DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.02.007
利用钛铁矿制备纳米钛基功能材料
陶涛1,李鹏2,胡慧萍1,陈启元1,尹周澜1
(1. 中南大学 化学化工学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 宁夏大学 天然气转化重点实验室,宁夏 银川,750021)
摘要:为了有效控制纳米钛基材料的晶型、结构和生产成本,提出一种可直接制备高质量的纳米钛基产品的新方法。将球磨后的钛铁矿粉末经稀盐酸工艺处理后可全部转换为二氧化钛纳米棒,其长度、宽度和厚度分别为50~100,5~20和2~5 nm。研究结果表明:二氧化钛纳米棒负极材料具有较好的锂离子存储性能。通过球磨、焙烧结合酸浸工艺处理钛铁矿,可获得具有双孔特征的二氧化钛纳米颗粒,其中大孔(50~80 nm)对应于团聚在一起的纳米颗粒之间的间隙,小孔(3~20 nm)则对应纳米粒子表面上的洞,此外,所获得的多孔结构的二氧化钛纳米产品显示出较高的光催化活性。
关键词:钛铁矿;球磨;钛基纳米材料;储能;光催化
中图分类号:TM912.9 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)02-0401-07
Synthesis of titanium-based nanostructures from ilmenite
TAO Tao1, LI Peng2, HU Huiping1, CHEN Qiyuan1, YIN Zhoulan1
(1.School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Natural Gas Conversion, Ningxia University, Yinchuan 750021, China)
Abstract: It was found that a new method could be good for producing high quality titanium based nanomaterials to effectively control its morphology, structure and cost. Ball milling and acid solution treatment of natural ilmenite result in the products of TiO2 nanorods. The lengths, width and thickness of the nanorods are 50-100, 5-20 and 2-5 nm, respectively. The results show that the nanorods exhibit a good electrochemical performance when they are used as an anode material for the lithium-ion batteries. A method which includes ball milling, annealing and acid leaching to obtain porous TiO2 from ilmenite has been demonstrated. The porous products show a bimodal pore size distribution. The typical range of big pores (50-80 nm) is attributed to the spaces between nanoparticles in aggregates, and the typical range centered at 3-20 nm corresponds to holes within nanoparticles. The obtained porous TiO2 shows an excellent photocatalytic activity.
Key words: ilmenite; ball milling; titanium based nanomaterials; energy storage; photocatalysis
纳米钛基材料因其具有特殊的性能和广泛的用途而备受各国科研人员的青睐[1-5],并已被成功地应用于各个领域,如光催化、锂离子电池和太阳能电池[6-7]。纳米钛基材料的电子传导性能、光催化能力等物化特性强烈地依赖于其晶体结构、粒径、形貌和微结构等特征。为有效控制纳米钛基材料的晶型和结构,JUNG等[8-14]尝试采用多种不同的物理或化学的手段,如模板法、水热和溶剂热法、各向异性腐蚀、溶胶-凝胶法、原子层沉积、微波辐射和钛膜阳极氧化等。虽然这些工艺在制备纳米钛基材料方面都具有各自的优势,但它们存在共同的缺点,如制备工艺条件苛刻和原材料成本太高,因此,极大地限制了其在实际生产过程中的应用。FeTiO3(钛铁矿)为天然氧化物矿产资源,具有廉价、无毒、储量丰富等优点,是一种带隙宽度为2.54~2.58 eV和具有明显磁特性的半导体,常被用来制备钛基材料[15-19],主要分布在南美洲(巴西)、大洋洲(澳大利亚)、北美洲(美国和加拿大)、亚洲(印度、中国和越南) 欧洲(俄罗斯和挪威)和非洲(南非和莫桑比克)。根据2004—2008年的市场调查[16],钛铁矿存量约为6.8×108 t,其价格为80~100美元/t,包含(3.5~4.0)×108 t二氧化钛。中国四川攀枝花钛铁矿以显微粒状或片状的形式分布于磁铁矿颗粒之间或裂理中,为大型的钛铁矿产地。此外,著名的钛铁矿山还有挪威的克拉格勒、俄罗斯的伊尔门山、美国怀俄明州的铁山和加拿大魁北克的埃拉德湖等。若直接利用天然的钛铁矿制备纳米钛基材料,则可能会极大地降低纳米钛基材料的生产成本。因此,可发展新工艺或新技术从天然矿物中直接提取纳米材料。本文作者以天然钛铁矿为原料,通过精确调控制备工艺,以期分别获得多孔纳米二氧化钛和二氧化钛纳米棒产品,并分析产品的结构和性能。
1 实验
1.1 原料
钛铁矿由澳大利亚综合金红石有限公司(Consolidated Rutile Ltd., Australia,纯度为99%)提供,其化学成分(质量分数)为:TiO2 49.6%, Fe(总数) 35.1% (FeO 32.8%, Fe2O3 13.7%), Al2O3 0.47%, Cr2O3 0.25%, SiO2 0.45%。活性炭由英国BDH化学试剂有限公司提供。
在利用钛铁矿制备纳米钛基材料的过程中,采用的工艺总体包括球磨预处理及焙烧或化学湿法热处理。
1.2 球磨
将约10 g的钛铁矿与4个直径为25.4 mm的不锈钢球一起装入球磨罐进行球磨,球磨时间为150 h,保护气氛为100 kPa 氩气,转速为160 r/min。整个球磨过程均在磁力的辅助作用下进行,磁铁与水平方向呈45°[8]。
1.3 TiO2纳米棒的制备
将1 g钛铁矿球磨粉混入2 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液(100 mL)中,在120 ℃下加热2 h。停止加热后,通过过滤收集固体样品,将获得的样品经反复洗涤后在烘箱中烘干,烘干温度为90 ℃,时间为4 h。将1 g碱液处理钛铁矿球磨粉所得的样品,溶解于4 mol/L盐酸溶液中(100 mL),时间为4 h,溶解温度为90 ℃。反应完成后,通过过滤收集固体样品,并将所得到的样品反复洗涤后,转移至烘箱中烘干,烘干时间为4 h,温度为90 ℃。所有的溶液加热试验通过油浴实现,加热过程伴随着搅拌,搅拌速率恒定为800 r/min。
1.4 多孔TiO2纳米颗粒的制备
采用联合工艺处理钛铁矿制备孔状结构的纳米二氧化钛产品。整个工艺按照处理钛铁矿的先后顺序,可具体分为球磨预处理、碳热还原、盐酸溶解和空气中焙烧4个步骤:1) 球磨:将4个直径为25.4 mm的不锈钢球与6 g左右的钛铁矿和活性炭的混合物一起球磨,混合物中的钛铁矿与活性炭的质量比为4:1,球磨条件与上述过程相同;2) 碳热还原:2 g球磨混合物在水平管式炉中和氩气保护下从室温加热到1 000 ℃,时间约为30 min,接着在1 000 ℃下恒温1 h,停止加热后让样品自然冷却到室温(氩气保护下);3) 溶解:将还原焙烧后的样品(1 g)溶解于4 mol/L盐酸溶液(100 mL)中,溶解温度为90 ℃,时间为4 h,整个溶解过程伴随着搅拌(800 r/min),溶解完成后,通过过滤收集固体样品,并将所得到的样品反复洗涤后,转移至烘箱中烘干,烘干温度为90 ℃,时间为4 h;4) 焙烧:将烘干后的样品,在管式炉中、空气气氛和600 ℃下焙烧2 h。
参考文献[20-23]描述了材料表征和性能测试(光催化和锂离子电池)的全过程。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 二氧化钛纳米棒
球磨钛铁矿粉经碱浸和酸浸工序连续处理后,其微观形貌发生了明显的变化。图1所示为钛铁矿通过球磨、碱浸和酸浸连续处理后所获得的样品的扫描电镜照片和透射电镜照片。由图1(a)可知:酸浸后所获得的产品形貌为纳米棒状结构。这些纳米棒分布较密集,其长度为50~100 nm,宽度为5~20 nm,厚度为2~5 nm。产品的TEM明场照片进一步证实了其纳米
棒状结构的微观形貌(图1(b)和图1(c))。相应的选区电子衍射图证明了纳米棒晶体属于金红石型。图1(d)所示为单个纳米棒局部的高分辨率TEM照片,图1(d)中的晶格条纹像清晰地显示出纳米棒2个相邻晶格间的间距为0.33 nm。
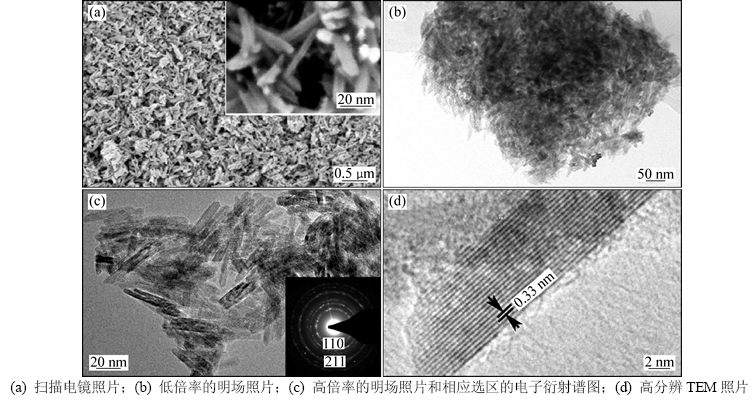

图1 钛铁矿通过球磨、碱浸和酸浸连续处理后所得样品的扫描电镜照片和透射电镜照片
Fig. 1 SEM and TEM images of samples obtained by milled, alkali treated and acid leached ilmenite
图2所示为纳米棒产品的XRD谱。由图2可知:样品XRD衍射峰都对应于四方金红石相二氧化钛(JCPDS号01-076-1939),证实了通过球磨、碱浸和盐酸浸出工艺处理天然钛铁矿原料后,可获得大量金红石型二氧化钛单晶纳米棒产品。
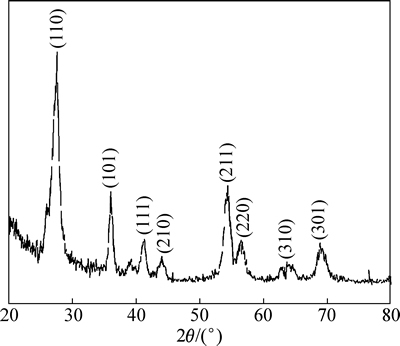
图2 钛铁矿通过球磨、碱浸和酸浸工序连续处理后所获得的样品的X线衍射谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of products obtained from milled,alkali treated and acid leached ilmenite
球磨工序可降低钛铁矿的反应活化能,加快钛铁矿在盐酸溶液中的溶解速度。碱洗工序有利除去钛铁矿中的杂质,从而提高产品的纯度。盐酸浸出工序可全部溶解纳米化的钛铁矿,生成不稳定钛盐的中间相,中间相随后会水解并产生大量的二氧化钛晶核,这些晶核会重新结晶和附聚长大,最终形成二氧化钛纳米棒产品。因此,可以认为上述获得的二氧化钛纳米棒产品的形成机理是溶解—水解—沉淀机理。
图3(a)所示为二氧化钛纳米棒作为锂离子电池负极时的循环伏安曲线。由图3(a)可知:样品的循环伏安曲线中明显存在1对氧化还原峰 (1.81 V/1.91 V),峰型尖锐,分别对应Li+在活性材料TiO2中嵌入和嵌出的反应。图3(b)所示为二氧化钛纳米棒电极在33.6 mA/g电流密度和电压扫描窗口1~3 V下的循环性能曲线图。由图3(b)可知:其首次放电比容量为249.9 mA·h/g,充电比容量为157.5 mA·h/g,不可逆容量损失达92.0 mA·h/g, 经过100次循环后, 其比容量降至121.0 mA·h/g。此外,其库仑效率在循环过程中除前6 次外均保持在98%以上,说明电极反应具有较好的可逆性。图3(c)所示为其倍率性能的测试结果。由图3(c)可知:当电流密度从168.0 mA/g增大至3.36 A/g时,其比容量从约127.0 mA·h/g降为52.0 mA·h/g,说明较低的电流密度可获得更高的放电比容量,这可能是由于较小的电流有利于更多的活性
材料参与储能反应。当电流密度从33.6 mA/g增至 1.68 A/g时,其30次循环后的比容量仅衰减约16 mA·h/g(见图3(d))。图3(e)所示为商业二氧化钛颗粒与二氧化钛纳米棒100次循环的恒流充放电曲线。由图3(e)可知:纳米棒的性能明显优于商业化产品。纳米棒较高的锂离子存储性能可能归因于其独特的结构特征, 因为纳米棒状结构不仅可提高材料本身的导电能力和缩短电极材料充放电过程中锂离子的传输路径,而且可使电解液与电极材料充分接触。

图3 二氧化钛纳米棒电化学性能
Fig. 3 Electrochemical properties of rutile TiO2 nanorods
2.2 多孔二氧化钛纳米颗粒
钛铁矿和活性炭的混合物通过球磨、焙烧、酸溶和煅烧连续的4道工序处理后,获得的产品的TEM的照片如图4所示。由图4(a)可知:产品的晶粒粒度小于100 nm。纳米颗粒相应的电子衍射(SADP)图如图4(b)所示,进一步证实了获得的产品为金红石型的二氧化钛。图4(c)和图4(d)所示为单个颗粒的TEM照片,由图4(c)和图4(d)可见:箭头所标示的区域为颗粒较薄的区域,其表面上布满了纳米小孔。纳米颗粒选定区域的电子衍射图(如图4(d)中的插入的图)表明透射电镜照片中的这些晶格条纹是穿越整个孔的区域,并且孔的厚度的不同可能导致对比度的变化。其水平和偏斜条纹的晶格间距分别为0.23 nm和0.28 nm,相对应晶面为{200}和{101}。
图5(a)所示为多孔TiO2产品的孔径分布图。由图5(a)可知:样品的孔径具有双峰特征。TEM(如图4所示)的结果表明小孔(2~20 nm)主要分布于颗粒的内部和表面,大孔(25~150 nm)主要分布于聚合在一起的小颗粒之间的间隙。经标定分析可知,多孔TiO2产品XRD谱(如图5(b)所示)中标出的所有衍射峰与金红石TiO2的标准图谱 (JCPDS file no. 01-077-0440)完全吻合,并没有出现明显的其他杂质的衍射峰,说明产品是单一的TiO2相。
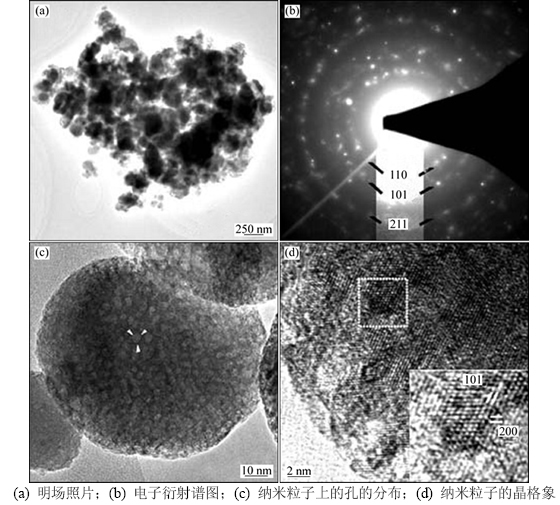
图4 所获得的多孔样品的透射电镜照片
Fig. 4 TEM images of obtained porous samples
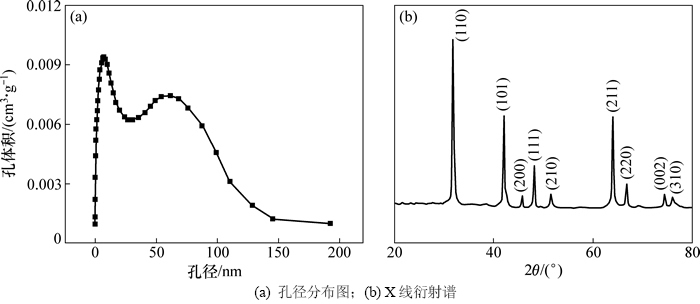
图5 金红型孔状结构的二氧化钛产品的孔径分布图和X线衍射谱
Fig. 5 Pore size distribution and XRD pattern of obtained rutile porous TiO2 products
钛铁矿经过球磨焙烧后,转变为二氧化钛和铁的混合物,混合产物经过酸浸处理后,铁杂质可被除去,从而获得多孔结构的二氧化钛产品。当焙烧时间较短时,钛铁矿的还原程度较低,铁杂质的粒径较小,经酸浸工序处理后,容易形成小孔;当焙烧时间较长时,钛铁矿的还原程度较高,铁杂质的粒径较大,容易形成大孔;当焙烧时间适中时,会存在2种粒径的铁杂质,这样产品就具有双孔特征。当然可能存在多种因素影响多孔的二氧化钛产品的生成,如球磨、碳热还原和酸浸工序中的各种工艺条件。
图6所示为多孔结构的金红石型TiO2纳米颗粒和商业金红石型TiO2粉末的紫外漫反射光谱和光催化测试结果,每次实验中的总碳量为1 mg。由图6可知:商业二氧化钛(颗粒的直径<100 nm,比表面积>130 m2/g)和多孔结构的二氧化钛在禁带起始的光吸收波长分别为360 nm和458 nm,且商业样品在可见光区域(波长λ>400 nm) 没有任何光吸收,而多孔结构的材料在禁带过渡区域则明显存在红移现象。这个红移现象可能是多孔材料中存在的缺陷或杂质诱使电子在二氧化钛的导带和杂质带间发生迁移所引起的。在大于320 nm的区域存在较强的光吸收,说明多孔二氧化钛材料可能在可见光区域会有一定的光催化活性,但这已经超越了所研究的范畴。多孔二氧化钛产品与商业二氧化钛的光催化性能的测试结果证实了孔状结构的二氧化钛矿化有机物苯酚的速率明显高于商业二氧化钛的速率,且孔状结构的二氧化钛能够矿化溶液中所有的有机碳,说明多孔结构的金红石型二氧化钛有较高的光催化性能,其较高的光催化性能可能与其形貌密切相关[24]。
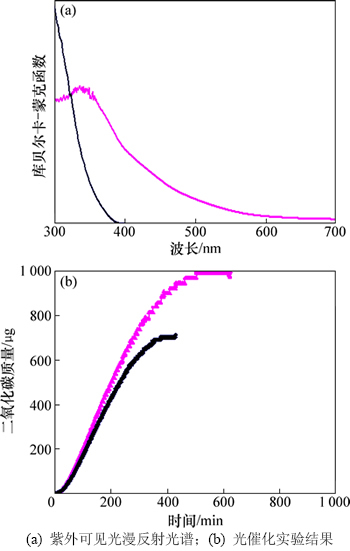
图6 紫外可见光漫反射光谱和光催化的实验结果对比
Fig. 6 UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra and results of photocatalytic tests
3 结论
1) 以天然钛铁矿为原料,经几个联合工序处理,得到了结构不同的纳米钛基产品。
2) 通过球磨、碱洗和酸浸工序,可以从天然钛铁矿中提取大量的金红石型二氧化钛纳米单晶棒。酸浸8 h后,获取的长度为50~100 nm、宽度为5~20 nm和厚度为2~5 nm的纳米棒具有良好的结晶性,所获得二氧化钛纳米棒作为锂离子电池负极时具有较好锂离子存储性能。
3) 以廉价丰富的钛铁矿和活性炭为原料,采用了新的联合工艺(球磨、焙烧、酸溶和煅烧),获得了大量多孔纳米二氧化钛颗粒。并通过控制工艺条件,可实现产品孔径的调节。光催化测试结果表明,多孔结构的金红石型二氧化钛具有较强的光吸收和光催化性能,其提高的性能可能归因于其特殊的多孔结构。
参考文献:
[1] CHEN X B, MAO S S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2007, 107(7): 2891-2959.
[2] CHEN Z H, BELHAROUAK I, SUN Y K, et al. Titanium-based anode materials for safe lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(8): 959-969.
[3] ROY P, BERGER S, SCHMUKI P. TiO2 nanotubes: synthesis and applications[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(13): 2904-2939.
[4] LIU Jiehua, LIU Xuewei. Two-dimensional nanoarchitectures for lithium storage[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(30): 4097-4111.
[5]  F, TALIN A A. Electrical contacts to one-and two-dimensional nanomaterials[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2011, 6(12): 773-783.
F, TALIN A A. Electrical contacts to one-and two-dimensional nanomaterials[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2011, 6(12): 773-783.
[6] YANG Z G, CHOI D W, KERISIT S, et al. Nanostructures and lithium electrochemical reactivity of lithium titanites and titanium oxides: a review[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 192(2): 588-598.
[7] ZHU Guannan, WANG Yonggang, XIA Yaoyong. Ti-based compounds as anode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(5): 6652-6667.
[8] JUNG J H, KOBAYASHI H, VAN BOMMEL K J C, et al. Creation of novel helical ribbon and double-layered nanotube TiO2 structures using an organogel template[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2002, 14(4): 1445-1447.
[9] TSAI M C, CHANG J C, SHEU H S, et al. Lithium ion intercalation performance of porous laminal titanium dioxides synthesized by sol-gel process[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21(3): 499-505.
[10] GONG D, GRIMES C A, VARGHESE O K, et al. Titanium oxide nanotube arrays prepared by anodic oxidation[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2001, 16(12): 3331-3334.
[11] PRADHAN S K, REUCROFT P J, YANG F Q, et al. Growth of TiO2 nanorods by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2003, 256(1/2): 83-88.
[12] KASUGA T, HIRAMATSU M, HOSON A, et al. Titania nanotubes prepared by chemical processing[J]. Advanced Materials, 1999, 11(15): 1307-1311.
[13] ARMSTRONG A R, ARMSTRONG G, CANALES J, et al. TiO2-B nanowires[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2004, 43(17): 2286-2288.
[14] CHUNG C C, CHUNG T W, YANG T C K. Rapid synthesis of titania nanowires by microwave-assisted hydrothermal treatments[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(7): 2301-2307.
[15] WELHAM N J. A parametric study of the mechanically activated carbothermic reduction of ilmenite[J]. Minerals Engineering, 1996, 9(12): 1189-1200.
[16] LI Chun, LIANG Bin, CHEN Sengpin. Combined milling–dissolution of Panzhihua ilmenite in sulfuric acid[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 82(1/2): 93-99.
[17] GINLEY D S, BUTLER M A. The photoelectrolysis of water using iron titanate anodes[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1977, 48(5): 2019-2021.
[18] ZHOU F, KOTRU S, PANDEY R K. Nonlinear current–voltage characteristics of ilmenite–hematite ceramic[J]. Materials Letters, 2003, 57(13/14): 2104-2109.
[19] MCDONALD P F, PARASIRIS A, PANDEY R K, et al. Paramagnetic resonance and susceptibility of ilmenite, FeTiO3 crystal[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1991, 69(2): 1104-1107.
[20] TAO T, GLUSHENKOV A M, CHEN Q Y, et al. Porous TiO2 with a controllable bimodal pore size distribution from natural ilmenite[J]. Cryst Eng Comm, 2011, 13(5): 1322-1327.
[21] TAO Tao, CHEN Ying, ZHOU Dan, et al. Expanding the applications of the ilmenite mineral to the preparation of nanostructures: TiO2 nanorods and their photocatalytic properties in the degradation of oxalic acid[J]. Chemistry: A European Journal, 2013, 19(3): 1091-1096.
[22] TAO Tao, CHEN Ying. Direct synthesis of rutile TiO2 nanorods with improved electrochemical lithium ion storage properties[J]. Materials Letters, 2013, 98: 112-115.
[23] TAO T, GLUSHENKOV A M, RAHMAN M M, et al. Electrochemical reactivity of ilmenite FeTiO3, its nanostructures and oxide-carbon nanocomposites with lithium[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 108: 127-134.
[24] ISKANDAR F, NANDIYANTO A B D, YUN K M, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of brookite TiO2 macroporous particles prepared by spray drying with colloidal templating[J]. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(10): 1408-1412.
(编辑 刘锦伟)
收稿日期:2015-02-27;修回日期:2015-04-26
基金项目(Foundation item):宁夏自然科学基金资助项目(NZ15004);中南大学博士后基金资助项目(109004);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51174231)(Project (NZ15004) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia; Project (109004) supported by the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Central South University; Project (51174231) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:胡慧萍,博士,教授,从事湿法冶金及高分子化学的研究;E-mail:phuhuiping@126.com