铝阳极氧化层的耐化学腐蚀性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2011年第7期
论文作者:W. BENSALAH M. FEKI M. WERY H.F. AYEDI
文章页码:1673 - 1679
关键词:铝;阳极氧化层;草酸-硫酸阳极化;溶解速率;阳极氧化膜生成比
Key words:aluminum; anodic oxide layer; oxalic acid?sulphuric anodization; dissolution rate; coating ratio
摘 要:将铝放入草酸-硫酸溶液中,在其表面形成耐化学腐蚀的阳极氧化层。生成的阳极氧化层的酸性溶解试验在38 ℃的35 mL/L 85%H3PO4+20 g/L CrO3溶液中按ASTM B 680-80标准进行。研究了硫酸浓度为160 g/L时,草酸浓度、溶液温度、阳极电流密度对溶解速率和阳极氧化膜生成比R的影响。结果发现,在低温(5 ℃)和高电流密度(3 A/dm2)的条件下,得到耐化学腐蚀性强、致密的氧化层。添加18 g/L草酸有利于阳极氧化层的形成。采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、原子力显微镜(AFM)和辉光发射光谱(GDOES)来分析阳极氧化层的形貌和组成。
Abstract:
Chemically resistant anodic oxide layers were formed on pure aluminum substrates in oxalic acid-sulphuric acid bath. Acid dissolution tests of the obtained anodic layers were achieved in accordance with the ASTM B 680-80 specifications: 35 mL/L 85% H3PO4+20 g/L CrO3 at 38 ℃. Influence of oxalic acid concentration, bath temperature and anodic current density on dissolution rate and coating ratio was examined, when the sulphuric acid concentration was maintained at 160 g/L. It was found that chemically resistant and compact oxide layers were produced under low operational temperature (5 ℃) and high current densities (3 A/dm2). A beneficial effect was observed concerning the addition of oxalic acid (18 g/L). The morphology and the composition of the anodic oxide layer were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM) and glow-discharge optical emission spectroscopy (GDOES).

W. BENSALAH1, M. FEKI1, M. WERY2, H. F. AYEDI1
1. Unité de recherche de Chimie Industrielle et Matériaux (URCIM), ENIS. B.P.W. Sfax, Tunisie;
2. IUT Mesures Physiques d’Orsay- Université Paris XI, Plateau du Moulon, 91400 ORSAY, France
Received 17 August 2010; accepted 8 October 2010
Abstract: Chemically resistant anodic oxide layers were formed on pure aluminum substrates in oxalic acid-sulphuric acid bath. Acid dissolution tests of the obtained anodic layers were achieved in accordance with the ASTM B 680-80 specifications: 35 mL/L 85% H3PO4+20 g/L CrO3 at 38 °C. Influence of oxalic acid concentration, bath temperature and anodic current density on dissolution rate and coating ratio was examined, when the sulphuric acid concentration was maintained at 160 g/L. It was found that chemically resistant and compact oxide layers were produced under low operational temperature (5 °C) and high current densities (3 A/dm2). A beneficial effect was observed concerning the addition of oxalic acid (18 g/L). The morphology and the composition of the anodic oxide layer were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM) and glow-discharge optical emission spectroscopy (GDOES).
Key words: aluminum; anodic oxide layer; oxalic acid-sulphuric anodization; dissolution rate; coating ratio
1 Introduction
As weight-saving materials, aluminum alloys are becoming increasingly important, especially in the automotive and aerospace industries. The substitution of aluminum for steel in the transport industry correlates to the benefits of energy-saving and environmental protection [1-2]. However, in many instances inadequate corrosion properties have greatly restricted the application of aluminum alloys. The corrosion resistance of aluminum alloys can be further improved when they are anodized.
By balancing the conditions used in the anodizing process [3], oxides can be produced with almost any desired properties, from thin oxides used in decorative applications to the extremely hard corrosion-resistant oxides used in engineering applications [4-7].
In fact, it was reported by SPOELSTRA et al [8-9] that anodizing reduced the filiform corrosion of aluminum. They demonstrated that the filiform corrosion was reduced considerably by increasing the porous layer thickness. REN and ZUO [10] reported that after anodizing, the pitting resistance of aluminum was improved remarkably. These works were focused on the anodizing treatment conditions and the composition of single acid electrolyte. But in recent years, the modified electrolytes, instead of single electrolytes, were implemented [11-12] to improve the anodic layer properties. In fact, some mixed acid and organic acid as anodizing electrolytes were developed, which can decrease the film dissolution rate, then increase the film formation efficiency and improve the film properties [13-14]. Previous study of LI et al [7] showed that working in a modified anodizing bath, an environmentally friendly coating method, produced a hard coating with corrosion protection of an Al-Si alloy. The most important mixed acid electrolytes treated in the literature were oxalic acid-chromic acid [15], nitric acid-sulphuric acid and boric acid–sulphuric acid [16-17].
This study is intended to systematically investigate the performance of an oxalic acid-sulphuric acid electrolyte on the chemical resistance of anodic oxide layers elaborated on aluminum compared with the conventional anodic film obtained in sulfuric acid. For a sulphuric acid concentration (ρsul) maintained at 160 g/L, the effect of anodizing conditions, namely, oxalic acid concentration (ρox), bath temperature (t) and current density (J) on dissolution rate (vd) and coating ratio (R) of the anodic oxide layers is investigated. Correlations between the two studied responses are, then, established. The morphology and the composition of the anodic oxide layer are examined by scanning electron microscope (SEM-FEG), atomic force microscope (AFM) and glow-discharge optical emission spectroscope (GDOES).
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and procedures
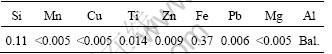
Al specimens with dimensions of 100 mm×25 mm×3 mm were used as substrate for anodic conversion treatment. The composition of Al is given in Table 1.
Table 1 Chemical composition of the used aluminium (mass fraction, %)
The substrates were mechanically ground to P1000 grade paper. Prior to anodizing, specimens were treated as follows: 1) chemical polishing in a 15:85 (volume ratio) mixture of concentrated HNO3 and H3PO4 at 85 °C for 2 min, 2) cold water rinsing, 3) etching in 1 mol/L NaOH solution at room temperature for 1 min, 4) cold water rinsing, 5) chemical pickling in 30% (volume ratio) HNO3 solution at room temperature for 30 s, and 6) deionised water rinsing and drying. Afterwards, those specimens with an exposed area of 85 mm×25 mm were anodized in vigorously stirred oxalic acid-sulphuric acid electrolyte maintained within ±0.1 °C of the set temperature for 90 min, and then washed in deionised water and dried.
Anodizing parameters were varied from 1 to 3 A/dm2 for the current density, from 5 to 25 °C for the temperature and from 0 to 18 g/L for the oxalic acid concentration.
The used cathodes were also aluminum sheets, with larger size than the specimens. Sulphuric, nitric, oxalic and phosphoric acids were analytical grade chemicals.
2.2 Testing methods
2.2.1 Thickness measurement
Thickness of the anodic oxide layer was measured using ELCOMETER 355 Top Thickness Gauge equipped with eddy current probe. The average thickness of 10 measuring points evenly distributed on both sides was taken.
2.2.2 Acid dissolution testing
Acid dissolution tests of the anodized samples were achieved in accordance with the ASTM B 680-80 specifications: 35 mL/L 85%H3PO4+20 g/L CrO3 at 38 °C [18]. The mass loss of the anodic oxide was recorded versus immersion time until the total layer dissolution.
When the oxide layer dissolution was achieved, the sample was weighed in order to calculate the coating ratio, R, i.e., the coulombic efficiency for the formation of porous oxide layer on aluminium. R is equal to the ratio of the mass of the formed oxide to the total mass of aluminium consumed [19-20].
2.2.3 Surface characterization
AFM, performed using model Digital instrument-Nanoscope probe II (contact mode), was used to examine and to determine the surface topography of the anodized surfaces. The morphology of the oxide layer was studied from the top side of the layer using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Jeol JSM-6400F).
2.2.4 Glow-discharge optical emission spectroscopy (GDOES)
The distribution of Al, O, S and C species in the anodic oxide layer was determined by depth profiling using a Jobin Yvon GD Profiler instrument equipped with a 4 mm-diameter anode and operated at pressure of 800 Pa and power of 600 W in an argon atmosphere. The relevant wave-lengths were as follows: Al, 396.15 nm; O, 130.22 nm; S, 181.73 nm and C, 156.14 nm. The sputtering layer was 6 ?m thick.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Evolution of mass loss of anodic oxide versus immersion time
Figure 1 shows a general evolution of the mass loss versus immersion time. As can be seen, the mass loss increases linearly with increasing the immersion time up to a critical value.
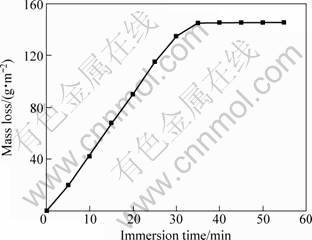
Fig. 1 Typical mass loss vs immersion time for anodized specimen elaborated under conditions: ρox=10 g/L, t=5 °C, J=2.5 A/dm2 and ρsul=160 g/L
After that, no increase of the mass loss was observed, indicating that the oxide layer was completely dissolved. The slope of the linear part represents the value of the dissolution rate (per surface unit), vd. Here vd=4.12 g/(m2?min). It is worth noting that all slopes were taken with a determination coefficient R2 equal to 0.99.
3.2 Effect of various parameters on dissolution rate of anodic oxide layer
Figure 2(a) presents the relationship between the dissolution rate vd of the anodic oxide layers and the current density (J) at two temperatures. At t=20 °C, vd increases with increasing J while it decreases with increasing J at t=5 °C. In Fig. 2(b), vd is plotted against temperature for two current densities. As can be seen, the same behaviour is observed for both current densities. In fact, rising t and J simultaneously leads to less chemical resistant layers. From Figs.2(a) and (b), it can be concluded that low vd values (high chemical resistance) are obtained at high current densities and low temperatures. With regard to the obtained results, t and J are the most important factors influencing the chemical resistance of the anodic oxide layer. They act synergically, then the augmentation of theses two factors simultaneously conducts to high dissolution at the oxide/electrolyte interface [16]. The increase of current density provokes high dissolution rate of the oxide in the bottom of pores and favours, thus, the layer growth [16]. But rising temperature in the same time will act negatively and the dissolution at the interface of oxide/electrolyte, from top of pores and pore-walls, will be accentuated. As a result, the produced layers are with large pore diameters, low density and less resistant to chemical dissolution.
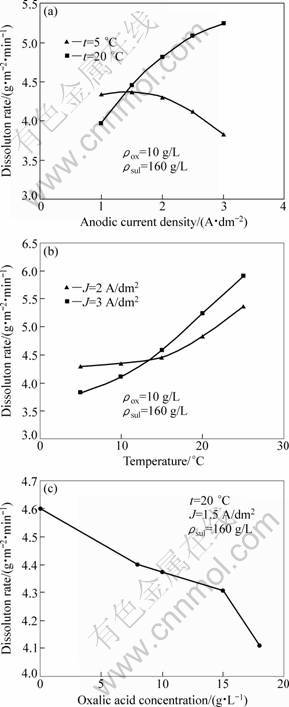
Fig. 2 Relationship between dissolution rate of anodic oxide layer and current density (a), temperature and oxalic acid concentration (c)
Figure 2(c) shows the relationship between dissolution rate and oxalic acid concentration. As can be seen, the addition of oxalic acid improves the chemical resistance of anodic oxide layers.
Figure 3 shows the scanning electron microscopy images (SEM) of anodic oxide layers elaborated under high temperature (t=28 °C) and current density (J=2 A/dm2) with oxalic acid additions of 14 g/L (Fig. 3(a)) and 18 g/L (Fig. 3(b)). Both reveal nanopores distributed macroscopically in a random fashion. Their distribution on the surface is homogeneous and does not show the feature of self organized hexagonal pore array due to the random pore nucleation which is in accordance with previous works [21]. Furthermore, it seems that, the higher the oxalic acid concentration, the more compact the layer.
On the other hand, Fig. 4 shows that oxalic acid addition improves anodic film growth. In fact, the addition of oxalic acid (weak acid) to sulphuric acid (strong acid) decreases the acidity of the electrolyte which favours the oxide layer growth and minimizes the dissolution reactions at the interface of oxide/electrolyte [15]. Metal dissolution is accompanied by the emission of Al into the solution without the formation of oxide. The Al dissolution process has complicated character, representing a combination of chemical dissolution of Al and dissolution assisted by electric field [16]. In addition to the field assisted dissolution, the formed oxide films dissolve chemically on the outer surface and pore walls during anodizing, since they are exposed to strong acid solutions. Accordingly, prolonged anodizing damages the porous structure of oxide films. The oxalate species present in the outer part of oxide film may increase the resistance to the dissolution by sulphuric acid during anodizing, though the amount is not large at a later stage of anodizing.
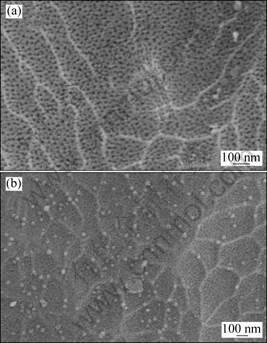
Fig. 3 SEM images of anodized surface obtained under conditions: (a) ρox=14 g/L, t=28 °C, J=2 A/dm2, ρsul=160 g/L; (b) ρox=18 g/L, t=28 °C, J=2 A/dm2, ρsul=160 g/L
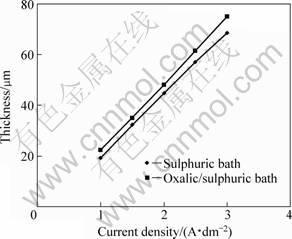
Fig. 4 Oxide layer thickness vs current density: Sulphuric bath, t=20 °C and ρsul=160 g/L; oxalic/sulphuric bath, ρox=10 g/L, t=20 °C and ρsul=160 g/L
In order to identify the effect of oxalic acid addition on the morphological aspect of the oxide layer, three typical 3-dimensional AFM images of anodized samples in sulphuric and oxalic/sulphuric acid were depicted (Fig. 5). As can be seen, the topography of the oxide layer seems to be dependant on the elaboration conditions and on the aggressiveness of acidic electrolytes [22].
3.3 Effect of various parameters on coating ratio of anodic oxide layer
It is worth noting that the coating ratio R gives information on the porosity of the oxide and is usually used as indicator of the conversion efficiency of metal into oxide. According to YOUNG’s result [19], when the total transformation of metal into oxide occurs, R is equal to 1.89. Generally, R is lower than 1.89, and this fact is indicative of the existence of an incomplete conversion of metal to oxide.
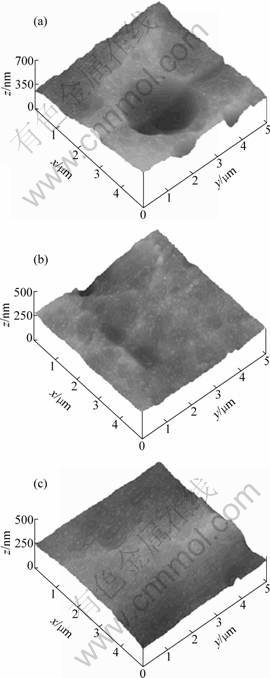
Fig. 5 AFM images of anodized surfaces obtained under conditions of t=25 °C, J=2 A/dm2: (a) ρsul=160 g/L; (b) ρox=10 g/L; (c) ρox=14 g/L
Figure 6(a) shows the relationship between the coating ratio and the current density at various temperatures. As can be seen, compact layers are obtained with high current densities and low temperatures. Thus, it may be noted that Al dissolution reaction is more favorable than oxide formation with lower J and higher t.
The addition of oxalic acid leads to oxide layers with higher compactness (Fig. 6(c)). However, anodic layers appear more compact when they are formed in oxalic acid [15]. In fact, some authors relate the steady state anodizing behaviour of porous films formed in the major anodizing acids to the distribution of anions within the anodic oxide which influences the anodic layer compactness [23].
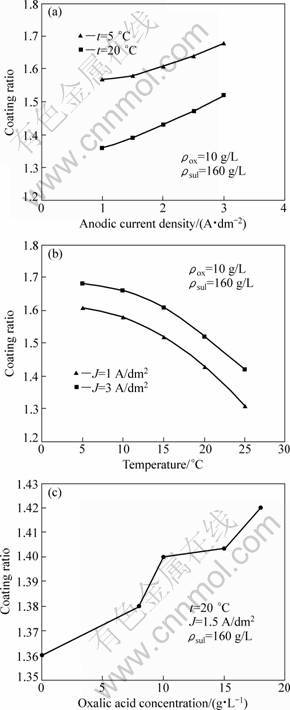
Fig. 6 Relationship between coating ratio of anodic oxide layer and current density (a), temperature (b) and oxalic acid concentration (c)
In order to identify possible acid anion incorporations, it was judicious to conduct a chemical analysis of the oxide layer. In previous works [24], we have investigated the anodic layers formed in sulphuric acid bath using GDOES technique. SO42- anion incorporation was clearly shown.
Figure 7(a) shows a depth profile of the oxide layer. The distributions of Al, O, S and C species are revealed clearly. The signal intensity of aluminium is highly stable throughout the GDOES analysis, indicating that film sputtering proceeds uniformly. Turning to the sulphur and carbon profiles, the inward migration of SO42- and (COO-)2 anions is clearly shown. The partial magnification of S and C profiles superimposed to those of anodic oxide layer elaborated in sulphuric acid bath (Fig. 7(b)) shows a relatively narrow peak located at the inner interface of metal/oxide, suggests an accumulation of SO42- ions (inner interface) and C to be uniform along the oxalic/sulphuric oxide layer and absent in the sulphuric one. In agreement with our results, other authors reported that the contamination of the anodic oxide by anions present in the anodizing bath increases in the following acid sequence [25-27]: chromic< oxalic
It seems that the presence of oxalic acid leads to high incorporation of sulphate ions into the oxide structure during anodizing.

Fig. 7 GDOES profiles of anodized surface obtained under conditions of ρox=18 g/L, t=16.5 °C, J=2 A/dm2, ρsul=160 g/L: (a) Distribution of Al, O, C and S; (b) Partial magnification of (a)
3.4 Correlation between dissolution rate and coating ratio responses
From the overall obtained results, the dissolution rate and the coating ratio seem to have a similar behaviour to the anodizing conditions. Figure 8(a) represents the variation of the dissolution rate as a function of the coating ratio at temperatures of 5 and 20 °C. At each temperature the corresponding response was depicted according to the following current densities: 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5 and 3 A/dm2. Equally, Figure 8(b) shows the variation of the latest responses for current densities of 2 and 3 A/dm2, and varying the temperature as follows: 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 °C. As can be seen, the dissolution rate and the coating ratio seem to be highly correlated. In fact, according to the formation mechanism of porous anodic oxide film and GDOES, certain amounts of foreign species present on the surface are incorporated into the oxide film. Furthermore, it may be possible that a small proportion of oxalates species are included into the oxide film during the very initial stage in which a very high electric field is generated in the thin surface layer. It is also probable that the dissolved oxalates species present near the surface are incorporated together with electrolyte anions (sulphate ions). Accordingly, oxide layers with higher compactness are produced, which suggests the obtaining of chemically resistant oxide layers [28].
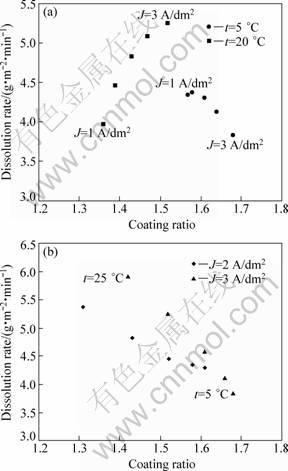
Fig. 8 Dissolution rate vs coating ratio under conditions of ρox=10 g/L and ρsul=160 g/L: (a) J=1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3 A/dm2 at t=5, 20 °C; (b) t=5, 10, 15, 20, 25 °C at J=1, 3 A/dm2
4 Conclusions
1) It was found that chemically resistant and compact oxide layers were produced under low operational temperatures (5 °C) and high current densities (3 A/dm2). A beneficial effect was observed concerning the addition of oxalic acid (18 g/L).
2) Possible correlations between dissolution rate and coating ratio of the anodic oxide layers was proposed.
3) SEM and AFM characterizations revealed the nano-porous structure of top surface of the anodic oxide layers. The distributions of Al, O, S and C in the depth of the oxide layer were shown using GDOES technique. The presence of sulphur and carbon species suggested the migration of sulphate and oxalate anions inward in the thickening film.
4) The chemical resistance of oxide layers can be correlated to their morphologies revealed by AFM, SEM observations and their chemical composition determined by GDOES.
References
[1] BAUMEISTER J, BANHART J, WEBER M. Aluminium foams for transport industry [J]. Materials and Design, 1997,18: 217-220.
[2] MEZLINI S, ELLEUCH K, KAPSA P H. The effect of sulphuric anodization of aluminium alloys on contact problems [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 201: 7855-7864.
[3] WERNICK S, PINNER R, SHEASBY P. The surface treatment of aluminum and its alloys [M]. 5th ed. UK: Finishing Publication Ltd, 1987.
[4] CHOO Y H, DEVEREUX O F. Mechanical failure of anodic films on aluminium and tantalum [J]. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 1976, 123: 1868-1876.
[5] MAEJIMA M, SARUWATARI K, ISAWA K. Abrasion resistance of anodized coatings on aluminium alloys tested with an abrasive metal wheel wear tester [J]. Metal Finishing, 1998, 10: 36-41.
[6] ELLEUCH K, FOUVRY S, KAPSA P H. Fretting maps for anodized aluminium alloys [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2003, 426: 271-280.
[7] LI X, NIE X, WANG L, NORTHWOOD D O. Corrosion protection properties of anodic oxide coatings on Al-Si alloy [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2005, 200: 1994-2000.
[8] SPOELSTRA M B, BOSCH A J, van der WEIJDE D H, de WIT J H W. Anodizing as pretreatment of durable aluminium: The behaviour of several aluminium alloys to filiform corrosion [J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2000, 51: 155-160.
[9] SPOELSTRA M B, van WESTING E P M, de WIT J H W. Characterisation of unsealed anodic oxide layers on aluminium [J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2001, 52: 661-666.
[10] REN J, ZUO Y. Study of electrochemical behaviour and morphology of pitting on anodized 2024 aluminum alloy [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2004, 182: 237-241.
[11] MOUTARLIER V, GIGANDET M P, NORMAND B, PAGETTI J. EIS characterisation of anodic films formed on 2024 aluminium alloy, in sulphuric acid containing molybdate or permanganate species [J]. Corrosion Science, 2005, 47: 937-951.
[12] MOUTARLIER V, GIGANDET M P, PAGETTI J, RICQ L. Molybdate/sulphuric acid anodizing of 2024 aluminium alloy: Influence of inhibitor concentration on film growth and corrosion resistance [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2003, 173: 87-95.
[13] PAEZ M A, ZAGAL J H, BUSTOS O. Effect of benzotriazole on the efficiency of anodizing of Al-Cu alloys [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1997, 42: 3453-3459.
[14] TAKENAKA T, HABAZAKI H, KONNO H. Formation of black anodic films on aluminum in acid electrolytes containing titanium complex anion [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2003, 169-170: 155-159.
[15] MOUTARLIER V, GIGANDET M P, PAGETTI J, NORMAND B. Influence of oxalic acid addition to chromic acid on the anodizing of Al 2024 alloy [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2004, 182: 117-123.
[16] SHIH H H, TZOU S L. Study of anodic oxidation of aluminium in mixed acid using a pulsed current [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2000, 124: 278-285.
[17] DOMINGUES L, FERNANDES J C S, BELO M D C, FERREIRA M G S, ROSA L G. Anodizing of Al2024-T3 in a modified sulphuric acid/Boric acid bath for aeronautical applications [J]. Corrosion Science, 2003, 45: 149-160.
[18] HAO L, CHENG B R. Sealing processes of anodic coatings—Past, present, and future [J]. Metal Finishing, 2000, 12: 8-17.
[19] YOUNG L. Anodic oxide films [M]. London: Academic Press, 1961.
[20] TAJIMA S, BABA N, MORI T. Properties and mechanism of formation of thick anodic oxide films on aluminium from the non-aqueous sustem boric-acid-formamide [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1964, 9: 1059-1519.
[21] CHENG S Y, SANIGER J M. Characterization of anodic porous alumina by AFM [J]. Materials Letters, 2001, 48: 127-136.
[22] FURNEAUX R C, RIGBY W R, DAVIDSON A P. The formation of controlled-porosity membranes from anodically oxidized aluminium [J]. Nature, 1989, 337: 147-149.
[23] Thompson G E, Wood G C. Porous anodic film formation on aluminium [J]. Nature, 1981, 290: 230-232.
[24] BENSALAH W, ELLEUCH K, FEKI M, WERY M, GIGANDET M P, AYEDI H F. Optimization of mechanical and chemical properties of sulphuric anodized aluminium using statistical experimental methods [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2008, 108: 296-305.
[25] THOMPSON G E, FURNEAUX R C, WOOD G C, RICHARDSON J A, GOODE J S. Nucleation and growth of porous anodic films on aluminium [J]. Nature, 1978, 272: 433-435.
[26] SHIMIZU K, HABAZAKI H, SKELDON P, THOMPSON G E, WOOD G C. Migration of sulphate ions in anodic alumina [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2000, 45: 1805-1809.
[27] SHIMIZU K, HABAZAKI H, SKELDON P, THOMPSON G E, WOOD G C. Migration of oxalate ions in anodic alumina [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2001, 46: 4379-4382.
[28] KONNO H, UTAKA K, FURUICHI R. A two step anodizing process of aluminum as means for improving the chemical and physical properties of oxide films [J]. Corrosion Science, 1996, 38: 2247-2256.
W. BENSALAH1, M. FEKI1, M. WERY2, H.F. AYEDI1
1. Unité de recherche de Chimie Industrielle et Matériaux (URCIM), ENIS. B.P.W. Sfax, Tunisie;
2. IUT Mesures Physiques d’Orsay- Université Paris XI, Plateau du Moulon, 91400 ORSAY, France
摘 要:将铝放入草酸-硫酸溶液中,在其表面形成耐化学腐蚀的阳极氧化层。生成的阳极氧化层的酸性溶解试验在38 °C的35 mL/L 85%H3PO4+20 g/L CrO3溶液中按ASTM B 680-80标准进行。研究了硫酸浓度为160 g/L时,草酸浓度、溶液温度、阳极电流密度对溶解速率和阳极氧化膜生成比R的影响。结果发现,在低温(5 °C)和高电流密度(3 A/dm2)的条件下,得到耐化学腐蚀性强、致密的氧化层。添加18 g/L草酸有利于阳极氧化层的形成。采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、原子力显微镜(AFM)和辉光发射光谱(GDOES)来分析阳极氧化层的形貌和组成。
关键词:铝;阳极氧化层;草酸-硫酸阳极化;溶解速率;阳极氧化膜生成比
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Corresponding author: W. BENSALAH; E-mail: walbensalah@yahoo.fr
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60913-8

