
ARTICLE
J. Cent. South Univ. (2019) 26: 404-409
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4012-z
Preliminary assessment of revegetation potential through ryegrass growing on bauxite residue
LYU Fei(吕斐)1, 2, SUN Ning(孙宁)1, 2, SUN Wei(孙伟)1, 2,Sultan Ahmed KHOSO1, 2, TANG Hong-hu(唐鸿鹄)1, 2, WANG Li(王丽)1, 2
1. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Hunan Province for Clean and Efficient Utilization of Strategic Calcium-Containing Mineral Resources, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2019
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2019
Abstract: Bauxite residue (BR), a by-product of the industrial production of alumina, has raised environmental concerns in the last decades, due to the presence of high amounts of alkali and various heavy metal ions. Limited studies on the application of abandoned BR with massive consumption have been reported. In this study, the possibility of the revegetation using ryegrass growing on BR was discussed mainly through the growth indications and transfer of heavy metal ions in BR and plants. In the pot trails, ryegrass was seeded on BR, de-alkali BR, with (DBRO) or without (DBR) organic fertilizer, respectively. The results indicated that the remediation of bauxite residue can be achieved through de-alkali with acid neutralization. Elemental analysis indicated that the elements, except for Fe, Mn and Pb, were stable in plant roots, and ryegrass could hardly absorb Cd. But, some heavy metals such as Cu enriched in plants, which should be noted in revegetation on bauxite residue.
Key words: bauxite residue; revegetation; bioconcentration factor; translocation factor
Cite this article as: LYU Fei, SUN Ning, SUN Wei, Sultan Ahmed KHOSO, TANG Hong-hu, WANG Li. Preliminary assessment of revegetation potential through ryegrass growing on bauxite residue [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(2): 404–409. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4012-z.
1 Introduction
Bauxite residue (BR) is a harmful solid waste generated from alumina-refining industries [1–4]. In the Bayer process, 0.5–2 t of BR would be generated for every ton of alumina produced [5]. The global inventory of BR had exceeded 4 billion tons in 2015 [6], and is growing at a rate of approximately 150 million tons per year [7]. As there are abundant bauxite resources [8], China has been a major producer of alumina and BR. When improperly managed, BR poses significant concerns to surrounding environments and becomes a potential hazard to surface and ground water quality due to its high alkalinity and toxic metal content [9–12].
As the amounts of solid wastes, such as fly ash, BR, sludge, and other mine wastes, continually increase, heavy metal pollution, damaging the ecosystem, has also become a major concern in the society [13–16]. The accumulation of BR can cause dust, air, and water pollution, creating a harmful environment for humans and livestock [13, 17].Therefore, studies should focus on repairing abandoned lands to allow substrate fertility and slow down global warming through reclamation [13, 18–21]. However, considering its very fine particle size distribution at 2–2000 μm [22], BR features a high bulk density and low water permeability and porosity [23, 24]. What is more, BR is a strong saline residue with high conductivity, exchangeable sodium content, and cation exchange capacity [9, 22, 25]. Especially, the heavy metal pollution caused by massively discharged BR not only adversely affects soil microbes and plant growth due to its inauspicious substrate chemistry [26], but also poses a risk of heavy metal element enrichment in plants grown on it, which ultimately threatens human health.
Prior to the study, several plant species, such as Vetiver and Saccharum bengalense Retz., were tested at abandoned BR deposit sites to restore vegetation in the area [13, 22, 27]. Ryegrass is a gramineous plant, prefers warm and moist soil, suitable for soil pH 6–7. It has strong regeneration ability and short growth period at 12–27 °C, which can be used to improve soil organic matter content. Previous studies have shown that it has strong adaptability to bauxite residue pH and is suitable for planting on de-alkali bauxite residue. This work evaluated the possibility of revegetation using ryegrass growing on BR mainly through the growth indications and transfer of heavy metal ions in BR and plants.
2 Material and methods
2.1 Description of samples
The BR samples used in this study were obtained from Shandong, China. All samples were air dried naturally before use. Prior to pot trials, a subsample of the BR was pretreated with acid neutralization, where the pH was lowered to the region of 6–7. As a result, the de-alkali bauxite residue was obtained. The pot trials were conducted for both the bauxite residue and de-alkali bauxite residue. When preparing the pot trails, 500 g of the de-alkali bauxite residue samples with or without 8% organic fertilizer were placed in free-draining plastic pots with diameter of 13 cm and height of 9 cm, and marked as DBRO and DBR, respectively. Then, they were well watered before 50 full ryegrass seeds soaked with 50 mg/L gibberellin were sown in each pot of bauxite residue samples. The ryegrass was planted in untreated bauxite residue for comparison. The ryegrass was grown for 40 d in a PRX-450C intelligent incubator (Ningbo Safe Experimental Instrument Co., Ltd, Ningbo, China) with a day temperature of 25 °C and a night temperature of 20 °C.
2.2 Samples collection, preparation and analysis
BR samples were collected from the root area of ryegrass. Dried homogeneous BR samples were sieved with a 2 mm stainless steel mesh for the analysis of chemical parameters and elements. pH and electrical conductivity (EC) of the samples were measured using a PHS-3C pH meter (Shanghai Electronics Science Instrument Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China) and a DDS-307A conductivity meter (Shanghai Electronics Science Instrument Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China), respectively. Indices of soil bulk density and soil density were also measured. The test process was independently performed thrice, and the results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation.
Potted ryegrass was harvested for subsequent processing. The roots, stems, and leaves of ryegrass were separately collected and carefully washed with deionized water to remove the adhering soil particles. The washed plant samples were dried to a constant weight at 105 °C. The dried plant samples were cut, and 0.1 g of plant was digested with 5 mL of 65% HNO3 and 1 mL of 30% H2O2 at 220 °C for 1 h. The concentrations of different elements were then analyzed through inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES, SPECTRO Analytical Instruments GmbH, Germany).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Performance of pot trails
Ryegrass grown on BR failed to germinate. Figure 1 shows the growth of ryegrass in DBR and DBRO. Table 1 shows the growth indicators of ryegrass and physicochemical properties of original BR, BR conducted with pot trials, DBR, and DBRO. The BR was strongly alkaline, which mainly caused the absence of seed growth on BR through germination, whereas DBR was non-alkaline, which is suitable for most plants to grow. The pH of BR conducted with pot trials is lower than that of original BR, consistent with the results of previous studies [28]. The difference in pH and EC between original BR and BR conducted with pot trials may be due to the ion loss in BR after long-term placement and watering. However, the EC difference between DBR and DBRO may be due to the addition of organic fertilizer. Long-term stacking caused few effects on the density of BR, whereas de-alkali increased the density of BR, mainly because alkali removal changes the mineral species in BR, thus increasing density.

Figure 1 Ryegrass grown on DBR (a) and DBRO (b)
Table 1 Growth indications of ryegrass and physicochemical properties of original BR, BR conducted with pot trials, DBR, and DBRO
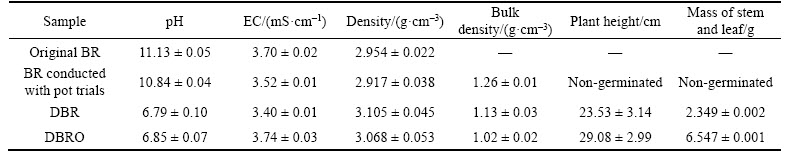
Soil bulk density significantly affects water infiltration, which refers to the process of water flow throughout or on certain parts of the surface, moving and storing soil and forming soil water [29]. Numerous studies have been carried out to support that infiltration rate at the same texture soil will decrease with increasing bulk density [30, 31]. As expected, the bulk density of DBRO was lower than that of DBR and the ryegrass grown on DBRO exhibited better growth indications. This finding may be caused by the addition of organic fertilizer, which provided more nutrients for ryegrass growth.
3.2 Elemental analysis of plant parts and substrate
Figure 2 shows the concentration of heavy metals in plant tissues (root, stem, and leaf) and corresponding BR. The concentrations of Fe in DBR and DBRO were considerably higher than those of other heavy metals. The concentration of metal ions in plants grown on DBR and DBRO varied in size, but their proportions were approximately the same.
In comparison with the contents of Zn, Cd, and Cu, the contents of Mn and Cr in DBR and DBRO samples were higher. This finding is caused by the ability of certain plants to hold specific elements in soil [32]. Iron, which is involved in the redox process of plants, is an essential element in chlorophyll synthesis and is essential for plant growth [33]. The iron contents in ryegrass roots grown on DBR and DBRO were 1.13 and 1.08 μg/g, respectively, which were much lower than those in the corresponding stems and leaves. These findings indicate that the growth of ryegrass on BR after de-alkali can extract sufficient Fe from the soil through the roots.
In comparison with other heavy metals, the accumulation of Cd and Pb in plant roots was pretty low. Exactly, Cd is rarely found in plants, and ryegrass contains low levels of Pd. As Cd and Zn belong to the same group in the periodic table, the chemical properties of Zn were similar to those of Cd, hence enriched Zn subsequently inhibited the root absorption of Cd. Although plants treated with organic fertilizer flourished more than the untreated plants, the latter absorbed more metals in heavy metal treatment, and the remaining metal ions in DBR were relatively less.
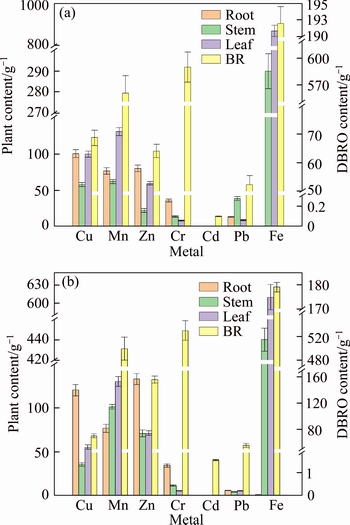
Figure 2 Concentration of heavy metals in plant tissues (root, stem, and leaf) growing on BR (a) and DBRO (b)
3.3 Bioconcentration factor (BCF) and translocation factor (TF)
The value of BCF represents the ability of plants to accumulate elements from the matrix [34].BCF was determined as the following equation: BCF=metal in plant parts (such as root, stem, and leaf)/metal in substrate [35]. Whereas, TF was determined as the following equation: element in plant stem/element in plant root, which is an important indicator for evaluating the potential of phytoremediation. TF indicates whether the element can be effectively transferred from roots to buds [36, 37]. According to previous literatures, BCF>1 indicates that plants can effectively accumulate elements from the matrix [38], whereas TF>1 indicates that elements can be efficiently transferred from roots to shoots [35].
Figure 3 shows the BCF in the roots, stems, and leaves as well as the TF of ryegrass grown on DBR and DBRO. The red and blue dotted lines in Figure 3 are the reference of BCF=1 and TF=1, respectively. Figure 3(a) shows that the BCF of Cu, Zn, and Cd in the roots and that of Cu in the leaves exceeded 1. However, only the BCF of Cu in the root exceeded 1 in Figure 3(b). These findings indicate that plants grown on DBR feature a stronger ability to accumulate heavy metals than those grown on DBRO. These results may also be attributed to the addition of organic fertilizer, which provides sufficient nutrients for plants, resulting in fewer components directly obtained from bauxite residue. As comparison, all the nutrients needed for plant growth on BR can only be obtained from the bauxite residue. This analysis agrees with the conclusions in Section 3.2, where the plants without organic fertilizer absorb more heavy metals. In addition, only the TF of Pd (except Fe) exceeded 1 Figure 3(a) and only that of Mn (except Fe) in Figure 3(b) exceeded 1, inferring effective transfer into leaf part. Whereas other metals were largely retained into root parts. Fe is not considered because it is an essential element for plant metabolism.
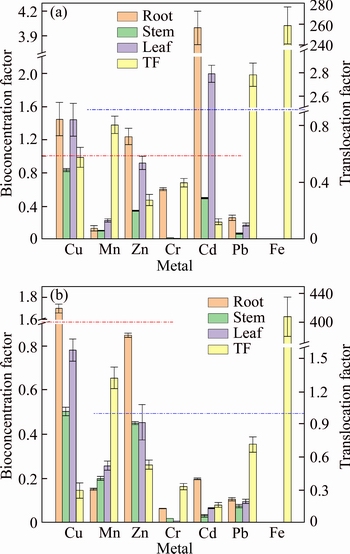
Figure 3 BCF in roots, stems, and leaves and TF of ryegrass grown on DBR (a) and DBRO (b)
4 Conclusions
This study was conducted to determine the possibility of revegetation through ryegrass growing on bauxite residue and transfer of heavy metal ions in bauxite residue and plant tissue. The pot trails indicated that the remediation of bauxite residue can be achieved through de-alkali with acid neutralization. Ryegrass could grow on de-alkali bauxite residue and with a well growth status treated by organic fertilizer; but no ryegrass germinated on original bauxite residue. The elemental analysis results show that, whether with or without organic fertilizer treatment, the elements, except for Fe, Mn and Pb, were stable in plant roots and ryegrass could hardly absorb Cd. But, some heavy metals such as copper enriched in plants, which require attention in revegetation on bauxite residue. Moreover, the addition of organic fertilizer enhanced the growth of ryegrass, but its phytoremediation ability was lower than that without organic fertilizer.
References
[1] KONG Xiang-feng, GUO Ying, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, WU Chuan, YE Yu-zhen, CHENG Qing-yu. Natural evolution of alkaline characteristics in bauxite residue [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 143: 224–230.
[2] XUE Sheng-guo, KONG Xiang-feng, ZHU Feng, HARTLEY W, LI Xiao-fei, LI Yi-wei. Proposal for management and alkalinity transformation of bauxite residue in China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(13): 12822–12834.
[3] KONG Xiang-feng, LI Meng, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, CHEN Cheng-rong, WU Chuan, LI Xiao-fei, LI Yi-wei. Acid transformation of bauxite residue: Conversion of its alkaline characteristics [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 324: 382–390.
[4] ZHU Feng, CHENG Qing-yu, XUE Sheng-guo, LI Chu-xuan, HARTLEY W, WU Chuan, TIAN Tao. Influence of natural regeneration on fractal features of residue microaggregates in bauxite residue disposal areas [J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2018, 29(1): 138–149.
[5] KONG Xiang-feng, JIANG Xing-xing, XUE Sheng-guo, HUANG Ling, HARTLEY W, WU Chuan, LI Xiao-fei. Migration and distribution of saline ions in bauxite residue during water leaching [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 534–541.
[6] XUE Sheng-guo, LI Meng, JIANG Jun, MILLAR G J, LI Chu-xuan, KONG Xiang-feng. Phosphogypsum stabilization of bauxite residue: Conversion of its alkaline characteristics [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 77: 1–10.
[7] LIAO Jia-xin, JIANG Jun, XUE Sheng-guo, CHENG Qing-yu, WU Hao, MANIKANDAN R, HARTLEY W, HUANG Long-bin. A novel acid-producing fungus isolated from bauxite residue: The potential to reduce the alkalinity [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2018, 35(10): 840–847.
[8] LYU Fei, GAO Jian-de, SUN Ning, LIU Run-qing, SUN Xiao-dong, CAO Xue-feng, WANG Li, SUN Wei. Utilisation of propyl gallate as a novel selective collector for diaspore flotation [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 131: 66–72.
[9] XUE Sheng-guo, ZHU Feng, KONG Xiang-feng, WU Chuan, HUANG Ling, HUANG Nan, HARTLEY W. A review of the characterization and revegetation of bauxite residues (Red mud) [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(2): 1120–1132.
[10] MISHRA T, SINGH N B, SINGH N. Restoration of red mud deposits by naturally growing vegetation [J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2017, 19(5): 439–445.
[11] ALSHAAL T, DOMOKOS-SZABOLCSY E, MARTON L, CZAKO M, KATAI J, BALOGH P, ELHAWAT N, EL-RAMADY M, FARI M. Phytoremediation of bauxite- derived red mud by giant reed [J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2013, 11(3): 295–302.
[12] ZHU Feng, LIAO Jia-xin, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, ZOU Qi, WU Hao. Evaluation of aggregate microstructures following natural regeneration in bauxite residue as characterized by synchrotron-based X-ray micro- computed tomography [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 573: 155–163.
[13] MISHRA T, PANDEY V C, SINGH P, SINGH N B, SINGH N. Assessment of phytoremediation potential of native grass species growing on red mud deposits [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 182: 206–209.
[14] ZHANG Ye, HU Yue-hua, SUN Ning, LIU Run-qing, WANG Zhen, WANG Li, SUN Wei. Systematic review of feldspar beneficiation and its comprehensive application [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 128: 141–152.
[15] SUN Wei, JI Bin, KHOSO S A, TANG Hong-hu, LIU Run-qing, WANG Li, HU Yue-hua. An extensive review on restoration technologies for mining tailings [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(34): 33911–33925.
[16] XUE Sheng-guo, WU Yu-jun, LI Yi-wei, KONG Xiang-feng, ZHU Feng, WILLIAM H, LI Xiao-fei, YE Yu-zhen. Industrial wastes applications for alkalinity regulation in bauxite residue: A comprehensive review [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(2): 268–288.
[17] ZHU Feng, HOU Jing-tao, XUE Sheng-guo, WU Chuan, WANG Qiong-li, HARTLEY W. Vermicompost and gypsum amendments improve aggregate formation in bauxite residue: Bauxite residue, gypsum, vermicompost, soil formation [J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2017, 28(7): 2109–2120.
[18] WANG Li, JI Bin, HU Yue-hua, LIU Run-qing, SUN Wei. A review on in situ phytoremediation of mine tailings [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 184: 594–600.
[19] VERMA S K, SINGH K, GUPTA A K, PANDEY V C, TRIVEDI P, VERMA R K, PATRA D D. Aromatic grasses for phytomanagement of coal fly ash hazards [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2014, 73: 425–428.
[20] ZHU Feng, LI Yu-bing, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, WU Hao. Effects of iron-aluminium oxides and organic carbon on aggregate stability of bauxite residues [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(9): 9073–9081.
[21] WANG Li, SUN Ning, WANG Zhen, HAN Hai-sheng, YANG Yue, LIU Kun-qing, HU Yue-hua, TANG Hong-hu, SUN Wei. Self-assembly of mixed dodecylamine-dodecanol molecules at the air/water inter face bayed on large-scale molecular dynamics [J]. Journal of Molecular liquids, 2019, 276: 867–874.
[22] GAUTAM M, AGRAWAL M. Phytoremediation of metals using vetiver (Chrysopogon zizanioides (L.) Roberty) grown under different levels of red mud in sludge amended soil [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017: 182–218, 227.
[23] JONES B E H, HAYNES R J. Bauxite processing residue: A critical review of its formation, properties, storage, and revegetation [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 41(3): 271–315.
[24] XUE Sheng-guo, YE Yu-zhen, ZHU Feng, WANG Qiong-li, JIANG Jun, HARTLEY W. Changes in distribution and microstructure of bauxite residue aggregates following amendments addition [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 78: 276–286. DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.10.010.
[25] KONG Xiang-feng, TIAN Tao, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, HUANG Long-bin, WU Chuan, LI Chu-xuan. Development of alkaline electrochemical characteristics demonstrates soil formation in bauxite residue undergoing natural rehabilitation [J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2018, 29(1): 58–67.
[26] PANDEY V C, SINGH B. Rehabilitation of coal fly ash basins: Current need to use ecological engineering [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2012, 49(12): 190–192.
[27] GUPTA A K, SINHA S. Decontamination and/or revegetation of fly ash dykes through naturally growing plants [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 153(3): 1078–1087.
[28] ZHU Feng, ZHOU Jia-yi, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, WU Chuan, GUO Ying. Aging of bauxite residue in association of regeneration: A comparison of methods to determine aggregate stability & erosion resistance [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 92(3): 47–54.
[29] BOUWER H, KLUTE A. Intake rate: Cylinder infiltrometer [J]. Methods of Soil Amnalysis Part Physical & Mineralogical Methods, 1986, 32: 825–844.
[30] WU Fa-qi, ZHAO Xi-ning, SHE Diao. Analysis on affecting factors of soil infiltration in slope farmland [J]. Bulletin of Soil & Water Conservation, 2003, 23(1): 16–18. (in Chinese)
[31] WANG Guo-liang, LIU Guo-bin, ZHOU Sheng-lu. The effect of vegetation restoration on soil stable infiltration rates in small watershed of loess gully region [J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2003, 18(1): 529–535. (in Chinese)
[32] NOURI J, KHORASANI N, LORESTANI B, KARAMI M, HASSANI A H, YOUSEFI N. Accumulation of heavy metals in soil and uptake by plant species with phytoremediation potential [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2009, 59(2): 315–323.
[33] BURKE D H, HEARST J E, SIDOW A. Early evolution of photosynthesis: Clues from nitrogenase and chlorophyll iron proteins [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1993, 90(15): 7134–7138.
[34] MACKAY D. Correlation of bioconcentration factors [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1982, 16(5): 274–278.
[35] KUMARI A, PANDEY V C, RAI U N. Feasibility of fern Thelypteris dentata for revegetation of coal fly ash landfills [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 128: 147–152.
[36] REZVANI M, ZAEFARIAN F. Bioaccumulation and translocation factors of cadmium and lead in Aeluropus littoralis [J]. Australian Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 2(4): 114–119.
[37] PANDEY V C, SINGH K, SINGH R P, SINGH B. Naturally growing Saccharum munja L. on the fly ash lagoons: A potential ecological engineer for the revegetation and stabilization [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2012, 40(3): 95–99.
[38] ZAYED A, GOWTHAMAN S, TERRY N. Phytoaccumulation of trace elements by wetland plants: I. Duckweed [J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1998, 27(3): 715–721.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
中文导读
黑麦草在赤泥堆场复垦潜能的初步评价
摘要:赤泥是氧化铝工业生产的副产品,由于存在大量的碱和各种重金属离子,在过去几十年中逐渐引起了人们对环境的关注。目前,有关赤泥大宗消纳利用的研究还比较少。本文主要从生长指标和重金属离子在黑麦草和植物体内的转移来探讨利用黑麦草在赤泥堆场上进行复垦的可能性。盆栽试验表明,通过酸中和脱碱,可以实现赤泥的修复。元素分析表明,除铁、锰、铅外,大部分元素在植物根系中是稳定的,而黑麦草几乎不能吸收镉。但是,一些重金属如铜在植物体内富集,这在赤泥的植物修复中应引起重视。
关键词:赤泥;植物复垦;生物富集系数;转移系数
LYU Fei and SUN Ning contributed equally to this work
Foundation item: Projects(51704329, 51705540) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2018JJ3671) supported by the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China; Project(2015CX005) supported by the Innovation Driven Plan of Central South University, China; Project(B14034) supported by the National 111 Project, China
Received date: 2018-10-10; Accepted date: 2018-12-05
Corresponding author: WANG Li, PhD, Professor; Email: li_wang@csu.edu.cn; ORCID: 0000-0002-8625-9659