DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.01.018
巴布亚盆地晚古生代—新生代构造演化与油气成藏条件
刘湘1, 2,郭建华1, 2,张琳婷3,蔡文杰4,许晓明4,李杰1, 2,黎彩凤1, 2,刘婉芬1, 2,张振1
(1. 中南大学 地球科学与信息物理学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属成矿预测与地质环境监测教育部重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083;
3. 华北理工大学,河北 唐山,600039;
4. 中海油研究总院,北京,100028)
摘要:为了进一步系统研究巴布亚盆地构造特征及演化史,分析其勘探远景,通过对二维地震资料进行解释,并结合地球化学特征,分析盆地构造演化与油气成藏条件的关系。分析构造演化对盆地中、新生界主力烃源岩Imburu组、Koi-Iange组、Barikewa组及Magobu组和背斜圈闭与断层圈闭两大构造圈闭发育的控制作用,在此基础上提出古生新储—垂向排烃—多期次成藏的成藏模式。研究结果表明:巴布亚盆地经历了陆内裂谷阶段、冈瓦纳大陆裂解阶段、珊瑚海扩张阶段、美拉尼西亚岛弧碰撞阶段共4期多旋回的构造演化阶段。
关键词:澳大利亚板块;巴布亚盆地;构造演化史;烃源岩
中图分类号:TE112 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2018)01-0131-10
Late Paleozoic—Cenozoic tectonic evolutions and hydrocarbon accumulation conditions of Papuan basin
LIU Xiang1, 2, GUO Jianhua1, 2, ZHANG Linting3, CAI Wenjie4, XU Xiaoming4, LI Jie1, 2, LI Caifeng1, 2, LIU Wanfen1, 2, ZHANG Zhen1
(1. School of Geosciences and Info-physics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Metallogenic Prediction of Nonferrous Metals and Geological Environment Monitoring of Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 600039, China;
4. CNOOC Research Center, Beijing 100028, China)
Abstract: In order to research tectonic characteristics and evolutions and analyze the exploration prospect, the relationship between the tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation conditions was analyzed based on the interpretation of the 2D seismic data. The tectonic evolution of Papuan basin on the control action of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic hydrocarbon source rock, Imburu Fm, Koi-Iange Fm, Barikewa Fm and Magobu Fm and the tectonic traps of anticline and fault was analyzed. The patterns of hydrocarbon accumulation for generation were proposed from Mesozoic and accumulation in Cenozoic to vertical hydrocarbon expulsion and multiple accumulation. The results show that Papuan basin undergones tectonic evolution of four polycyclic tectonic evolution stages, i.e. intracontinental rift, gondwana continent dissociation, the Coral Sea expansion, Melanesia arc collision.
Key words: Australian plate; Papuan basin; tectonic evolution history; source rock
巴布亚盆地位于巴布亚新几内亚和澳大利亚北部边缘之间,整体延伸趋势为北西—南东向,为陆上和近海盆地。盆地覆盖面积超过6.0×105 km2,包括新几内亚南部大部分区域、西巴布亚的东南部、巴布亚海湾和托雷斯海峡,盆地内有多达6 km厚的中生代和新生代沉积物,油气资源丰富[1]。HILL[2]认为澳大利亚北部边缘构造格局的形成是澳大利亚大陆与相邻板块运动所致;骆宗强等[3]认为由于巴布亚盆地北部处于澳大利亚板块与太平洋板块交界处,南部处于珊瑚海裂谷的肩部,复杂的构造背景使得盆地东西部地区的构造特征存在明显的差异性。巴布亚盆地的油气勘探工作始于20世纪20年代,目前已有钻井186口,地震测线基本分布全区,测线密度从1 km×1 km至8 km×15 km不等。据美国地质调查局(USGS)2012年评价结果显示,目前巴布亚盆地已发现油气田38个,天然气可采储量为7.1×1011 m3,原油可采储量为1.5×108 t,待发现天然气资源量为1.0×1012 m3,待发现原油3.1×108 t。但由于该盆地地质背景及油气成藏保存条件复杂,造成勘探难度大,之前的研究主要集中在构造演化上,未对构造与成藏形成系统认识。为此,本文作者通过对巴布亚盆地晚古生代—新生代的构造演化史进行分析,研究构造演化对盆地烃源岩、圈闭发育的控制作用,并总结成藏模式,以便为下一步勘探提供参考。
1 巴布亚盆地演化与形成特征
1.1 构造特征
巴布亚盆地主要由9个二级构造单元组成,分别为Papuan褶皱带、Fly台地、Aure活动构造带、Papuan活动带、Moresby凹陷、Owen Stanley复杂构造带、Milne蛇绿岩带、Papuan高地和东部高地(见图1)。其中,Papuan褶皱带、Fly台地和Aure活动构造带为盆地的主体。Papuan褶皱带主要以平卧褶皱和逆冲推覆构造为主,其中前展式冲断层推覆体上发育的大量逆掩断层背斜是中生代主要的储集层,如晚侏罗世—早白垩世的Toro组砂岩,粒度以细—中粒为主,埋藏深度为2.0~4.0 km,分选性和孔隙度较好,是一套良好的储集层。已知的沉积岩有中生界边缘海至广海相碎屑岩、古近系至新近系下段的大陆架、盆地灰岩和碎屑岩及新近系上段海相至陆相碎屑岩。Fly台地位于巴布亚盆地西南部相对稳定的地区,以平缓褶皱变形、轻度至中等块断和扭断构造为主;发育大量正断层,以中生界碎屑岩、古新统—上新统碳酸盐以及上新 统—更新统碎屑岩和火山岩为主。Aure活动构造带处于Fly台地东部,其构造类型与Papuan褶皱带类似,但也有一些明显差别,主要沉积岩有中生界细粒碎屑岩、古近系半深海石灰岩和碎屑岩、中新统浊积岩及上新统—更新统海相至陆相碎屑岩[4-6]。
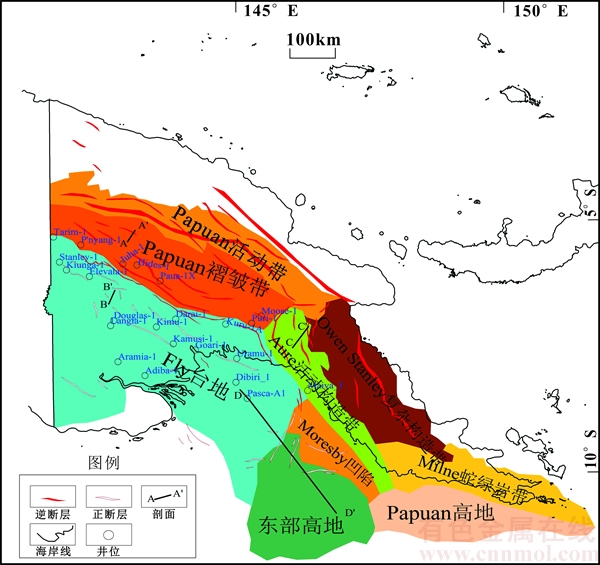
图1 巴布亚盆地构造单元分布(据文献[2])
Fig. 1 Tectonic provinces of Papuan basin (according to Ref. [2])
1.2 构造样式
巴布亚盆地的构造样式复杂多样。分析图1可知,断裂活动强烈地带主要集中在北部Papuan褶皱带与Papuan活动带的弧—陆碰撞带和西南Fly台地地区以及Aure活动构造带和Owen Stanley复杂构造带,这些断层在平面上呈现雁式或平行排列,是划分二级构造单元的重要依据。在盆地内部断裂系统中,逆断层主要分布在Papuan褶皱带和Aure活动构造带,在Papuan褶皱带逆断层呈北西向,至Aure活动构造带转为北北西向。这种断裂系统在盆地内部的分布规律反映了盆地东西部地区构造环境和动力学背景的差异性,为深入研究盆地构造演化与油气成藏提供了基础。本文通过综合分析,同时结合地震资料解释,将巴布亚盆地内部主要的断裂带特征总结为以下几点。
1) Papuan褶皱带与Papuan活动带的弧—陆碰撞带。该断裂带北部受到来自太平洋板块与澳大利亚板块汇聚边界俯冲带的挤压应力作用,逆冲断层发育,其中,Papuan活动带北部以1条长约350 km的北西向左旋走滑断层为边界,以变质沉积为主;Papuan褶皱带与Papuan活动带以1条长约400 km的北西向逆冲断层为边界,形成强烈冲断带,以中生代泥页岩为滑脱面,形成以叠瓦式冲断构造(图2)、前展式逆冲构造以及早期正断层的强烈反转构造为主的构造样式,往南是推覆体的锋缘,延伸至Fly台地北部边界,冲断褶皱变形有所减弱,规模逐渐减小。
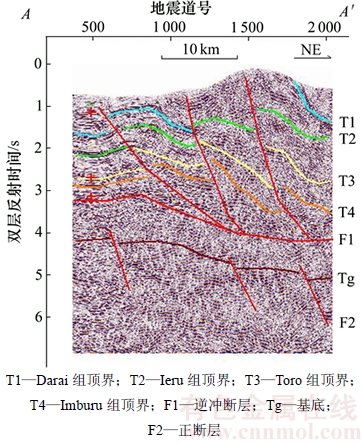
图2 Papuan褶皱带叠瓦式冲断构造(测线位置见图1中A-A′)
Fig. 2 Imbricated thrust type structure of Papuan fold belt (line position is in line A-A′of Fig. 1)
2) Fly台地地区。该区域是巴布亚盆地构造运动相对稳定的地带,逆断层主要发育在稳定台地北部与Papuan褶皱带的边界区域,走向与Papuan褶皱带一致,大部分为北西向;Fly台地中部的构造样式以反转构造为主。Fly台地南部地区由于远离挤压应力作用,晚白垩世珊瑚海扩张期发育的正断层广泛分布,断层剖面组合形式主要以阶梯式组合为主(见图3),断面东倾,产状平直且断距较短。
3) Aure活动构造带和Owen Stanley复杂构造带。该区域是Papuan褶皱—冲断带的一部分,是Papuan褶皱带在巴布亚盆地东部的延伸,在晚中新世受到北部俯冲综合作用,形成大规模逆冲断层和反转断层。断裂系统与Papuan褶皱带相似,但也有一些明显区别。Aure活动构造带不发育大规模以泥岩为滑脱面的薄皮构造,而被基底卷入型逆冲构造取代。与Papuan褶皱带相比,Aure活动构造带的范围明显变小,逆冲断裂带产状更加陡直(见图4)。从地震剖面上看,断面西倾,上盘发育强烈的紧闭褶皱,其中T2界面是全盆地中1个广泛的剥蚀界面,不仅是Ieru组的顶界,同时大致与白垩系顶界重合,作为中生界与新生界的分界面。
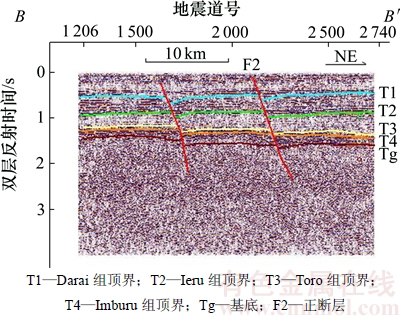
图3 Fly台地正断层典型剖面(测线位置见图1中B-B′)
Fig. 3 Typical profile of normal fault in Fly platform (line position is in line B-B′ of Fig. 1)
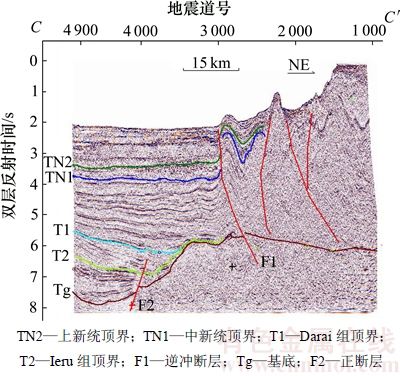
图4 Aure活动构造带逆冲断层构造样式(测线位置见图1中C-C′)
Fig. 4 Thrust fault tectonic style of Aure tectonic belt (line position is in line C-C′of Fig. 1)
1.3 盆地构造演化
COLE等[7]认为,巴布亚盆地南部的Fly台地是澳大利亚陆壳的北部延伸部分,它保存了中生代和部分古生代的构造。HILL等[8]认为,伴随着晚渐新世—中新世的弧—陆碰撞,巴布亚盆地北部陆壳发生褶皱变形,逆冲断层发育,形成巴布亚褶皱带。HILL等[9]的研究表明,巴布亚盆地受控于太平洋板块和澳大利亚板块间的裂离与拼合,经历了裂谷、裂后和前陆盆地三大构造演化阶段。杨磊等[10]认为巴布亚盆地为澳大利亚板块边缘古生界花岗岩基底上发育的中生代和新生代弧后前陆盆地,在基底之上沉积了一套侏罗—白垩纪的碎屑岩和古近—新近纪的碳酸盐岩。骆宗强等[3]通过二维构造解释,认为巴布亚盆地现今结构—构造存在明显的东西部差异,盆地西部以薄皮构造为主,在此基础上形成大规模的冲断—褶皱构造;盆地东部则形成前陆盆地结构,并将盆地构造演化归纳为冈瓦纳裂谷—裂后阶段、珊瑚海裂谷—裂后阶段、达赖弧后阶段、前陆盆地阶段。由此可见,前人对巴布亚盆地构造演化的研究主要集中在巴布亚褶皱带和Fly台地,范围比较局限,而且对构造演化的表述不够系统全面。本文在前人研究基础上,结合地震资料解释成果(见图5),将巴布亚盆地晚古生代—新生代构造演化史系统总结为4个主要阶段(见图6),即陆内裂谷阶段、冈瓦纳大陆裂解阶段、珊瑚海扩张阶段、美拉尼西亚岛弧碰撞阶段,并分析了每个构造演化阶段对整个盆地的控制作用。
1) 陆内裂谷阶段(二叠纪—早三叠世)。在此时期,地壳活动比较活跃,各板块间的相对运动加剧,劳亚大陆和冈瓦纳大陆拼接形成联合古大陆(泛大陆),巴布亚盆地所在区域可能受滇缅马苏和羌塘扩张的影响,发育大量的半地堑,此时,盆地处于形成初期,与澳大利亚大陆连接在一起,构造变形特征与澳大利亚西北陆架联系紧密,盆地东部处于活动大陆边缘,西部是冈瓦纳大陆裂解期的克拉通地块,东西部大致以塔斯曼线为分界线(图6(a))。塔斯曼线是由北往南纵穿东部澳大利亚大陆的1条Z字型的线,开始形成于早寒武世,是划分西部罗迪尼亚超级大陆裂解范围的构造缝合线,随后沿着东部冈瓦纳大陆边界的造山带增长[11]。分析表明,该时期地壳的构造运动把巴布亚盆地划分为多个沉积中心,盆地内部地堑、半地堑大量发育,在塔斯曼造山带,广泛沉积了一套变质岩,并推测该时期盆地沉积了一套潜在的烃源岩。
2) 冈瓦纳大陆裂解阶段(晚三叠世—早白垩世)。在早三叠世,冈瓦纳大陆开始裂解,受其影响,盆地内地堑式裂谷广泛发育;从巴布亚盆地现今所处的构造背景推测(图6(b)),在中三叠世—晚三叠世,澳大利亚东北部新英格兰造山带西南向的俯冲可能沿着边缘广泛分布的火山岛弧一直延伸到巴布亚岛的北部边界,该地区局部有花岗岩侵入[7];在中侏罗世—早白垩世,随着晚三叠世火山活动延续,部分岛弧区域开始从澳大利亚板块分离,在此背景下形成的隆起强烈影响了裂谷作用,巴布亚盆地在此期间为冈瓦纳大陆裂后单元,盆地处于被动大陆边缘,开始热沉降,是盆地主要的烃源岩(Imburu组、Koi-Iange组、Barikewa组及Magobu组等)、储层(Toro组、Magobu组等)、盖层(Ieru组、Chim组泥岩等)的沉积时期。盆地东北部地区至澳大利亚东部沿线火山活动剧烈,表明该区域有新的俯冲事件发生,导致侏罗系洋壳沿海沟向大陆侧形成增生楔[12-13]。
3) 珊瑚海扩张阶段(晚白垩世—早中新世)。在晚白垩世,由于太平洋板块向澳大利亚板块的俯冲作用,断裂开始沿着澳大利亚北部边界发育,这导致陆壳边缘分离出来的岩屑在盆地边缘组合在一起;古新世巴布亚岛开始与澳大利亚昆士兰分离,沿着巴布亚岛北部海岸线,使大陆边缘盆地逐渐形成。南部地区由于临近珊瑚海扩张作用强烈地带(见图6(c)和图7),抬升剥蚀了一部分晚古生代基底之上沉积的中生代地层[14]。盆地Papuan褶皱带—Fly台地—Aure活动构造带的构造演化史表明(图5):在古新统沉积之前,中生代地层厚度明显大于上新统沉积之前的厚度,因为巴布亚盆地在接受古新统—中新统沉积之前,盆地正处于晚白垩世的珊瑚海扩张期,中生代地层遭受抬升剥蚀之后,才开始沉积古新统之后的地层,往北西向,抬升剥蚀作用减弱,盆地东部地区受珊瑚海扩张影响,挤压变形强烈,中生代地层充填在基底之上,呈现残洼充填分布。从盆地东部地震剖面(图7)中可见明显的上超特征,推断该部位出现充填现象。在始新世时期,伴随着珊瑚海扩张,盆地进入裂后热沉降阶段。虽然在盆地南部地区表现得尤为突出,但在盆地北部的Papuan活动带和部分Papuan褶皱带沉积了一套良好的灰岩和碎屑。到渐新世,澳大利亚板块继续向北运动,导致巴布亚盆地边缘临近菲律宾—卡罗林海俯冲带(图6(c)。该区域的综合俯冲作用[15]导致盆地再次隆升,遭受剥蚀,特别是盆地西部地区影响最大,几乎缺失整套古近纪地层,东部地区则广泛接受了新生代的沉积物。与中生代时期相比,该地区的沉积特点恰恰相反,即在呈残洼分布的中生代地层之上覆盖了巨厚的新生代沉积物。
4) 美拉尼西亚岛弧碰撞阶段(中新世中期—现今)。自中新世以来,由于澳大利亚板块北部与美拉尼西亚岛弧碰撞[8],导致主要的板块重组,处于澳大利亚西北大陆和古大洋俯冲带之间的巴布亚盆地开始进入前陆盆地演化阶段,盆地普遍接受了1.0~2.0 km厚的中新世碳酸盐沉积物。盆地北部随着所罗门海附近火山和岛弧的活动,沉积了大量火山碎屑岩。在晚中新世,随着盆地北部俯冲带的活动,Papuan褶皱带因强烈挤压而变形、遭受剥蚀,基底冲断层发育,形成逆冲推覆构造一直持续至今(见图2)。在此期间(见图6(d)),盆地东西部地区呈现了截然不同的演化阶段,西部地区受控于北部弧—陆碰撞的影响,以侏罗系底界为滑脱面,形成大规模逆冲推覆构造,东部地区则以Aure活动构造带为中心,形成前陆盆地系统。
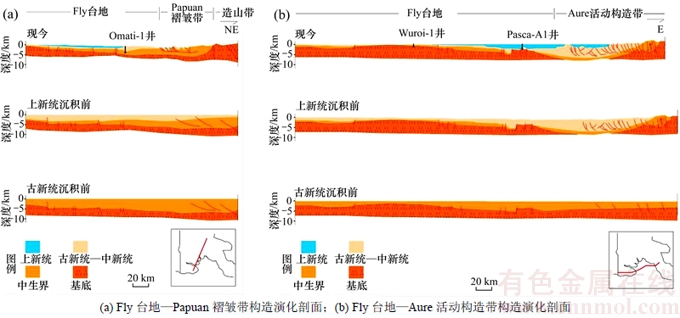
图5 巴布亚盆地构造演化剖面
Fig. 5 Tectonic evolution sections of Papua basin

图6 巴布亚盆地晚古生代—新生代构造位置图(据文献[8])
Fig. 6 Late Paleozoic—Cenozoic tectonic setting of Papuan basin (according to Ref. [8])
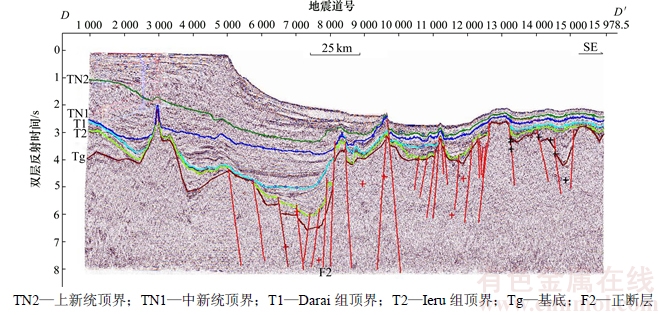
图7 珊瑚海扩张作用典型剖面(测线位置见图1中D-D′线)
Fig. 7 Seismic section of Coral Sea extension (line position is in line D-D′ of Fig. 1)
2 构造演化与油气成藏条件
2.1 对烃源岩的控制
巴布亚盆地发育了中生界、新生界共2套主要烃源岩。中生界烃源岩主要发育在侏罗系,新生界烃源岩主要发育在新近系[16]。中生界烃源岩包括白垩系Ieru组和侏罗系Imburu组、Koi-Iange组、Barikewa组及Magobu组等,主要岩性为泥岩、页岩、碳质泥岩,烃源岩有效分布面积为1.26×105 km2,主要分布于Fly台地和Papuan褶皱带(见图8),平均厚度为350 m,主要为三角洲相、滨岸相、浅海陆棚相沉积。其中Fly台地东部地区烃源岩沉积最厚,普遍厚度为500~1 000 m;Papuan褶皱带烃源岩亦较发育,厚度为200~700 m;新生界烃源岩主要分布于Fly台地东部及Moresby地槽,以新近系Orubadi组为主,灰色泥岩、灰色页岩及少量页岩砂岩互层,连续性强,厚度为200~2 100 m,平均厚度为900 m,有效分布面积约2.45×104 km2(见图8)。以Dibiri-1—Pasca C1—Orokolo-1井区附近烃源岩最为发育,为一套三角洲相、浅海陆棚相泥岩、页岩、碳质页岩沉积,厚度为700~2 100 m,见表1。从表1可见:Dibiri-1井Orubadi组烃源岩累计厚度达2 151.0 m,占地层厚度的92.6%,烃源岩发育条件好;而在Dibiri-1井以西,烃源岩沉积相对较小,厚度为200~500 m。Moresby地槽因缺乏钻井资料不能定量评价,但运用外推法与类比法可推测该区烃源岩沉积厚度较大。
根据前面构造演化分析,裂谷作用和碰撞作用对盆地的形成产生了重要的影响。在冈瓦纳大陆裂解阶段,以裂谷作用强烈为主要特征,Fly台地为主要沉降中心,处于浅海陆棚沉积环境,有利于烃源岩沉积,白垩系Ieru组和侏罗系Imburu组、Koi-Iange组、Barikewa组及Magobu组等盆地主力烃源岩沉积于该时期; 自中新世以来,澳大利亚板块北部与美拉尼西亚岛弧的弧—陆碰撞加剧,盆地进入前陆盆地演化阶段,普遍接受沉积,沉积了该时期较厚的Orubadi组烃源岩(见表2)。
根据表2中的烃源岩镜质体反射率(Ro)可以有效地分析其有机质成熟度,由此可知:中生界烃源岩主要发育在Fly台地,大部分处于低熟—成熟阶段,少数到高成熟阶段如Magobu组,Ro 最高达2.6%,有机碳质量分数(w(TOC))范围为0.77%~6.62%,是一套很好的烃源岩;新生界烃源岩分布较局限,由于北部的弧—陆碰撞,导致新生界地层抬升剥蚀,该时期盆地东部沉积的碳酸盐虽然w(TOC)高,但由于其埋深浅,Ro<0.4%,大部分处于未成熟阶段。
Dibiri-1井地史模拟结果见图9。分析图9可知:该井区在白垩纪晚期以前为连续沉积,厚度达6.0 km;其后,上部地层遭剥蚀,至始新世晚期,共剥蚀3.7 km厚的沉积物,被剥蚀掉的沉积物为晚侏罗世至白垩纪的沉积物;在上升剥蚀时期(白垩纪晚期至始新世晚期),剥蚀层段以下各沉积层深度变浅,但厚度不变;在始新世晚期,盆地又恢复下降,接受沉积,沉积的厚度远远小于先前剥蚀掉的沉积物厚度,不整合面以下地层没有受到压实作用的影响;在渐新世期间,既无沉积作用,又无剥蚀作用,为沉积间断,在此期间,各层厚度不变,深度也不变;至渐新世末期,盆地又恢复下降,接受沉积,沉积的厚度等于先前剥蚀掉的沉积物厚度,不整合面以下地层基本没有受到压实作用的影响。
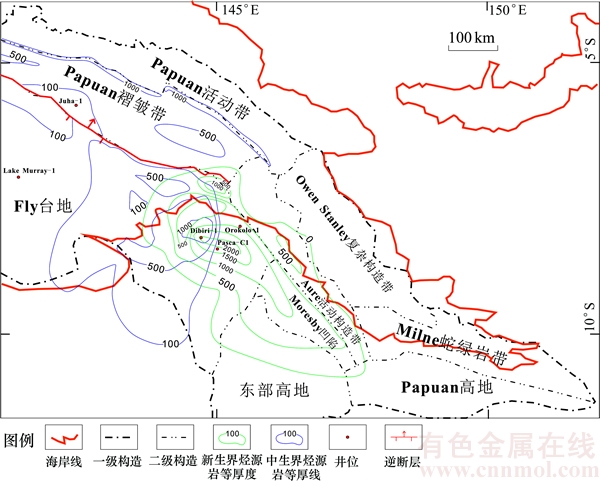
图8 巴布亚盆地中生界—新生界烃源岩等厚图
Fig. 8 Mesozoic—Cenozoic hydrocarbon source rocks isopach map of Papuan basin
表1 巴布亚盆地烃源岩厚度
Table 1 Source rocks thickness of Papuan basin
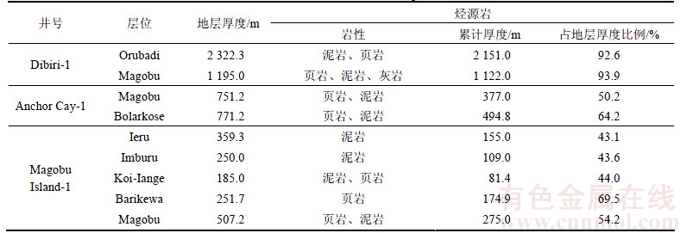
表2 巴布亚盆地烃源岩地球化学特征
Table 2 Geochemistry characteristics of hydrocarbon source rocks of Papuan basin
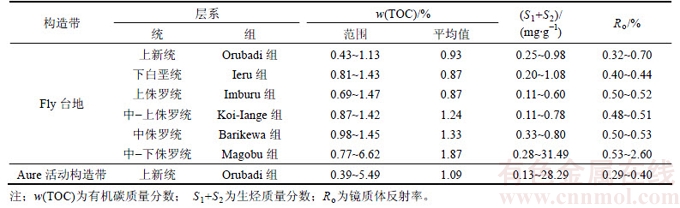
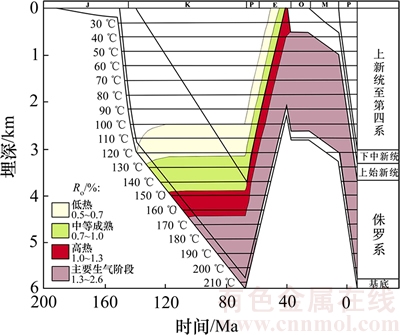
图9 Dibiri-1井埋藏史和热史图
Fig. 9 Burial history and thermal history of Dibiri-1
该井区中—上侏罗统主力烃源岩在白垩纪早期进入早成熟阶段,Ro范围为0.5%~0.7%;在白垩纪中晚期,已全部进入成熟—高成熟阶段,Ro范围为0.7%~1.3%,部分烃源岩进入过成熟阶段,Ro范围大于1.3%;在上升剥蚀时期(白垩纪晚期至始新世晚期)与沉积间断期(渐新世),该井区主力烃源岩的成熟度变化不明显;在渐新世末期至现今,盆地又恢复下降,接受沉积,该井区主力烃源岩全部进入过成熟阶段,Ro范围为1.3%~2.6%。
2.2 构造演化对圈闭的控制
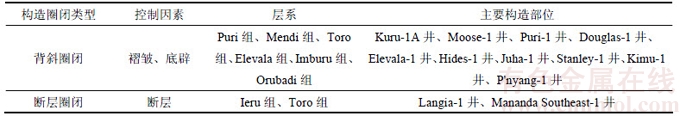
受多期构造影响,Papuan褶皱带和Aure活动构造带主要发育逆冲挤压推覆褶皱,构造样式主要是基底卷入型和盖层滑脱型;Fly台地西部构造不太发育,可能存在一些低幅断块构造;盆地东部台地边缘发育生物礁及部分浊积体。在构造演化控制下,盆地主要发育以下2类构造圈闭(见表3):
1) 背斜圈闭,为盆地主要的圈闭类型,其中Juha-1井、Hides-1井等圈闭与Papuan褶皱带的逆冲推覆构造活动有关,自晚白垩世以来,一直受到挤压应力影响,在此背景下形成的挤压背斜圈闭是该区最有利的油气聚集区; Elevala-1井、Stanley-1井等圈闭的形成受Fly台地地区底辟拱升影响,在以广泛分布的泥页岩为塑性层与其上下的刚性灰岩和基底组成的“三明治”式地层结构上,发育底辟拱升背斜圈闭,Orubadi组厚度大,分布广,为该区域主要的盖层,Imburu组为局部盖层。
2) 断层圈闭,主要分布在Papuan褶皱带及Fly台地北部,其中Papuan褶皱带受晚中新世盆地北部俯冲带活动影响,因强烈挤压而变形、遭受剥蚀,基底冲断层发育,发育大量逆掩断层,以断层圈闭为主,为油气成藏提供了良好的先决条件;Ieru组多为泥岩,为该区域提供了良好的封盖条件,局部盖层为Toro组。
2.3 分布规律
从控制因素分析,控制本区中生界油气分布和富集的重要因素为构造圈闭与断裂的共同作用,而控制本区新生界油气分布和富集的重要因素为构造与地层作用。Papuan褶皱带和Aure活动构造带主要发育逆冲挤压推覆褶皱,构造样式主要是基底卷入型和盖层滑脱型;Fly台地西部构造不太发育,可能存在一些低幅断块构造;盆地东部台地边缘新生界发育生物礁及部分浊积体。从已发现的油气藏类型统计结果可知[17-22]:盆地内已发现的油气藏类型主要是构造油气藏(背斜油气藏)(表3),因此,巴布亚盆地中生界油气藏分布受构造控制明显,大的油气藏发现主要集中在Papuan褶皱带及Aure活动构造带。该区带圈闭条件好,烃源岩成熟度高,油气富集,是盆地的勘探重点区。盆地新生界油气藏分布受构造与地层的共同控制,该时期形成的碳酸盐岩生物礁油气藏也具有较大潜力。
表3 巴布亚盆地构造圈闭类型
Table 3 Trap types of Papuan basin
根据以上综合分析,将油气成藏模式归结为古生新储—垂向排烃—多期次成藏,即本区中生界(Ieru组、Toro组、Imburu组等)油气主要来自下部主力烃源区中、上侏罗统烃源岩(Barikewa组、Magobu组、Koi-Iange组等),通过白垩纪中晚期长期生烃、排烃,沿不整合面及断裂垂向运移至中生界Ieru组、Toro组等圈闭中,在白垩纪晚期、新近纪晚期聚集成藏;本区新生界(Darai组、Puri组等)油气主要来自下部主力烃源区中、上侏罗统烃源岩,Orubadi组为主要盖层,通过白垩纪中晚期长期生、排烃,沿不整合面及断裂垂向运移至新生界Darai组、Puri组等生物礁与构造圈闭中,在更新世中晚期聚集成藏,见图10。
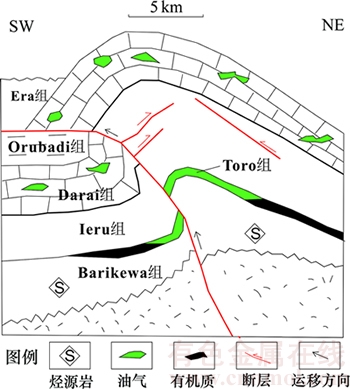
图10 巴布亚盆地油气成藏模式示意图(根据Paua-1X井)
Fig. 10 Diagram of hydrocarbon accumulation model of Papuan Basin (according to Paua-1X)
3 结论
1) 巴布亚盆地东西部构造差异明显,西部地区广泛分布中生代地层,在东部地区中生代地层呈残洼分布,巨厚的新生代沉积物覆盖在中生代残洼之上,自西向东,沉积中心发生迁移;纵向上,自北东向南西挤压强度变弱,构造分带明显,以冲断带、褶皱带为主,局部分布背斜、断鼻、断块构造等。
2) 巴布亚盆地经过四期多旋回的构造演化,即陆内裂谷阶段、冈瓦纳大陆裂解阶段、珊瑚海扩张阶段、美拉尼西亚岛弧碰撞阶段,这使得盆地自晚古生代以来,沿塔斯曼造山带东西两侧出现明显的构造差异,这一点明显控制了盆地形态及含油气系统,奠定了现今的构造格局。
3) 构造演化对该区油气成藏条件有明显的控制作用,首先多期的构造运动控制烃源岩的发育,在盆地冈瓦纳裂解阶段,盆地大部分地区处于沉积中心,沉积了盆地的主力烃源岩Imburu组、Koi-Iange组、Barikewa组及Magobu组等;其次,在构造演化的控制下,盆地主要发育了背斜圈闭和断层圈闭,其中Papuan褶皱带和Aure活动构造带发育的大量构造圈闭是盆地的勘探重点。总结出古生新储-垂向排烃-多期次成藏的成藏模式,可为该区下一步勘探提供指导。
参考文献
[1] IHS Energy Group. Basin monitor, Papua basin, Papua New Guinea[R]. Englewood, Colorado, 2010: 2-5.
[2] HILL K C. Structure of the Papuan Fold Belt[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 1991, 75(5): 857-872.
[3] 骆宗强, 阳怀忠, 刘铁树, 等. 巴布亚盆地构造差异演化及其对油气成藏的控制[J]. 中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(S1): 143-145.
LUO Zongqiang, YANG Huaizhong, LIU Tieshu, et al. Distinct tectonic evolutions and its effect on hydrocarbon accumulation of the Papuan Basin[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2012, 37(S1): 143-145.
[4] 陈书平, 汤良杰, 张一伟. 前陆、前陆盆地和前陆盆地系统[J]. 世界地质, 2001, 20(4): 332-338.
CHEN Shuping, TANG Liangjie, ZHANG Yiwei. Foreland basin and Foreland basin system[J]. Global Geology, 2001, 20(4): 332-338.
[5] 陈国达. 地洼学说的理论结构和发展纲领[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1991, 15(4): 273-290.
CHEN Guoda. Theoretic construction and developmental program of the theory of activated (geodepression or Diwa) tectonics[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1991, 15(4): 273-290.
[6] CRAIG M S, WARVAKAI K. Structure of an active foreland fold and thrust belt, Papua New Guinea[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2009, 56(5): 719-738.
[7] COLE J P, PARISH M, SCHMIDT D. Sub-thrust plays in the Papuan Fold Belt: the next generation of exploration targets[C]// BUCHANAN P G,GRAINGE A M,THORNTON R C N. Papua New Guinea’s Petroleum Industry in the 21st Century: Proceedings of Fourth PNG Petroleum Conference. Port Morseby, PNG: PNG Chamber of Mines and Petroleum, 2000: 87-100.
[8] HILL K C, RAZA A. Arc-continent collision in Papua Guinea: constraints from fission track thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 1999, 18(6): 950-966.
[9] HILL K C, KEETLEY J T, KENDRICK R D, et al. Structure and hydrocarbon potential of the New Guinea Fold Belt[C]// MCCLAY K R. AAPG Memoir 82: Thrust Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Systems. New York, America: AAPG Special Publication, 2004: 494-528.
[10] 杨磊, 康安. 巴布亚盆地安特洛普生物礁气田地质特征和成礁模式[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2011, 32(2): 207-208.
YANG Lei, KANG An. Geological characteristics and reef-forming pattern of antelope reef gas field in Papua Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2011, 32(2): 207-208.
[11] DIREEN N G, CRAWFORD A J. The Tasman line: where is it, what is it, and is it Australia’s Rodinian breakup boundary[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2003, 50(4): 491-502.
[12] NORVICK M S, SMITH M A, POWER M R. The plate tectonic evolution of Eastern Australasia guided by the stratigraphy of the Gippsland Basin[C]// HILL K C, BERNECKER T. Eastern Australasian Basins Symposium, A Refocussed Energy Perspective for the Future. Melbourne, Australasia: Petroleum Exploration Society of Australia Special Publication, 2001: 15-23.
[13] SUTHERLAND R, KING P, WOOD R. Tectonic evolution of Cretaceous rift basins in south-eastern Australia and New Zealand: Implications for exploration risk assessment[C]// HILL K C, BERNECKER T. Eastern Australasian Basins Symposium, A Refocussed Energy Perspective for the Future. Melbourne, Australasia: Petroleum Exploration Society of Australia Special Publication, 2001: 3-13.
[14] HOME P C, DALTION D G, BRANNAN J. Geological evolution of the western Papuan Basin[C]// CANMAN G J, CARMAN Z. Petroleum Exploration in Papua New Guinea: Proceedings of the First PNG Petroleum Convention. Port Moresby, PNG: PNG Petroleum Association, 1990: 107-118.
[15] GURNIS M, MORESI L, MULLER R D. Models of mantle convection incorporating plate tectonics: the Australian region since the Cretaceous[C]// RICHARDS M A, GORDON R G, VAN DER HILST R D. The History and Dynamics of Global Plate Motions: Geophysical Monograph. Washington D C, America: American Geophysical Union, 2001: 211-238.
[16] VAN WYCK N, WILLIAMS I S. Age and provenance of basement metasediments from the Kubor and Bena Bena blocks, east Central Highlands, Papua New Guinea-constraints on the tectonic evolution of the northern Australian cratonic margin[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2002, 49(3): 565-577.
[17] 斯图尔特W D, 杜凯E F, 熊琦华. 巴布亚盆地的石油潜力[J]. 国外油气勘探, 1986(6): 18-19.
STEWART W D, DURKE E F, XIONG Qihua. Petroleum potential of Papuan basin[J]. Oil and Gas Prospecting Abroad, 1986(6): 18-19.
[18] 郭建华, 旷理雄, 朱锐, 等. 湘中涟源凹陷杨家山地区下石炭统天然气成藏条件[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 39(1): 180-181.
GUO Jianhua, KUANG Lixiong, ZHU Rui, et al. Gas accumulation conditions of Lower Carboniferous in Yangjiashan region of Lianyuan Sag[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2008, 39(1): 180-181.
[19] 龚承林. 北波拿巴盆地及典型被动大陆边缘深水盆地构造演化及层序地层学研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学海洋与地球学院, 2009: 90-94.
GONG Chenglin. The tectonic evolution and sequence stratigraphy research of northern Bonaparte basin and typical passive margins deep-water basin[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University. College of Ocean and Earth, 2009: 90-94.
[20] 崔金栋, 郭建华, 李群. 塔河油田S75井区卡拉沙依组沉积特征与演化[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(4): 1579-1596.
CUI Jindong, GUO Jianhua, LI Qun. Sedimentary characteristics and evolution of Kalashayi Formation of S75 Well Field in Tahe Oil field[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(4): 1579-1596.
[21] 黄太柱, 蒋华山, 马庆佑. 塔里木盆地下古生界碳酸盐岩油气成藏特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(6): 781-787.
HUANG Taizhu, JIANG Huashan, MA Qingyou. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics in Lower Paleozoic Carbonate reservoirs of Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(6): 781-787.
[22] 黎彩凤, 旷理雄, 郭建华, 等. 巴布亚盆地中上侏罗统烃源岩油气地球化学特征研究[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 13(7): 13-16.
LI Caifeng, KUANG Lixiong, GUO Jianhua, et al. Geochemical characteristics and evaluation of middle-upper Jurassic hydrocarbon source rock in Papuan Basin[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 13(7): 13-16.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2016-12-20;修回日期:2017-03-06
基金项目(Foundation item):国家科技重大专项(2011ZX05030-002-005) (Project(2011ZX05030-002-005) supported by the Major Project of National Science and Technology)
通信作者:郭建华,博士,教授,从事沉积学、储层地质学及层序地层学研究;E-mail: gjh796@csu.edu.cn