文章编号:1004-0609(2007)04-0572-08
FCC晶体中晶体取向对孔洞长大和聚合的影响
刘文辉,张新明,唐建国,周卓平
(中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:通过编制率相关有限元用户子程序,采用包含一个和两个球形孔洞的单胞探求了FCC晶体中晶体取向对孔洞长大和聚合的影响。计算结果表明:晶体取向对孔洞长大的影响较大,孔洞的形状和长大方向与晶体取向密切相关;由于变形不均匀,孔洞在晶界处产生尖角,易形成裂纹。由于约束较少,孔洞周围和两孔洞间的区域塑性变形较大,晶体的转动和滑移主要集中在孔洞周围以及两孔洞间的区域。
关键词:晶体取向;孔洞;晶体塑性;有限元;聚合
中图分类号:TG 146 文献标识码:A
Effects of crystallographic orientation on void growth and coalescence
LIU Wen-hui, ZHANG Xin-ming, TANG Jian-guo, ZHOU Zhuo-ping
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The influence of crystallographic orientation on void growth and coalescence in FCC single crystal was simulated with 3D crystal plasticity finite element, and the rate-dependent crystal plasticity theory was implemented as a user material subroutine. A 3D unit cell including one sphere void and two sphere voids was employed with three-dimensional 12 slip systems. The computed results of different crystallographic orientations were compared. The results show that the crystallographic orientation has significant influence on the growth behavior of void, and the void growth direction and shape significantly depend on the crystallographic orientation. Due to inhomogeneous deformation, some corners where crack will initiate can be induced at grain boundaries. The rotation of the crystalline lattice and plastic activity on slip systems are mainly concentrated in the region around voids.
Key words: crystallographic orientation; void; crystal plasticity; FEM; coalescence
材料的韧性断裂是材料失效的主要形式之一,一般经过孔洞的形核、长大、聚合3个阶段。有关孔洞长大和聚合的有限元计算大都采用包含一个或多个孔洞的单胞来进行分析的,其中大部分都是把基体当成各向同性的材料或采用改进的本构模型来研究孔洞的长大和聚合[1-4]。由于晶体有限元可以考虑材料的各向异性和各种微观结构,如晶体滑移、晶界以及晶粒之间的相互作用的情况,最近不少学者采用晶体有限元研究孔洞的长大和聚合。Shu[5]通过采用粘弹塑性应变梯度晶体塑性理论研究了含孔洞的单晶的变形情况,发现小孔洞长大的趋势比大孔洞的小。Orisini和Zikry[6]采用率相关的晶体塑性模型研究了FCC铜单晶中的孔洞长大的情况,研究结果表明晶体的转动和塑性滑移主要集中在孔洞之间的区域。O’Regan等[7]采用二维有限元模型模拟了不同孔洞百分比、加载条件和不同的晶体取向对孔洞长大和聚合的影响。Potriniche和Hearndon[8]采用2D晶体有限元研究了单向和双向载荷情况下,晶体取向对FCC单晶中孔洞的长大和聚合的影响。然而孔洞在第二相粒子周围形核,一般大至呈球状。因此有必要采用3D晶体有限元对问题进行分析。本文作者采用包含一个和两个球形孔洞的单胞,通过编制率相关的用户子程序,运用3D晶体有限元模型分析了晶体取向对孔洞长大和聚合的影响。
1 率相关晶体塑性本构关系
Hill[9]、Hill和Rice[10]以及Asaro等[11-13]认为可以将位移梯度张量作如下的乘积分解:
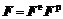 (1)
(1)
式中 F e表示晶格畸变和刚性转动所产生的变形梯度;F p则表示晶体沿滑移方向的均匀剪切所对应的变形梯度。速度梯度L也分解成弹性和塑性两部分:
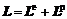 (2)
(2)
式中 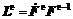 ,
, 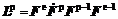 。
。
速度梯度张量为所有滑移系的速度梯度张量的叠加:
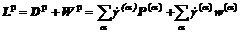 (3)
(3)
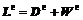 (4)
(4)
式中 α为第α个滑移系;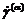 为α滑移系中的滑移率;D p、W p分别为变形率张量和旋转张量。
为α滑移系中的滑移率;D p、W p分别为变形率张量和旋转张量。
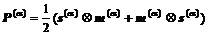 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
式中 m代表垂直于滑移面的单位向量;s代表相应滑移面的滑移方向的单位向量,在面心立方晶体中,滑移系为{111}〈110〉。
剪切应变率采用方程(7)的率相关的硬化方程来描述:
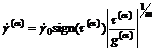 (7)
(7)
式中 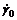 为参考剪切应变速率;
为参考剪切应变速率;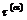 是第α滑移系上的切分应力,
是第α滑移系上的切分应力,  称为参考剪切应力;m为应变速率敏感因子。当
称为参考剪切应力;m为应变速率敏感因子。当 时,
时, 的初值为τ0,它的演变由下式来确定:
的初值为τ0,它的演变由下式来确定:
 (8)
(8)
式中 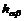 是硬化系数,通常当
是硬化系数,通常当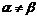 的时候称为潜在硬化系数。 本研究采用了广泛使用的一种描述方式,即:
的时候称为潜在硬化系数。 本研究采用了广泛使用的一种描述方式,即:
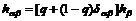 (9)
(9)
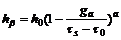 (10)
(10)
式中 q是潜在硬化率,对于共面滑移系q=1.0,非共面滑移系q=1.0~1.4,h0和α为常数,τs为饱和应力。
2 几何模型和边界条件
率相关的本构关系采用FORTRAN编写的用户子程序实现[14-15]。
孔洞的初始体积百分比f=1%。因此,含单个孔洞时,d/l=0.267 3;含两个孔洞的单胞中,d/l=0.212,孔洞间韧带的宽度为d。图1所示为分析所采用模型的1/4。(如图1(a)所示)当晶粒1和2的取向相同时,单胞表示孔洞在单晶中的长大情况;当取向不同时,则表示孔洞在晶界的长大情况。
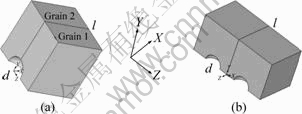
图1 孔洞长大和聚合的单胞
Fig.1 Unit cells for void growth and coalescence: (a) One sphere void; (b) Two sphere voids
为了得到变形过程中孔洞体积的变化情况,采用给定位移边界条件。这样既可以得到孔洞的体积,又可以避免计算过程中的不稳定性。单胞的边界条件如图2(a)所示,轴X的给定位移为δ,轴Y和Z方向的位移分别为aδ,bδ,其中a=b=-0.235(负号表示与图中位移的方向相反),δ=0.15,轴X平行于样品轧向,Z轴平行于板法向。网格化分采用3D单元,为了较好地模拟孔洞的变形,孔洞周围的网格较细小,图2(b)所示为含一个孔洞时的网格化分。
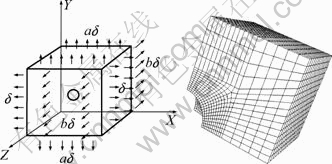
图2 边界条件和网格化分
Fig.2 Boundary conditions and finite element mesh
计算中考虑的材料为铝单晶,其材料参数为:弹性常数C11=170 GPa,C22=124 GPa,C44=75 GPa[16],参考剪切应变速率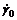 =0.001,应变速率敏感因子m=0.02,方程(9)和(10)中的硬化参数为h0=250 MPa,τ0=16 MPa,τs=190 MPa,a=2.25。
=0.001,应变速率敏感因子m=0.02,方程(9)和(10)中的硬化参数为h0=250 MPa,τ0=16 MPa,τs=190 MPa,a=2.25。
3 结果分析
3.1 单晶中孔洞的长大
图3和4所示分别为Cube(0?, 0?, 0?)和Goss(0?, 45?, 90?)取向的铝单晶等效塑性变形的XY和XZ截面图。
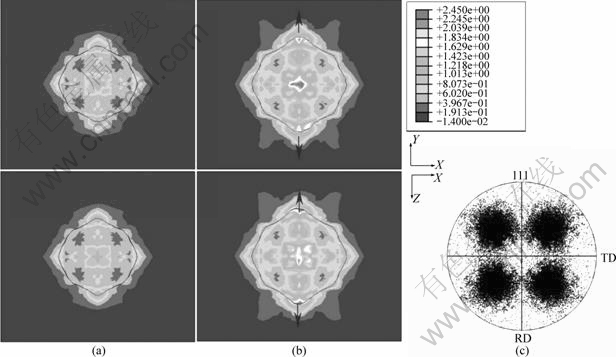
图3 Cube取向等效塑性变形和极图
Fig.3 Equivalent plastic strain and pole figure for Cube orientation: (a) εx=0.05; (b) εx =0.1; (c) Pole figure, εx =0.1
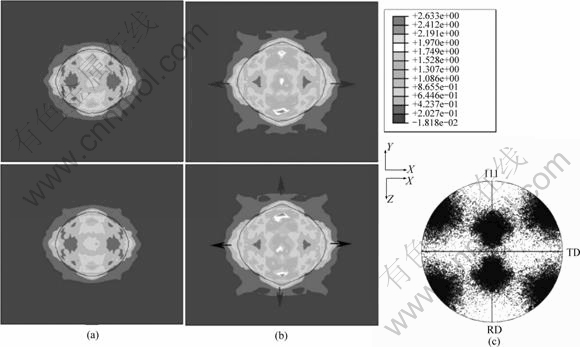
图4 Goss取向等效塑性变形和极图
Fig.4 Equivalent plastic strain and pole figure for Goss orientation: (a) εx=0.05; (b) εx =0.1; (c) Pole figure, εx =0.1
图3(a)和(b)及图4(a)和(b)所示分别为εx=0.05及εx=0.1时,不同取向的塑性变形分布图,图3(c)和图4(c)所示为在εx=0.1的计算结果以及经MATLAB程序处理后的{111}极图。图3所示为立方取向的变形情况,该取向的变形较为对称,孔洞沿Z轴方向长大较为迅速。Goss取向的变形情况如图4所示,孔洞沿轴X方向长大较快。
从图3、4(a)和(b)可观察到非均匀的塑性变形。由于各向异性,孔洞的形状变得不规则,而且不同取向的孔洞形状也不相同。在变形过程中,孔洞的长径比也随着改变。从图4(c)可看出,变形后,晶体取向偏离初始取向,有的偏离初始取向较大,这可能是孔洞周围地区。
图5所示为Brass取向的单胞偏离平均取向θAVE的统计分析结果。图5(a)和(b)所示分别为整个单晶和孔洞周围地区在εx=0.1时的统计分析结果。从图中可看出,对于整个单晶,变形后取向偏离较小,主要集中在θAVE=5?之内;而对于孔洞周围地区,分布宽度较宽。这说明了孔洞周围变形较大,可能与以下两个原因有关:1) 由于孔洞周围约束较少,变形较为自由,塑性变形较大,这也可以从图3和4中看出;2) 由于给定位移边界条件,单胞的体积增加,而塑性变形时,基体体积变化较小,因此孔洞体积增加,在孔洞周围地区产生应变集中。
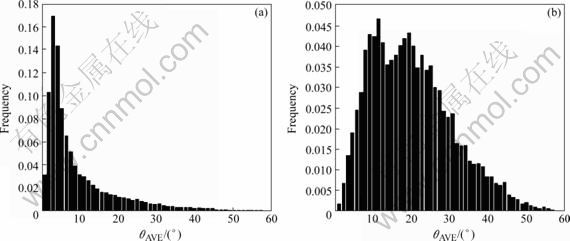
图5 θAVE的统计分布特征
Fig.5 Statistical distribution feature: (a) Whole crystal; (b) Near void
3.2 晶界上孔洞的长大
当晶粒1和2的取向不同时,图1(a)所示的单胞可表示孔洞在晶界的长大情况。在计算中,假设晶粒2的取向保持不变,为(0?, 45?, 90?)。晶粒1的取向采用(15?, 45?, 90?),(35?, 45?, 90?),(45?, 45?, 90?),(60?, 45?, 90?),分别对应于单胞A、B、C、D。图6所示为Goss取向和单胞A、B、C、D在a=b=-0.235加载条件下的等效应力-应变曲线。从图可看出,单胞A最易变形,单胞C最难变形,单胞B和D应力—应变曲线相差不多。
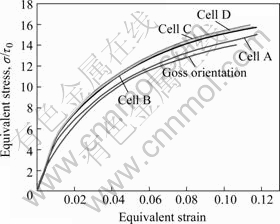
图6 单晶的等效应力—应变曲线
Fig.6 Curves of equivalent stress vs equivalent strain for single crystals
图7和8所示分别为单胞A、B、C、D在εx=0.05和εx=0.1时的等效塑性应变的XZ截面图。从图7和8可以看出,所有单胞中孔洞趋向晶粒1方向长大,单胞C最为明显,单胞B和D相差不多。从图6可以看出,在这种加载条件下,晶粒1比晶粒2难变形,也就是说,在这种加载条件下,孔洞朝着硬取向的晶粒长大,这可能与加载方式有关。因为在a=b=-0.235的加载条件下,X方向的变形最大,而晶粒1和晶粒2在X轴方向应变相等,这就使得硬取向晶粒的X轴方向应力较大,可能在硬取向的晶粒中形成大的应力三轴度[17],因而有利于孔洞的长大,使得孔洞趋向硬取向(晶粒1)方向长大。
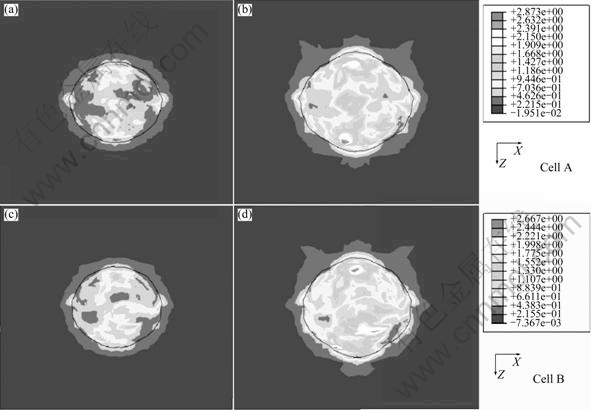
图7 单胞A和B的等效塑性变形
Fig.7 Equivalent plastic strain for cells A and B: (a) Cell A, εx=0.05; (b) Cell A, εx=0.1; (c) Cell B, εx=0.05; (d) Cell B, εx=0.1
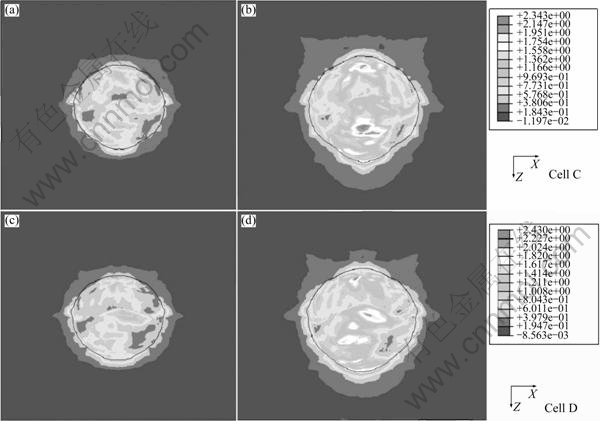
图8 单胞C和D的等效塑性变形
Fig.8 Equivalent plastic strain for cells C and D: (a) Cell C, εx=0.05; (b) Cell C, εx=0.1; (c) Cell D, εx=0.05; (d) Cell D, εx=0.1
Nemat-Nasser等[18]和Solanki等[19]通过有限元计算发现:由于塑性变形的局部化,在孔洞周围产生了一些尖角,并通过实验观察到非圆形的边界。在这些尖角处,由于应力较大,易产生位错,并产生裂纹。由图7和8可发现,由于变形不均匀,孔洞在晶界处产生尖角,使得在晶界处产生裂纹。
图9(a)~(d)所示分别为单胞A、B、C、D在应变εx=0.01时的等效塑性应变分布图。从图中可看出单胞A在晶界处的等效塑性应变大于单胞B和C,这可能是由于单胞A较易变形而引起的。而对于应力应变曲线相近的单胞B和D,取向差分别为35?和60?,单胞D在晶界处的等效塑性应变大于单胞B。这可能是由于单胞D的取向差较大,两晶粒在晶界处滑移系启动不同,使得晶界处的变形不均匀,因而裂纹易于在取向差较大的单胞D的晶界上形成。
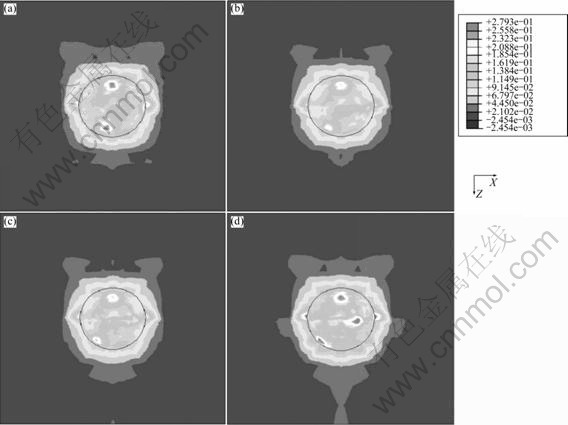
图9 单胞A、B、C和D的等效塑性变形
Fig.9 Equivalent plastic strain for cells A, B, C and D when εx=0.01: (a) Cell A; (b) Cell B; (c) Cell C; (d) Cell D
3.3 单晶中孔洞的聚合
Potirniche等[8]采用一个二维单胞研究了双轴应变载荷下不同取向的孔洞的聚合情况。他们的计算结果表明,在双轴载荷情况下,不同取向的孔洞体积变化变化相差不大。本研究采用含两个球形孔洞的3D模型来分析取向对孔洞聚合的影响。由于给定位移边界条件,单胞的体积增长已经确定,而基体变形相差不大,因此在变形过程中,不同取向的单晶中孔洞的体积变化相差较小。
图10和11所示分别为Cube取向和Cu(90?, 35?, 45?)取向的单晶在εx=0.02和εx=0.05时XZ截面的等效塑性变形。从图中可以看出的:在变形过程中孔洞的形状和孔洞之间韧带的宽度随着取向不同而变化。Cube取向在εx=0.02时,孔洞间形成了强烈的剪切带,最大塑性应变为2.917;在εx=0.05时,最短的韧带值与初始韧带宽度的比值为0.010 7,如图10所示。Cu取向的塑性应变分布如图11所示,在εx=0.02时,该取向形成了较强的剪切带;在εx=0.05时,最大塑性应变为2.092;但聚合效果没有Cube取向明显。
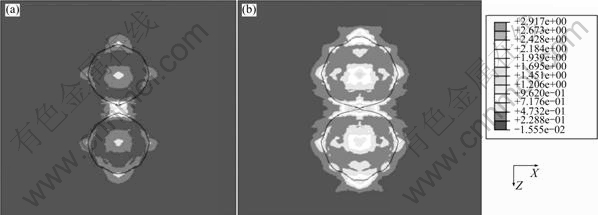
图10 Cube取向等效塑性变形
Fig.10 Equivalent plastic strain for Cube orientation: (a) εx=0.02; (b) εx=0.05
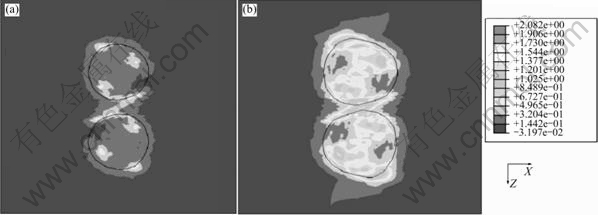
图11 Cu取向等效塑性变形
Fig.11 Equivalent plastic strain for Cu orientation: (a) εx=0.02; (b) εx=0.05
图12所示为在εx=0.05时含两个孔洞的Cu取向的单胞偏离平均取向θAVE统计分析结果。从图中可看出,对于整个单晶,变形后取向偏离较小,主要集中在θAVE=3?之内,而对于两孔洞之间区域,分布宽度较宽。这说明该区域的变形不均匀,塑性变形较大。由于两孔洞之间区域约束较少,变形较为自由,因此塑性变形较大,如图10和11所示。这表明晶体的转动和滑移主要集中在两孔洞之间的区域,与Orsini和Zikry[6]的研究结果一致。
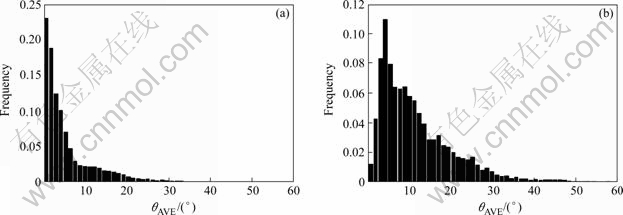
图12 θAVE的统计分布特征
Fig.12 Statistical distribution feature: (a) Whole crystal; (b) Inter-void ligament
4 结论
1) 晶体的取向对孔洞长大的影响较大,孔洞的形状和长大方向与晶体取向密切相关。
2) 由于变形不均匀,孔洞在晶界处产生尖角,易在晶界处产生裂纹。
3) 单胞A在晶界处的等效塑性应变大于单胞B和C。而对于应力应变曲线相近的单胞B和D,单胞D在晶界处的等效塑性应变远大于单胞B。
4) 在变形过程中,晶体发生转动,偏离初始取向,由于孔洞周围约束较少,变形较为自由,塑性变形较大,偏离初始取向较大。
REFERENCES
[1] Gologanu M, Leblond J B, Devaux J. Approximate models for ductile metals containing non spherical voids-case of axisymmetric prolate ellipsoidal cavities[J]. J Mech Phys Solids, 1993, 41: 1723-1754.
[2] Pardoen T, Dumont D, Deschamps A, Brechet Y. Grain boundary versus transgranular ductile failure[J]. J Mech Phys Solids, 2003, 51: 637-665.
[3] Gologanu M, Leblond J B, Devaux J. Approximate models for ductile metals containing non-spherical voids-case of axisymmetric oblate ellipsoidal cavities[J]. J Eng Mater Technol, 1994, 116: 290-297.
[4] Pardoen T, Hutchinson J W. An extended model for void growth and coalescence[J]. J Mech Phys Solids, 2000, 48: 2467-2512.
[5] Shu J Y. Scale dependent deformation of porous single crystals[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 1998, 14: 1085-1107.
[6] Orsini V C, Zikry M A. Void growth and interaction in crystalline materials[J]. Int J Plasticity, 2001, 17: 1393-1417.
[7] O’Regan T L, Quinn D F. Howe M A, McHugh P E. Void growth simulations in single crystals[J]. Comput Mech, 1997, 20: 115-121.
[8] Potirniche G P, Hearndon J L, Horstemeyer M F, Ling X W. Lattice orientation effects on void growth and coalescence in fcc single crystals[J]. Int J Plasticity, 2006, 22: 921-942.
[9] Hill R. Generalized constitutive relations for incremental deformation of metals crystals by multislip[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1966, 14: 95-102.
[10] Hill R, Rice J R. Constitutive analysis of elastic-plastic crystals at arbitrary strain[J]. J Mech Phys Solids, 1972, 20: 401-413.
[11] Asaro R J. Crystal plasticity[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1983, 50: 921-934.
[12] Asaro R J. Geometrical effects in the inhomogeneous deformation of ductile single crystals[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1979, 27: 445-453.
[13] Asaro R J. Micromechanics of crystals and polycrystals[J]. Advances in Applied Mechanics, 1983, 23: 1-115.
[14] Tang J G, Zhang X M, Deng Y L. Simulation of rolling textures of FCC metals with crystal plasticity finite element model[J]. Mater Sci Technol, 2006, 22(10): 1171-1176.
[15] Tang J G, Zhang X M, Chen Z Y, Deng Y L. Simulation influence of inhomogeneous deformation on the development of rolling textures with crystal plasticity finite element[J]. J Cent South University, 2006, 13: 117-121.
[16] 唐建国. FCC金属不均匀滑移变形的织构多晶体有限元模拟[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2006.
[17] TANG Jian-guo. Simulation of Inhomogeneous Slip Deformation in FCC Metals With Textured Polycrystal Plasticity Finite Element[D]. Changsha: Central Sourth University, 2006.
[18] Pardoen T, Dumont D, Brechet Y, Deschamps A. Grain boundary versus transgranular ductile failure[J]. J Mech Phys Solids, 51: 637-665.
[19] Nemat-Nasser S, Okinaka T, Nesterenko V, Liu M. Dynamic void collapse in crystals: computational modelling and experiments [J]. Philos Mag A, 1998, A78: 1151-1174.
[20] Solanki K, Horstemeyer M F, Baskes M I, Fang H. Multiscale study of dynamic void collapse in single crystals [J]. Mech Mater, 2005, 37: 317-330.
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划(2005CB623706); 国际科技合作重点项目(2004DFA00200)
收稿日期:2006-09-08;修订日期:2006-01-09
通讯作者:刘文辉;电话:0731-8830265; E-mail: wealth9733221@sohu.com
(编辑 何学锋)