强磁场下亚共晶Al-Cu合金初生相形核与生长行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2012年第z1期
论文作者:李传军 任忠鸣 任维丽 武玉琴
文章页码:1 - 6
关键词:Al-Cu合金;强磁场;形核;过冷;差热分析
Key words:Al-Cu alloy; high magnetic field; nucleation; undercooling; differential thermal analysis
摘 要:应用差热分析法研究了强磁场下Al-20.8%Cu(质量分数)亚共晶合金初生相形核与生长特性。差热分析曲线表明,初生相的形核温度随磁场强度的增大而降低,其生长速率则随磁场强度增大而增大。初生相枝晶由无磁场时无序生长转变为磁场下规则生长。研究表明,10 T量级的磁场对Al晶体形核驱动力的影响可以忽略,初生相形核温度的降低主要归结为磁场下固液界面自由能的增加。枝晶形貌转变则源于磁场对熔体流动的抑制及铝晶体的磁各向异性。
Abstract: The nucleation and growth behaviors of primary Al phase in the hypoeutectic alloy of Al-20.8%Cu (mass fraction) in high static magnetic fields were investigated by differential thermal analysis (DTA). The DTA curves indicate that the nucleation temperature of primary Al phase decreases as the magnetic induction increases. The average growth rates of primary crystals increase with the increase of magnetic induction. The dendrite structures show that primary Al phase dendrites change from disorderly without the magnetic field to regularly with the field. The effect of magnetic field with the magnetic induction order of 10 T on driving force for the nucleation of Al crystals is negligible. The reduction of nucleation temperature of primary Al phase is mainly caused by the increase of the interfacial free energy between the melt and the nucleus. The change in dendrite morphology can be attributed to the suppression of melt flows in the magnetic field and magnetic anisotropy of Al crystals.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s1-s6
LI Chuan-jun1, REN Zhong-ming1, REN Wei-li1, WU Yu-qin2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China;
2. College of Electromechanical Engineering, Wuhan Textile University, Wuhan 430073, China
Received 9 July 2012; accepted 3 August 2012
Abstract: The nucleation and growth behaviors of primary Al phase in the hypoeutectic alloy of Al-20.8%Cu (mass fraction) in high static magnetic fields were investigated by differential thermal analysis (DTA). The DTA curves indicate that the nucleation temperature of primary Al phase decreases as the magnetic induction increases. The average growth rates of primary crystals increase with the increase of magnetic induction. The dendrite structures show that primary Al phase dendrites change from disorderly without the magnetic field to regularly with the field. The effect of magnetic field with the magnetic induction order of 10 T on driving force for the nucleation of Al crystals is negligible. The reduction of nucleation temperature of primary Al phase is mainly caused by the increase of the interfacial free energy between the melt and the nucleus. The change in dendrite morphology can be attributed to the suppression of melt flows in the magnetic field and magnetic anisotropy of Al crystals.
Key words: Al-Cu alloy; high magnetic field; nucleation; undercooling; differential thermal analysis
1 Introduction
Metal solidification in a high magnetic field is an interesting field for the study with the development of magnet technologies. It is well known that the high magnetic field not only changes the flow of electronically conducting melts like damping convection [1] and inducing thermoelectric magnetic convection [2], but also distinctly influences solidification behaviors of metallic alloys such as solute distribution [3], solidification rate [4], crystallographic orientation [5] and dendrite morphology [6].
The nucleation and growth are two most fundamental processes during metal solidification. Some studies showed the effect of the magnetic field on the nucleation of crystals. ESIN et al [7] observed that the average undercooling of liquid tin increased in the magnetic field with magnetic induction of 2 T. AOKI et al [8] found that the external magnetic field enhanced the nucleation of grains in Zn-Cu alloys. HASEGAWA and ASAI [9] experimentally demonstrated that the maximum undercooling of copper melt in glass slag in the magnetic field with magnetic induction of 0.5 T was higher than that without the magnetic field. Recently, ZHANG et al [10] compared the change in undercooling of pure copper and germanium melt in the high magnetic field and found that undercooling of Cu melt increased but liquid Ge did not show noticeable change. LIU et al [11] investigated the nucleation behaviors of Ni-Cu alloy and pure Sb in external magnetic field and found that undercooling of two melts increased and grains were refined. Additionally, some studies also showed that the external magnetic field changed the growth behaviors of alloys. AOKI et al [12] indicated that the magnetic field with magnetic induction of 3.5 T suppressed the development of primary Al phase dendrites in the hypoeutectic Al-Si alloy. The above studies convincingly demonstrated that the external magnetic field changed the nucleation and growth behaviors of metallic alloys. However, the mechanism for the changes of nucleation and growth in the magnetic field is still unclear and needs further investigation.
In previous work, it was found that the nucleation temperature of pure aluminum decreased with the increase of magnetic induction and proposed that the external magnetic field modified the interfacial free energy and thus lowered the nucleation temperature [13]. In this work, the hypoeutectic alloy of Al-20.8%Cu (mass fraction) was chosen and the differential thermal analysis (DTA) was used to examine the nucleation temperature and growth rates of primary phase in the magnetic field. The physical mechanisms of nucleation and growth behaviors of primary phase in the magnetic field were further discussed.
2 Experimental
The experimental apparatus mainly consisted of superconducting magnet, 2700 multimeter/data acquisition system, programming controller and DTA apparatus. The magnet with cylindrical core with inner diameter of 98 mm can produce a vertical static magnetic field up to 14 T. The DTA apparatus was depicted in detail in previous publication [14].
The hypoeutectic alloy of Al-20.8%Cu used in this work was prepared with aluminum and copper of 99.99% purity. The alloy was melted in induction furnace in argon atmosphere and cast into ingots, from which cylindrical samples with size of d 4 mm × 4 mm for DTA runs were obtained by wire cutting. The samples were ultrasonically cleaned with powerful acetone before DTA runs in order to get rid of contaminant of their surface. In experiments, the sample in the DTA apparatus was placed in the center of the magnet. The samples were heated to a given temperature of 700 °C above melting point at the rate of 10 °C/min, held for 20 min and subsequently cooled to the room temperature at the constant cooling rate of -5 °C/min. In DTA runs, the furnace chamber was fluxed with high-purity argon in order to reduce the oxidation of samples during runs. These measurements under the same conditions were repeatedly carried out more than three times using different samples in order to confirm the reproducibility. The relating parameters like melting temperature and nucleation temperature can be obtained from DTA runs.
The post-treated samples were sectioned along the radial and axial directions. The longitudinal and transversal microstructures were examined with optical microscope and scanning electronic microscope after polishing and etching. The crystallographic orientation was examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Cu Kα.
3 Results and discussion
In order to observe the nucleation and growth behaviors of primary phase in the hypoeutectic alloys of Al-20.8%Cu with and without the magnetic field, DTA experiments were carried out. Figure 1 shows DTA curves for the solidification of the alloy at a cooling rate of -5 °C/min in various magnetic fields. Since the alloy is off-eutectic, the right exothermic peak originates from the precipitation of primary Al phase and the left one denotes the crystallization of Al-Al2Cu eutectics on each curve. Here, only right exothermic peaks were investigated, indicating the nucleation temperature tn and peak temperature tp of primary Al phase.
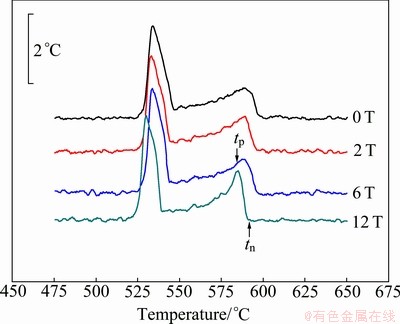
Fig. 1 DTA curves for hypoeutectic alloy of Al-20.8%Cu at cooling rate of -5 °C/min
The related parameters for the solidification of the hypoeutectic alloy obtained from DTA experiments are listed in Table 1. It is found that the nucleation temperature tn for primary Al phase in the Al-20.8%Cu alloy slightly decreases in low magnetic fields, such as magnetic induction of 2 and 6 T in comparison with that in the zero field. However, the value markedly shifts to a lower temperature in the magnetic induction of 12 T. This means that the external magnetic field retards the nucleation of primary α-Al phase in the process of solidification of the alloy. Moreover, the higher the magnetic induction is, the lower the nucleation temperature is. Additionally, the quantity (tn-tp), which is a measure of the average growth rate [15], decreases with the magnetic induction. Therefore, growth rates of primary Al phase increase in the magnetic field.
Table 1 Parameters obtained from DTA runs for Al-20.8%Cu alloys at cooling rate of -5 °C/min
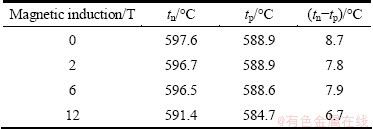
Figure 2 indicates the dendrite morphology on different sections in the Al-20.8%Cu alloy in various magnetic fields. In the absence of a magnetic field, primary dendrites disorderly distribute in the eutectic matrix and the majority of dendrites show a seaweed-like pattern as displayed in Figs. 2(a) and (b). While applying the magnetic field with magnetic induction of 6 T, a part of dendritic structures become regular, as shown in Figs. 2(c) and (d). Namely, the secondary dendrite arms grow perpendicularly to primary dendrite arms. In the magnetic field with magnetic induction of 12 T, dendrites structures are most regular as displayed in Figs. 2(e) and (f). In addition, it is found that the orientation of primary Al phase dendrites occurs in magnetic fields. Especially, primary dendrite arms regularly give a tilt angle to the direction of magnetic field with magnetic induction of 12 T in comparison with disorganized dendrites without a magnetic field. Figure 3 displays XRD patterns of the Al-20.8%Cu alloy on longitudinal and transversal sections without and with the magnetic field of 12 T. The diffraction intensity of the (111) direction of Al crystals significantly increases at magnetic induction of 12 T compared with that at 0 T. Hence, the external magnetic field induced crystallographic orientation of primary α(Al) crystals and the <111> direction oriented along the magnetic field.
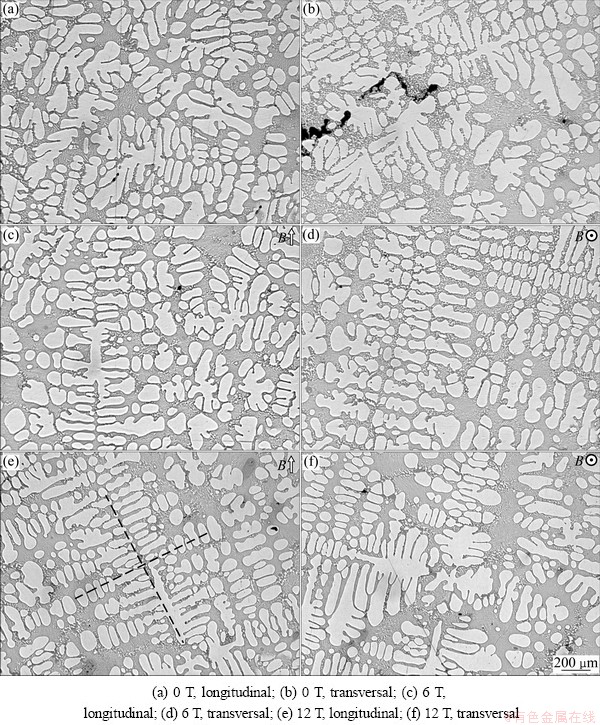

Fig. 3 Microstructures of Al-20.8%Cu hypoeutectic alloy on different sections
These experimental results demonstrate that the external magnetic fields lower the nucleation temperature, accelerate the growth rate and alter the dendritic structures of primary Al phase in the Al-20.8%Cu alloy.
In classical nucleation theory, the activation energy △G* for the nucleation can be expressed as:
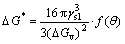 (1)
(1)
where ysl and △Gv denote the interfacial free energy and difference in Gibbs free energy between solid and liquid phases, respectively; f(θ) is the catalytic factor and read as f(θ)=1/4(2-3cosθ +cos3θ); θ is the wetting angle.

Fig. 3 XRD patterns of Al-20.8%Cu alloy on longitudinal (a) and transversal (b) sections
In order to explore the effect of the magnetic field on the nucleation, the change of parameters in Eq. (1) under the action of magnetic field must be reexamined. Since the wetting angle varies the interfacial energy for the same materials, provided that the catalytic factors are equal for the same materials regardless of the magnetic field, the conclusion on the magnetic field effect from Eq. (1) is not altered. Thus, the effect of magnetic field on interfacial energy and Gibbs free energy is discussed below.
The difference in Gibbs free energy is the driving force for the nucleation while the interfacial free energy is the resistive force for the nucleation. The ability of the nucleation for a given substance depends on the two physical parameters. There have been a great many reports showing that the external magnetic field significantly changes Gibbs free energy of ferromagnetic phase and thus leads to the change in the equilibrium transition point and the shift of phase boundary [16]. This is because the magnetic energy induced by the magnetic field is so large that it may compare with thermal energy in the same order of magnitude. For example, the magnetic field with magnetic induction of 1 T alters Gibbs free energy per atom in iron by about the same amount as the temperature by 1 K. However, some studies demonstrate that the magnetic energy is rather feeble for non-magnetic materials and hardly changes its phase transformation point [17]. Herein, the magnetic energy and thermal Gibbs free energy may be compared. The former is written as -μ0(χl-χs)H2/2, where χ is the magnetic susceptibility and superscripts s and l denote solid and liquid phases, respectively, H is the magnetic induction, and μ0 is the vacuum permeability. For solid and liquid Al phases, the difference of magnetic susceptibilities is 2.1×10-13 m3/mol at melting point [18]. The contribution of magnetic energy to Gibbs free energy is 1.2×10-5 J in the magnetic field with magnetic induction of 12 T. Nevertheless, the difference of thermal Gibbs free energy between solid and liquid phases is 5.4 J when the melt is undercooled to 0.5 °C below equilibrium temperature according to the thermodynamic data [19]. The magnetic energy is only about 2×10-6 of thermal Gibbs free energy. Indeed, the effect of magnetic field with the order magnetic induction of 10 T on Gibbs free energy of non-magnetic Al crystal is much feeble and hardly changes activation energy for the nucleation.
Hence, the reduction of nucleation temperature in a magnetic field is probably due to the change in interfacial free energy between the melt and the nucleus. In reality, there are studies showing that the external magnetic field can change the interfacial energy. FUJIMURA and IINO [20] found that the surface tension of water increased linearly with the suqare of the magnetic field and the value increased by about 1.8% at 10 T. LI et al [21] applied the ring method to measure the surface tension of actone and found that the surface tension linearly increased with external magentic field. Although those findings focused on the magnetic field effect on the surface tensions of liquids at room temperature, they suggested that the magentic field significantly modified the interfacial energy of non-magnetic substances. From the view of interfacial structure, the solid-liquid interface generally includes multilayer atoms. The thicker the solid-liquid interface is, the smaller the interfacial energy is. It is reasonably inferred that liquid atoms near solid-liquid interface hardly attch themselves to nucleus due to spiral movement under the action of Lorentz force and thus the solid-liquid interface is smoother [13]. In this case, liquid atoms need more energy to migrate from liquid to solid phase. Therefore, the melt is undercooled to a lower temperature to provide a larger driving force. This is testified by the reduction of nucleation temperature in the magetic field. Certainly, the mechanism of change in interfacial energy in the magnetic field needs further investigation and is now in progress.
The driving force for dendrite growth is determined by the melt undercooling △t. In general, the relationship between the solidification rate v and undercooling △t is described as follows [22]:
v∝(△t)β (2)
where β is a constant. Equation (2) indicates the exponent relationship between v and △t. From Table 1, parameter (tn-tp ) decreases with increasing a magnetic field. This means that the average growth rate of primary α-Al crystals increases with the increase of undercooling in a magnetic field. Thus, the relationship between v and △t in a magnetic field still seems to qualitatively obey Eq. (2). Therefore, it is difficult to determine the effect of magnetic field on the growth rate of Al crystals at present in the case of the lack of the exact data of growth rates.
Additionally, it is well known that the dendrite morphology is markedly influenced by melt flows. In the absence of a magnetic field, the temperature gradient and concentration gradient in the melt might produce natural convection in the melt which causes dendrites to grow disorderly during the solidification. Hartmann number Ha=BL(σ/η)-1/2 is used to characterize the suppression effect (Ha is Hartmann number, B is the magnetic induction, L is the characteristic length, σ and η are electrical conductivity and viscosity, respectively). If Ha is much larger than unity, the convection of the melt is thought to be suppressed. One may calculate the Hartmann number in the work by adopting the following parameters: B=12 T, L=4 mm, σ=1×106/(W·m), η=1 mPa×s. In the presence of 12 T, Ha is 1500. The value will be far larger than unity. This means that the convection of the melt will be suppressed in the case of 12 T. Since the convection of the melt is suppressed and the crystal growth mainly depends on heat flow, the effect results in the regular growth of dendrites as shown in Fig. 2. For the growth orientation of primary dendrite, this is because the <111> direction of Al crystals is the easy magnetization direction. The imposition of the magnetic field induces the <111> direction of Al crystals to orient along the direction of a magnetic field. The magnetic suppression of the convection and the magnetic anisotropy of Al crystals lead to regular dendrites and crystallographic orientation.
4 Conclusions
1) The nucleation and growth characteristics of primary phase in the hypoeutectic alloy of Al-20.8%Cu in magnetic fields were explored by differential thermal analysis. The nucleation of primary Al crystals becomes more difficult and the average growth rate increases in magnetic fields. Although the effect of the magnetic field with the magnetic induction order of 10 T on the driving force for the nucleation is neglected, the increase of solid-liquid interfacial free energy in the magnetic field makes the nucleation more difficult and thus nucleation temperature is lowered.
2) Solidified structures show that dendrites grow from disorderly without a magnetic field to orderly with a magnetic field and the <111> direction of Al crystals orients along the magnetic field. The change in dendritic morphology is due to the suppression of the convection in a magnetic field and magnetic anisotropy of Al crystals.
References
[1] CHANDRASEKHAR S, XLV I. On the inhibition of convection by a magnetic field [J]. Philosophical Magazine Series 7, 1952, 43: 501-532.
[2] MOREAU R, LASKAR O, TANAKA M, CAMEL D. Thermoelectric magnetohydrodynamic effects on solidification of metallic alloys in the dendritic regime [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1993, 173: 93-100.
[3] YOUDELIS W V, DORWARD R C. Directional solidification of aluminum-copper alloys in a magnetic field [J]. Canadian Journal of Physics, 1966, 44: 139-150.
[4] KISHIDA Y, TAKEDA K, MIYOSHINO I, TAKEUCHI E. Anisotropic effect of magnetohydrodynamics on metal solidification [J]. ISIJ International, 1990, 30: 34-40.
[5] MIKELSON A E, KARKLIN Y K. Control of crystallization processes by means of magnetic fields [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1981, 52: 524-529.
[6] UHLMANN D R, SEWARD T P, CHALMERS B. The effect of magnetic fields on the structure of metal alloys castings [J]. Transactions of the Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1966, 236: 527-531.
[7] ESIN V O, PANKIN G N, KORSHUNOV I P, RYABINKIN A M. Effect of a constant magnetic field on the supercooling [J]. Rasplavy, 1988, 1: 102-104.
[8] AOKI Y, HAYASHI S, KOMATSU H. The effect of magnetic field on crystallization of γ-phase alloy in the Cu-Zn system [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1991, 108: 121-128.
[9] HASEGAWA M, ASAI S. Effects of static magnetic field on undercooling of a copper melt [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1992, 27: 6123-6126.
[10] ZHANG Y K, ZHOU Y L, GAO J R, HE J C. Undercooling of pure Cu and Ge melts in a static magnetic field [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2010, 649: 281-286.
[11] LIU Tie, WANG Qiang, LIU Feng, LI Guo-jian, HE Ji-cheng. Nucleation behavior of bulk Ni–Cu alloy and pure Sb in high magnetic fields [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2011, 321: 167-170.
[12] AOKI Y, HAYASHI S, KOMATSU H. Directional solidification of aluminium-silicon eutectic alloy in a magnetic field [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1983, 62: 207-209.
[13] LI Chuan-jun, YANG Hui, REN Zhong-ming, REN Wei-li, WU Yu-qin. On nucleation temperature of pure aluminum in magnetic fields [J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research Letters, 2010, 15: 45-52.
[14] LI Chuan-jun, REN Zhong-ming, REN Wei-li, DENG Kang, CAO Guang-hui, ZHONG Yun-bo, WU Yu-qin. Design and application of differential thermal analysis apparatus in high magnetic fields [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2009, 80: 073907-5.
[15] CHEN C, FEI B, PENG S, ZHUANG Y, DONG L, FENG Z. Nonisothermal crystallization and melting behavior of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) and maleated poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) [J]. European Polymer Journal, 2002, 38: 1663-1670.
[16] GAO M C, BENNETT T A, ROLLETT A D, LAUGHLIN D E. The effects of applied magnetic fields on the α/γ phase boundary in the Fe–Si system [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2006, 39: 2890-2896.
[17] MAGOMEDOV M N. On the magnetic-field-induced changes in the parameters [J]. Technical Physics Letters, 2002, 28: 116-118.
[18] TERZIEFF P,  R. Magnetic investigations in liquid Al–In [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2003, 360: 205-209.
R. Magnetic investigations in liquid Al–In [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2003, 360: 205-209.
[19] DINSDALE A T. SGTE data for pure elements [J]. Calphad, 1991, 15: 317-425.
[20] FUJIMURA Y, IINO M. The surface tension of water under high magnetic fields [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 103: 124903.
[21] LI Chuan-jun, CHEN Long, REN Zhong-ming. Application of ring method to measure surface tensions of liquids in high magnetic field [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83: 043906-5.
[22] LIPTON J, KURZ W, TRIVEDI R. Rapid dendrite growth in undercooled alloys [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1987, 35: 957-964.
李传军1,任忠鸣1,任维丽1,武玉琴2
1. 上海大学 材料科学与工程学院,上海 200072;
2. 武汉纺织大学 机械工程与自动化学院,武汉 430073
摘 要:应用差热分析法研究了强磁场下Al-20.8%Cu(质量分数)亚共晶合金初生相形核与生长特性。差热分析曲线表明,初生相的形核温度随磁场强度的增大而降低,其生长速率则随磁场强度增大而增大。初生相枝晶由无磁场时无序生长转变为磁场下规则生长。研究表明,10 T量级的磁场对Al晶体形核驱动力的影响可以忽略,初生相形核温度的降低主要归结为磁场下固液界面自由能的增加。枝晶形貌转变则源于磁场对熔体流动的抑制及铝晶体的磁各向异性。
关键词:Al-Cu合金;强磁场;形核;过冷;差热分析
(Edited by CHEN Wei-ping)
Foundation item: Project (2011CB610404) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project (51001068) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (20110490712) supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation; Project (50911130365) supported by Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges NSFC, China
Corresponding author: REN Zhong-ming; Tel: +86-21-56331102; E-mail: zmren@staff.shu.edu.cn

