DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.01.017
基于液相传质的锌电解过程多物理场仿真分析
邓亦梁,谢永芳,李勇刚,阳春华
(中南大学 信息科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:针对锌电解槽中流速场、离子浓度场、电场耦合严重及其与电解能耗关系复杂的问题,基于液相传质原理,结合组分质量守恒、流体动力学及电极动力学方程建立锌电解槽多物理场仿真模型。利用仿真软件Comsol Multiphysics对锌电解槽多物理场模型进行数值求解,通过对比计算结果与锌电解实验结果验证模型的正确性。研究结果表明:阴极板表面电解液的流动方向主要有斜向上和斜向下,且斜向下的流速随着阴极板与进液口的距离增大而迅速减小;极板间锌离子的浓度呈现“上低下高”分布;阴极板表面电解液流速低的区域,锌离子浓度低而氢离子浓度高,电流效率低而能耗高。
关键词:锌电解过程;液相传质;多场仿真
中图分类号:TF813 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2017)01-0119-08
Multiphysics simulation analysis for zinc electrowinning based on liquid-phase mass transfer
DENG Yiliang, XIE Yongfang, LI Yonggang, YANG Chunhua
(School of Information Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Considering the complicated relationship between energy consumption of zinc electrowinning and seriously coupled multiphysics such as velocity field, concentration field and electric field in zinc electrolytic cell, a multiphysical simulation model of zinc electrolytic cell was established based on liquid-phase mass transfer by combining species mass conservation, fluid dynamics and electrode kinetics equation. The model was calculated numerically using simulation software Comsol Multiphysics and verified by comparing calculated results with experimental results. The results show that the electrolyte mainly flows slantingly upwards and downwards on cathode surfaces. The flow rate of the inclined downward decreases rapidly with the increase of distance from cathode to the inlet. The concentration distribution of zinc ions between electrode plates has an increasing tendency from top to bottom. The area with low flow rate has low concentration of zinc ion and low current efficiency but high concentration of hydrogen ion and high energy consumption on cathode surfaces, and vice versa.
Key words: zinc electrowinning process; liquid-phase mass transfer; multiphysics simulation
电解过程是湿法炼锌中的主要耗能工序[1-2],降低锌电解能耗对湿法炼锌的节能降耗意义重大。在锌电解生产中,主要通过控制电解过程的电流密度及电解液的酸锌离子浓度以保证锌产量并降低电解能耗。酸锌离子随着电解液的流动而发生转移,故电解槽内的离子浓度分布与电解液流场密切相关。酸锌离子浓度分布通过浓差极化作用影响电极反应,进而影响锌电解能耗,此外,锌电解过程要消耗锌离子并产生氢离子,因此,锌电解是一个电解液流场、离子浓度场和电场互相影响的过程。研究锌电解过程中各物理场之间的相互作用及场分布对电解能耗的影响,可为从物理场对锌电解过程进行优化控制提供依据。国内外研究者对电解槽内的场分布进行了大量的研究。针对铜电解槽,HELEN 等[3-9]建立了三维的计算流体力学模型,在ANSYS平台上对模型求解得到了铜离子浓度场、电解液流场分布,并讨论了入口电解液流量、极距、电流密度、电解液的循环方式对铜离子浓度场及电解液流场的影响。针对锌冶炼过程,苏寅彪等[10-13]在ANSYS-Fluent上分别采用 -ε湍流模型和DPM离散相模型对电解液流场和锌离子浓度场进行数值求解,基于仿真结果优化了电解槽结构。上述研究虽然分析了电解过程中离子浓度场和电解液流场的分布,但在建模时忽略了电极反应与离子浓度场之间的相互作用,且未讨论极板表面离子浓度分布与电解能耗间的关系。为此,本文作者拟利用多物理场耦合仿真软件Comsol Multiphysics对锌电解槽内的电解液流场、离子浓度场、电场、电流效率和电解能耗分布进行数值模拟并对仿真结果进行分析,以便为后续锌电解过程的优化控制提供参考。
-ε湍流模型和DPM离散相模型对电解液流场和锌离子浓度场进行数值求解,基于仿真结果优化了电解槽结构。上述研究虽然分析了电解过程中离子浓度场和电解液流场的分布,但在建模时忽略了电极反应与离子浓度场之间的相互作用,且未讨论极板表面离子浓度分布与电解能耗间的关系。为此,本文作者拟利用多物理场耦合仿真软件Comsol Multiphysics对锌电解槽内的电解液流场、离子浓度场、电场、电流效率和电解能耗分布进行数值模拟并对仿真结果进行分析,以便为后续锌电解过程的优化控制提供参考。
1 锌电解过程多物理场模型
1.1 液相传质过程
在锌电解过程中,电极反应都是在极板表面进行的,反应离子在电解液与极板表面之间的转移是通过液相传质进行的。极板附近的电解液层按与极板表面的距离由远到近依次可分为对流区、扩散区和双电层区,对应的主要传质方式为对流、扩散和电迁移。电解液中含有大量的支持电解质,电解液的电导率较高,电迁移作用很弱,且双电层厚度数量级为纳米级[14-15],因此,本文只考虑扩散和对流的传质作用。
下面以锌离子为例说明在扩散和对流的传质作用及电极反应的作用下,阴极板及其附近区域的锌离子浓度变化。当阴极板通过直流电流时,阴极板表面发生的锌沉积反应要消耗大量的锌离子,而电解液中锌离子扩散系数很小,扩散区锌离子的扩散流量不能满足沉积反应锌离子的消耗量,故从扩散区到阴极板表面锌离子浓度逐渐降低,但对流区的锌离子通过电解液的流动即对流传质向扩散区补充锌离子。在传质和电解的共同作用下,阴极板表面及临近区域的锌离子浓度将达到动态平衡,如图1所示。

图1 传质和电解作用下阴极板及临近区域的锌离子浓度曲线
Fig. 1 Concentration curve of zinc ion on cathode and nearing regions under mass transfer and electrolysis
1.2 组分质量守恒方程
当发生电极反应时,阴极板表面要消耗大量锌离子和少量氢离子,而阳极板表面生成大量氢离子。电极反应的发生伴随着反应离子的消耗和生成,要满足组分质量守恒方程。对于反应离子i,组分质量守恒方程的具体形式如下:
 (1)
(1)
式中:ci为离子i的浓度,其在整个电解槽中的分布称为离子i的浓度场;vl为电解液的流速,其在整个电解槽中的分布称为电解液流场;D为离子i的扩散系数;Si为外加源项,在本文中定义为单位时间内单位体积通过电极反应生成或消耗离子i的物质的量。由定义知Si与电极反应的电流密度有关,可通过求解电极反应动力学方程得到,而电解液流场通过求解 -ε湍流模型得到。
-ε湍流模型得到。
1.3  -ε湍流模型
-ε湍流模型
反应离子i的对流流量与电解液流场密切相关。电极反应要生成气体(主要是氧气),气体的密度和体积相对于槽内的电解液来说都很小,因此,忽略气体对电解液流场的影响。考虑到极板对电解液流动的阻碍作用,电解液会出现回流和绕流现象,因此,本文使用 -ε湍流模型来描述电解液流场。该模型不仅包括电解液的动量守恒方程和连续性方程,而且包含湍流特征变量即湍动能
-ε湍流模型来描述电解液流场。该模型不仅包括电解液的动量守恒方程和连续性方程,而且包含湍流特征变量即湍动能 和湍流能量耗散率ε的输运方程。
和湍流能量耗散率ε的输运方程。
电解液的动量守恒方程是基于Navier-Stokes方程推算而来的,其具体形式如下:

 (2)
(2)
式中:p为压强; 为电解液的密度;g为重力加速度;
为电解液的密度;g为重力加速度; 为电解液的动力黏度;
为电解液的动力黏度; 为紊流黏度。紊流黏度
为紊流黏度。紊流黏度 定义为
定义为
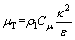 (3)
(3)
式中: 为常数,其值为0.09。湍动能
为常数,其值为0.09。湍动能 的输运方程为
的输运方程为
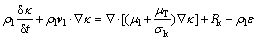 (4)
(4)
式中: 为常数,其值为1。未知项
为常数,其值为1。未知项 定义如下:
定义如下:
 (5)
(5)
湍流能量耗散率ε的输运方程定义为
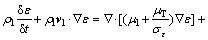
 (6)
(6)
式中: ,
,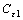 ,
, 和
和 都为常数,取值分别为1.30,1.44,1.92和1.40。
都为常数,取值分别为1.30,1.44,1.92和1.40。
电解液的连续性方程表示如下:
 (7)
(7)
1.4 电极反应动力学方程
由图1可知:在液相传质和电极反应的共同作用下,极板表面反应离子浓度与对流区的离子浓度有较大偏差,此时,电极反应的平衡电极电位 要偏离标准平衡电极电位
要偏离标准平衡电极电位 ,即
,即
 (8)
(8)
式中: 为标准平衡电极电位;R为摩尔气体常数;T为电解液热力学温度;F为法拉第常数;z为反应的电子数;
为标准平衡电极电位;R为摩尔气体常数;T为电解液热力学温度;F为法拉第常数;z为反应的电子数; 为离子活度系数,下标o和r分别代表电极反应的氧化物和还原物。在电解过程中,相邻阴、阳极板之间的电位差定义为槽电压V,由以下公式计算:
为离子活度系数,下标o和r分别代表电极反应的氧化物和还原物。在电解过程中,相邻阴、阳极板之间的电位差定义为槽电压V,由以下公式计算:
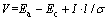 (9)
(9)
式中:Ea和Ec分别表示阳极板和阴极板电极电位;I,l和 分别为总电流密度、极距、电解液电导率。
分别为总电流密度、极距、电解液电导率。
当电极表面发生电极反应时,电极电位偏离电极反应的平衡电极电位即发生极化作用,偏差为电极反应过电势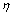 ,计算公式为
,计算公式为
 (10)
(10)
式中:E为电极电位;Ee为平衡电极电位。电极反应的电流密度i与反应过电势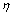 密切相关,描述两者之间的关系有2个方程即Tafel方程和电流-过电势公式。Tafel方程假设电极反应的速率决定步骤是电极表面的电荷转移过程,而不是物质转移过程;而电流-过电势公式综合考虑了电荷转移过程和传质过程对电极反应的影响。
密切相关,描述两者之间的关系有2个方程即Tafel方程和电流-过电势公式。Tafel方程假设电极反应的速率决定步骤是电极表面的电荷转移过程,而不是物质转移过程;而电流-过电势公式综合考虑了电荷转移过程和传质过程对电极反应的影响。
对于有气体生成的电极反应,电极表面电荷转移过程进行缓慢,电荷转移速度决定了电极反应的速度,所以,用Tafel方程计算电流密度iH:
 (11)
(11)
式中:iH为氢气析出电流密度;i0,H为氢交换电流密度; 为氢析出对称因子;
为氢析出对称因子; 为氢超电压;z H为氢反应原子价;F为法拉第常数。
为氢超电压;z H为氢反应原子价;F为法拉第常数。
而阴极板上锌沉积反应没有气体生成,电荷转移过程较快;阴极板表面锌离子由极板间的电解液通过液相传质进行补充,因此,要同时考虑电荷转移和传质过程对锌沉积反应的影响。锌沉积反应电流密度iZn的电流-过电势计算公式为

 (12)
(12)
式中:iZn为锌析出电流密度;i0,Zn为锌交换电流密度; 为锌析出对称因子;
为锌析出对称因子;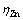 为锌超电压;zZn为锌反应原子价;i0和
为锌超电压;zZn为锌反应原子价;i0和 分别为电极反应的交换电流密度和转移系数;
分别为电极反应的交换电流密度和转移系数; 和
和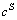 分别为极板间和阴极板表面的锌离子浓度。
分别为极板间和阴极板表面的锌离子浓度。
2 电解槽几何结构和仿真结果分析
2.1 电解槽几何结构
为了研究锌电解槽内多物理场的分布及场分布对电解能耗的影响,采用小型电解槽对某锌冶炼厂进行锌电解实验。实验电解槽几何结构如图2所示。
呈电中性的电解液(主要含Zn2+,H+和SO42-)通过进液管流入1个装有2对阴阳极板的锌电解槽内,阴阳极板尺寸相同,厚度为3 mm。实验中把阴极板A正对进液管的那个面记为阴极面A1,背对面记为阴极面A2;把阴极板B正对进液管的那个面记为阴极面B,而背对面用胶布粘贴,防止在此阴极面沉积出锌。本文通过仿真软件Comsol Multiphysics[16]建立的锌电解槽几何结构与实验电解槽几何结构一致。

图2 实验电解槽的几何结构
Fig. 2 Geometry of experimental electrolytic cell
2.2 边界条件及模型参数
2.2.1 入口边界条件
电解液以一定流速由进液管流入电解槽内,因此,入口处设定为速度入口,通过计算得到速度为0.056 59 m/s。根据电解实验设定入口酸锌离子质量浓度分别为170 g/L和55 g/L。
2.2.2 出口边界条件
电解液从与大气直接接触的电解槽右侧面流出,故出口处设置为压力出口。
2.2.3 模型参数
电解液温度保持为313.15 K,总电流密度i为500 A/m2,电解周期为12 h。本文在文献[17-19]的基础上,结合电解实验得到锌电解多物理场模型中所用到的物性参数:单质锌、氢气、氧气的活度都为1.0,水的活度为0.9;酸锌离子活度系数分别为0.5和0.1;电解液的密度为1.123 75 t/m3;锌沉积反应和氢气析出反应的转移系数分别为0.4和0.5。
2.3 电解液流场分析
在1个电解周期内,锌电解槽进液管的电解液流量保持不变,阴极板表面沉积的金属锌厚度在5 mm左右。对电解槽结构的改变可忽略不计,故电解槽内电解液流场最终会达到稳定,如图3所示。
由图3可知电解槽内电解液流场呈现几何对称,这是因为进液管位于电解槽左侧面的几何中心。由图3(a)和3(c)可见:阴极板表面电解液流动的方向主要有斜向下和斜向上,这有利于电解液在极板表面流通与更新,但也导致相向流动的电解液在极板中间相遇时流速很低,形成“流动死区”。对比图3(a)和3(c)可知:在极板的阻碍作用下,随着与入口距离加大,阴极板上部电解液斜向下的流速迅速下降,而下部电解液斜向上的流速基本保持不变。由下向上流的电解液主要从极板两侧流出极板表面,如图3(b)所示。由图3(d)可知:大部分电解液直接从电解槽底部流向出口,只有少部分由极板底部和侧部流入极板间;此外,极板间电解液流速比电解槽底部电解液流速低2个数量级,但比阴极板表面电解液流速至少高1个数量级,这表明极板间的主要传质方式是对流。

图3 电解槽不同位置的电解液流场
Fig. 3 Electrolyte velocity field in different locations of cell
2.4 离子浓度场分析
当电解液流场处于稳定时,由于入口电解液的酸锌离子浓度保持不变,在液相传质过程和电极反应的共同作用下电解槽内酸锌离子的浓度分布最终将趋于稳定,因为锌沉积反应的电流密度与阴极板表面的锌离子浓度直接相关。为了证实液相传质理论,本文主要给出阴极板表面酸锌离子浓度分布以及阴极板临近区域锌离子浓度的变化曲线,如图4所示。

图4 电解槽的酸锌离子质量浓度场
Fig. 4 Mass concentration field of zinc and acid ions of cell
结合图3和图4可知:阴极板表面电解液流速低的区域,锌离子浓度低而氢离子浓度高;反之,流速高的区域,锌离子浓度高而氢离子浓度低。这是因为在流速低的区域,对流传质的锌离子流量小,为保证有足够多的锌离子参与锌沉积反应,扩散传质要加强,即阴极板表面与极板间的锌离子浓度梯度要加大,故在流速低的区域,锌离子浓度相对于其他区域更低,而电解液呈电中性,所以,氢离子浓度更高;电解槽上部电解液的流动性比底部的流动性差,导致极板间的锌离子浓度呈现“上低下高”的分布,如图4(e)所示。由图4(f)可知:随着与阴极板垂直距离增大,阴极板附近锌离子浓度先升高后保持稳定,这与液相传质理论的推导结论一致。
2.5 阴极板电场、电流效率和能耗分布
在保证锌产量的前提下,电解生产最关注的是如何优化控制锌电解过程以尽可能降低电解能耗。电流效率 是锌电解过程的重要能耗指标,定义为实际析出的锌产量与通过相同电量时理论上的锌产量之比,也可用阴极板上锌沉积电流密度与总电流密度(锌沉积电流密度iZn与氢气析出电流密度iH之和)之比来表示电流效率,即
是锌电解过程的重要能耗指标,定义为实际析出的锌产量与通过相同电量时理论上的锌产量之比,也可用阴极板上锌沉积电流密度与总电流密度(锌沉积电流密度iZn与氢气析出电流密度iH之和)之比来表示电流效率,即
 (13)
(13)
电解工业一般用电解直流单耗来表征电解能耗。锌电解直流单耗W定义为电解产出1 t单质锌所消耗的直流电能。直流单耗W与电流效率 、槽电压V的关系式如下:
、槽电压V的关系式如下:
 (14)
(14)
式中:q为锌的电化学当量,取为1.219 8 g/(A·h)。
锌电解直流单耗与电流密度、阴极板表面酸锌离子浓度分布密切相关[20]。在仿真软件Comsol Multiphysics上进行锌电解仿真实验,3个阴极面施加相等的电流密度,然后在给定入口流量及入口酸锌离子浓度的边界条件下进行数值计算,得到阴极板表面酸锌离子浓度不同时,阴阳极板间的槽电压、阴极板表面电流效率和直流单耗分布如图5所示。
由图5(a)可见,阴阳极板间的槽电压变化很小,但靠近极板边缘槽电压较高,这是极板的边缘效应所致。结合图4和图5可知:阴极板表面锌离子浓度高的区域,电流效率高,能耗低;反之,极板表面锌离子浓度低的区域,电流效率低,能耗高。这是因为在锌离子浓度低的区域浓差极化作用强,致使该区域沉积的单质锌返溶。此外,氢气的析出电位随着锌离子浓度的降低而下降,这意味着氢气更容易在阴极板表面析出,因此,锌离子浓度低的区域电流效率低,能耗高,更容易发生“烧板”现象。由图5(b)和图5(c)可知:同一阴极板上的电流效率最大相差4%,但直流单耗相差143 (kW·h)/t,这说明锌电解过程的优化目标要综合考虑电流效率和直流单耗。
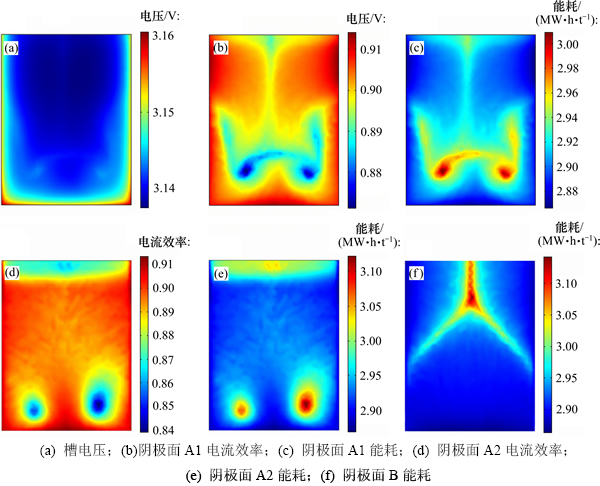
图5 槽电压、阴极板表面电流效率和能耗分布
Fig. 5 Distribution of cell voltage, current efficiency and energy on cathode surfaces
3 模型验证
在不同的电解条件下,通过对比析出锌产量的理论计算值和实际值来验证所建立多物理场模型的准确性,结果如表1所示。
表1 不同电解条件下析出锌产量的计算值和实验值
Table 1 Calculated value and experimental value of zinc production under different electrolytic conditions

由表1可知:析出锌产量的理论计算值与实际值的相对误差平均值为5.15%,表明本文建立的多物理场模型能够较准确地描述锌电解过程,但析出锌产量的理论计算值比实际值大,这是因为在多物理场模型中没有考虑电解液中的杂质金属离子、电解液温度的波动及导电棒与极板的接触电阻等因素对电解过程的影响。
4 结论
1) 阴极板表面电解液的流动方向主要有斜向上和斜向下;阴极板上方的电解液斜向下流速随着与入口距离的加大而迅速下降,而下方的电解液斜向上的流速基本保持不变;电解液的相向流动造成阴极板表面存在一些“流动死区”。
2) 锌电解能耗与阴极板表面离子浓度场、电解液流场两者密切相关:电解液流速高的区域,锌离子浓度高而氢离子浓度低,对应的电流效率高,能耗低;反之,电解液流速低的区域,锌离子浓度低,而氢离子浓度高,对应的电流效率低。
3) 在“流动死区”锌离子浓度低,电流效率低,能耗高,易发生“反溶烧板”现象。对此可采取合理设置进液管的数量和位置,适当加大进液管电解液的流量等措施来优化电解液流场,降低电解能耗。
参考文献:
[1] 梅光贵, 王德润, 周敬元, 等. 湿法炼锌学[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2001: 340-409.
MEI Guanggui, WANG Derun, ZHOU Jingyuan, et al. Hydrometallurgy of zinc[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2001: 340-409.
[2] SEVENS K, KERSTIEN B, RUNKEL M. Recent experiences with modern zinc processing technology[J]. Erzmetall, 2003, 56(2): 91-103.
[3] HELEN H, ALI M, ATAALLAH S, et al. CFD modeling of the electrolyte flow in the copper electrorefining cell of Sarcheshmeh copper complex[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 139: 54-63.
[4] MAHJABIN NAJMINOORI, ALI MOHEBBI, BABAK GHADAMI ARABI, et al. CFD simulation of an industrial copper electrowining cell[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 153: 88-97.
[5] KAWAI S, MIYAZAWA T. CFD modelling and simulation of industrial-scale copper electrorefining process[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 63(4): 81-90.
[6] LEAHY M J, SCHWARZ M P. Flow and mass transfer modelling for copper electrowinning: development of instabilities along electrodes[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014, 147(8): 41-53.
[7] LEAHY M J, SCHWARZ M P. Modeling natural convection in copper electrorefining-describing turbulence behavior for industrial-sized systems[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2011, 42(B): 875-890.
[8] LEAHY M J, SCHWARZ M P. Experimental validation of a computational fluid dynamics model of copper electrowinning[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2010, 41(B): 1247-1260.
[9] KIM K R, CHOI S Y, PARK S, et al. Electrochemical hydrodynamics modeling approach for a copper electrowinning cell[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2013, 8(11): 12333-12347.
[10] 苏寅彪. 锌电解槽流场数值模拟及其优化[D]. 长沙: 中南大学能源科学与工程学院, 2012: 16-35.
SU Yinbiao. Numerical simulation and optimization for the flow field of the zinc electrowinning cell[D]. Changsha: Central South University. School of Energy Science and Engineering, 2012: 16-35.
[11] LI Haolan, HU Jie, ZHOU Ping, et al. Optimization of Operating conditions and structure parameters of zinc electrolytic cell based on numerical simulation for electrolyte flow[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(5): 1604-1609.
[12] SCHWARZ M P. Improving zinc processing using computational fluid dynamics modeling: successes and opportunities[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2012, 30(1): 12-18.
[13] ZHOU Ping, LI Dongmei, CHEN Zhou. Mass transfer process in replacement-column purification device in zinc hydrometallurgy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(8): 2660-2664.
[14] 阿伦.J.巴德, 拉里.R.福克纳. 电化学方法原理和应用[M]. 邰元华, 朱果逸, 董献堆, 等译. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005: 8-20.
Allen J Bard, Larry R Faulkner. Electrochemical methods fundamentals and applications[M]. SHAO Yuanhua, ZHU Guoyi, DONG Xiandui, et al, trans. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 8-20.
[15] 余国琮, 袁希钢. 化工计算传质学导论[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 2011: 33-56.
YU Guocong, YUAN Xigang. Introduction to computational mass transfer theory of chemical industry[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 2011: 33-56.
[16] 王刚, 安琳. COMSOL Multiphysics工程实践与理论仿真:多物理场数值分析技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2012: 67-150.
WANG Gang, AN Lin. COMSOL Multiphysics engineering practice and theoretical simulation: multiphysics numerical analysis technology[M]. Beijing: Electronics Industry Press, 2012: 67-150.
[17] BARTON G W, SCOTT A C. A validated mathematical model for a zinc electrowinning cell[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1992, 22(2): 104-115.
[18] MAHON M, WASIK L, ALFANTAZI A. Development and implementation of a zinc electrowining process simulation[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(8): 486-492.
[19] 邓仕钧, 阳春华, 李勇刚, 等. 锌电解全流程酸锌离子浓度在线预测模型[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(7): 2588-2594.
DENG Shijun, YANG Chunhua, LI Yonggang, et al. On-line prediction model for concentrations of zinc ion and sulfuric acid in zinc electrowining process[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2015, 66(7): 2588-2594.
[20] 李志杰, 邓欣, 阳春华, 等. 基于改进粒子群优化算法的锌电解过程模型研究[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2008, 16(6): 805-810.
LI Zhijie, DENG Xin, YANG Chunhua, et al. Parameters estimation of zinc electrowinning model based on improved PSO optimization[J]. Computer Measurement and Control, 2008, 16(6): 805-810.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2016-01-02;修回日期:2016-03-22
基金项目(Foundation item):国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)项目(2014AA041803);中南大学创新驱动计划项目(2015cx007);国家自然科学基金资助项目(61673400) (Project(2014AA041803) supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program) of China; Project(2015cx007) supported by the Innovation-driven Plan of Central South University; Project(61673400) supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:李勇刚,博士,教授,从事复杂工业过程建模、控制与优化研究;E-mail: liyonggang@csu.edu.cn