文章编号:1004-0609(2015)10-2905-08
焙烧温度对低硅含镁球团矿还原膨胀率的影响及机理
青格勒1, 2,吴 铿1,刘洪松2, 员 晓1,田筠清2
(1. 北京科技大学 钢铁冶金新技术国家重点实验室,北京 100083;
2. 首钢总公司 首钢技术研究院,北京 100043)
摘 要:研究焙烧温度对MgO含量分别为1.5%和3.0%(质量分数)的低硅含镁球团的抗压强度、矿相和还原膨胀率的影响,并基于Arrhenius方程和还原度测定计算低硅含镁球团还原反应的表观活化能,分析还原反应的速率限制性环节。结果表明:当焙烧温度较低时,低硅含镁球团内形成的铁酸镁数量较少,存在未反应的MgO颗粒,其还原过程主要受气体扩散和界面化学反应混合控制,还原膨胀率高,还原后强度低。1280 ℃高温下,焙烧的低硅含镁球团形成的铁酸镁数量多、强度高,还原过程后期主要受固相扩散即铁离子扩散控制,尤其是低硅高镁球团受固相扩散控制更明显,还原过程中未出现针状铁晶粒,还原膨胀率低。
关键词:低硅含镁球团矿;焙烧温度;还原膨胀率;表观活化能
中图分类号:TF533 文献标志码:A
Effect and mechanism of calcination temperature on reduction swelling rate of low silica magnesium pellets
QING Ge-le1, 2, WU Keng1, LIU Hong-song2, YUAN Xiao1, TIAN Yun-qing2
(1. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
2. Shougang Research Institute of Technology, Shougang Group, Beijing 100043, China)
Abstract: The compressive strength, microstructure and reduction swelling rate of low silica magnesium pellets with 1.5% MgO and 3.0% MgO (mass fraction) calcinated at different temperatures were studied. Apparent activation energy of low silica magnesium pellets calcinated at different temperatures was also obtained by Arrhenius formula and reduction test. The rate controlling mechanism of reduction reaction was determined from apparent activation energy together. The results show that, when the calcination temperature is low, few magnesium ferrites form in low silica magnesium pellets and unreacted MgO exists, and the reduction process is controlled mainly by gas diffusion and interfacial chemical reaction, which results in high reduction swelling rate and deteriorates the strength. While calcination temperature increases to 1280 ℃, there forms large amount of magnesium ferrites in pellets and the compressive strength of pellets increase significantly. Later stage of reduction reaction of low silica magnesium pellets (specially the pellets with 3.0%MgO) calcinated at high temperature is mainly controlled by solid diffusion, that is ferric ion solid diffusion, so almost no iron whiskers form, which decreases the pellet swelling rate.
Key words: low silica magnesium pellet; calcination temperature; reduction swelling rate; apparent activation energy
还原膨胀率是球团矿的重要冶金性能指标之一。一般球团矿在还原过程中都会出现体积膨胀、强度相应降低的情况。球团矿体积膨胀不超过一定范围时,高炉可正常生产,但如果球团矿体积超过一定值后,高炉炉内透气性变差,炉尘量显著增加,甚至出现悬料、崩料等问题,将严重影响高炉的正常生产。关于球团矿还原膨胀率问题,国内外进行了大量的研究。ELKASABGY[1]和周取定等[2]研究了碱金属对球团矿还原膨胀行为的影响,认为当球团中存在较多的钾、钠时,在还原过程K+和Na+离子会以置换或填隙的形式渗入到铁氧化物晶格中而引起晶格畸变,导致球团异常膨胀。ILJANA等[3]研究了橄榄石和酸性球团矿在动态和等温条件下的还原膨胀率。其研究结果显示,等温下的球团还原膨胀率比动态条件下的球团还原膨胀率要高,高脉石酸性球团矿抑制还原膨胀能力比橄榄石球团强。CaO、MgO、SiO2和Al2O3可显著降低赤铁矿球团的还原膨胀率,SiO2和MgO在一定程度上能降低磁铁矿球团的还原膨胀率,而CaO和Al2O3则不利于磁铁矿球团还原膨胀率[4-6]。王兆才等[7]研究了还原气氛和脉石成分对氧化球团还原膨胀率的影响。提高球团矿SiO2、MgO含量或在还原气氛中增加H2含量都有利于降低球团矿的还原膨胀率。DWARAPUDI等[8-9]研究了碱度和MgO对赤铁矿球团微观结构和还原膨胀率的影响。研究结果显示,当碱度为0.6时,球团矿的还原膨胀率相对较高;而增加MgO含量后,能形成高熔点液相,抑制其还原膨胀率增加。另外,提高焙烧温度、延长焙烧时间能降低球团矿的还原膨胀率[10-11]。刘牡丹等[12]采用纯物质试验、等温还原法和微观结构分析法研究硫酸钠和碳酸钠对高铝铁矿钠化还原动力学规律的影响。高铝铁矿石还原初期,以硫酸钠为添加剂时,球团内部金属铁晶粒明显,而用碳酸钠为添加剂时,球团内部金属铁晶粒几乎不可见。张建良等[13]研究钒钛球团矿在不同还原温度下的物相组成。朱德庆等[14-15]研究了低品位赤铁矿球团在直接还原过程中成核剂强化还原机理,并通过Arrhenius方程计算了还原反应的表观活化能。在还原温度900~1050 ℃、时间120 min、以CO和N2体积比为30:70的气氛下还原时,无成核剂和成核剂球团都受气体内扩散控制。不同铁矿石的还原过程各阶段控制环节不同。如攀枝花钛精矿在温度为1000~1150 ℃还原时,还原过程受界面化学反应控制,表观活化能为95.25 kJ/mol[16]。红土镍矿还原第一阶段的控速环节是化学反应,第二阶段控速环节是扩散,表观活化能逐渐增大[17]。
球团矿是高炉炼铁的主要原料之一,降低球团矿SiO2等脉石含量对高炉降低渣量和燃料消耗有重要意义。但SiO2含量过低,会引起球团矿的还原膨胀率上升,不能满足高炉入炉要求的问题,SiO2含量2.0%以下的球团矿还原膨胀率达到了60%以上[18],远超过了高炉的要求(20%以下)。国内球团矿的产能已超过了2亿吨,但球团矿的SiO2含量普遍高,基本在4%以上。国内外关于焙烧温度对低硅含镁球团矿还原膨胀率及还原反应活化能的影响方面研究报道较少。本文作者通过焙烧试验、还原试验、微观结构观察及还原过程Arrhenius方程计算,研究焙烧温度对SiO2含量为1.9%的低硅含镁(MgO含量分别为1.5%和3.0%)球团矿还原膨胀率的影响及机理。
1 实验
实验用矿粉是低硅磁铁矿粉,SiO2含量是1.52%(质量分数),品位69.58%。MgO含量(质量分数)的添加采用轻烧后的菱镁石即镁粉,其MgO含量是80.69%。造球过程的粘结剂使用膨润土,配比为0.8%。试验用原料的化学成分见表1。试验时矿粉分别配1.3%和3.2%的镁粉,得到SiO2含量为1.9%,MgO含量分别为1.5%和3.0%的球团矿。本实验中称为1.5%镁球和3.0%镁球,球团矿化学成分见表2。
生球制备是在直径为800 mm的圆盘造球机上进行,造球时间为10 min,造球后筛取直径为10~12.5 mm的生球在120 ℃的烘箱内干燥2 h,然后进行预热和焙烧。预热和焙烧试验采用高温管式电炉。预热温度是950 ℃,预热时间20 min,然后分别在1200、1230、1260、1280和1300 ℃的不同温度下焙烧20 min。球团矿的矿物组成采用X衍射和扫描电镜分析。还原膨胀率测定试验是选取18个直径为10~12.5 mm的焙烧后球团矿,在900 ℃的温度下,用CO和N2混合气体进行还原1 h。混合气体流量为15 L/min,CO和N2体积比为3:7。然后测定还原后的球团矿体积与还原前体积并进行比较,得到还原膨胀率。还原前后球团矿的体积测定采用排汞法。还原试验采用与还原膨胀率试验相同的组成和流量的还原气体还原球团试样3h,记录还原过程的质量损失,然后计算还原度。还原试验温度分别是850、900、950和1000 ℃。
表1 试验用原料化学成分及粒度
Table 1 Chemical compositions and particle size of experimental materials
表2 球团矿的化学成分
Table 2 Chemical compositions of pellets
2 结果与分析
2.1 焙烧温度对低硅含镁球团矿抗压强度的影响
分别在1200、1230、1260、1280和1300 ℃的温度下焙烧了1.5%镁球和3.0%镁球,图1所示为焙烧过程球团矿抗压强度随焙烧温度的变化曲线。从图1可知,当焙烧温度低于1230 ℃时,1.5%镁球和3.0%镁球的抗压强度都比较低,在1700 N/pellet以下。随着焙烧温度的提高,两种球团的抗压强度都提高。当焙烧温度提高到1280 ℃时,抗压强度分别达到了 2848 N/pellet和2613 N/pellet;当焙烧温度为1300 ℃时,抗压强度超过3000 N/pellet。图2所示为不同温度下焙烧后球团矿的SEM像。由图2可知,当焙烧温度为1200 ℃时,1.5%镁和3.0%镁球内产生的铁酸镁和液相很少(见图2(a)和2(b));3.0%镁球内还存在一些未反应的镁粉颗粒,且球团内部结构比较松散,所以抗压强度低。当焙烧温度提高到1280 ℃后,球团内形成的铁酸镁数量增多(见图2(c)和2(d)),尤其是3.0%镁球内产量了大量的铁酸镁。
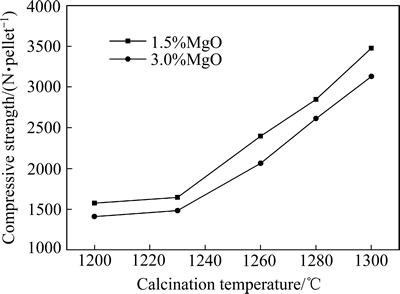
图1 低硅含镁球团矿抗压强度随焙烧温度的变化曲线
Fig. 1 Changing curves of compressive strength of low silica magnesium pellets with calcination temperature
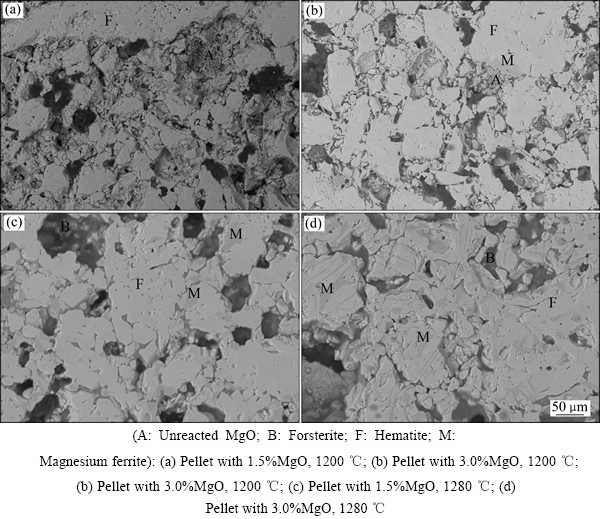
图2 不同温度下焙烧的球团矿SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of pellets calcinated under different temperatures
图3所示为1200和1280 ℃下焙烧的1.5%镁球和3.0%镁球产物的XRD谱。从图3可以看出,焙烧温度较低(即1200 ℃)时,球团内存在未反应的MgO。随着焙烧温度的升高,含镁球团内铁酸镁数量增多。
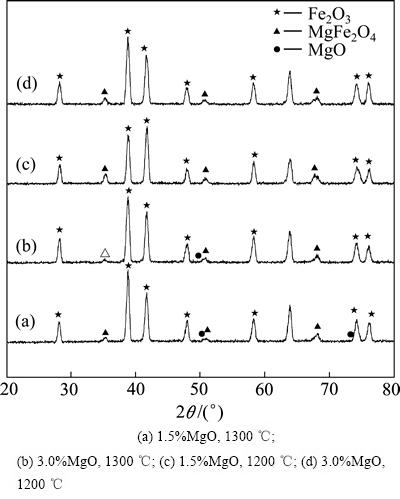
图3 低硅含镁球团不同温度下焙烧产物的XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of low silica magnesium pellets calcinated under different temperatures
2.2 不同温度下焙烧的低硅含镁球团矿的还原膨胀率
图4所示为1.5%镁球和3.0%镁球的还原膨胀率随焙烧温度的变化情况。图5所示为两种球团在900 ℃还原1 h即还原膨胀实验后测定的抗压强度结果。从图4可知,当焙烧温度较低时,即1230 ℃以下时,两种球团的还原膨胀率都比较高,超过45%以上,其中3.0%镁球的还原膨胀率比1.5%镁球的还原膨胀率还要高。随着焙烧温度的提高,还原膨胀率降低。焙烧温度提高到1260 ℃时,3.0%镁球的还原膨胀率降低幅度较大,焙烧温度提高到1280和1300 ℃时,3.0%镁球的还原膨胀率分别下降到18.43%和15.69%,1.5%镁球的还原膨胀率下降到25.28%和24.43%。在高温下焙烧3.0%镁球时,球团内形成的铁酸镁数量多,有利于抑制球团还原过程的膨胀。从还原膨胀后的球团抗压强度结果看,还原膨胀率45%以上时,还原膨胀后球团的抗压强度很低,只有60 N/pellet左右,还原膨胀率25%左右时,还原膨胀后球团抗压强度在300~325 N/pellet,还原膨胀率在20%以下的球团,还原膨胀后的抗压强度较高,达到了432 N/pellet。
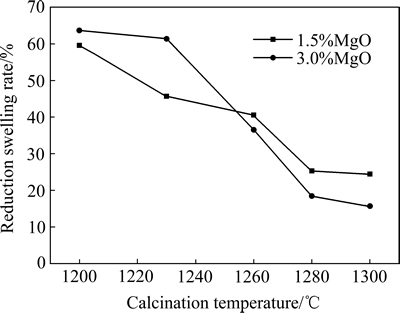
图4 球团还原膨胀率随焙烧温度的变化曲线
Fig. 4 Changing curves of pellet reduction swelling rate with calcination temperature
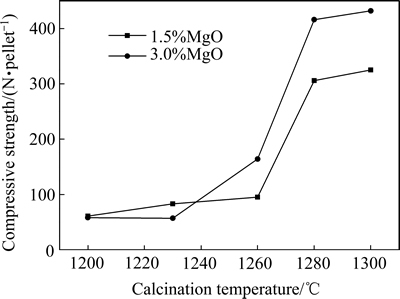
图5 还原膨胀后球团抗压强度随焙烧温度的变化曲线
Fig. 5 Changing curves of compressive strength of pellets with calcination temperature after reduction swelling
2.3 通过表观活化能判断还原反应限制性环节
铁矿球团还原遵循逐级转变,由Fe2O3-Fe3O4- FexO-Fe逐级进行。其中赤铁矿还原成磁铁矿过程是由六方晶系转变成立方晶系,体积增大,新生成的Fe3O4还原成FexO时,体积会再膨胀4%~11%。因此球团矿在还原过程的体积膨胀是不可避免的,但浮氏体还原成铁的过程中若析出大量针状金属铁则会破坏球团的内部结构,体积膨胀率增加,球团强度大幅度下降。浮氏体还原过程符合未反应核模型,其还原过程可认为受3个环节限制,即界面化学反应控制、铁离子扩散控制和两者混合控制。如果还原过程受界面化学反应控制,则铁离子扩散快,容易引起球团在还原过程的异常膨胀。
利用Arrhenius公式计算化学反应的表观活化能(Ea),判断化学反应限制性环节是研究化学反应动力学的常用方法之一。Arrhenius公式为
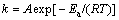 (1)
(1)
假设球团矿的还原反应是n级化学反应,其反应速率公式为
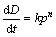 (2)
(2)
联立式(1)和(2)可得
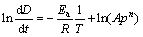 (3)
(3)
由上式可计算出化学反应表观活化能Ea:
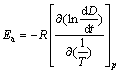 (4)
(4)
式中:k为化学反应速率常数,单位与反应级数有关;A为指前因子,单位与速率常数相同;Ea为反应表观活化能,J/mol;T为温度,K;D为还原度,%;t为时间,min;p为还原气体分压,kPa;R为摩尔气体常数;n为化学反应级数。
为了分析在不同温度下焙烧低硅含镁球团时,其还原过程中限制性环节,选择在1200和1280 ℃下焙烧的1.5%镁球和3.0%镁球进行了不同温度下的还原试验,还原温度分别是850、900、950、1000 ℃。还原气体组成和流量与还原膨胀率试验一致。图6所示为4种球团矿在不同温度下的还原度曲线。
图7中的阿雷尼乌斯曲线反映了化学反应速率ln(dD/dt)与不同还原度(10%、30%、50%)下温度倒数(1/T)之间的关系。从图7可见,随着还原温度的提高,还原反应速率逐渐提高,且随着还原度的提高,还原速率逐渐变缓。在同一还原度下,还原反应速率的对数ln(dD/dt)与温度的倒数1/T之间呈线性下降关系。
表3所列为根据图7阿雷尼乌斯曲线的斜率计算得到的不同还原度下的反应表观活化能。表4所列为国外研究者给出的反应活化能值与反应速率控制环节间的对应关系[19]。
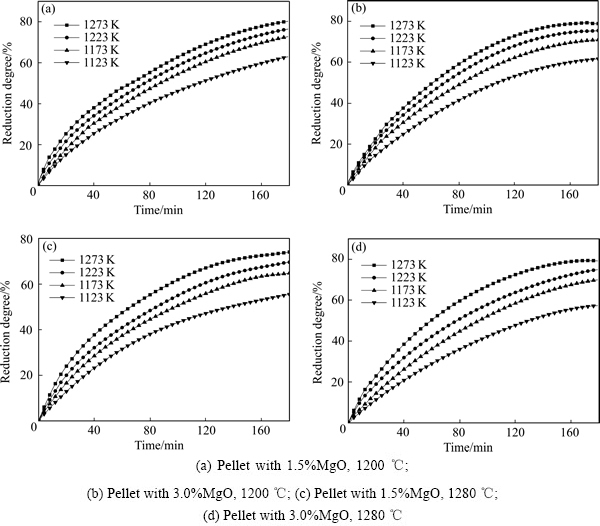
图6 不同还原温度下还原度与还原时间的关系
Fig. 6 Relationship between reduction degree and reduction time at different temperatures
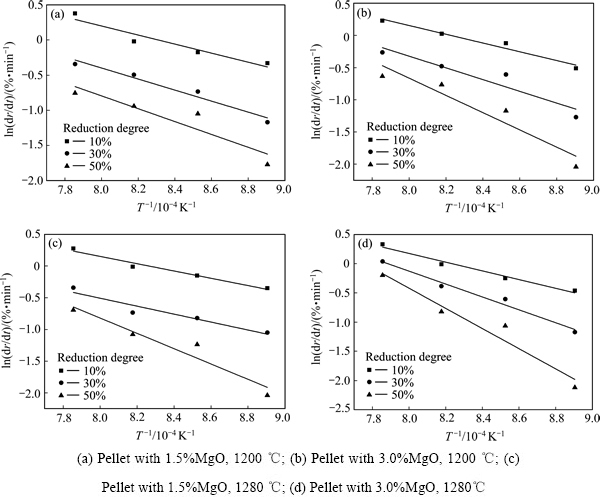
图7 球团还原反应阿雷尼乌斯图
Fig. 7 Arrhenius plots of reduction reaction of pellet
表3 球团矿还原反应的表观活化能值
Table 3 Apparent activation energies of pellet reduction reaction
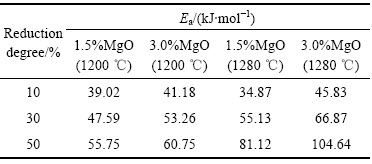
由表3可以看出,在1200 ℃下焙烧的1.5%镁球和3.0%镁球,当还原度为10%为30%时,其反应活化能值分别为39.02和47.59 kJ/mol以及41.18和53.26kJ/mol。根据表4的对应关系,此时的还原过程基本属于气体扩散和界面化学反应混合控制。还原度达到50%时,反应活化能值分别是55.75和60.75 kJ/mol,基本属于界面化学反应控制,此时铁离子向晶格内的扩散速度快,铁离子优先聚集在容易形核的位置,形成铁核。由于晶核下面的氧晶格相对固定,铁核被迫向外长大,形成定向晶,出现针状晶和铁晶须。1280 ℃下焙烧的1.5%镁球和3.0%镁球在还原度达到50%时,反应活化能值分别是81.12和104.64 kJ/mol,基本属于固相扩散控制。尤其3.0%镁球还原后期是固相扩散控制,所以其还原膨胀率低。
图8所示为还原1 h后球团的微观结构扫描电镜图。从图8也可以看到,1200 ℃下焙烧的1.5%和3.0%镁球还原1 h后球团内部出现了明显的铁晶须和针状铁晶粒(见图8(a)和图8(b)),所以还原膨胀率高。
表4 速率限制性环节与反应活化能值间的对应关系
Table 4 Corresponding relationship between apparent activation energy and rate-controlling machanism of reduction reaction
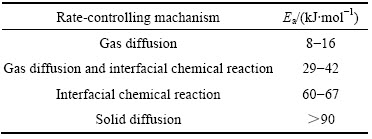
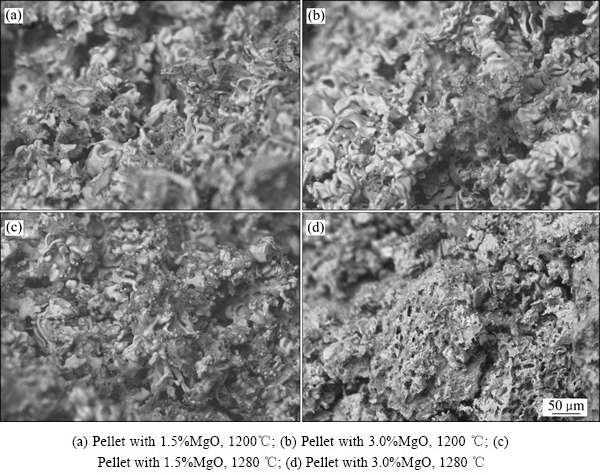
图8 还原膨胀后球团矿的SEM像
Fig. 8 SEM images of pellets after reduction swelling
高温下(1280 ℃)焙烧的1.5%镁球和3.0%镁球在还原度10%时,活化能值分别是34.87和45.83 kJ/mol,属于气体内扩散和界面化学反应混合控制。在还原后期,即还原度30%以上时,活化能值提高,尤其是3.0%镁球,当其还原度达到50%时,活化能值是104.64 kJ/mol,属于固相扩散即铁离子扩散控制。铁离子来不及向晶格内扩散,并在短时间内形成许多独立的核,形成致密的铁层,不出现针状的铁晶粒,因此,球团矿还原膨胀率低。从图8(c)和(d)可以看出,高温下焙烧的1.5%镁球还原时出现了少量的铁晶须,而3.0%镁球未出现明显的针状铁晶须,与还原反应限制环节相吻合,从而印证了以上分析的结果。
3 结论
1) 提高MgO含量可以抑制低硅球团(SiO2<2%)还原膨胀率的上升,而提高焙烧温度能够显著降低低硅含镁球团矿的还原膨胀率。
2) 当焙烧温度较低时,含镁球团内部结构松散,产生的液相和铁酸镁数量很少,且存在未反应的镁粉颗粒,球团抗压强度较低;而随着焙烧温度的提高,低硅含镁球团矿内铁酸镁数量增多,球团内部结构变致密,抗压强度提高。
3) 随着焙烧温度的提高,低硅含镁球团矿的还原膨胀率降低,同时还原膨胀后球团的抗压强度提高。焙烧温度1230 ℃以下时,MgO含量为1.5%和3.0%的球团还原膨胀率在45%以上,还原膨胀后的球团抗压强度在60 N/pellet左右。焙烧温度提高到1280 ℃后,MgO含量为1.5%的球团矿还原膨胀率降低到了25.28%,MgO含量为3.0%的低硅球团还原膨胀率降到15.69%。
4) 通过Arrhenius方程和还原度测定,得到了不同温度下焙烧的低硅含镁球团矿还原反应表观活化能。低温下焙烧的低硅含镁球团还原过程前期气体扩散和界面化学反应混合控制,后期界面化学反应控制,铁离子扩散快,球团内出现明显的针状铁晶须,加重球团矿的还原膨胀。高温下焙烧的低硅含镁球团矿在还原度较低时是气体扩散和界面化学反应控制,但随后是固相扩散即铁离子扩散控制。铁离子来不及向晶格内扩散,并在短时间内形成许多独立的核,形成致密的铁层,尤其低硅高镁球团还原过程固相扩散控制更明显,球团内未出现明显的针状铁晶粒,还原膨胀率低。
REFERENCES
[1] ELKASABGY T. Effect of alkalis on reduction behavior of acid iron ore pellets[J]. Transactions ISIJ, 1984, 24: 612-621.
[2] 周取定, 郭春泰. 碱金属和氟对球团矿还原膨胀影响机理的研究[J]. 金属学报, 1986, 22(6): 13249-13255.
ZHOU Qu-ding, GUO Chun-tai. Effect of alkalis and fluorine on swelling properties of pellet during production[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 1986, 22(6): 13249-13255.
[3] ILJANA M, MATTILA O, ALATARVAS T, KURIKKALA J, PAANANEN T, FABRITIUS T. Effect of circulating elements on the dynamic reduction swelling behavior of olivine and acid iron ore pellets under simulated blast furnace shaft conditions[J]. ISIJ International, 2013, 53(3): 419-426.
[4] 姜 涛, 何国强, 李光辉, 范晓慧, 催智鑫. 脉石成分对铁矿石球团还原膨胀性能的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2007(5): 8-11.
JIANG Tao, HE Guo-qiang, LI Guang-hui, FAN Xiao-hui, CUI Zhi-xin. Effect of gangue composition on reduction swelling of iron ore pellets[J]. Iron and Steel, 2007(5): 8-11.
[5] FAN Xiao-hui, GAN Min, JIANG Tao, YUAN Li-shun, CHEN Xu-ling. Influence of flux additives on iron ore oxide pellets[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2010, 17(4): 732-737.
[6] LI Guang-hui, TANG Zhao-kun, ZHANG Yuan-bo, CUI Zhi-xin, JIANG Tao. Reduction swelling behavior of hematite/magnetite agglomerates with addition of MgO and CaO[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2010, 37(6): 393-397.
[7] 王兆才, 储满生, 唐 珏, 薛向欣. 还原气氛和脉石成分对氧化球团矿还原膨胀率的影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(1): 94-97.
WANG Zhao-cai, CHU Man-sheng, Tang Jue, XUE Xiang-xin. Effects of reducing atmosphere and gangue composition on reduction swelling of oxidized pellet[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2012, 33(1): 94-97.
[8] DWARAPUDI S, GHOSH T K, SHANKAR A, TATHAVADKAR V, BHATTACHARJEE D, VENUGOPAL R. Effect of pellet basicity and MgO content on the quality and microstructure of hematite pellets[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processiing, 2011, 99: 43-53.
[9] DWARAPUDI S, GHOSH T K, TATHAVADKAR V, MARK B D, BHATTACHARJEE D, VENUGOPAL R. Effect of MgO in the form of magnesite on the quality and microstructure of hematite pellets[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processiing, 2012, 112: 55-62.
[10] SHARMA T, GUPTA R C, PRAKASH B. Effect of reduction rate on the swelling behavior of iron ore pellets[J]. ISIJ International, 1992, 32(7): 812-818.
[11] SHARMA T, GUPTA R C, PRAKASH B. Effect of firing condition and ingredients on the swelling behavior of iron ore pellets[J]. ISIJ International, 1993, 33(4): 446-453.
[12] 刘牡丹, 姜 涛, 李光辉. 硫酸钠和碳酸钠对高铝铁矿钠化还原动力学规律的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 23(1): 220-226.
LIU Mu-dan, JIANG Tao, LI Guang-hui. Effects of Na2SO4 and Na2CO3 on sodium-reduction dynamics law of high aluminum iron ores[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 23(1): 220-226.
[13] 张建良, 杨广庆, 国宏伟, 邵久刚, 李 建, 文永才. 含钒钛铁矿球团还原过程中微观结构变化[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2013, 35(1): 41-48.
ZHANG Jian-liang, YANG Guang-qing, GUO Hong-wei, SHAO Jiu-gang, LI Jian, WEN Yong-cai. Microstructure changes of V-Ti magnetite concentrate pellets during reduction[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2013, 35(1): 41-48.
[14] 朱德庆, 春铁军, 潘 建. 低品位赤铁矿矿球团成核剂强化还原机理研究[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2011, 33(11): 1325-1330.
ZHU De-qing, CHUN Tie-jun, PAN Jian. Mechanism of action of improving reduction on low grade hematite pellets by adding nucleating agent[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2011, 33(11): 1325-1330.
[15] 朱德庆, 肖永忠, 春铁军, 潘 建. 低品位赤铁矿直接还原过程中铁晶粒的长大行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(11): 3242-3247.
ZHU De-qing, XIAO Yong-zhong, CHUN Tie-jun, PAN Jian. Growth behavior of metal iron grain during direct reduction of low grade hematite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(11): 3242-3247.
[16] 危雪梅, 鲁雄刚, 肖 玮. 攀枝花预氧化钛精矿的H2还原行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(11): 3248-3253.
WEI Xue-mei, LU Xiong-gang, XIAO wei. Reduction behavior of Panzhihua pre-oxidized ilmenite by hydrogen[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals. 2013, 23(11): 32248-3253.
[17] 张建良, 毛 瑞, 黄冬华, 邵久刚, 李峰光. 红土镍矿脱水机理及还原过程动力学[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(3): 843-851.
ZHANG Jian-liang, MAO Rui, HUANG Dong-hua, SHAO Jiu-gang, LI Feng-guang. Dehydration mechanism and reduction process dynamics of laterite nickel ore[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals. 2013, 23(3): 843-851.
[18] 青格勒, 王朝东, 侯恩俭, 刘洪松, 马 丽, 吴 铿. 低硅含镁球团矿抗压强度及冶金性能[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2014, 26(4): 7-12.
QING Ge-le, WANG Chao-dong, HOU Jian-en, LIU Hong-song, MA Li, WU Keng. Compressive strength and metallurgical property of low silicon magnesium pellet[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2014, 26(4): 7-12.
[19] NASR M I, OMAR A A, KHEDR M H, ELGEASSY A A. Effect of nickel oxide doping on the kinetics and mechanism of iron oxide reduction[J]. ISIJ International, 1995, 35(9): 1043-1049.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51274026;51474002)
收稿日期:2015-01-12;修订日期:2015-06-17
通信作者:吴 铿,教授,博士;电话:010-62333442;传真:010-62333442;E-mail: wukeng@metall.ustb.edu.cn