
Electrochemical hydrogen storage characteristics of nanocrystalline and amorphous Mg2Ni-type alloys prepared by melt-spinning
ZHANG Yang-huan1, 2, L? Ke1, 2, ZHAO Dong-liang1, GUO Shi-hai1, QI Yan1, WANG Xin-lin1
1. Department of Functional Material Research, Central Iron and Steel Research Institute, Beijing 100081, China;
2. Elected State Key Laboratory, Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, Baotou 014010, China
Received 19 May 2010; accepted 29 July 2010
Abstract: The nanocrystalline and amorphous Mg2Ni-type alloys with nominal compositions of Mg2Ni1-xMnx (x=0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) were synthesized by melt-spinning technique. The spun alloy ribbons with a continuous length, a thickness of about 30 μm and a width of about 25 mm are obtained. The structures of the as-spun alloy ribbons were characterized by XRD and HRTEM. The electrochemical hydrogen storage characteristics of the as-spun alloy ribbons were measured by an automatic galvanostatic system. The electrochemical impedance spectrums (EIS) were plotted by an electrochemical workstation. The hydrogen diffusion coefficients (D) in the alloys were calculated by virtue of potential-step measurement. The results show that all the as-spun (x=0) alloys hold a typical nanocrystalline structure, whereas the as-spun (x=0.4) alloy displays a nanocrystalline and amorphous structure, confirming that the substitution of Mn for Ni facilitates the glass formation in the Mg2Ni-type alloy. The substitution of Mn for Ni significantly improves the electrochemical hydrogen storage performances of the alloys, involving the discharge capacity and the electrochemical cycle stability. With an increase in the amount of Mn substitution from 0 to 0.4, the discharge capacity of the as-spun (20 m/s) alloy increases from 96.5 to 265.3 mA?h/g, and its capacity retaining rate (S20) at the 20th cycle increases from 31.3% to 70.2%. Furthermore, the high rate dischargeability (HRD), electrochemical impedance spectrum and potential-step measurements all indicate that the electrochemical kinetics of the alloy electrodes first increases then decreases with raising the amount of Mn substitution.
Key words: Mg2Ni-type alloy; electrochemical hydrogen storage; melt-spinning; substituting Ni with Mn
1 Introduction
Some Mg-based hydrides have been extensively studied because of the great abundance, the light weight of Mg, and high hydrogen capacity of the hydrides, e.g. 3.6% (mass fraction) for Mg2NiH4, 4.5% for Mg2CoH5 and 5.4% for Mg2FeH6. The compounds have been expecting to be used as hydrogen storage materials or negative anode electrode in Ni-MH batteries[1]. However, these kinds of the hydrides suffer from high thermodynamic stability, resulting in sluggish hydriding/dehydriding kinetics which makes them still far from practical applications. A variety of attempts, mechanical alloying (MA)[2], melt spinning[3], hydriding combustion synthesis[4], surface modification[5], adding catalysts[6], etc, have been developed to improve the above-mentioned imperfection. Although remarkable progress has been achieved for overcoming the above-mentioned drawbacks, the practical applications of the Mg2Ni-type hydrides as the negative electrode of the Ni-MH battery are largely frustrated by their extremely poor electrochemical cycle stability. The key challenge faced by the researches in this area still remains intact, enhancing electrochemical cycle stability and reducing the thermodynamic stability of the hydrides.
Intensive ball-milling, however, is a very powerful method for the fabrication of the nanocrystalline and amorphous Mg and Mg-based alloys. Particularly, it is quite appropriate to solubilize the particular elements into MgH2 or Mg2NiH4 above the thermodynamic equilibrium limit. This may facilitate the destabilization of MgH2 or Mg2NiH4[7]. Whereas, the milled Mg2Ni-type alloy electrodes exhibit very poor electrochemical cycle stability on account of the evanishment of the metastable structures formed by ball milling during the multiple electrochemical charging and discharging cycles[8]. Alternatively, the melt-spun treatment may prohibit the rapid degradation of the hydrogen absorbing and desorbing cyclic characteristics of Mg and Mg-based compounds[9]. Furthermore, the melt-spinning technique is an effective method to yield a nanocrystalline structure and has been regarded to be the most appropriate for the mass-production of the nanocrystalline Mg-based alloys. SPASSOV and K?STER[10] have prepared Mg2(Ni,Y) hydrogen storage alloy with the composition of Mg63Ni30Y7 by rapid solidification process to yield a maximum hydrogen absorption capacity of about 3.0%. In addition, the hydrogenation kinetics of the melt-spun Mg2(Ni, Y) have been observed to exceed that of the conventionally prepared polycrystalline Mg2Ni alloy and also found to be comparable to that of the nanocrystalline ball-milled Mg2Ni.
The objective of present work is to synthesize the Mg-Ni-based nanocrystalline and amorphous Mg2Ni1-xMnx (x=0-0.4) alloys by melt spinning technology and to examine their structures and electrochemical hydrogen storage characteristics.
2 Experimental
The nominal compositions of the experimental alloys were Mg2Ni1-xMnx (x=0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4). For convenience, the alloys were denoted with Mn content as Mn0, Mn0.1, Mn0.2, Mn0.3 and Mn0.4, respectively. The alloy ingots were prepared using a vacuum induction furnace in a helium atmosphere at a pressure of 0.04 MPa. A part of the as-cast alloys were re-melted and spun by melt-spinning with a rotating copper roller. The spinning rate was approximately expressed by the linear velocity of the copper roller. The spinning rates used in the experiment were 15, 20, 25 and 30 m/s, respectively.
The phase structures of the as-cast and spun alloys were determined by XRD (D/max/2400). The diffraction, with the experimental parameters of 160 mA, 40 kV and 10 (°)/min respectively, was performed with Cu Kα1 radiation filtered by graphite. The effective crystal sizes were calculated from Scherrer’s formula following Williamson-Hall procedure[11].
The thin film samples of the as-spun alloys were prepared by ion etching method for observing the morphology with HRTEM (JEM-2100F, operated at 200 kV), and for determining the crystalline state of the samples with selected area electron diffraction (SAED). The average grain sizes of the as-spun alloys were measured using linear intercept method on the HRTEM micrographs.
The alloy ribbons were pulverized and then mixed with carbonyl nickel powder in a mass ratio of 1:4. The mixture was cold pressed under a pressure of 35 MPa into round electrode pellets of 10 mm in diameter and total mass of about 1 g. The electrochemical character- istics of the alloy electrodes were tested by a three- electrode open cell, consisting of a metal hydride electrode, a sintered NiOOH/Ni(OH)2 counter electrode and a Hg/HgO reference electrode. The electrolyte was 6 mol/L KOH solution. The voltage between the negative electrode and the reference electrode was defined as the discharge voltage. In every cycle, the alloy electrode was first charged at a constant current density, and following the resting for 15 min, it was discharged at the same current density to -0.500 V cut-off voltage. The environ- ment temperature of the measurement was kept at 30 °C.
The electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) were measured using an electrochemical workstation (PARSTAT 2273). Prior to measuring the impedance, several electrochemical charging and discharging cycles were carried out in order to fully activate it. The fresh electrodes were fully charged and then rested for 2 h up to the stabilization of the open circuit potential. The EIS spectra of the alloy electrodes were obtained in the frequency range from 10 kHz to 5 mHz at 50% depth of discharge (DOD). For the potentiostatic discharge, the test electrodes in the fully charged state were discharged at 500 mV potential step for 3 500 s on electrochemical workstation (PARSTAT 2273), using the CorrWare electrochemistry corrosion software.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure characteristics
Fig.1 shows the HRTEM micrographs and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns of the as-spun (20 m/s) Mn0, Mn0.1 and Mn0.3 alloys, exhibiting a nanocrystalline microstructure with an average crystal size of about 5 nm for Mn0 alloy, and its ED pattern displays sharp multi-halo, corresponding to a crystal structure. The morphologies of the as-spun Mn0.1 and Mn0.3 alloys demonstrate an evident feature of the nanocrystalline embedded in the amorphous matrix, and their ED rings consist of broad and dull halo, confirming the presence of an amorphous structure.
The XRD patterns of the as-cast and spun alloys are depicted in Fig.2. Fig.2 shows that the substitution of Mn for Ni, instead of changing the major phase of Mg2Ni in the as-cast alloy, leads to the formation of secondary phases Mg and MnNi, and the amounts of these phases increase with raising Mn content. It is quite evident that no amorphous phase is detectable in the as-spun Mn0 alloy, but the presence of an amorphous phase is clearly visible in the as-spun Mn0.4 alloy. Therefore, it can be concluded that the substitution of Mn for Ni intensifies the glass forming ability of the Mg2Ni-type alloy. Two possibilities can be regarded as the reasons for the
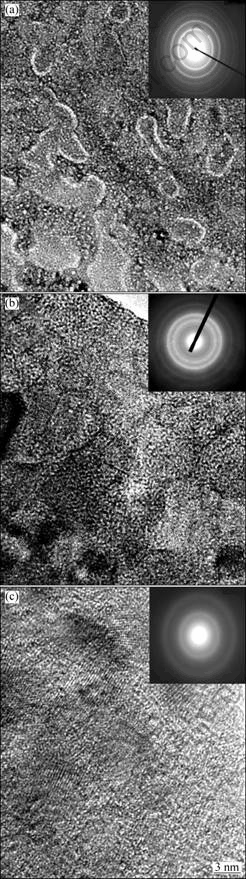
Fig.1 HRTEM micrographs and SAED patterns of as-spun alloys (20 m/s): (a) Mn0 alloy; (b) Mn0.1 alloy; (c) Mn0.3 alloy
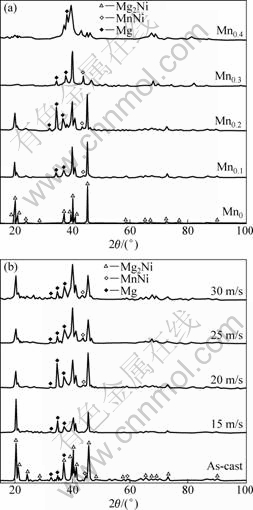
Fig.2 XRD patterns of as-cast and spun alloys: (a) As-spun alloys (20 m/s); (b) Mn0.2 alloys
enhanced glass forming ability of Mg2Ni-type alloy subjected by Mn substitution. Firstly, the addition of a third element to Mg-Ni or Mg-Cu alloys highly facilitates the glass-formation[12-13]. Secondary, atomic radius of Mn larger than that of Ni accounts for the fact that the glass forming ability of the alloy is closely related to the difference of the atom radius of the alloy. A bigger difference of the atom radius predicates a higher glass forming ability of the alloy[14]. Tables 1 and 2 list the lattice parameters, cell volume and full width at half maximum (FWHM) values of the main diffraction peaks of the as-cast and spun alloys which were calculated by software of Jade 6.0 based on the data in Fig.2. It is viewable in Table 1 that the substitution of Mn for Ni increases the FWHM values of the main diffraction peaks. Furthermore, it leads to a sharp enlargement of the lattice parameter and cell volume of the alloys owing to the larger atomic radius of Mn than Ni. Table 2 reveals that the melt spinning causes a notable enhancement in the FWHM values of the main
Table 1 Lattice parameters, cell volumes and FWHM values of major diffraction peaks of as-spun (20 m/s) alloys
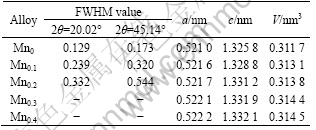
Table 2 Lattice parameters, cell volumes and FWHM values of major diffraction peaks of Mn0.2 alloys
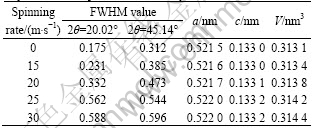
diffraction peaks of the alloys, which is undoubtedly attributed to the refined grains and the accumulated stress in the grains conduced by the melt spinning. The crystallite sizes D of the as-spun alloys were calculated by utilizing the FWHM values of the broad diffraction peak (203) in Table 1 by employing the Scherer’s equation. The grain sizes of the as-spun alloys are determined to be in the range of 2-6 nm, approximately consistent with the results reported by FRIEDLMEIER et al[15]. It is noteworthy that the D values were calculated by using the similar peak having the Miller indices (203) for the comparison purposes.
As the XRD analysis, a multiphase structure in the as-spun alloy is detected by HRTEM. A grey block (denoted as A) and a white block with a regular polygon morphology (denoted as B) can been seen in Fig.3, which are confirmed to be MnNi and Mg phases by EDS.
3.2 Electrochemical hydrogen storage performances
3.2.1 Discharge potential and discharge capacity
Fig.4 shows the discharge curves of the as-cast and spun alloy electrodes at 20 mA/g at first charging/discharging cycle due to the fact that all the alloys can be easily activated to reach the maximum capacity at first cycles. Fig.4 evidently exhibits that discharge curves have different widths of the discharge potential plateau based on the oxidation of desorbed hydrogen from the hydride. It can be obviously seen that the substitution of Mn for Ni notably modifies discharge potential characteristics of the as-spun (20 m/s) alloys, enhancing discharge potential and lengthening discharge plateau. It is noteworthy that the discharge plateau of the Mn0.4 alloy shifts towards a more negative potential with increasing spinning rate. It is quite evident that, for a
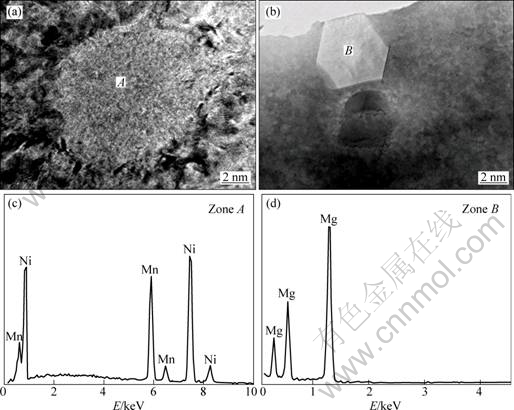
Fig.3 HRTEM observation of Mg (a) and MnNi (b) phases in as-spun (30 m/s) Mn0.4 alloy together with typical EDS patterns of zones A (c) and B (d)
fixed spinning rate of 20 m/s, the substitution of Mn for Ni markedly enhances the discharge capacity of the alloys. It is derived in Fig.4(a) that the discharge capacity grows from 96.5 to 265.3 mA?h/g as the amount of Mn substitution rises from 0 to 0.4. Fig.4(b) displays that the melt spinning exerts a highly beneficial impact on the discharge capacity of the Mn0.4 alloy. With the increase in the spinning rate from 0 (As-cast one was defined as spinning rate of 0 m/s) to 30 m/s, the discharge capacity of the Mn0.4 alloy mounts up from 92.3 to 311.5 mA?h/g.
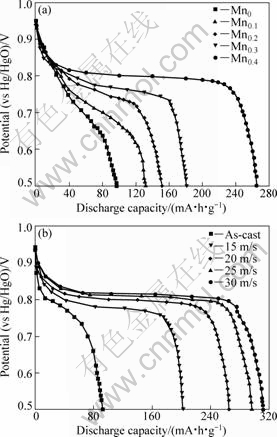
Fig.4 Discharge curves of as-cast and spun alloys: (a) As-spun alloys (20 m/s); (b) Mn0.4 alloy
Fig.5 exhibits the relationship between the maximum discharge capacity of the alloys and the Mn content. Fig.5 indicates that the substitution of Mn for Ni clearly enhances the discharge capacity of the alloys. As Mn content grows from 0 to 0.4, the discharge capacity rises from 30.3 to 92.3 mA?h/g for the as-cast alloy, and from 116.7 to 311.5 mA?h/g for the as-spun (30 m/s) alloy. The result evidently reveals that the positive impact of such substitution on the discharge capacity is more pronounced for the as-spun alloy as compared with that for the as-cast one. Several explanations may be offered as the reason why both the substitution of Mn for Ni and the melt spinning notably enhance the discharge capacity of the alloy. For the as-cast alloys, the substitution of Mn for Ni in Mg2Ni compound declines the stability of the hydride which facilitates the hydrogen desorption reaction[16-17]. The secondary phase MnNi probably works as a catalyst to activate the Mg2Ni phase to reversibly absorb/desorb hydrogen in the alkaline electrolyte. For the as-spun alloys, the increased discharge capacity is ascribed to the intensified glass forming ability of the alloys by Mn substitution since an appropriate ratio of amorphous and nanocrystalline exhibits an excellent discharge property of the Mg-Ni-based alloy[18]. The viewed essential differences in the discharge capacity of the alloys caused by melt spinning most probably have to be associated with the differences in their microstructures. The crystalline material, when melt spun, becomes at least partially disordered and its structure changes to nanocrystalline or amorphous. Consequently, high densities of the crystal defects such as dislocations, stacking faults and grain boundaries are introduced. The large number of interfaces and grain boundaries available in the nanocrystalline materials accelerates the hydrogen absorbing/desorbing process on account of the fact that the easy pathways for hydrogen diffusion are provided. Additionally, as a result of the defects introducing distortion of crystal lattice, the stored sufficient energy as chemical disorder and the introduced defects (including both stacking faults as well as grain boundaries) will produce internal strain. It has been proposed by NIU and NORTHWOOD[19] that the exchange current density and H-diffusion coefficient are directly proportional to the internal strain. Therefore, it is understandable that the introduction of defects and internal strain leads to an increase in the discharge capacity.
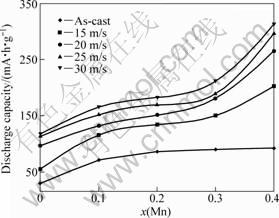
Fig.5 Relationship between maximum discharge capacity of alloys with Mn content
3.2.2 Charging and discharging cycle stability
Electrochemical cycle stability is signified by capacity retaining rate (Sn), being defined as Sn=Cn/Cmax×100%, where Cmax is the maximum discharge capacity and Cn is the discharge capacity at the nth charge-discharge cycle, respectively. The Mn content dependence on the S20 (n=20) values of the as-cast and spun alloys is plotted in Fig.6. It reveals that the substitution of Mn for Ni notably enhances the S20 values of the alloys. With the increase in the percent of Mn substitution from 0 to 0.4, the S20 value grows from 33.5% to 36.7% for the as-cast alloy, and from 30.4% to 78.7% for the as-spun (30 m/s) alloy. Apparently, such substitution engenders a more prominent impact on the capacity retaining rate of the as-spun alloy than the as-cast one. It is noteworthy that, for a fixed Mn content, a higher spinning rate means a larger capacity retaining rate except Mn0 alloy. In order to signally view the process of the capacity degradation of the alloy electrode, the evolution of the Sn values of the as-cast and spun alloys with the cycle number is presented in Fig.7. An evident tendency can be seen that the decay rates of the discharge capacity of the as-spun alloys evidently fall with increasing Mn content, suggesting that the substitution of Mn for Ni enhances the cycle stability of the as-spun alloy. It is well known that the severe corrosion of Mg in the alkaline KOH solution is the essential reason leading to the capacity degradation of the Mg-based alloy electrodes. Especially, during the discharging process, the anodic polarization of alloys facilitates the faster corrosion rate[20]. On the other hand, the metastable structures formed by melt spinning or ball milling tend to vanish during multiple charging/ discharging cycles, which is an important factor for the capacity decay of the alloys[21]. The positive impact of Mn substitution on the cycle stability of the alloy is ascribed to following reasons. One is that the enlarged cell volume caused by Mn substitution reduces the ratios of expansion/contraction of the alloys in the process of the hydrogen absorption/desorption, which means increasing the anti-pulverization capability of the alloy. On the other hand, the glass forming ability enhanced by Mn substitution is extremely important because an
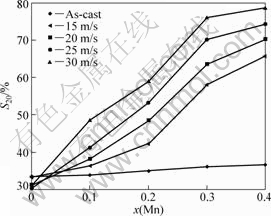
Fig.6 Evolution of S20 values of alloys with Mn content
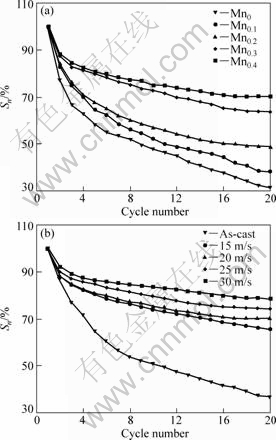
Fig.7 Evolution of capacity retaining rate of alloys with cycle number: (a) As-spun alloys (20 m/s); (b) Mn0.4 alloy
amorphous phase improves not only anti-pulverization ability but also anti-corrosion and anti-oxidation abilities of the alloy electrode in a corrosive electrolyte[22]. Additionally, the addition of a third element significantly stabilizes the nanostructure of the as-spun alloy[10], reflecting an increase of the cycle stability of the alloy.
3.2.3 High rate discharge ability (HRD) and electrochemical kinetics
It is very important to restrain the rapid decline of the discharge capacity even at a high charge/discharge current density for practical application of the hydride electrode in Ni-MH battery. Generally, the electrochemical kinetics of the alloy is characterized by its high rate discharge ability (HRD), being calculated according to following formula: HRD=C100,max/C20,max× 100%, where C100,max and C20,max are the maximum discharge capacities of the alloy electrode charged-discharged at the current densities of 100 and 20 mA/g, respectively. The HRD values of the alloy electrodes as a function of Mn content are shown in Fig.8. It is clearly viewable in Fig.8 that the HRD value of the as-cast alloy electrode monotonously augments whereas that of the as-spun alloy first mounts up then falls with the variation of Mn content. As the amount of Mn substitution increases from 0 to 0.4, the HRD value rises from 30.7% to 53.2% for the as-cast alloy, and it mounts from 60.9% (x=0) to 64.5% (x=0.1) then declines to 43.2% (x=0.4) for the as-spun (30 m/s) alloy. The HRD value is a kinetic performance of hydrogen absorbing/desorbing of the alloy electrode, which principally depends on the charge transfer at the alloy-electrolyte interface and the hydrogen diffusion process from the interior of the bulk to the surface of alloy particle[23]. The substitution of Mn for Ni noticeably enhances the HRD values of the as-cast alloys, for which two reasons are mainly responsible. On the one hand, the MnNi phase created by Mn substitution is helpful to the diffusion of hydrogen atoms. On the other hand, Mn substitution accelerates the formation of a concentrated metallic Ni layer on the alloy surface of the alloy electrode which is highly beneficial to enhance electrochemical catalytic property and to improve the reaction rate of hydrogen [24]. For the as-spun alloy, the HRD value first increases then decreases with the variation of Mn content, meaning that the Mn substitution exerts beneficial and harmful impacts on the HRD value of the alloy. The benefaction of Mn substitution has been mentioned previously. The detrimental impact of Mn substitution on the HRD value of the alloy is attributed to the emergence of an amorphous phase created by Mn substitution. It is well known that the diffusion of hydrogen atoms is markedly easer in the crystal alloy than in the amorphous one due to the fact that the large number of interfaces and grain boundaries available can act as paths for hydrogen diffusion[25]. Furthermore, an amorphous phase can effectively prohibits the pulverization of the alloy in charging and discharging cycle[26] which may decrease the rate of charge transfer at the alloy-electrolyte interface due to available new surface of the alloy electrode becoming lower. These result in an optimum Mn content.
Fig.9 shows the electrochemical impedance spectra
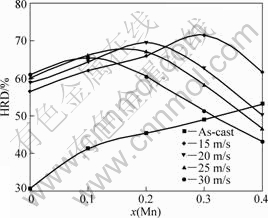
Fig.8 Evolution of HRD values of alloys with Mn content
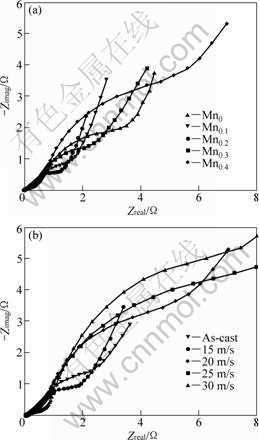
Fig.9 Electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) of alloy electrodes measured at 50% depth of discharge (DOD): (a) As-spun alloys (20 m/s); (b) Mn0.4 alloy
(EIS) of the as-cast and spun alloy electrodes at 50% depth of discharge (DOD). As shown in Fig.9, each EIS spectrum contains two semicircles followed by a straight line. KURIYAMA et al[27] suggested a model in which the smaller semicircle in the high frequency region is attributed to the contact resistance between the alloy powder and the conductive material, and the larger semicircle in the low frequency region is attributed to the charge-transfer resistance on the alloy surface. The linear response at low frequencies is indicative of hydrogen diffusion in the bulk alloy. So, the larger the radius of the semicircle in the low frequency region, the larger the charge-transfer resistance of the alloy electrode.
It can be seen in Fig.9(a) that, for a fixed spinning rate of 20 m/s, the radius of the large semicircle in the low frequency first shrinks with the increase in Mn content (x) from 0 to 0.2 then expands when x reaches 0.3. This indicates that the charge-transfer resistance of the alloy electrode first decreases then increases. Fig.9(b) shows that the radius of the large semicircle in the low frequency first declines as melt spinning rises from 0 to 15 m/s then mounts up as the melt spinning reaches 20 m/s. The increase of the active surface area of the Mn substituted alloy electrode due to the oxidation of Mn, which dissolves subsequently in the 6 mol/L KOH electrolytic solution, and thus, generates a porous surface, results in a decline of the polarization resistance of the alloy electrodes. On the other hand, the melt spinning may enhance the rate of the hydrogen diffusion due to the increasing defects such as dislocations and grain boundaries which can act as fast diffusion paths for hydrogen atoms[25]. The function of the melt spinning on the electrochemical kinetics basically relies on the structure generated by melt spinning. The refined grains originated by the melt spinning is highly favorable for hydrogen diffusion, whereas an amorphous created by the melt spinning exerts a completely contrary impact. Whether the melt spinning heightens or depresses the rate of hydrogen diffusion depends which one of the above-mentioned factors will predominate.
The diffusion coefficient of hydrogen in the bulk of the alloys is determined with the potential-step method. Fig.10 shows the semilograrithmic curves of anodic current versus working duration of the as-cast and spun alloy electrodes. Fig.10 can be divided into two time regions based on the model founded by NISHISA et al[28]. In the first time region, the current rapidly declines due to a consumption of hydrogen on the surface. In the other time region, however, the current slowly falls in a linear fashion. In this region, the current is controlled by the diffusion of hydrogen atoms with time. Thus, the diffusion coefficient D of the hydrogen atoms in the bulk of the alloy can be calculated through the slope of the linear region of the corresponding plots according to the following formulae[29]:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
where i is the diffusion current density (A/g); D is the hydrogen diffusion coefficient (cm2/s); c0 is the initial hydrogen concentration in the bulk of the alloy (mol/cm3); cs is the hydrogen concentration on the surface of the alloy particles (mol/cm3); a is the alloy particle radius (cm); d is the density of the hydrogen storage alloy (g/cm3); t is the discharge time (s), respectively. The hydrogen diffusion coefficient D signifies the hydrogen diffusion rate in the bulk. The larger the diffusion coefficient, the faster the diffusion of the hydrogen atoms in the alloy, and the better the electrochemical kinetics property of the alloy electrodes[30]. The D values calculated by Eq.(2) are also summarized in Fig.10. It can be seen that both the substitution of Mn for Ni and melt spinning exert a notable effect on H diffusion in the alloy. For a fixed spinning rate of 20 m/s, the D of the alloy electrode increases from 1.72×10-11 cm2/s (x=0) to 4.07×10-11 cm2/s (x=0.2) then decreases to 0.82×10-11cm2/s (x=0.4). And for a fixed Mn0.4 alloy, the H diffusion coefficient D in the alloy electrode rises from 3.49×10-11cm2/s (at 0 m/s) to 3.98×10-11 cm2/s (at 15 m/s) then falls to 0.82×10-11cm2/s (at 30 m/s). The above results apparently indicate that Mn substitution and melt spinning engender beneficial and harmful effects on H diffusion coefficient D. The benefaction of the Mn substitution and the melt spinning on the H diffusion coefficient has also been attributed to the formed secondary phase MnNi motivated by Mn substitution and the refined grain caused by melt spinning. An increased interface and grain boundary is highly helpful for enhancing the ability of H diffusion in the alloy electrode. The baneful action of the Mn substitution and the melt spinning is undoubtedly ascribed to the formation of an amorphous phase due to the well known fact that H diffusion in the crystal alloy is markedly easer than in the amorphous one.
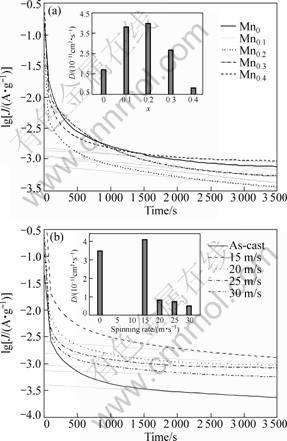
Fig.10 Semilogarithmic curves of anodic current vs. time responses of as-cast and spun alloy electrodes in fully charged state: (a) As-spun alloys (20 m/s); (b) Mn0.4 alloy
4 Conclusions
1) The investigation of the structures of the as-cast and spun Mg2Ni1-xMnx (x=0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) alloys reveals that there is no amorphous phase in the as-spun Mn0 alloy, but the as-spun Mn0.4 alloys present a feature of the nanocrystalline embedded in the amorphous matrix, confirming that the substitution of Mn for Ni facilitates the glass formation in the Mg2Ni-type alloys.
2) The substitution of Mn for Ni markedly improves the electrochemical hydrogen storage performances of the alloy, enhancing the discharge capacity and the cycle stability, which is mainly attributed to the enlarged cell volume and the intensified glass forming ability by Mn substitution.
3) The high rate dischargeability (HRD) of the as-spun alloy electrodes first increases then decreases with incremental variation of Mn content, and the optimum Mn content in which the alloy electrode obtains the largest HRD will change with the variation of the spinning rate. Moreover, the results obtained from EIS and potential-step measurements agree well with the change of HRD.
References
[1] EBRAHIMI-PURKANI A, KASHANI-BOZORG S F. Nanocrystalline Mg2Ni-based powders produced by high-energy ball milling and subsequent annealing [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2008, 456: 211-215.
[2] KWON S N, BAEK S N, MUMM D R, HONG S H, SONG M Y. Enhancement of the hydrogen storage characteristics of Mg by reactive mechanical grinding with Ni, Fe and Ti [J]. J Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33: 4586-4592.
[3] PALADE P, SARTORI S, PRINCIPI G, LO R S, LAZARESCU M, SCHINTEIE G, KUNCSER V, FILOTI G. Hydrogen storage in Mg-Ni-Fe compounds prepared by rapid quenching and ball milling [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2006, 415: 170-176.
[4] LIU X F, ZHU Y F, LI L Q. Structure and hydrogenation properties of nanocrystalline Mg2Ni prepared by hydriding combustion synthesis and mechanical milling [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2008, 455: 197-202.
[5] JANOT R, DAROK X, ROUGIER A, AYMARD L, NAZRI G A, TARASCON J M. Hydrogen sorption properties for surface treated MgH2 and Mg2Ni alloys [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2005, 404–406: 293-296.
[6] SAKINTUNA B, LAMARI-DARKRIM F, HIRSCHER M. Metal hydride materials for solid hydrogen storage: A review [J]. J Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32: 1121-1140.
[7] LIANG G Y. Synthesis and hydrogen storage properties of Mg-based alloys [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2004, 370: 123-128.
[8] HUANG L J, LIANG G Y, SUN Z B, ZHOU Y F. Nanocrystallization and hydriding properties of amorphous melt-spun Mg65Cu25Nd10 alloy [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2007, 432, 172-176.
[9] SAVYAK M, HIRNYI S, BAUER H D, UHLEMANN M, ECKERT J, SCHULTZ L, GEBERT A. Electrochemical hydrogenation of Mg65Cu25Y10 metallic glass [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2004, 364: 229-237.
[10] SPASSOV T, K?STER U. Thermal stability and hydriding properties of nanocrystalline melt-spun Mg63Ni30Y7 alloy [J]. J Alloys Comp, 1998, 279: 279-286.
[11] WILLIAMSON G K, HALL W H. X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram [J]. Acta Met, 1953, 1: 22-31.
[12] YAMAURA S I, KIM H Y, KIMURA H, INOUE A, ARATA Y. Thermal stabilities and discharge capacities of melt-spun Mg-Ni-based amorphous alloys [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2002, 339: 230-235.
[13] INOUE A, MASUMOTO T. Mg-based amorphous alloys [J]. Mat Sci Eng A, 1993, 173: 1-8.
[14] CHEN H S. Thermodynamic considerations on the formation and stability of metallic glasses [J]. Acta Met, 1974, 22(12): 1505-1511.
[15] FRIEDLMEIER G, ARAKAWA M, HIRAIA T, AKIBA E. Preparation and structural, thermal and hydriding characteristics of melt-spun Mg-Ni alloys [J]. J Alloys Comp, 1999, 292: 107-117.
[16] WOO J H, LEE K S. Electrode characteristics of nanostructured Mg2Ni-type alloys prepared by mechanical alloying [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1999, 146: 819-823.
[17] TAKAHASHI Y, YUKAWA H, MORINAGA M. Alloying effects on the electronic structure of Mg2Ni intermetallic hydride [J]. J Alloys Comp, 1996, 242: 98-107.
[18] HUANG L J, LIANG G Y, SUN Z B, WU D C. Electrode properties of melt-spun Mg-Ni-Nd amorphous alloys [J]. J Power Sources, 2006, 160: 684-687.
[19] NIU H, NORTHWOOD D O. Enhanced electrochemical properties of ball-milled Mg2Ni electrodes [J]. J Hydrogen Energy, 2002, 27: 69-77.
[20] SIMI?I? M V, ZDUJI? M, DIMITRIJEVI? R, NIKOLI?- BUJANOVI? L, POPOVI? N H. Hydrogen absorption and electrochemical properties of Mg2Ni-type alloys synthesized by mechanical alloying [J]. J Power Sources, 2006, 158: 730-734.
[21] LIANG G Y, Wu D C, Li L, HUANG L J. A discussion on decay of discharge capacity for amorphous Mg-Ni-Nd hydrogen storage alloy [J]. J Power Sources, 2009, 186: 528-531.
[22] ZHANG Y H, LI B W, REN H P, CAI Y, DONG X P, WANG X L. Investigation on structures and electrochemical performances of the as-cast and -quenched La0.7Mg0.3Co0.45Ni2.55-xFex (x=0-0.4) electrode alloys [J]. J Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32: 4627-4634.
[23] IWAKURA C, MATSUOKA M, ASAI K, KOHNO T. Surface modification of metal hydride negative electrodes and their charge/discharge performance [J]. J Power Source, 1992, 38: 335-343.
[24] GASIOROWSKI A, IWASIECZKO W, SKORYNA D, DRULIS H, JURCZYK M. Hydriding properties of nanocrystalline Mg2-xMxNi alloys synthesized by mechanical alloying (M=Mn, Al) [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2004, 364: 283-288.
[25] WU Y, HAN W, ZHOU S X, LOTOTSKY M V, SOLBERG J K, YARTYS V A. Microstructure and hydrogenation behavior of ball-milled and melt-spun Mg-10Ni-2Mm alloys [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2008, 466: 176-181.
[26] ZHANG Y H, LI B W, REN H P, CAI Y, DONG X P, WANG X L. Cycle stabilities of the La0.7Mg0.3Ni2.55-xCo0.45Mx (M = Fe, Mn, Al; x=0, 0.1) electrode alloys prepared by casting and rapid quenching [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2008, 458: 340-345.
[27] KURIYAMA N, SAKAI T, MIYAMURA H, UEHARA I, ISHIKAWA H, IWASAKI T. Electrochemical impedance and deterioration behavior of metal [J]. J Alloys Comp, 1993, 202: 183-197.
[28] NISHISA T, URA H, UCHIDA I. Determination of chemical diffusion coefficients in metal hydride particles with a microelectrode technique [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1997, 144: 1273-1277.
[29] ZHANG G, POPOV B N, WHITE R E. Electrochemical determination of the diffusion coefficient of hydrogen through a LaNi4.25Al0.75 electrode in alkaline aqueous solution [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1995, 142: 2695-2698.
[30] NAITO K, MATSUNAMI T, OKUNO K, MATSUOKA M, IWAKURA , APPL C. Factors affecting the characteristics of the negative electrodes for nickel-hydrogen batteries [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1993, 23: 1051-1055.
快淬纳米晶/非晶Mg2Ni型合金的电化学贮氢性能
张羊换1,2,吕 科1,2,赵栋梁1,郭世海1,祁 焱1,2,王新林1
1. 钢铁研究总院 功能材料研究所,北京 100081;
2. 内蒙古科技大学 国家重点实验室培育基地,包头 014010
摘 要:用快淬工艺制备纳米晶和非晶Mg2Ni型Mg2Ni1-xMnx (x=0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4)合金,获得长度连续、厚度约30 μm,宽度约25 mm的薄带。用XRD、HRTEM分析快淬合金薄带的微观结构,用程控电池测试仪测试合金薄带的电化学性能,用电化学工作站(PARSTAT 2273)测试快淬薄带的交流阻抗谱(EIS),测试电位阶跃后的阳极电流—时间响应曲线,并计算氢在合金中的扩散系数(D)。结果表明,快淬(x=0)合金均具有典型的纳米晶结构,而快淬(x=0.4)合金显示纳米晶和非晶结构,这证实Mn替代Ni有利于Mg2Ni型合金形成非晶相。Mn替代Ni显著地改善了合金的电化学贮氢性能,包括放电容量和电化学循环稳定性。当Mn替代量从0增加到0.4时,20 m/s快淬态合金的放电容量从96.5 mA?h/g增加到265.3 mA?h/g,20次充放循环后的容量保持率(S20)从31.3%增加到70.2%。此外,高倍率放电能力(HRD)、交流阻抗(EIS)以及电位阶跃测试结果都表明,随着Mn替代量的增加,合金电极的电化学动力学性能先增加而后降低。
关键词:Mg2Ni型合金;电化学贮氢;快淬;Mn替代Ni
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Project (2007AA03Z227) supported by the High-tech Research and Development Program of China; Projects (50871050, 50701011) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (200711020703) supported by Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia, China; Project (NJzy08071) supported by Higher Education Science Research Project of Inner Mongolia, China
Corresponding author: ZHANG Yang-huan; Tel: +86-10-62187570; E-mail: zyh59@yahoo.com.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60743-7