钛种植体结构和弹性模量对骨界面应力分布的影响
陈良建1, 2,李益民2
(1. 中南大学 湘雅三医院,湖南 长沙,410013;
2. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:采用CAD(Pro/E)软件建立颌骨和钛种植体的三维模型,设置3种不同结构钛种植体,即全致密型(1号样品)、穿皮质区致密而松质骨区外层多孔内芯致密型(2号样品)与整体低弹性模量型(3号样品),分析钛种植体结构和弹性模量对骨界面应力分布的影响,研究能有效地转移应力至周围骨组织的新型种植体。研究结果表明:在相同载荷下,3种钛种植体颈部皮质骨均为高应力区,3号种植体的应力最高,为7.128 MPa;在松质骨区2号种植体的应力比1号与3号种植体的低,且呈均匀递减趋势。在加载条件下,2号种植体随着弹性模量的降低,骨界面应力降低,且明显比1号种植体的低,当多孔层的弹性模量为致密钛的40%或以下时,骨界面应力明显降低;3号种植体随着弹性模量降低,皮质骨区骨界面应力增加,而松质骨区骨界面应力降低不明显。钛种植体的结构和弹性模量均影响骨界面应力分布;穿皮质区致密而松质骨区外层多孔内芯致密型钛种植体有利于界面应力转移到周围骨组织,降低多孔层的弹性模量,能有效地降低骨界面应力。
关键词:钛种植体;弹性模量;有限元分析;多孔结构⊙
中图分类号:R783.1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)02-0400-06
Influence of structure and elastic modulus of titanium implant on implant-bone interfacial stress distribution
CHEN Liang-jian1, 2, LI Yi-min2
(1. Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410013, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: To investigate the effect of structure and elastic modulus of titanium implant on stress distribution in the implant–bone interface, and explore a new style of titanium implant which could effectively transfer stress to the surrounding bone, the 3-D finite element analysis models of a posterior mandible segment with an implant bone were constructed by the CAD (Pro/E Widefire 2.0) software. Three different structure implant models were created, including the whole dense structure style (No.1), porous structure style (No.2) and the overall low elastic modulus structure style (No.3). The results show that the cervical cortical bones in three titanium implants are all high stress region under the same load-bearing, and the maximum Von-Misese value is 7.128 MPa (No.3). In the cancellous bone region, the Von-Misese value of No.2 implant is lower than those of No.1 and No.3 implants. Under load-bearing, the implant-bone interface stress of No.2 implant decreases with the decrease of the elastic modulus, and the stress of No.2 implant is significantly lower than that of No.1 implant. When the elastic modulus of porous titanium layer of No.2 implant is 40% of dense titanium, the implant-bone interface stress decreases notably. In No.3 implant, with the elastic modulus decreasing, the stress on cortical bone interface increases, and the stress does not obviously decrease on cancellous bone region. It is proved that the structure and elastic modulus of titanium implant affect the distribution of stress on bone interface. The implant which has dense structure in the cortical bone area and porous-outer and dense-interior in the cancellous bone area contribute to transferring the stress to the surrounding bone. Furthermore, with the decrease of elastic modulus of porous layer, implant-bone interface stress will effectively reduce in the cancellous bone region.
Key words: titanium implant; elastic modulus; finite element analysis; porous structure
钛种植体材料由于与骨组织相容性优良,是目前牙科医学上广泛应用的一种医用植入材料。但是,钛种植体与周围骨组织间为刚性结合,种植体的硬度明显大于周围骨质的硬度,在骨结合界面易导致应力屏蔽或应力集中。而种植体骨结合界面应力转移到周围骨组织的方式决定种植修复成败[1-2],有研究表明:骨界面应力集中区多位于种植体的颈部和根端部,与种植体的直径、长度、弹性模量有关[3-4]。颌骨的结构特性为外层为致密的皮质骨,内层为疏松的松质骨,皮质骨与松质骨的弹性模量和力学特性不同,目前,临床应用为整体全致密型钛种植体,未考虑颌骨内外结构和弹性模量的差别,种植体与周围骨组织的力学相容性难题仍未解决。本文作者根据颌骨结构特点,提出一种仿生种植体的设想,即穿皮质区致密而松质骨区外层多孔内芯致密新型钛种植体,采用CAD(Pro/E)软件建立颌骨和种植体的三维模型,应用Ansys Workbench 10.0有限元分析软件比较研究穿皮质区致密而松质骨区外层多孔内芯致密型、全致密型与整体低弹性模量型3种钛种植体的结构和弹性模量对骨界面应力分布的影响,探讨能有效转移应力至周围骨组织的新型钛种植体材料。
1 模型建立
应用CAD 软件Pro/Engineer2001在计算机上建立包含种植体的下颌后牙区骨块。以第一前磨牙的横断切面作为基底面,将其进行近远中的拉伸形成三维的下颌骨骨块。该骨块具有较厚的皮质骨以及密度较高的松质骨(模拟Lekholm 和Zarb 颌骨分类的B/2型),牙槽嵴顶的皮质骨厚度为2.0 mm,骨块的几何参数为:高35 mm,颊舌宽14 mm,近远中长20 mm,松质骨的近远中未被皮质骨包绕。模拟一圆柱形种植体,按种植体的弹性模量和结构特点,建立全致密型、整体低弹性模量型和穿皮质区致密而松质骨区外层多孔区内芯致密型3种钛种植体,直径×高均为4.1 mm×12 mm,同时模拟高为5 mm的基台,基台和种植体简化为一个同质整体。
应用Ansys Workbench 10.0 软件进行有限元分析。利用Ansys与Pro/E的专用接口,将实体模型导入Ansys,用3D实体单元(solid45)进行相同网格密度的智能网格划分,生成颌骨块与种植体的三维有限元模型,通过智能网格的划分,控制单元的大小,并对单元进行自动优化。模型如图1和图2所示,单元数与节点数如下:种植体模型有2 498节点、11 501单元,颌骨模型有6 425节点、33 382单元。

图1 种植体有限元模型
Fig.1 Finite element models of implant
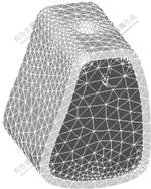
图2 颌骨有限元模型
Fig.2 Finite element models of partial mandibular bone
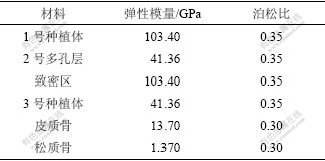
将模型中的各种材料和组织假设为连续、均匀、各向同性的小变形线弹性材料,种植体与骨组织界面均考虑为100%的骨性结合。将皮质骨模型的侧面及松质骨模型的侧面和底面完全约束,并将此边界条件扩展到相应节点上。从种植体根部向上对模型施加相同的全约束,即限制根部以上种植体的自由度。1号钛种植体为全致密型,2号为穿皮质区致密而松质骨区外层多孔内芯致密型,3号为整体低弹性模量型。分析种植体结构因素对骨界面应力影响时,设置致密钛的弹性模量103.4 GPa,2号多孔层和3号的弹性模量为致密钛模量的40%。分析种植体弹性模量对2号和3号种植体骨界面应力影响时,设置4种弹性模量分别为致密钛模量的20%,40%,60%和80%。各种材料的力学参数如表1所示。
表1 模拟的各种钛种植体的力学参数
Table 1 Mechanical properties of used titanium implants
2 模拟计算结果
2.1 不同结构的钛种植体骨界面应力分布比较
模拟正常的咬合运动,以接近正常成人咬合力给予种植义齿-骨块模型加载,分别从轴向加载150 N 和从颊舌向45?加载25 N。
取Von Mises应力作为衡量应力水平的主要指标。比较分析3种钛种植体界面的应力分布以及颌骨模型骨界面上应力分布状况。
在相同载荷下,3种钛种植体骨界面最大Von-Misese应力在皮质骨、松质骨和根端区均不同。在皮质骨区,3号种植体的Von-Misese应力最高,为7.128 MPa,而在松质骨区和根端区,1号种植体的Von-Misese应力最高,为6.704 MPa(见表2)。从界面应力分布云图可看出:3种钛种植体颈部皮质骨均为高应力区(见图3);皮质骨与松质骨交界区、根端区为高应力区,1号与3号种植体在松质骨区的高应力区域大于2号种植体的高应力(见图4);在松质骨区,2号种植体的Von-Misese应力低于1号与3号种植体的应力,且呈均匀递减趋势(见图5)。
表2 3种不同结构钛种植体骨界面最大Von-Misese应力
Table 2 Maximum Von Mises stresses in implant-bone interface of three different structure titanium implants p/MPa
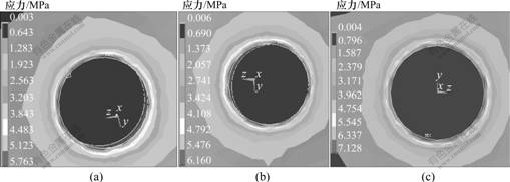
(a)1号; (b) 2号; (c) 3号
图3 3种钛种植体皮质骨区Von-Misese应力分布云图
Fig.3 Stress distribution in cortical bone area of three titanium implants
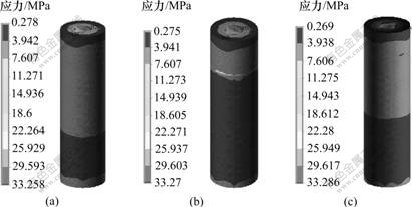
(a) 1号; (b) 2号; (c) 3号
图4 3种钛种植体轴向骨界面Von-Misese应力分布云图
Fig.4 Stress distribution in axial bone-implant interface of three titanium implants
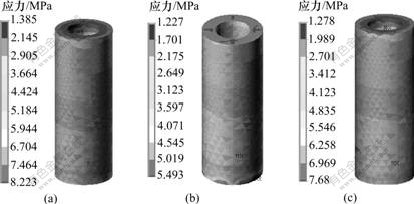
(a) 1号; (b) 2号; (c) 3号
图5 3种钛种植体在松质骨区骨界面的应力分布云图
Fig.5 Stress distribution in cancellous bone-implant interface of three titanium implants
2.2 不同结构种植体轴向骨界面Von-Misese应力分布的比较
根据种植体在颌骨中位置关系,从皮质区至松质根端部沿种植体长轴方向均分6个截面,截面1 为颈部,截面4 为牙根正中部,截面6 为根端部。在轴向加载或轴向与颊舌向联合加载下,3种种植体的界面应力分布状况如下:2号种植体从皮质区至松质骨区界面应力呈均匀降低趋势,其界面应力比1号和3号种植体的低;1号种植体在松质骨区的界面应力比2号和3号的高,3号种植体在皮质区界面应力明显增大;在根端区,3种种植体界面应力均表现增大,1号种植体应力增加明显(见图6和图7)。
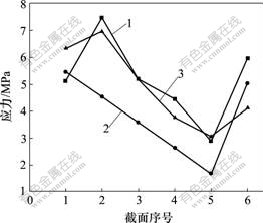
1—1号; 2—2号; 3—3号
图6 轴向加载下3种不同种植体骨界面应力分布图
Fig.6 Stress distribution in bone-implant interface of three different titanium implants in an axial loading
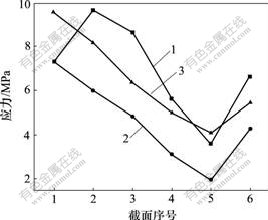
1—1号; 2—2号; 3—3号
图7 联合加载下3种不同种植体受压侧界面应力分布图
Fig.7 Stress distribution in oppressed flank of three different titanium implants in united loading
2.3 不同弹性模量的2号与3号种植体骨界面应力分布的比较
设置4种弹性模量分别为致密钛模量的20%,40%,60%和80%,在相同载荷下,研究弹性模量对2号与3号种植体骨界面应力分布的影响。研究发现:在负载下,2号种植体骨界面应力随弹性模量的降低而减小,且明显比全致密型种植体的低,当多孔层的模量为致密钛的40%或以下时,松质骨区界面应力降低明显(见图8);而3号种植体骨界面应力随弹性模量降低,皮质骨区界面应力增加,而松质骨区界面应力降低不明显(见图9)。
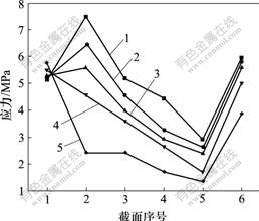
1—全致密;2—80%模量;3—60%模量;
4—40%模量;5—20%模量
图8 轴向加载下不同弹性模量的2号种植体骨界面应力分布图
Fig.8 Stress distribution in bone-implant interface of different elastic modulus No.2 titanium implants in an axial loading
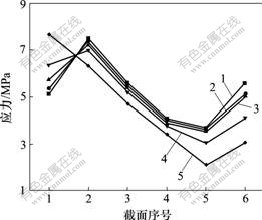
1—全致密;2—80%模量;3—60%模量;
4—40%模量;5—20%模量
图9 轴向加载下不同弹性模量的3号种植体骨界面应力分布图
Fig.9 Stress distribution in bone-implant interface of different elastic modulus No.3 titanium implants in an axial loading
3 分析和讨论
种植体主要依靠与周围骨组织的直接结合行使功能,骨结合界面的可靠性和稳定性决定种植修复长期成功率。要确保种植体长期稳定的行使功能,一方面尽量降低载荷,以免超过其生理耐受限度,超载荷易致界面骨质吸收或种植体应力疲劳失败,而低载荷可引起废用性骨萎缩和骨量丧失[5-6];另一方面,要增加种植体的表面面积,即增加与骨的接触面积,降低骨界面应力。为改善种植体与骨组织的结合强度和质量,可以改变种植体形状、表面特征,复合各种成骨因子等措施,来增加种植体与骨组织的接触面积和骨结合强度,改善种植体的生物力学环境。
从医学和生物力学角度看,骨替代材料硬度不能太高,以免降低新骨形成所需负荷,造成骨应力吸收;由于材料应用于承载部位,要有足够的抗疲劳强度;植入金属材料的弹性模量越小,越接近骨的弹性模量,两者在承受应力时由于应变差异造成的相对位移越小,从而减小界面松动倾向,避免应力屏蔽造成的骨吸收和退化。自然骨的强度范围为3~20 MPa,皮质骨的弹性模量为10~18 GPa,松质骨为1.3~4 GPa。弹性模量对孔隙敏感,即使25%的孔隙度也会引起弹性模量下降50%[7-9]。具有独特结构的多孔植入材料能极大地提高植入体生物相容性[10-12],有利于成骨细胞的粘附生长、细胞外基质沉积、营养和氧气进入,促使新生骨长入孔隙,实现生物固定;通过改变孔隙度来调整金属材料的密度、强度和弹性模量,达到与被替换硬组织相匹配的力学性能,实现材料的力学相容性;多孔结构为生物活性涂层提供支架,促进骨整合[13-15]。
计算模拟结果表明,在相同载荷下,全致密型和整体低弹性模量型种植体界面的应力分布规律大致相同,从上至下,种植体颈部周围皮质骨区的界面应力基本上呈逐级递增的趋势,在皮质骨与松质骨的交界部出现一个明显的下降过程,而松质骨界面沿种植体长轴的分布表现为逐级递减,在根端区应力增加,这与大多数学者所得出的分布规律一致[3-4, 8];而穿皮质区致密而松质骨区外层多孔内芯致密型种植体的界面应力在皮质骨和松质骨区均表现为逐级递减,根端区应力增加,在松质骨区,种植体骨界面应力低于全致密型和整体低弹性模量型种植体应力。这说明,设计穿皮质区致密而松质骨区外层多孔内芯致密为结构特性的种植体能有效地降低种植体骨界面应力,有利于骨界面应力转移至周围骨组织。
4 结 论
a. 在相同载荷下,3种钛种植体颈部皮质骨均为高应力区,3号种植体的应力最高,为7.128 MPa;在松质骨区2号种植体的应力比1号与3号种植体的低,且呈均匀递减趋势。
b. 在加载条件下,2号种植体随着弹性模量的降低,骨界面应力降低,且明显比1号种植体的低,当多孔层的弹性模量为致密钛的40%或以下时,骨界面应力明显降低; 3号种植体随着弹性模量降低,皮质骨区骨界面应力增加,而松质骨区骨界面应力降低不明显。
c. 钛种植体的结构和弹性模量均影响骨界面应力分布;穿皮质区致密而松质骨区外层多孔内芯致密型钛种植体有利于界面应力转移到周围骨组织,降低多孔层的弹性模量,能有效地降低骨界面应力。
参考文献:
[1] Van Osterwyck H, Duyck J, Vander S, et al. The influence of bone mechanical properties and implant fixation upon bone loading around oral implants[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 1998, 9(6): 407-412.
[2] Geng J, Tan K B, Liu G R. Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: A review of the literature[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2001, 85(6): 585-598.
[3] Iplikcioglu H, Akca K. Comparative evaluation of the effect of diameter, length and number of implants supporting three-unit fixed partial prostheses on stress distribution in the bone[J]. J Dent, 2002, 30(1): 41-46.
[4] 邹敬才, 刘宝林, 唐文杰, 等. 影响人工种植牙-骨界面应力分布规律因素的多元逐步回归分析[J]. 医用生物力学, 2000, 15(4): 216-221.
ZOU Jing-cai, LIU Bao-lin, TANG Wen-jie, et al. Multivariate step regression analysis of influencing factors on the stress distribution patients at the bone interface around dental implants[J]. Journal of Medical Biomechanics, 2000, 15(4): 216-221.
[5] Pilliar R M, Deporter D A, Watson P A, et al. Dental implant design effect on bone remodeling[J]. J Biomed Mater Res, 1991, 25(4): 467-483.
[6] Vaillancourt H, Pillar R M, McCammond D. Factors affecting cortical bone loss with dental implants partially covered with a porous coating: A finite element analysis[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1996, 11: 351-359.
[7] Sato Y, Wadamoto M, Tsuga K, et al. The effectiveness of element downsizing on a three-dimensional finite element model of bone trabeculae in implant biomechanics[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 1999, 26(4): 288-291.
[8] Sahin S, Cehreli M C, Yalcn E. The influence of functional forces on the biomechanics of implant-supported prostheses—A review[J]. J Dent, 2002, 30(8): 271-282.
[9] Becker B S, Bolton J D, Youseffi M. Production of porous sintered Co-Cr-Mo Alloys for possible surgical implant applications[J]. Powder metallurgy, 1995, 38(3): 201-208.
[10] St-Pierre J P, Gauthier M, Lefebvre L P, et al. Three-dimensional growth of differentiating MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts on porous titanium scaffolds[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(35): 7319-7328.
[11] Otsukia B, Takemotoa M, Fujibayashia S, et al. Pore throat size and connectivity determine bone and tissue ingrowth into porous implants: Three-dimensional micro-CT based structural analyses of porous bioactive titanium implants[J]. Biomaterials, 2006, 27(35): 5892-5900.
[12] Takemoto M, Fujibayashi S, Neo M, et al. Mechanical properties and osteoconductivity of porous bioactive titanium[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(30): 6014-6023.
[13] Oguz K, Emir Y, Fehmi E. Static, dynamic and fatigue behaviors of dental implant using finite element method[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2006, 37(10): 649-658.
[14] 赵 峰, 韩彦峰, 胡江峰.弹性模量和初始应力对种植体骨界面应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国口腔种植学杂志, 2006, 11(2): 55-58.
ZHAO Feng, HAN Yan-feng, HU Jiang-feng. Three-dimensional finite element method analysis of relation of implant elastic modulus and initial stress and bone-implant surface stress distribution[J]. Chinese Journal of Oral Implantology, 2006, 11(2): 55-58.
[15] 高 勃, 赵 峰, 刘振侠.螺旋形种植体弹性模量与骨界面应力分布关系的三维有限元分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2006, 22(11): 667-670.
GAO Bo, ZHAO Feng, LIU Zhen-xia. Three-dimensional finite element method analysis of relation of screw implant elastic modulus and bone-implant surface stress distribution[J]. Journal of Clinical Stomatology, 2006, 22(11): 667-670.
收稿日期:2008-09-10;修回日期:2008-11-20
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(35770576);“863”计划新材料技术领域专项资助项目(2007AA03Z114);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(2007JJ5109)
通信作者:陈良建(1967-),男,湖南攸县人,博士,副教授,从事新型钛种植体开发与临床研究;电话:0731-8618554;E-mail: chen0313@xy3yy.com