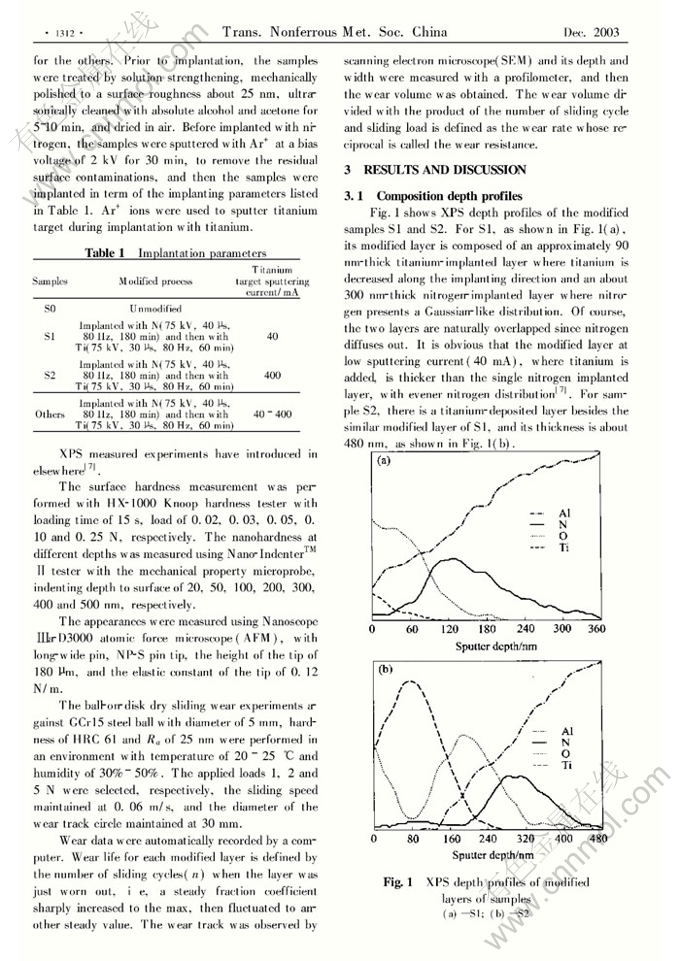
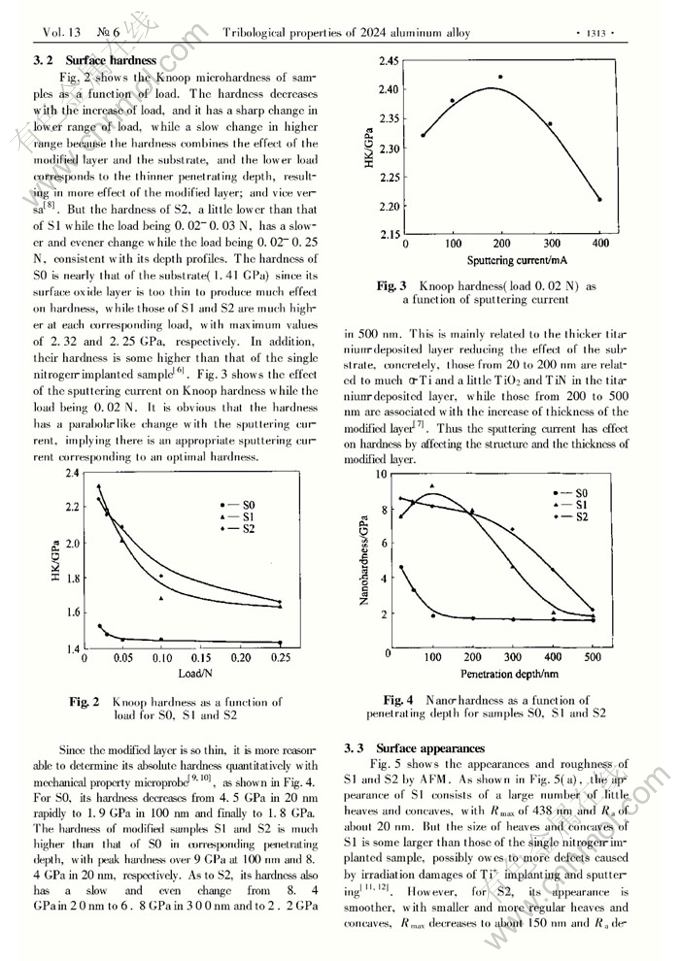
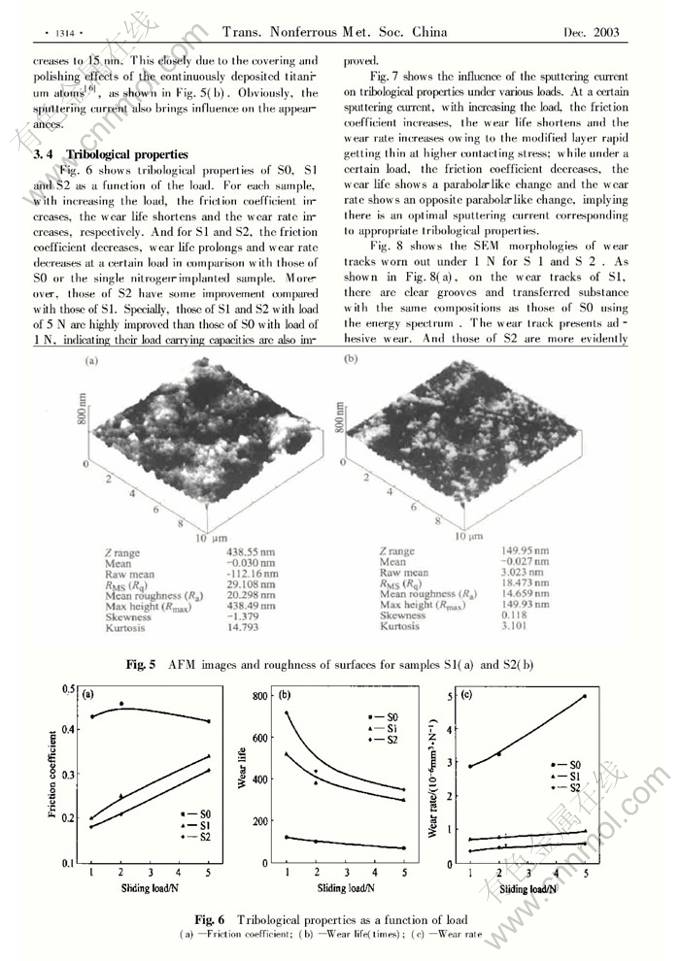
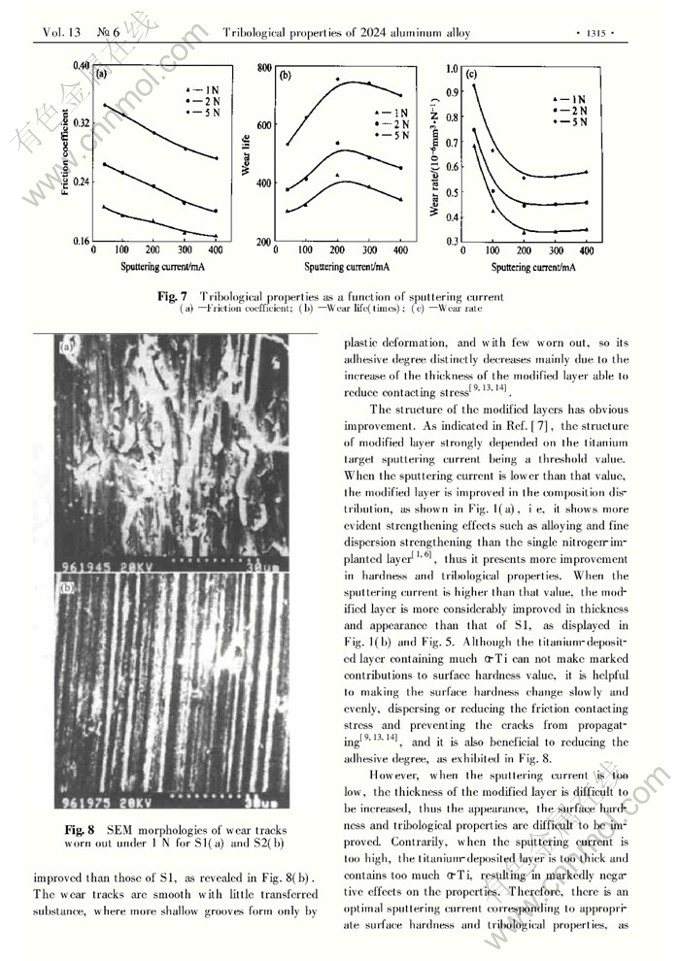
Tribological properties of 2024 aluminum alloy plasma-based ion implanted with nitrogen then titanium
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2003年第6期
论文作者:廖家轩 夏立芳 孙明仁 孙跃 刘维民 徐洮 薛群基
文章页码:1311 - 1316
Key words:aluminum alloy; plasma-based ion implantation; sputtering current; tribological properties
Abstract: 2024 aluminum alloy was implanted with nitrogen then titanium at different titanium target sputtering currents by plasma-based ion implantation(PBII). The appearances were observed by atomic force microscope, and the surface hardness was measured with Knoop hardness tester and the mechanical property microprobe. Ball-on-disc dry wear experiments were performed under ambient air conditions, to study the tribological properties of the modified layers against GCr15 steel ball, employing various loads and a constant sliding speed. After dual modifications, surface hardness at 100nm depth could reach to 9GPa, increasing by about 5 times; tribological properties at lower load(e.g. 1N) were obviously improved, with the friction coefficient(below 0.2) decreasing by over 60%, and the wear life(800 times) increasing by about 5 times. Meanwhile, with the increase of the sputtering current, the appearance is smooth, the surface hardness tends to a slow and even variation, the wear life presents a parabola-like change, and the friction coefficient and the adhesive wear degree decrease. However, tribological properties are reduced with the increase of the load due to the modified layer rapidly getting thin.