温度作用下与GPB区相关的Al-Cu-Mg合金中S相的各向异性生长机制
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2016年第1期
论文作者:尹美杰 陈江华 王双宝 刘自然 茶丽梅 段石云 伍翠兰
文章页码:1 - 11
关键词:铝合金;析出相;时效强化;各向硬性;晶体生长
Key words:aluminum alloy; precipitation; age hardening; anisotropy; crystal growth
摘 要:采用原子分辨率成像和第一性原理计算,研究S析出相颗粒在高强Al-Cu-Mg合金晶粒内部的生长行为。结果表明,S相的形核和生长具有很强的各向异性特征和受温度影响的特征,同时伴随低维相转变。事实上,在较高的时效温度下(高于180°C),存在两种特征的GP区, 它们决定S相晶体的生长机制。一种是S相本身的前驱体相,另一种是Guinier–Preston–Bagaryatsky (GPB)区的结构单元或其前驱体相。在较高温度下,GPB区的结构单元会在S相周围形成,并阻碍S相沿宽度方向的生长,导致S相长成柱状晶体;而在低温下,S相的生长不受GPB区的干扰,形成板条状形貌。
Abstract: By employing atomic-resolution imaging and first principles energy calculations, the growthbehavior of S-phase precipitates in a high strength Al-Cu-Mg alloy was investigated. It is demonstrated that the nucleation and growth of theS-phase precipitate are rather anisotropic and temperature-dependent companying with low dimensional phase transformation. There are actually two types of Guinier-Preston (GP) zones that determine the formation mechanism of S-phase at high aging temperatures higher than 180 °C. One is the precursors of the S-phase itself, the other is the structural units or the precursors of the well-known Guinier–Preston–Bagaryatsky (GPB) zones. At high temperatures the later GPB zone units may form around S-phase precipitate and cease its growth in the width direction, leading to the formation of rod-like S-phase crystals; whereas at low temperatures the S-phase precipitates develop without the interference with GPB zones, resulting in S-phase precipitates with lath-like morphology.
Mei-jie YIN, Jiang-hua CHEN, Shuang-bao WANG, Zi-ran LIU, Li-mei CHA, Shi-yun DUAN, Cui-lan WU
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
Received 15 April 2015; accepted 26 August 2015
Abstract: By employing atomic-resolution imaging and first principles energy calculations, the growth behavior of S-phase precipitates in a high strength Al-Cu-Mg alloy was investigated. It is demonstrated that the nucleation and growth of the S-phase precipitate are rather anisotropic and temperature-dependent companying with low dimensional phase transformation. There are actually two types of Guinier-Preston (GP) zones that determine the formation mechanism of S-phase at high aging temperatures higher than 180 °C. One is the precursors of the S-phase itself, the other is the structural units or the precursors of the well-known Guinier–Preston–Bagaryatsky (GPB) zones. At high temperatures the later GPB zone units may form around S-phase precipitate and cease its growth in the width direction, leading to the formation of rod-like S-phase crystals; whereas at low temperatures the S-phase precipitates develop without the interference with GPB zones, resulting in S-phase precipitates with lath-like morphology.
Key words: aluminum alloy; precipitation; age hardening; anisotropy; crystal growth
1 Introduction
For nearly 100 years the AA2024 Al-Cu-Mg alloys have been important materials for the aerospace industry due to their excellent strength and plasticity [1,2]. As one of the widely used age-hardenable aluminum alloys, both their precipitate characteristics, such as the morphology, the crystallographic orientation and the structure type of the precipitates, and their precipitation behaviors during ageing treatments have been important issues for understanding the relations between the properties and the processes of the alloys [3-30].
In high-strength Al-Cu-Mg alloys with relatively high Mg/Cu ratios, like the AA2024 (Al-4.57Cu- 1.34Mg, mass fraction, %) alloy investigated in the present study, three types of fine precipitates may form. The first type of precipitates that always form upon ageing is the solute clusters. They are structurally less ordered and therefore are less effective in hardening the alloys. They can be visualized in atom-probe ion-field microscopy [5-8] but normally cannot be seen in scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) and in high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). The second type of precipitates that may form in the alloys is the 1D crystals, known as Guinier-Preston-Bagaryatsky (GPB) zones [8-11], as illustrated in Figs. 1(a), (b) and (d). The GPB zones are effective hardening particles and can form rapidly if ageing temperature is higher than 190 °C. Their formation can be depressed if the alloys are aged at 180 °C or below. Significant progresses have recently been achieved in characterizing their structures with STEM [3,4,9] after pioneer made efforts with different tools [5,6,12-16]. One GPB zone is usually assembled by more than one GPB units (Fig. 1(d)). The third type of precipitates in the Al-Cu-Mg alloys is the most effective strengthening particles known as S-phase precipitates (Figs. 1(a)-(c)). They are 3D-nanocrystals of an equilibrium phase with a composition of Al2CuMg. Their typical morphology is either lath-like or rod-like, depending on aging temperature and aging duration. The S-phase precipitates have a principle orientation relationship (OR) with the matrix [27], but can be tolerant of a few degrees of deviation from their principle OR [17-26]. The S-phase is of a centered-orthorhombic crystal structure, as originally proposed by PERLITZ and WESTGREN [27].
It has generally been believed that the GPB zones, or somewhat different phases named by “S ” [11,13,21], are the precursors of the S-phase, though significant controversies have long existed about the formation of S-phase precipitates [5-8,11-13,15-17,20,21]. According to our recent study [3], the S-phase precipitates always have, without exception, an even number of Cu-Mg atomic-layers that parallel to the (210)Al plane ( perpendicular to its thickness). In this way, an S-phase precipitate can be specified by its thickness or the number of Cu-Mg atomic-layers in the precipitate, e.g., an S2n precipitate means that it contains 2n Cu-Mg atomic-layers in thickness. An S2 precipitate contains two Cu-Mg atomic-layers in thickness and is the thinnest S-phase precipitate. So, the nucleation and growth of an S-phase precipitate can be understood in details. It has been shown [3] that driving by energy decrements, the main precipitation sequence towards S-phase formation is as follows: SSSS→GPS2-I(Al3MgCu)→ GPS2-II (Al2MgCu)→S2 (Al2MgCu)…→S2n, where SSSS stands for super-saturated solid solution, GPS2-I and GPS2-II are the precursors (GP zones) of an S2 precipitate (Fig. 1(e)). This implies that the formation of S-phase is independent of the GPB zones, at least for low temperature aging [3].
However, at a higher temperature (above 190 °C) the S-phase precipitates and the GPB zones may nucleate and grow simultaneously. In this case, the two types of precipitates must compete for their developments. Interestingly, it has been observed that the structure of one type of GPB zones has a close relation with the S-phase structure [9,10]. Hence, to date, the following questions still remain unclear: 1) how do the GPB zones interfere the development of the S-phase precipitates? 2) At above 190 °C, will an S-phase crystal grow in the same manner as it develops at a lower temperature? 3) Can an S-phase precipitate be formed based on a pre-existed GPB zone?
In the present work, using atomic-resolution imaging and first principles energy calculations, we investigated the S-phase precipitates for their growth mechanism and temperature-dependency, as well as for the influence of the co-existed GPB zones on their morphology. It is shown that advanced high-angle- annular-dark-field (HAADF) imaging in STEM, in combination with recent progresses in the structure determination of early-stage S-phase precipitates zones [3,4] and GPB zones [9,10], has made it possible to well understand the relations between the two important types of hardening precipitates in the Al-Cu-Mg alloys.
2 Experimental
2.1 Alloy samples and thermal aging
The materials used in the present work were supplied in the form of homogenized rolled sheets and had a composition of Al-4.57Cu-1.34Mg-0.81Mn (mass fraction, %). Prior to the hardening age, the alloy was solution heat-treated at 495 °C for 1 h and then water quenched to room temperature (20 °C). Subsequent thermal aging was carried out in an oil bath at 20, 130, 150, 180, 190, 200, 220 and 250°C, respectively. Specimens for the STEM and HRTEM
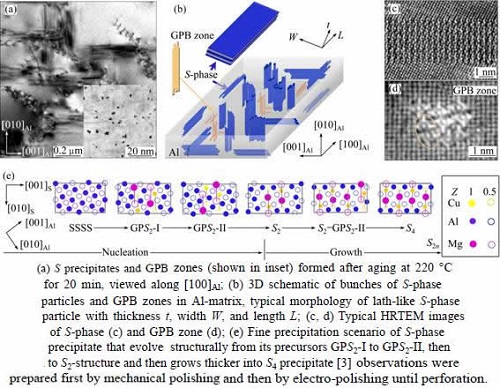
Fig. 1 Illustrative overviews of S-phase and GPB zones formed in AA2024 alloy upon thermal aging
2.2 Atomic-resolution imaging in electron microscopy
2.2.1 High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) image
An FEI Tecnai F20 HRTEM and a JEOL 3010 HRTEM instruments, operating at 200 and 300 kV respectively, were employed in the present study. Two atomic-resolution imaging techniques are available with the FEI Tecnai F20 HRTEM microscope: one is to perform through-focus exit-wave function reconstruction (TF-EWR) over focus-variation series of about 20 images per series that are automatically recorded in the HRTEM imaging mode [31-34]; the other is to perform high-angle-annular-dark-field (HAADF) imaging in the STEM imaging mode. The highest point resolution of the microscope achievable by performing TF-EWR is 0.14 nm (information limit) [35], while its best point resolution achievable in HAADF-STEM is 0.16 nm. The key issue of performing atomic-resolution imaging was to obtain images that reflect truly the real atomic structures of the observing objects (within the resolution limitation of the microscope).
2.2.2 HAADF imaging in STEM
In the HAADF-STEM imaging mode, the obtained image shows a Z-contrast (where Z represents the atomic number of the atoms in the specimen) proportional to Z1.7-2.0 [36-38]. Hence, the HAADF image contrast is relatively easy to interpret in terms of the structure, so long as the composition of the observing material is known, though the light atoms are more difficult to be visualized than the heavy atoms when they are largely different in Z and co-exist in the structure. The imaging parameters are as follows: operating at 200 kV, with a half-angle of about 12 mrad for probe convergence and with a collection inner semi-angle of 36 mrad.
2.3 First principles energy calculations
The first-principles calculations were performed using density functional theory (DFT) implemented in the Vienna ab initio simulation package (VASP) with efficient ultrasoft pseudo potentials [39-43]. The generalized gradient approximation (GGA) with the exchange-correlation functional of PERDEW [44,45] was employed. Convergence tests indicated that 260 eV was a sufficient cutoff for the ultrasoft pseudo potential to achieve high precision in the Al-Cu-Mg system. For all structures, k-points sampling using Monkhorst-Pack method [46] was increased to reach the precision of 0.1 kJ/mol. The thermal contributions and zero-vibration energy differences or contributions were ignored because of their little effect on this alloy system [4]. Sufficiently large super cells were used in all calculations in order to include the interface energy and the strain energy for the particles [4]. The formation enthalpies were defined and calculated in kJ/mol per solute atom [47].
The formation enthalpy (with thermal contributions and zero-vibration energy difference or contribution being ignored) for an equilibrium phase AlxCuyMgz can be defined as [48]
ΔH(AlxCuyMgz)=E(AlxCuyMgz)-xAlE(Al)-yCuE(Cu)-zMgE(Mg) (1)
where E(AlxCuyMgz) is the total energy of AlxCuyMgz phase per atom, obtained by first-principles calculations. E(Al), E(Cu) and E(Mg) are energies for pure elements Al, Cu and Mg, respectively. xAl=x/(x+y+z), yCu=y/(x+y+z) and zMg=z/(x+y+z) are the fractional compositions of Al, Cu and Mg, respectively.
To include thermal contributions to the stability of S-phase at a finite temperature, both lattice thermal vibration and thermal electrons should be considered. The Helmholtz free energy (F) with an average atomic volume (V) at a temperature (T) can be obtained by [49,50]
F(V,T)=Ec(V)+Fvib(V,T)+Fe(V,T) (2)
where Ec is the energy (without zero-point vibration energy) obtained from first-principles calculations at 0 K; Fvib is the free energy for lattice vibration, which can be calculated with the quasi-harmonic approximation through employing the plane-wave self-consistent field (PWSCF) method [51] based on the ab initio linear- response theory [52-55]. Using the linear-response theory approach for one unit cell, the phonon frequencies can be found without much computation. Fe is the free energy of thermal electrons, which can be obtained via 1D numeric integrations over the electronic density of states (calculated using VASP) following the Fermi distribution [49,50].
We calculated all the zero-vibration energies (Ezero) for the related structures at 0 K using VASP, and obtained the values 3.4, 2.8, 3.1 and 4.8 kJ/(mol·atom) respectively for the S-phase (Al2MgCu), FCC-Al, HCP-Mg and FCC-Cu crystals. Their contribution to the formation enthalpy, ΔEzero=4ΔEzero(Al2CuMg)- 2ΔEzero(Al)-ΔEzero(Mg)-ΔEzero(Cu)≈0.1 kJ/(mol·atom), is rather small, as compared with other contributions, and therefore is negligible in these calculations.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Hardening responses of alloy at different aging temperatures
Figure 2 shows the hardness of the AA2024 alloy samples aged at various temperatures vs aging time. We roughly divided the samples into two groups: the group of low temperature (LT) samples aged at temperatures ranging from 20 to 180 °C, and the group of high temperature (HT) samples aged at temperatures ranging from 190 to 250 °C.
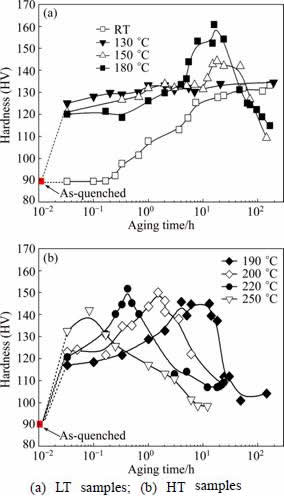
Fig. 2 Age-hardening curves of alloys aged at different temperatures against aging time
It is seen that the age-hardening responses of the LT samples (Fig. 2(a)) and the HT samples (Fig. 2(b)) are characteristically different. Figure 2(a) shows that upon thermal aging the LT samples (apart from the RT-sample) first demonstrate a rapid increase in hardness within 10 min, and then show a rather flat hardness plateau before reaching their peak hardness values. For the HT samples, it can be seen that upon thermal aging at above 190 °C, the HT samples generally demonstrate a faster increment in hardness. The hardness plateau observed among the LT samples becomes less and less obvious, and eventually vanishes for the sample aged at 250 °C. From previous studies, it is known that the highest hardness peaks are mainly due to the formation of S-phase precipitates, whereas the hardness plateaus are mainly due to the formation of the precursors of S-phase precipitates. Hence, Fig. 2 indicates that the nucleation and growth of the S-phase precipitates accelerate as the ageing temperature increases.
On the other side, in terms of hardness the sample aged at 180 °C demonstrates the highest hardness peak, indicating that near this aging temperature the S-phase precipitates can be formed mostly efficiently from the solute clusters and its precursors pre-exist in the matrix. Although the kinetics of the S-phase formation is enhanced in the samples being aged at temperatures above 180 °C, the hardness peaks achievable become lower and lower with the increase of temperature, implying that parallel to the formation of S-phase precipitates, other stable precipitates, which are less effective in strengthening the alloy with respect to the S-phase precipitates, are formed to have shared the super-saturated solute atoms in the matrix. These property variations will be reflected by the differences in precipitate microstructures, such as precipitate types and morphology of these samples.
3.2 Features of precipitate microstructures at different aging temperatures
Figure 3 shows the HRTEM images of typical precipitates formed in the LT and HT samples. It is shown that at 180 °C the GPB zones develop much more slowly than the S-phase precipitates and they appear at very late stages after the S-phase precipitates have fully developed, whereas at 220 °C very tiny GPB zones can be observed within a few minutes of aging. Figure 3(e) also demonstrates that since the GPB zones are 1D needle-like precipitates and are very small in cross-section at the early-stage of ageing, HRTEM imaging is not very handy to characterize their features, as compared with HAADF-STEM imaging.
Employing HAADF-STEM imaging, Figs. 4(a) and (b) demonstrate the featured difference between an S-phase precipitate, whose morphology is typically lath-like, formed in the LT samples and that typically with a rod-like morphology formed in the HT samples. In these atomic-resolution HAADF images of Z-contrast, the heavy Cu atoms in the precipitates are clearly seen. The S-phase precipitates formed at HT are frequently surrounded by “triangle-like” Cu clusters when they are visualized in HAADF images, as shown in Fig. 4(b). These “triangle-like” Cu clusters are actually the fundamental structure units of the well-known GPB zones as revealed in the recent literatures [9,10] and we therefore refer them to GPB units hereafter. Figures 4(c) and (d) show two possible structures of a GPB unit and energetically the one shown in Fig. 4(d) is more stable [9,10]. The GPB unit is actually a needle-like structure component growing along 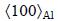 direction in 3D mode (Fig. 4(e)). When a few GPB units develop together, they will form various GPB zones structurally different in cross-section [9,10].
direction in 3D mode (Fig. 4(e)). When a few GPB units develop together, they will form various GPB zones structurally different in cross-section [9,10].
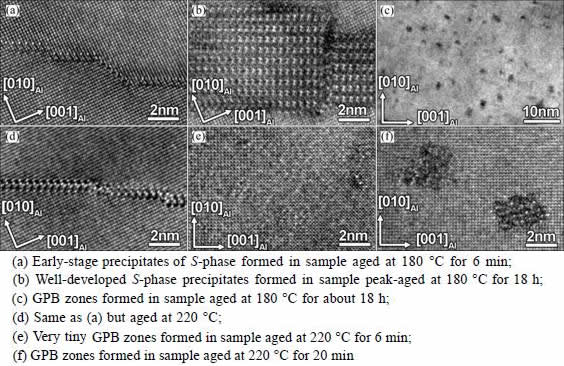
Fig. 3 HRTEM images of precipitate microstructures of AA2024 Al-Cu-Mg alloys upon thermal aging
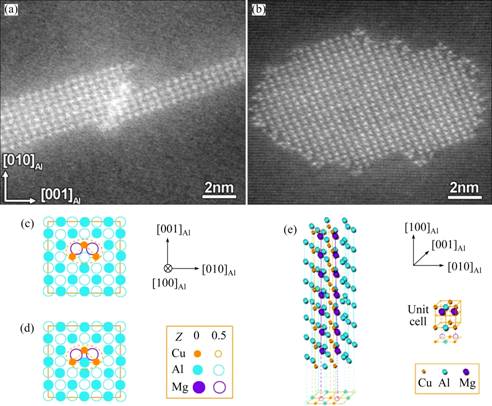
Fig. 4 Atomic-resolution HAADF-STEM images of one typical lath-like S-phase precipitate formed in sample peak-aged at 180 °C for about 18 h (a) and one typical rod-like S-phase precipitate formed in sample peak-aged at 220 °C for about 0.6 h (b), which is characteristically surrounded by featured tiny GPB units; atomic structure models (c, d) of GPB unit, and energetically model shown in (d) with Al-atom between two Cu atoms in unit shifted upwards by 0.5a is more favored [9,10], and 3D illustration of GPB unit (e)
For more examples of the interference of GPB zones and GPB units with the S-phase precipitates at elevated temperatures (190-250 °C), Fig. 5 shows other three atomic-resolution HAADF images taken from the samples aged at 220 °C for 1 h and 8 h, respectively. It is seen that in a HT sample the formation of S-phase precipitates is frequently accompanied by the formation of the GPB zones or the GPB units. From these images the following conclusions can be drawn. 1) Unlike those in a LT sample, the GPB zones can develop simultaneously as the S-phase precipitates form in a HT sample. 2) The GPB units strongly interfere with the growth of an S-phase precipitate in a HT sample, such that the precipitate complexes of GPB+S-phase can be formed frequently. For such complexes, if the core parts of S-phase are large, they can be recognized as S-precipitates (Figs. 5(a) and (c)); however, if the core parts of S-phase are small and the surrounding GPB zones and GPB units occupy a large portion (Fig. 5(b)), such a complex may easily be recognized as a GPB zone, especially when viewed in the conventional HRTEM imaging mode. 3) Although quick formation of GPB units around an S-phase precipitate has a strong influence on the development of the S-precipitate, the formation of S-phase precipitates in a HT sample seems to still follow the same fundamental rules as they form in a LT sample [3]: S-phase precipitates can grow thicker only through forming its precursor, the GPS2-II′ zone, on its side (Fig. 5(a)). Since a GPS2-II′ zone has two Cu-Mg-atomic layers, all S-phase precipitates developed always have, without exception, even numbers of Cu-Mg-atomic layers in the (210)Al plane, as shown in Fig. 5(c) by the two marked S-precipitates, S18 and S22. Hence, to accurately understand how the GPB units interfere with the S-phase precipitates in their developments, their early-stage structures have to be examined and studied in more details by using atomic-resolution imaging in association with first principles energy calculations. It is worth noting that in HAADF-STEM images, although the GPS2 zones and the S2 precipitates show very similar morphologies, their apparent and intuitive differences are in the separation distances between their two Cu-layers parallel to the (210)Al planes [3]. The S2 precipitates have the shortest separation distance between their two Cu-layers parallel to the (210)Al planes.
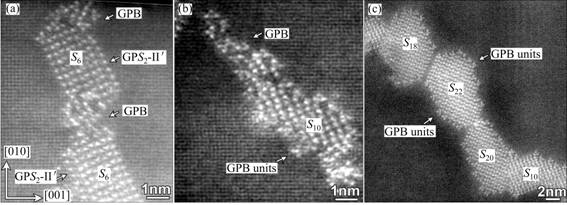
Fig. 5 HAADF images showing interaction among GPB units and S-phase precipitates in HT samples aged at 220 °C for 1 h (a, b) and 8 h (c) (Arrows indicate GPB zones or GPB units formed together with S-phase precipitates; two S6+GPS2-II′ precipitate complexes marked in (a) and S18 and S22 precipitates marked in (c) are to notice again fact that all S-phase precipitates have, without exception, even numbers of Cu-Mg layers in (210)Al plane, as revealed in our previous work [3])
3.3 Anisotropic and temperature-dependent growing mechanism of S-phase
Figure 6 shows the S-phase precipitates growing in thickness in their early stage at an elevated temperature of 220 °C. It can be seen that there are actually two variants of the GPS2-II zones attached to the thickening S-precipitates during their transformation from the GPS2-II zone structure to the S2 structure: one is the standard GPS2-II structure, the other refers to GPS2-II′ structure. Their subtle difference is in that one of the two Cu-Mg-atomic layers in the GPS2-II′ structure has become part of or integrated into the S-phase structure, whereas none of the two Cu-Mg-atomic layers in the GPS2-II structure has been integrated into the S-precipitates, as demonstrated clearly in Fig. 7.
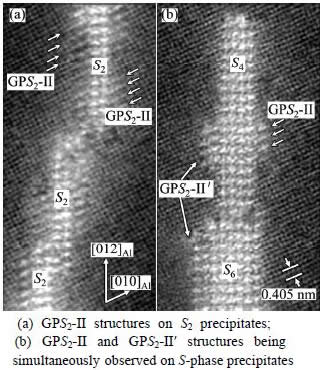
Fig. 6 HAADF images showing S-phase particles growing in their thickness direction through forming GPS2-II′ and GPS2-II structures on their sides, observed in samples aged at 220 °C for 6 to 10 min
Figure 7 illustrates the detailed thickening transformation stages from S4+GPS2-II complex precipitate to the S6-precipitate and the calculated formation enthalpies of each meta-stable structure. From Fig. 7, we can see the following points. 1) Energetically, a GPS2-II zone precipitate prefers to forming on the side of an existing S-precipitate rather than forming independently in the nearby matrix area. 2) When attached on the side of the S-precipitate, the contacting Cu-Mg-atomic layer of the GPS2-II zone can easily become a Cu-Mg-layer of the S-phase structure, forming the meta-stable GPS2-II′ structure. These subtle intermediate stages have not been observed previously in the LT samples. The final transformation from the S4+GPS2-II′ structure to S6 requires the Cu-atoms in the outwards Cu-Mg-atomic layer to shift upwards collectively by 0.5a and therefore needs more incubation time to complete, as discussed in our previous work [3].
To know the temperature influence on the formation of S-phase precipitates, Fig. 8 shows the free energies of the S2+GPS2-II′ complex precipitate (Fig. 8(a)) and S4-precipitate (Fig. 8(b)) as function of temperature (Fig. 8(c)). It can be seen that the higher the temperature is, the more stable the S-phase precipitates are. Nonetheless, the relative stability of an S2+GPS2-II′ complex precipitate with respect to its counterpart S4-precipitate is larger at a higher temperature than that at a lower temperature. This may partly explain the fact that the S2+GPS2-II′ complex precipitates are more frequently observed in the HT samples than in the LT samples, though they are not very sufficient.
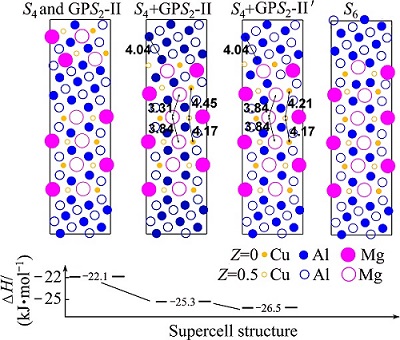
Fig. 7 Illustration of thickening transformation stages from S4+GPS2-II precipitate complex to S6-precipitate and calculated formation enthalpies of each meta-stable structure
To see how the S-phase growth at an elevated temperature is different from that at a low temperature, Fig. 9 shows more featured S2n+GPS2-II′ complex precipitates that are very frequently observed in HT samples rather than in the LT samples. Firstly, it can be noticed that at each of the two ends of a GPS2-II′ zone there is always a GPB unit formed with characteristic orientation, forming actually a (S2n+GPS2-II′ + GPB-unit) complex of triple components. Secondly, the width of such a GPS2-II′ zone varies with the number of unit cells of the GPS2-II′ structure between the two paired GPB units at its two ends. It can be speculated that in the HT samples the growth of a GPS2-II′ zone in its width direction will be restricted by the quick formation of the two paired GPB units at its two ends. As such, the (GPS2-II′+GPB-unit) complex attached to the side of S-phase precipitate can only grow in its length in order to reach a critical area for its final transformation to the S2-structure. This provides another reason why S2n+GPS2-II′ complex precipitates are more frequently observed in the HT samples than in the LT samples, since the GPS2-II′ components are much longer in average before being transformed to the S2n+S2-precipitate. For the same reason, it can be expected that the average aspect ratio (width-to-length ratio) of the S-phase precipitates formed in the HT samples will be smaller than that formed in the LT samples, i.e., the S-phase precipitates in the HT samples will be more rod-like, whereas those in the LT samples will be more lath-like. To confirm the above speculation about the morphology of S-phase precipitates, we measured statistically the average aspect ratios of S-phase precipitates in comparison, as shown in Fig. 9(c) for the result.
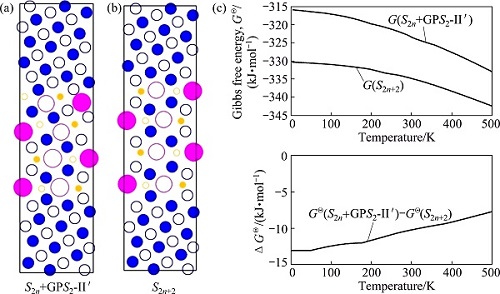
Fig. 8 Gibbs free energies (c) of S2n+GPS2-II′ complex precipitate (a) and S2n-precipitate with n=2 (b) in super cell models against temperature, calculated by first-principles energy calculations
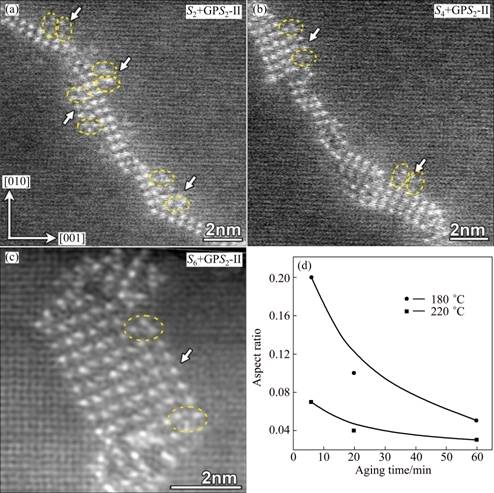
Fig. 9 Atomic-resolution HAADF images of early-stage growing S-phase precipitates in HT sample aged at 220 °C for 6 min (a), 10 min (b) and 1 h (c), respectively (S2+GPS2n-II+GPB-unit complexes attached on sides of growing S-phase precipitates are indicated by arrows) and average values of statistically measured aspect ratios of S-phase precipitates formed at 220 °C and 180 °C against aging time (d)
From these observations on the precipitate microstructures and their evolution with aging time and aging temperature, it can be understood that due to the quick formation of the GPB zones and the GPB units around the major hardening precipitates of S-phase in the HT samples, not all the supersaturated solute atoms of alloying elements, Cu and Mg, would contribute to the formation of the most effective hardening S-phase precipitates and therefore the height of hardness peaks will be lowered with increasing aging temperature (Fig. 2).
To summarize the difference between the anisotropic S-phase growth at an elevated temperature and that at a lower temperature, Fig. 10 illustrates the evolution paths of a thickening S-phase precipitate in a 3D view, which are subtly different depending on the aging temperature. The major reason for the difference is that during the nucleation and growth of the S-phase precipitate at an elevated temperature, the simultaneously formed GPB units will quickly cease the widening of the GPS2-II zones that are the inevitable precursors of the S-phase precipitate not only for its nucleation but also for its thickening growth. Since the limitation of the GPS2-II zones in width is imposed quickly by GPB units, they tend to grow more easily in length in order to reach the critical area required for their final transformation to the S2-structure during the whole stages of nucleation and growth of the S-phase precipitate. As the result of such a growth mechanism, in the HT samples the S-phase precipitates are more rod-like and also their average aspect ratios are smaller, as compared with those in the LT samples.
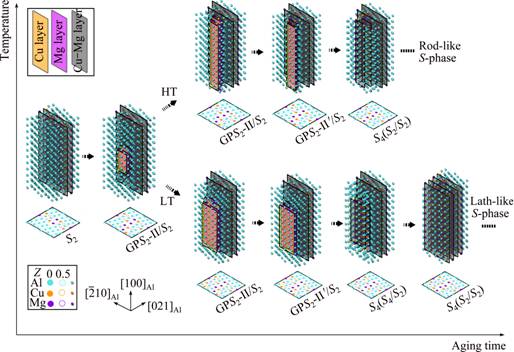
Fig. 10 Comprehensive 3D illustration of anisotropic and temperature-dependent growth mechanism of S-phase precipitates in AA2024 Al-Cu-Mg alloys
4 Conclusions
1) Using atomic-resolution imaging by HRTEM and STEM in association with first principles energy calculations, we systematically investigated the anisotropic and temperature-dependent growth mechanism of the S-phase precipitates in a typical AA2024 Al-Cu-Mg alloy in relation with its age-hardening responses. The one-dimensional GPB zones were studied and correlated with the formation of S-phase precipitates.
2) Consistent with the age-hardening responses of the alloy, the precipitate formation is temperature- dependent. At aging temperature below 180 °C, the formation of S-phase precipitates precedes that of GPB zones. With increasing aging temperature, the formation of GPB zones will be accelerated rapidly. At aging temperature above 220 °C, the S-phase precipitates and the GPB zones will form simultaneously in the alloy and strongly interfere with each other in structure and morphology.
3) The growth of S-phase precipitates in the Al-matrix is rather anisotropic due to their crystallographic features, and is also temperature- dependent due to the interference of the GPB zones at elevated aging temperatures. As such, the S-phase precipitates formed below 180 °C are more lath-like and those formed at elevated aging temperature are more rod-like.
4) The relation between the S-phase precipitates and the GPB zones in typical AA2024 Al-Cu-Mg alloys has not yet been convincingly clarified so far in literature. We demonstrated the following points about this issue: on one hand, at whatever a low or a high temperature, the S-phase precipitates can nucleate and grow independently without the existence of GPB zones. On the other hand, at a high temperature when two types of precipitates form simultaneously, the S-phase precipitates and their precursors (GPS2 zones) can quickly be surrounded by the GPB zone units, forming the GPB-GPS2 complexes. As such, when the core part of such a complex is in a larger portion, it may be recognized as an S-phase precipitate; whereas when the core part occupies only a very small portion of the complex, it may be seen as a GPB zone containing S-phase structure components. The existence of such complexes does not indicate that a GPB zone can directly transform to an S-phase precipitate, and vice versa.
References
[1] The Editorial Board of China Aeronautical Materials Handbook. China aeronautical materials handbook (vol.3): Aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2001: 148-167. (in Chinese)
[2] ROSALES B M, IANNUZZI M. Aluminium AA2024 T351 aeronautical alloy. Part 1: Microbial influenced corrosion analysis [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 472(1-2): 15-25.
[3] Wang S B, Chen J H, Yin M J, Liu Z R, Yuan D W, Liu J Z, Liu C H, Wu C L. Double-atomic-wall-based dynamic precipitates of the early-stage S-phase in AlCuMg alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2012, 60(19): 6573-6580.
[4] LIU Z R, CHEN J H, WANG S B, YUAN D W, YIN M J, WU C L. The structure and the properties of S-phase in AlCuMg alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2011, 59(19): 7396-7405.
[5] RINGER S P, HONO K, POLMEAR I J, SAKURAI T. Precipitation processes during the early stages of ageing in Al-Cu-Mg alloys [J]. Appl Surf Sci, 1996, 94-95: 253-260.
[6] RINGER S P, HONO K, POLMEAR I J, SAKURAI T. Nucleation of precipitates in aged AlCuMg(Ag) alloys with high Cu:Mg ratios [J]. Acta Mater, 1996, 44(5): 1883-1898.
[7] RINGER S P, SOFYAN B T, PRASAD K S, QUAN G C. Precipitation reactions in Al-4.0Cu-0.3Mg(wt.%) alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 2008, 56(9): 2147-2160.
[8] Sha G, Marceau R K W, Gao X, Muddle B C, Ringer S P. Nanostructure of aluminium alloy 2024: Segregation, clustering and precipitation processes [J]. Acta Mater, 2011, 59(4): 1659-1670.
[9] Kovarik L, Court S A, Fraswe H L, Mills M J. GPB zones and composite GPB/GPB II zones in Al-Cu-Mg alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2008, 56(17): 4804-4815.
[10] Kovarik L, Mills M J. Structural relationship between one-dimensional crystals of Guinier-Preston-Bagaryatsky zones in Al-Cu-Mg alloys [J]. Scripta Mater, 2011, 64(11): 999-1002.
[11] Ratchev P, Verlinden B, Smet P D, Houtte P V. Precipitation hardening of an Al-4.2wt%Mg-0.6wt%Cu alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46(10): 3523-3533.
[12] Silcock J M. The structural ageing characteristics of Al-Cu-Mg alloys with copper: Magnesium weight ratios of 7:1 and 2.2:1 [J]. J Inst Metals, 1960-1961, 89: 203-210.
[13] Bagaryatskii Y A. The mechanism of artificial aging of Al-Cu-Mg alloy [J]. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR, 1952, 87: 397-400.
[14] Ralston K D, Birbilis N, Weyland M, Hutchinson C R. The effect of precipitate size on the yield strength-pitting corrosion correlation in Al-Cu-Mg alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2010, 58(18): 5941-5948.
[15] Zahra A M, Zahra C Y, Alfonso C, Charai A. Comments on “cluster hardening in an aged Al-Cu-Mg alloy” [J]. Scripta Mater, 1998, 39(11): 1553-1558.
[16] Charai A, Walther T, Alfonso C, Zahra A M, Zahra C Y. Coexistence of clusters, GPB zones, S"-, S'- and S-phases in an Al-0.9%Cu-1.4%Mg alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 2000, 48(10): 2751-2764.
[17] Shih H C, Ho N J, Huang J C. Precipitation behaviors in Al-Cu-Mg and 2024 aluminum alloys [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 1996, 27: 2479-2494.
[18] Radmilovic V, Kilaas R, Dahmen U, Shiflet G J. Structure and morphology of S-phase precipitates in aluminum [J]. Acta Mater, 1999, 47(15-16): 3987-3997.
[19] Kovarik L, Miller M K, Court S A, Mills M J. Origin of the modified orientation relationship for S(S″)-phase in Al-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2006, 54(7): 1731-1740.
[20] Wang S C, Starink M J. Two types of S phase precipitates in Al-Cu-Mg alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2007, 55(3): 933-941.
[21] Wang S C, Starink M J. Precipitates and intermetallic phases in precipitation hardening Al-Cu-Mg-(Li) based alloys [J]. Int Mater Rev, 2005, 50(4): 193-215.
[22] Winkelman G B, Raviprasad K, Muddle B C. Orientation relationships and lattice matching for the S phase in Al-Cu-Mg alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2007, 55(9): 3213-3228.
[23] Feng Z Q, Yang Y Q, Huang B, Luo X, Li M H, Han M, Fu M S. Variant selection and the strengthening effect of S precipitates at dislocations in Al-Cu-Mg alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 2011, 59(6): 2412-2422.
[24] Shukla A K, Baeslack W A. Orientation relationships and morphology of S phase in friction stir welded Al-Cu-Mg alloy [J]. J Mater Sci, 2009, 44(2): 676-679.
[25] Parel T S, Wang S C, Starink M J. Hardening of an Al-Cu-Mg alloy containing Types I and II S phase precipitates [J]. Mater Design, 2010, 31: S2-S5.
[26] Styles M J, Hutchinson C R, Chen Y, Deschamps A, Bastow T J. The coexistence of two S (Al2CuMg) phases in Al-Cu-Mg alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2012, 60(20): 6940-6951.
[27] Perlitz H, Westgren A. The crystal structure of Al2CuMg [J]. Arkiv Kemi Min Geol, 1943, B16(13): 1-5.
[28] Wilson R N, Partridge P G. The nucleation and growth of S' precipitates in an aluminium-2.5% copper-l.2% magnesium alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 1965, 13: 1321-1327.
[29] Gupta A K, Gaunt P, Chaturvedi M C. The crystallography and morphology of the S'-phase precipitate in an Al(CuMg) alloy [J]. Phil Mag A, 1987, 55(3): 375-387.
[30] Radmilovic V, Thomas G, Shiflet G J, Starke E A. On the nucleation and growth of Al2CuMg (S′) in Al-Li-Cu-Mg and Al-Cu-Mg alloys [J]. Scripta Metall, 1989, 23(7): 1141-1146.
[31] Coene W, Janssen A J E M, op de Beeck M, van Dyck D. Improving HRTEM performance by digital processing of focal image series: Results from the CM20 FEG-Super TWIN [J]. Electron Opt Bull, 1992, 132: 15-28.
[32] Coene W, Janssen A J E M, op de Beeck M, van Dyck D. Phase retrieval through focus variation for ultra-resolution in field-emission transmission electron microscopy [J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 69: 3743-3746.
[33] Thust A, Coene W M J, op de Beeck M, van Dyck D. Focal-series reconstruction in HRTEM: Simulation studies on non-periodic objects [J]. Ultramicroscopy, 1996, 64(1-4): 211-230.
[34] Chen J H, Zandbergen H W, van Dyck D. Atomic imaging in aberration-corrected high-resolution transmission electron microscopy [J]. Ultramicroscopy, 2004, 98(2-4): 81-97.
[35] Jong A F, van Dyck D. Ultimate resolution and information in electron microscopy II: The information limit of transmission electron microscopes [J]. Ultramicroscopy, 1993, 49(1-4): 66-80.
[36] Nellist P D, Pennycook S J. Incoherent imaging using dynamically scattered coherent electrons [J]. Ultramicroscopy, 1999, 78(1-4): 111-124.
[37] Hillyard S, Silcox J. Detector geometry, thermal diffuse scattering and strain effects in ADF STEM imaging [J]. Ultramicroscopy, 1995, 58(1): 6-17.
[38] Kirkland E J, Loane R F, Silcox J. Simulation of annular dark field stem images using a modified multislice method [J]. Ultramicroscopy, 1987, 23(1): 77-96.
[39] Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set [J]. Comp Mater Sci, 1996, 6(1): 15-50.
[40] Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set [J]. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54: 11169-11186.
[41] Kresse G, Hafner J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals [J]. Phys Rev B, 1993, 47: 558-561.
[42] Vanderbilt D. Soft self-consistent pseudo potentials in a generalized eigen value formalism [J]. Phys Rev B, 1990, 41: 7892-7895.
[43] Kresse G, Hafner J. Norm-conserving and ultrasoft pseudo potentials for first-row and transition elements [J]. J Phys Condens Matter, 1994, 6(40): 8245-8257.
[44] Perdew J P, Chevary J A, Vosko S H, Jackson K A, Pederson M R, Singh D J. Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: Applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation [J]. Phys Rev B, 1992, 46(11): 6671-6687.
[45] Perdew J P, Wang Y. Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy [J]. Phys Rev B, 1992, 45(23): 13244-13249.
[46] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations [J]. Phys Rev B, 1976, 13(12): 5188-5192.
[47] van Huis M A, Chen J H, Zandbergen H W, Sluiter M H F. Phase stability and structural relations of nanometer-sized, matrix-embedded precipitate phases in Al-Mg-Si alloys in the late stages of evolution [J]. Acta Mater, 2006, 54(11): 2945-2955.
[48] Wolverton C, OzoliNS V. First-principles aluminum database: Energetics of binary Al alloys and compounds [J]. Phys Rev B, 2006, 73: 144104.
[49] Wang Y, Liu Z K, Chen L Q. Thermodynamic properties of Al, Ni, NiAl, and Ni3Al from first-principles calculations [J]. Acta Mater, 2004, 52(9): 2665-2671.
[50] Shang S L, Wang J, Wang Y, Du Y, Liu Z K. Phonon and thermodynamic properties of Al-Mn compounds: A first-principles study [J]. Comp Mater Sci, 2011, 50(7): 2096-2103.
[51] Giannozzi P, Baroni S, Bonini N, Bonini N, Calandra M, Car R, Cavazzoni C, Ceresoli D, Chiarotti G L, Cococcioni M, Dabo I, Corso A D, Gironcoli S, Fabris S, Fratesi G, Gebauer R, Gerstmann U, Gougoussis C, Kokalj A, Lazzeri M, Martin-Samos L, Marzari N, Mauri F, Mazzarello R, Paolini S, Pasquarello A, Paulatto L, Sbraccia C, Scandolo S, Sclauzero G, Seitsonen A P, Smogunov A, Umari P, Wentzcovitch R M. Quantum espresso: A modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials [J]. J Phys—Condns Mat, 2009, 21(39): 1-19.
[52] Baroni S, Gironcoli S, Corso A D, Giannozzi P. Phonons and related crystal properties from density-functional perturbation theory [J]. Rev Mod Phys, 2001, 73: 515-562.
[53] FALAHATI A, WU J, LANG P, AHMADI M R, POVODEN-KARADENIZ E, KOZESCHNIK E. Assessment of parameters for precipitation simulation of heat treatable aluminum alloys using differential scanning calorimetry [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(7): 2157-2167.
[54] GHEBOULI B, GHEBOULI M A, FATMI M, LOUAIL L, CHIHI T, BOUHEMADOU A. First-principles calculations of structural, electronic, elastic and thermal properties of phase M2SiC (M=Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta and W) [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(3): 915-925.
[55] WANG X H, ZHANG M, RUAN L Q, ZOU Z D. A first-principles study on elastic properties and stability of TixV1-xC multiple carbide [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(6): 1373-1377.
尹美杰,陈江华,王双宝,刘自然,茶丽梅,段石云,伍翠兰
湖南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410082
摘 要:采用原子分辨率成像和第一性原理计算,研究S析出相颗粒在高强Al-Cu-Mg合金晶粒内部的生长行为。结果表明,S相的形核和生长具有很强的各向异性特征和受温度影响的特征,同时伴随低维相转变。事实上,在较高的时效温度下(高于180 °C),存在两种特征的GP区, 它们决定S相晶体的生长机制。一种是S相本身的前驱体相,另一种是Guinier–Preston–Bagaryatsky (GPB)区的结构单元或其前驱体相。在较高温度下,GPB区的结构单元会在S相周围形成,并阻碍S相沿宽度方向的生长,导致S相长成柱状晶体;而在低温下,S相的生长不受GPB区的干扰,形成板条状形貌。
关键词:铝合金;析出相;时效强化;各向硬性;晶体生长
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Projects (51371081, 11427806, 51471067, 51171063) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2009CB623704) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: Jiang-hua CHEN; Tel: +86-731-88664009; E-mail: jhchen123@hnu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64082-7

