋关节处力矩;tc为当前时间;ti上次发生碰撞的时间;ta为在1个步行周期中力矩Ua的作用时间。
1个步行周期可以分为摆动过程和足与地的碰撞过程。假设摆动过程中支撑腿的足与地之间为无相对滑动的纯滚动。假设碰撞过程为完全非弹性碰撞,碰撞过程瞬间完成,原支撑腿碰撞后变成了摆动腿,原摆动腿变成了支撑腿。
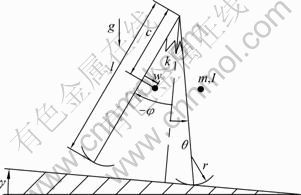
图1 半被动步行机器人模型
Fig.1 Sketch of model of quasi-passive dynamic walker
利用拉格朗日方程,对摆动过程的动力学模型进行了推导,得到其结果形式为:
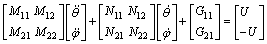 (2)
(2)
式中:


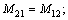
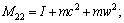


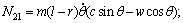


 。
。
对于碰撞过程,碰撞前、后角度不发生变化,但是,角速度发生突变。根据碰撞前、后整个机器人关于碰撞点动量矩守恒及碰撞前的支撑腿(即碰撞后的摆动腿)关于髋关节动量矩守恒,可以得到碰撞方程为:
 (3)
(3)
式中:q=[θ,φ]T;上标“-”和上标“+”分别代表碰撞前和碰撞后时刻;α为碰撞时两腿之间夹角的一半。由于碰撞前后角度不发生变化,但是,支撑腿与摆动腿发生了互换,有:
 (4)
(4)
式(2)~(4)构成了一整步的步行方程,也称之为Poincaré映射。定义Poincaré截面为碰撞后的瞬时,在此截面有:φ=-θ。因此,状态变量可以由 减少为
减少为 。若当前步Poincaré截面的状态变量值与下一步相同,则称此状态变量值为该截面的1个不动点。采用Newton-Raphson迭代求不动点,并根据雅克比矩阵特征值模来判定机器人的稳定性[15]。
。若当前步Poincaré截面的状态变量值与下一步相同,则称此状态变量值为该截面的1个不动点。采用Newton-Raphson迭代求不动点,并根据雅克比矩阵特征值模来判定机器人的稳定性[15]。
取机器人参数:g=9.81 m?s-2, m=2.06 kg, I=0.039 8 kg?m2, l=0.454 m, r=0.2 m, c=0.124 m, w=-0.002 5 m, k=0.95 N?m?rad-1, γ=0 rad,Ua=0.6 N?m,ta=0.2 s。按此参数进行数值仿真得到图2所示的摆动腿角度θ和支撑腿角度φ随时间变化曲线。仿真得到的不动点为:

其雅克比矩阵特征值模的最大值为0.679,因此,是1个稳定的单周期运动。
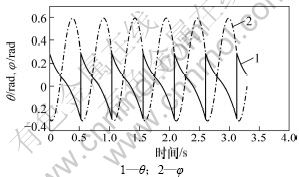
图2 数值仿真所得摆动腿和支撑腿角度曲线
Fig.2 Angles of swing leg and stance leg by numerical simution
为验证数值仿真的正确性,使用动力学仿真软件ADAMS建立虚拟样机进行验证。在ADAMS中定义两腿分别为腿1和腿2,则腿1与斜面法线的夹角α1和腿2与斜面法线的夹角α2随时间变化曲线如图3所示。与数值仿真不同的是在ADAMS软件仿真中,在碰撞过程发生后并没有支撑腿与摆动腿的角色转换过程。将图2与图3对比可以发现两者差异很小,验证了数值仿真的正确性。
1.2 控制方法
机器人的机械本体由两腿组成。髋关节处安装1个可进行力矩控制的伺服电机提供动力输入,两足底部各安装1个接触开关,用于检测机器人与地面间的接触状态。机器人还包含1个计时器对伺服电机的工作时间进行计时,1个控制器将采集到的接触开关信号和计时器信号进行分析,然后,向伺服电机发送控制指令。
当某一接触开关在某一时刻由非接触状态转变为接触状态时,表明此刻为足与地发生碰撞时刻,将计时器清零并开始计时,同时控制器发送指令使伺服电机输出给定的恒定力矩。当计时器的时间达到设定值时,伺服电机停止工作,机器人在惯性的作用下继续运动直至摆动腿与地面发生碰撞为止。碰撞发生后,机器人将周期性地重复前面的步行模式。

图3 ADAMS软件仿真所得两腿角度曲线
Fig.3 Angles of both legs by simulation with ADAMS software
2 参数对机器人性能的影响研究
以稳定性、效率和步行速度作为机器人性能评价指标[16],分析力矩Ua、力矩作用时间ta和斜坡角度γ 3个参数对机器人性能的影响。在分析某一参数影响时,保持其他参数不变。
吸引盆是能够使机器人稳定行走下去的所有初始状态的集合,被广泛用于衡量抗干扰能力[15, 17]。但是,吸引盆的计算时间过长,而且它不能够很好地量化稳定性[18]。
而Hobbelen等[18]提出的步态敏感范数 (The gait sensitivity norm),不仅可以很好地量化稳定性,而且计算时间很短。Hobbelen和Wisse多次成功地将步态敏感范数用于计算被动步行机器人的稳定性,并进行了实验验证[16, 19]。
2.1 步态敏感范数
图4描述了输入扰动e与输出步态指示T的偏差ΔT之间的关系[18]。这里沿用Hobbelen[18]的做法,取e为地面的下降高度,T为步行周期,ΔT为T与无扰动时步行周期T*的差。下标n和n+1分别代表第n步和第n+1步, ,v*为利用Newton-Raphson迭代所搜索到的不动点,Δv为v与v*的差。在Poincaré映射基础上定义包含扰动e和步态指示T的映射S:
,v*为利用Newton-Raphson迭代所搜索到的不动点,Δv为v与v*的差。在Poincaré映射基础上定义包含扰动e和步态指示T的映射S:
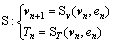 (5)
(5)

图4 步-步系统框图[18]
Fig.4 Block diagram of step-to-step system
v*和T*为:
 (6)
(6)
由图4所示框图得:
 (7)
(7)
式中: ,为第n步的Δv向第n+1步的Δv映射的矩阵,即雅克比矩阵;
,为第n步的Δv向第n+1步的Δv映射的矩阵,即雅克比矩阵; ,为第n步的e向第n+1步的Δv映射的矩阵;
,为第n步的e向第n+1步的Δv映射的矩阵; ,为第n步的Δv向第n步的ΔT映射的矩阵;
,为第n步的Δv向第n步的ΔT映射的矩阵;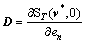 ,为第n步的e向第n步的ΔT映射的矩阵。
,为第n步的e向第n步的ΔT映射的矩阵。
定义步态敏感范数为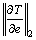 ,即对
,即对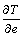 求H2范数,其计算公式为:
求H2范数,其计算公式为:
 (8)
(8)
式中:trace(X)表示矩阵X主对角线上元素之和。
采用无量纲步态敏感范数的倒数 来衡量机器人的稳定性。无量纲步态敏感范数的倒数越大,表示输入扰动e对输出步态指示的偏差ΔT的影响越小,机器人稳定性越好。下面提到的步态敏感范数均为无量纲化之后的步态敏感范数。
来衡量机器人的稳定性。无量纲步态敏感范数的倒数越大,表示输入扰动e对输出步态指示的偏差ΔT的影响越小,机器人稳定性越好。下面提到的步态敏感范数均为无量纲化之后的步态敏感范数。
2.2 效率
为了比较不同质量机器人的步行效率,定义无量纲步行能耗cm为单位质量的机器人步行单位距离所消耗的能量[5],其计算公式为:
 (9)
(9)
式中:s为步长;W为行走一步力矩U所做的功,其计算公式为:
 (10)
(10)
当力矩做负功时仍然要消耗能量,故对功率取绝对值以后再积分。
2.3 力矩对机器人性能的影响研究
力矩Ua对稳定性的影响如图5所示。从图5可见:当力矩较小时,随着力矩的增大,步态敏感范数的倒数增大,机器人的稳定性提高;当力矩在0.7 N?m附近时,机器人的稳定性达到最大,此后,随着力矩的增大,机器人的稳定性下降。当0.13<Ua<1.06 N?m时,机器人能够稳定步行,在此范围之外时,机器人不能够稳定步行。
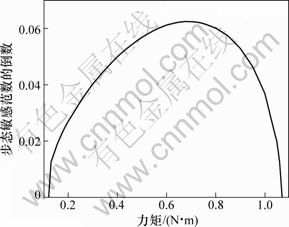
图5 力矩对稳定性的影响
Fig.5 Effect of amplitude of torque on stability
力矩Ua对无量纲步行能耗的影响如图6所示。从图6可见:随着力矩的增大,无量纲步行能耗增大,但力矩在整个范围内时,无量纲步行能耗与人类步行和其他几款半被动步行机器人的相当,但比Asimo小1~2个数量级[5]。说明该半被动步行机器人具有较高的步行效率。
当Ua=0.6 N?m时,力矩U的功率随时间变化如图7所示。由图7可以看出:力矩没有做负功,这使得机器人具有很高的效率;而传统型机器人为了满足轨迹跟踪的需要,在步行过程中经常需要做负功,使得效率低下。
力矩Ua对步行速度的影响如图8所示。从图8可见:随着力矩的增大,机器人步行速度也增大。
2.4 力矩作用时间对机器人性能的影响研究
力矩作用时间ta对稳定性的影响如图9所示。从图9可见:当力矩作用时间较小时,随着力矩作用时间的增大,步态敏感范数的倒数增大,机器人的稳定性提高;当力矩作用时间在0.20 s附近时,机器人的稳定性达到最大,此后,随着力矩作用时间的增大,机器人的稳定性下降。当0.05<ta<0.29 s时,机器人能够稳定步行,在此范围之外时,机器人不能够稳定步行。

图6 力矩对无量纲步行能耗的影响
Fig.6 Effect of amplitude of torque on dimensionless cost of transport

图7 功率随时间m的变化
Fig.7 Variation of power with time

图8 力矩对步行速度的影响
Fig.8 Effect of amplitude of torque on walking speed
力矩作用时间ta对无量纲步行能耗的影响如图10所示。从图10可见:随着力矩作用时间的增大,无量纲步行能耗增大。
力矩作用时间ta对步行速度的影响如图11所示。从图11可见:随着力矩作用时间的增大,机器人步行速度也增大。
2.5 斜坡角度对机器人性能的影响研究
斜坡角度γ对稳定性的影响如图12所示。从图12可见:当斜坡角度较小时,随着斜坡角度的增大,步态敏感范数的倒数增大,机器人的稳定性提高;当斜坡角度在0.04 rad附近时,机器人的稳定性达到最大,此后,随着斜坡角度的增大,机器人的稳定性下降。当-0.012<γ<0.066 rad时,机器人能够稳定步行,在此范围之外时,机器人不能够稳定步行。因此,该机器人可以在一定的斜坡角度范围内向上和向下步行。

图9 力矩作用时间对稳定性的影响
Fig.9 Effect of action time of torque on stability
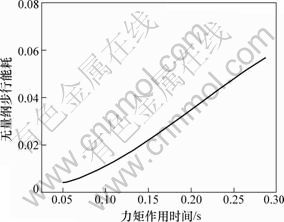
图10 力矩作用时间对无量纲步行能耗的影响
Fig.10 Effect of action time of torque on dimensionless cost of transport

图11 力矩作用时间对步行速度的影响
Fig.11 Effect of action time of torque on walking speed

图12 斜坡角度对稳定性的影响
Fig.12 Effect of slope angle on stability
斜坡角度γ对无量纲步行能耗的影响如图13所示。从图13可见:当斜坡角度较小时,随着斜坡角度的增大,无量纲步行能耗减小,当斜坡角度γ>0.04 rad时,无量纲步行能耗几乎不变。下坡时无量纲能耗小于平地步行时无量纲能耗,平地步行时无量纲能耗小于上坡时无量纲能耗。不同于传统机器人,该机器人能够利用下坡所产生的重力势能。
斜坡角度γ对步行速度的影响如图14所示。从图14可见:随着斜坡角度的增大,机器人步行速度也 增大。
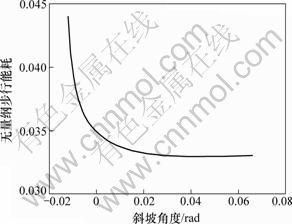
图13 斜坡角度对无量纲步行能耗的影响
Fig.13 Effect of slope angle on dimensionless cost of transport
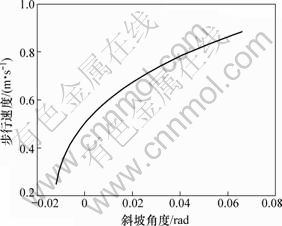
图14 斜坡角度对步行速度的影响
Fig.14 Effect of slope angle on walking speed
3 与正弦力矩的比较
以下将所提出的方波力矩与付成龙等[14]提出的正弦力矩进行比较。
(1) 方波力矩作用于无膝关节步行机器人,正弦力矩作用于有膝关节被动步行机器人。其力矩的起始时刻均为足与地发生碰撞后的瞬间,而方波力矩作用的结束时刻由计时器控制,正弦力矩作用的结束时间为摆动腿的膝关节碰撞时刻。因此,方波力矩很容易扩展到有膝关节步行机器人上,而若将正弦力矩扩展到无膝关节步行机器人上,则需要重新定义力矩的结束时刻。因此,没有将正弦力矩的性能与方波力矩的性能进行比较,但方波力矩与人类步行时的突变力矩更加相似。
(2) 通过对参数的调节2种方法均可以实现对步幅和步速的调节,正弦力矩可调参数有4个,可以调节的参数较多,可调范围大,但调节较复杂;而方波力矩可调参数有2个,可以调节的参数较少,可调范围小,但较简单。
4 结论
(1) 从人类步行的生物力学研究得到启发,提出一种半被动双足步行机器人的控制方法。使用该控制方法的机器人具有与人类步行相当的步行效率,且可以沿上坡、下坡和平地步行,在沿下坡步行时,能够利用斜坡所产生的重力势能。
(2) 当力矩在0.7 N?m附近时,机器人的稳定性达到最大。随着力矩的增大,无量纲步行能耗增大,步行速度增大。
(3) 当力矩作用时间在0.2 s附近时,机器人的稳定性达到最大;随着力矩作用时间的增大,无量纲步行能耗增大,步行速度增大。
(4) 当斜坡角度在0.04 rad附近时,机器人的稳定性达到最大。随着斜坡角度的增大,无量纲步行能耗减小,步行速度增大。
参考文献:
[1] McGeer T. Passive dynamic walking[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 1990, 9(2): 62-82.
[2] Collins S H, Ruina A. A bipedal walking robot with efficient and human-like gait[C]//Proceedings of 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 1983-1988.
[3] Tedrake R, Zhang T W, Fong M F, et al. Actuating a simple 3D passive dynamic walker[C]//Proceedings of 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2004: 4656-4661.
[4] Alexander R M. Walking made simple[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5718): 58-59.
[5] Collins S, Ruina A, Tedrake R, et al. Efficient bipedal robots based on passive-dynamic walkers[J]. Science, 2005, 307(5712): 1082-1085.
[6] Garcia M, Chatterjee A, Ruina A. Speed, efficiency, and stability of small-slope 2-D passive dynamic bipedal walking[C]// Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Part 3 (of 4). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1998: 2351-2356.
[7] Asano F, Yamakita M, Kamamichi N, et al. A novel gait generation for biped walking robots based on mechanical energy constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotic and Automation, 2004, 20(3): 565-573.
[8] Goswami A, Espiau B, Keramane A. Limit cycles in a passive compass gait biped and passivity-mimicking control laws[J]. Autonomous Robots, 1997, 4(3): 273-286.
[9] 李立国, 赵明国, 张乃尧. 平面双足机器人虚拟斜坡行走步态生成算法研究[J]. 机器人, 2009, 31(1): 77-81.
LI Li-guo, ZHAO Ming-guo, ZHANG Nai-yao. Research on virtual slope walking gait generation algorithm for planar biped robot[J]. Robot, 2009, 31(1): 77-81.
[10] Mao Y, Wang J, Jia P, et al. A reinforcement learning based dynamic walking control[C]//Proceedings of 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 3609-3614.
[11] Liu Z, Tian Y. Some control strategy on the compass gait biped[C]//Proceedings of IMACS Multiconference on "Computational Engineering in Systems Applications". Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2006: 1712-1718.
[12] Winter D A. The biomechanics and motor control of human movement[M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1990: 258-260.
[13] Goswami A, Thuilot B, Espiau B. A study of the passive gait of a compass-like biped robot: Symmetry and chaos[J]. Int J Robot Res, 1998, 17(12): 1282-1301.
[14] 付成龙, 黄元林, 王健美, 等. 半被动双足机器人的准开环控制[J]. 机器人, 2009, 31(2): 110-117.
FU Cheng-long, HUANG Yuan-lin, WANG Jian-mei, et al. Quasi open-loop control for semi-passive biped robots[J]. Robot, 2009, 31(2): 110-117.
[15] Liu N, Li J F, Wang T S. The effects of parameter variation on the gaits of passive walking models: Simulations and experiments[J]. Robotica, 2009, 27: 511-528.
[16] Hobbelen D G E, Wisse M. Controlling the walking speed in limit cycle walking[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2008, 27(9): 989-1005.
[17] Schwab A L, Wisse M. Basin of attraction of the simplest walking model[C]//Proceedings of 18th Biennial Conference on Mechanical Vibration and Noise. Washington, DC: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2001: 531-539.
[18] Hobbelen D G E, Wisse M. A disturbance rejection measure for limit cycle walkers: The gait sensitivity norm[J]. IEEE Transactions Robot, 2007, 23(6): 1213-1224.
[19] Hobbelen D G E, Wisse M. Swing-leg retraction for limit cycle walkers improves disturbance rejection[J]. IEEE Transactions Robot, 2008, 24(2): 377-389.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2010-04-04;修回日期:2010-06-22
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(59705011)
通信作者:倪修华(1980-),男,江西九江人,博士研究生,从事仿生机器人研究;电话:13651830703;E-mail:nixiuhua@gmail.com