仙鹤草挥发油化学成分的气相色谱-质谱分析
李雅文1,黄兰芳1, 2,梁 晟1,郭紫明2,戴云辉1, 2,吴名剑2,钟科军2,郭方遒1,梁逸曾1
(1. 中南大学 化学化工学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 常德卷烟厂技术中心,湖南 常德,415000)
摘 要:据化学计量学分辨方法,提出一个用气相色谱-质谱联用法定性定量分析仙鹤草中挥发油成分的方法。对重叠色谱峰采用直观推导式演进特征投影法进行分辨,从而获得每一组分的纯色谱和质谱,对每一组分纯质谱在NIST质谱库进行相似性检索并进行定性分析,用总体积积分法进行定量分析。从仙鹤草挥发油样品中共分离出56个色谱峰,鉴定出其中50个组分,占挥发油总含量的90.53%,其主要组分为醇和单萜类化合物,分别占总化合物的50.58%和18.34%。采用该方法可为进一步研究和开发仙鹤草的药用价值提供有用信息。
关键词:化学计量学;气相色谱-质谱分析;仙鹤草;挥发油
中图分类号:O657.72 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2007)03-0502-05
Analysis of the volatile components of Agrimonla Pilosa Ledeb by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
LI Ya-wen1, HUANG Lan-fang 1, 2,LIANG Chen1, GUO Zi-ming2, DAI Yun-hui1, 2, WU Ming-jian2, ZHONG Ke-jun 2, GUO Fang-qiu1, LIANG Yi-zeng1
(1. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Technical Center of Changde Cigarette Factory, Changde 415000, China)
Abstract: Based on chemometric resolution methods, a method for qualitative and quantitative determination of the volatile components in Agrimonla Pilosa Ledeb was developed by chromatography-mass spectrometry. The overlapping chromatographic peaks were resolved into pure chromatograms and spectra with heuristic evolving latent projections (HELP), qualitative analysis was performed by similar search in NIST library with the obtained pure mass spectrum of each component and the quantitative results were obtained by calculating the volume of total two-way response. The results show that 56 components are separated and 50 components are identified, accounting for 90.53% of the total content. The main components are alcohols and monoterpene, accounting for 50.58% and 18.34% of the total content, respectively. The present method can be used to provide useful information for further study and development of Agrimonla Pilosa Ledeb.
Key words: chemometrics; gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; agrimonla pilosa ledeb; the volatile component
仙鹤草为蔷薇科多年生草本植物龙芽草Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb的全草,主产于浙江、江苏、湖北,有止血、补虚、止痢功用和抗肿瘤的作用,主要用于治疗各种出血症及赤白痢疾、劳伤脱力等[1-5]。有关仙鹤草化学成分的研究报道很多[6-9],其主要化学成分为仙鹤草酚、仙鹤草内酯、挥发油、甾醇、皂甙及鞣质,但有关挥发性成分的研究报道很少。赵莹 等[10]用气相色谱-质谱联用方法测定仙鹤草挥发性成分,由于存在重叠色谱峰,因而定性定量鉴定的挥发性组分不多,占所测挥发油总含量不高,而且每一色谱峰的实际面积无法计算,因而定量分析也无法进行,或所得结果不可靠。随着化学计量学的发展,从气相色谱-质谱联用仪(GC-MS)获得的多维数据能用相关分辩方法解析。这些方法如渐近因子分析法[11]、窗口因子分析法[12]、直观推导式演进特征投影算法[13]、子窗口因子分析法[14]、渐进窗口正交投影法[15]和正交投影法[16]等,能提供色谱分离和光谱定性两方面的信息,使得分离解析重叠色谱峰成为可能[17-18],从而使定性和定量结果的准确度得到很大提高。在此,本文作者采用化学计量学分辨方法和气相色谱-质谱联用法(GC-MS),提出仙鹤草中挥发性成分的分析方法。用水蒸气蒸馏法萃取仙鹤草中的挥发性成分,然后在适宜条件下用气相色谱-质谱联用法分离和检测挥发性成分。用HELP方分辨GC-MS二维数据,从而获得每一组分的纯色谱和质谱。依靠每一组分的保留时间和纯质谱在NIST质谱库进行相似性检索和定性分析,最后用总体积积分法进行定量分析[19]。
1 实 验
1.1 仪 器
仪器为美国HP 6890A /HP 5973MSD色质联用仪,配G1701DA-D.00.00.38 Chemstation工作站软件和NIST107标准检索库。
1.2 挥发油的提取
取干燥仙鹤草100 g,按中华人民共和国药典(2005年版)挥发油提取法提取。仙鹤草购自湖南省药材公司,经鉴定为蔷薇科植物龙芽草Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb的全草。
1.3 分析测试条件
色谱柱 HP-5MS 石英毛细管柱长30 m、内径 0.25 mm,膜厚0.25 μm。起始温度为50 ℃,升温速率为 4 ℃/min, 升至290℃;载气为He气, 流速为 1.0 mL/min;进样口温度为280 ℃,进样量为1 μL,分流比为10?1。EI源电子能量为70 eV,离子源温度为230 ℃,质荷比为30~500。
1.4 数据分析
数据分析在Pentium III 850(Intel)计算机上进行,所有程序用Matlab 6.3编写,所分辨的质谱在NIST标准谱库(含有107 000种化合物)中进行检索。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 定性分析
虽然一些色谱联用仪器得到快速发展,但是在分析如中药这类复杂的样品时,仍难以单纯通过改变色谱条件来到达完全分离组分的目的,而采用化学计量学提出的许多分辨方法则能解决这些问题。在此,本文作者通过HELP方法对所有重叠峰进行分辨。HELP法原理见文献[13]。对于气相色谱-质谱联用仪产生的二维数据,设分析体系中有n个组分,且其质谱向量互不相关,按照Lambert-Beer定律,测得的二维数据矩阵Xm×n可表示为:
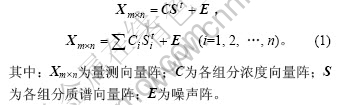
用HELP法能将二维数据分辨成各组分的纯光谱和色谱。
图1所示为仙鹤草挥发油总离子流图。由图1可知,存在许多组分,各组分含量差别很大。尽管优化了色谱条件,但有些色谱峰仍出现重叠现象,如果未对数据进行处理而直接在NIST质谱库中检索,有时会得到错误的定性结果;如果将重叠峰分辨成纯光谱和色谱,相似度将提高。这里以图1中峰簇A (13.70~ 13.94 min)为例说明此解析方法的整个过程。图2中曲线1表示峰簇A总离子流图。
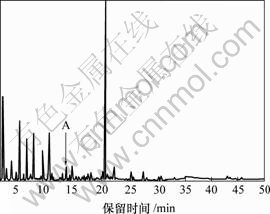
图1 仙鹤草挥发油的总离子流图
Fig.1 The total ion chromatograms (TIC) of the essential oil from agrimony
首先,用PCA法[16-17]扣除背景和基线漂移。图2中曲线2为扣除背景后的总离子流图。其次,用固定尺寸窗口渐进因子分析法 (FSMWEFA)[20]获得A重叠峰的秩图(见图3)。依据上述信息,用HELP法分辨由GC-MS所得的A重叠峰中各组分纯色谱 (图4)和质谱。用各组分的纯质谱在NIST质谱库中作相似性检索,并进行定性分析,结果表明A重叠峰中组分1和2分别为2-cyclopropylidene-1,7,7- trimethyl-bicylo[2,2,1] heptane和3,3,5,5-tetramethyl- cyclohexanol,相关系数分别为0.936 和 0.917,其结果见图5和图6。组分3 因相关系数很低而未能定性。用同样方法可得其他峰簇中各组分的纯色谱和质谱。表1所示为仙鹤草挥发油成分定性分析结果。
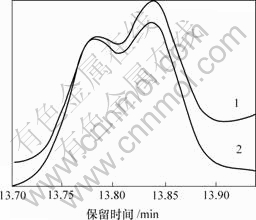
1—原总离子流;2—扣除背景后的总离子流
图2 峰簇A的总离子流图
Fig.2 The TIC chromatogram of peak cluster A

图3 移动窗口为8时峰簇A的特征跟踪示意图
Fig.3 The evolving eigenvalues of peak A obtained using FSMWEAF with a window size of 8
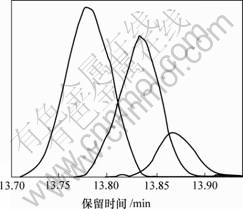
图4 A峰解析后的色谱图
Fig.4 Resolved chromatograms of peak A
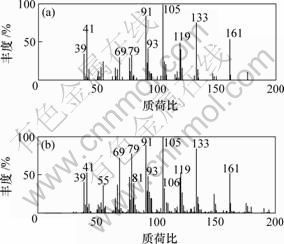
(a) 组分1质谱图;
(b) 亚环丙烷基-1,7,7-三甲基-二环[2,2,1]庚烷标准质谱谱图
图5 组分1质谱图与2-亚环丙烷基-1,7,7-三甲基-二环[2,2,1]庚烷标准质谱谱图
Fig.5 Resolved mass spectrum of component 1 by HELP(a) and standard mass spectrum of 2-cyclopropylidene-1,7,7- trimethyl-bicylo[2,2,1]heptane (C13H20)(b)
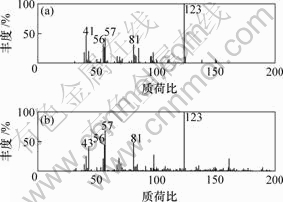
(a) 组分2质谱图;
(b) 3,3,5,5-四甲基环己醇标准质谱谱图
图6 组分2质谱图与3,3,5,5-四甲基环己醇标准质谱谱图
Fig.6 Resolved mass spectrum of component 2 by HELP(a) and standard mass spectrum of 3,3,5,5-tetramethyl- cyclohexanol(C10H20O)(b)
表1 仙鹤草挥发油成分分析结果
Table 1 Analytical results of the volatile components in Agrimonla Pilosa Ledeb

2.2 定量分析
在解析出各组分的纯色谱和质谱后,采用总体积积分(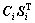 )和归一化法得到各组分的定量分析结果,其结果见表1。由表1可知,共鉴定出50种化学组分,占挥发油总量的90.53%。其中醇类14种,占总化合物的50.58%,以表雪松醇、芳樟醇和α-松油醇为主,相对含量分别为31.81%,5.29%和3.60%;单萜5种,占总化合物的18.34%,以α-蒎烯为主,相对含量为15.25%;倍半萜11种,占总化合物的4.76%;酯类6种,占总化合物的7.65%;酮类5种,占总化合物的6.376%;酚类2种,占总化合物的2.11%。
)和归一化法得到各组分的定量分析结果,其结果见表1。由表1可知,共鉴定出50种化学组分,占挥发油总量的90.53%。其中醇类14种,占总化合物的50.58%,以表雪松醇、芳樟醇和α-松油醇为主,相对含量分别为31.81%,5.29%和3.60%;单萜5种,占总化合物的18.34%,以α-蒎烯为主,相对含量为15.25%;倍半萜11种,占总化合物的4.76%;酯类6种,占总化合物的7.65%;酮类5种,占总化合物的6.376%;酚类2种,占总化合物的2.11%。
3 结 论
a. 借助直观推导式演进特征投影算法(HELP),提出了一个用气相色谱-质谱联用(GC-MS)定性定量分析仙鹤草中挥发性成分的方法。共分离出56个色谱峰,通过质谱库检索得到其中50个组分的定性定量结果,占挥发油总含量的90.53%。
b. 仙鹤草中主要组分为醇和单萜类化合物,分别占总化合物的50.58%和18.34%,通过对仙鹤草挥发油化学成分的分析,能为进一步研究和开发仙鹤草提供依据。
参考文献:
[1] 中华人民共和国卫生部药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[M]. 1部. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005: 67.
Editorial Committee of the Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China. The pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China[M]. Part Ⅰ. Beijing: Chemistry Industry Press, 2005: 67.
[2] 江苏新医学院. 中药大辞典[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1977: 665-667.
Jiangsu College of New Medicine Science. Thesaurus of Chinese traditional medicine[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science & Technology Press, 1977: 665-667.
[3] 李玉祥, 樊 华, 张劲松, 等. 中草药抗癌的体外试验[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 1999, 30(1): 37-42.
LI Yu-xiang, FAN Hua, ZHANG Jing-song, et al. In vitro evaluation of anticancer activity of extracts from Chinese medicinal herbs[J]. Journal of China Pharmaceutical University, 1999, 30(1): 37-42.
[4] 郭 炜, 赵泽贞, 单保恩, 等. 六种中草药抗突变及抗肿瘤活性的实验报告[J]. 癌变?畸变?突变, 2002, 14(2): 94-98.
GUO Wei, ZHAO Ze-zhen, Shan Bao-en, et al. Report on the antimu-agenicity and anti-tumor activity of six kinds of Chinese medicinal herbs[J]. Carcinogenesis, Teratogenesis and Mutagenesis, 2002, 14(2): 94-98.
[5] 王思功, 李予蓉, 王瑞宁, 等. 仙鹤草对人癌细胞裸鼠移植瘤的影响[J]. 第四军医大学学报, 1998, 19(6): 702-704.
WANG Si-gong, LI Yu-rong, WANG Rui-ning, et al. Effect of agrimonia pilosa ledeb on nude mice bearing human cancerous xenograft[J]. Journal of the Fourth Military Medical University, 1998, 19(6): 702-704.
[6] 赵 莹, 刘金平, 李平亚. 仙鹤草化学成分及药理研究进展[J]. 特产研究, 2001, 23(1): 50-53.
ZHAO Yin, LIU Jin-ping, LI Ping-ya. New developments of chemical and pharmacological study on Agrimonla Pilosa Ledeb[J]. Special Wild Economic Animal and Plant Research, 2001, 23(1): 50-53.
[7] 裴月湖, 李 铣, 朱廷儒. 仙鹤草根芽中化学成分的研究[J]. 药学学报, 1989, 24(6): 431-437.
PEI Yue-hu, LI Xian, ZHU Ting-ru. Studies on the chemical constituents from the rootsprouts of agrimonla pilosa ledeb[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 1989, 24(6): 431-437.
[8] 孙 磊, 贾俊梅, 李秀珍. 仙鹤草微量元素的测定方法[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2000, 17(6): 43.
SUN Lei, JIA Jun-mei, LI Xiu-zheng. The analytical method of trace elements from inhibition of Agrimonla Pilosa Ledeb[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2000, 17(6): 43.
[9] 李 霞, 叶 敏, 余修祥, 等. 仙鹤草化学成分的研究[J]. 北京医科大学学报, 1995, 27(1): 60-61.
LI Xia, YE Min, YU Xiu-xiang, et al. Studies on the chemical constituents of Agrimonla Pilosa Ledeb[J]. Journal of Peking University: Health Sciences, 1995, 27(1): 60-61.
[10] 赵 莹, 李平亚, 刘金平.仙鹤草挥发油化学成分的研究[J].中国药学杂志,2001,36(10):672-672.
ZHAO Yin, LI Ping-ya, LIU Jin-ping. Studies on the volatile chemical constituents of Agrimonla Pilosa Ledeb[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal, 2001, 36(10): 672-672.
[11] Maeder M, Zilian A. Evolving factor analysis: A new multivariate technique in chromatography[J]. Chemom Intell Lab Syst, 1988, 3(3): 205-213.
[12] WEI Den, Edmund R. Malinowski.Investigation of copper (II)—Ethylenediaminetetraacetate complexation by window factor analysis of ultraviolet spectra[J]. Journal of Chemometrics, 1993, 7(2):89-98.
[13] Liang Y Z, Kvalheim O M, Keller H R, et al. Heuristic evolving latent projections: resolving two-way multicomponent data. Part 2: Detection and resolution of minor constituents[J]. Anal Chem, 1992, 64(8): 946-953.
[14] Shen H L, Manne R, Xu Q S, et al. Local resolution of hyphenated chromatographic data[J]. Chemom Intell Lab Syst, 1999, 45(1/2): 323-330.
[15] Xu C J, Jiang J H, Liang Y Z. Evolving window orthogonal projections method for two-way data resolution[J]. Analyst, 1999, 124(10): 1471-1476.
[16] Sanchez F C, Rutan S C, Garcia N D. Resolution of multicomponent overlapped peaks by the orthogonal projection approach, evolving factor analysis and window factor analysis[J]. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 1997, 36(2): 153-164.
[17] GUO Fang-qiu, LIANG Yi-zeng, XU Cheng-jian, et al. Determination of the volatile chemical constituents of Notoptergium Incium by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and iterative or non-iterative chemometrics resolution methods[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2003, 1016(1): 99-110.
[18] HUANG Lan-fang, LI Bo-yan, LIANG Yi-zeng, et al. Application of combined approach to analyze the constituents of essential oil from angelica sinensis[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2004, 378(2): 510-517.
[19] Keller H R, Massart D L. Peak purity control in liquid chromatography with photodiode-array detection by a fixed size moving window evolving factor analysis[J]. Anal Chim Acta, 1991, 246(4): 379-390.
[20] LIANG Yi-zeng. White, grey and black multicomponent systems and their chemometric algorithms[M]. Changsha: Hunan Press of Science and Technology, 1996.
收稿日期:2006-11-08
基金项目:湖南省发展和改革委员会资助项目( [2004]714 );常德卷烟厂博士后科研基金资助项目
作者简介:李雅文(1981-), 男, 广西桂林人, 硕士研究生, 从事化学计量学与中药现代化研究
通讯作者:黄兰芳(1963-), 男, 湖南常德人, 博士, 教授; 电话: 0731-8836376; E-mail: lf18huang@yahoo.com.cn