文章编号:1004-0609(2011)07-1541-06
热连轧对GH4169合金蠕变行为的影响
李振荣1, 2, 田素贵1, 赵忠刚1, 陈礼清3, 刘相华3
(1. 沈阳工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,沈阳 110870;2. 辽宁大学 轻型产业学院,沈阳 110036;
3. 东北大学 轧制技术及连轧自动化国家重点实验室,沈阳 110004)
摘 要:通过对等温锻造和热连轧工艺制备的GH4169合金进行直接时效、蠕变性能测试和组织形貌观察,研究热连轧对GH4169合金组织结构及蠕变行为的影响。结果表明:与等温锻造合金相比,经热连轧后合金的晶粒尺寸较小,在等温锻造期间的变形特征仅为孪晶形变,而合金在热连轧期间除产生孪晶外,在孪晶中还存在位错的双取向滑移;采用不同工艺制备的合金均在{111}面上发生孪晶变形。在蠕变期间,热连轧期间形成的位错可促进孪晶内发生位错的不同取向滑移,减缓应力集中,提高合金蠕变抗力,致使合金在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下具有较长蠕变寿命。
关键词:GH4169合金;热连轧;孪晶;蠕变;变形特征
中图分类号:TG146.1 文献标志码:A
Influence of hot continuous rolling on
creep behaviors of GH4169 superalloy
LI Zhen-rong1, 2, TIAN Su-gui1, ZHAO Zhong-gang1, CHEN Li-qing3, LIU Xiang-hua3
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shenyang University of Technology, Shenyang 110178, China;
2. College of Light Industry, Liaoning University, Shenyang 110036, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Rolling and Automation, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110004, China)
Abstract:By means of direct aging treatment, the creep properties measurement and microstructure observation of the isothermal forged (ITF) and hot continuous rolling (HCR) GH4169 alloys, the influence of the HCR on the microstructure and creep behavior of GH4169 alloy was investigated. The results show that the grain size of HCR alloy is finer than that of the ITF alloy. The only deformed feature of the ITF alloy is twinning. However, the twinning and dislocation slippings with double orientations in the twinning appear in the alloy during HCR. Moreover, the deformed twinnings occur on {111} planes in the alloys prepared by different technics. During creep, the dislocations formed during HCR can promote the dislocations slipping of different orientations within the twinning to decrease the stress concentration, which may enhance the creep resistance and result in longer creep lifetime of the alloy under the applied stress of 700 MPa at 660 ℃.
Key words:GH4169 superalloy; hot continuous rolling; twinning; creep; deformation feature
GH4169合金是一种时效硬化型Ni-基变形高温合金,在700 ℃以下具有良好的抗热疲劳和抗氧化性能及良好的冷、热加工性能,是制备航空发动机涡轮盘构件的主要材料之一[1-3]。GH4169合金的组织结构由γ基体、γ ?、γ"相和碳化物组成,其中,γ″相为该合金的主要强化相,呈扁盘状形态在基体中析出,且与基体的{100}面保持共格界面,其惯习面为{100}γ″//{001}γ 及á100?γ″//á100?γ[4-6]。在高温长时间服役条件下,γ″相可转变成δ相,γ′相为合金的辅助强化相。在γ″和γ′相的共同作用下,该合金具有良好的中温力学及蠕变性能[7-9]。等温锻造(Isothermal forged,ITF)方法是GH4169合金传统的制备工艺,采用不同工艺进行热处理,可获得不同组织结构与性能的合 金[10-12],但生产效率较低。热连轧 (Hot continuous rolling,HCR) 技术生产GH4169合金是一种新工艺尝试。采用热连轧工艺制备变形GH4169高温合金,可达到节约能源、降低生产成本、提高生产效率的目的[13-15]。但热连轧制备工艺对合金组织结构及蠕变性能的影响并不清楚,特别是热连轧期间合金的变形特征及蠕变机制的影响有待于研究。
据此,本文作者首先采用等温锻造和热连轧两种工艺制备GH4169合金;然后,对合金进行直接时效处理,通过对采用两种工艺制备的合金进行蠕变性能测试和组织形貌观察,研究热连轧对GH4169合金组织与蠕变性能的影响,并对合金的蠕变机制进行讨论,试图为热连轧合金的发展与应用提供理论依据。
1 实验
经真空感应炉熔炼的GH4169合金分别采用等温锻造(ITF)和热连轧(HCR)工艺制备成合金棒材;将等温锻造与热连轧合金在720 ℃保温8 h,以冷却速率为50 ℃/h炉冷(FC)至620 ℃,保温8 h后空冷(AC),进行两级直接时效(DA)处理。合金的制备工艺参数如表1所列。
表1 合金的制备工艺参数
Table 1 Preparation technologies of GH4169 alloy

分别将经直接时效处理后的等温锻造和热连轧GH4169合金用线切割加工成横断面尺寸为4.5 mm×2 mm、标距长度为19 mm的片状蠕变试样。将经机械抛光后的样品置入GWT504型高温持久蠕变试验机中,在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下进行蠕变性能测试,绘制蠕变曲线。合金经蠕变断裂后,在SEM和TEM下进行组织形貌观察,根据合金的组织结构和微观表面变形特征,分析制备工艺对GH4169合金组织结构与蠕变行为的影响规律。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 不同工艺制备的合金的组织结构
采用不同工艺制备的合金经直接时效后的组织形貌如图1所示。图1(a)所示为等温锻造GH4169合金经过直接时效处理后的组织形貌。可以看出,合金的晶粒尺寸为8~12 mm,晶内呈现明显的孪晶变形特征,如图1(a)中长箭头所示,且在同一晶粒内存在不同取向的孪晶,如图1(a)中短箭头所示。

图1 采用不同工艺制备的合金经直接时效后的组织形貌
Fig.1 Microstructures of direct aging alloy prepared by different technologies: (a) ITF; (b) HCR
图1(b)所示为热连轧GH4169合金经直接时效处理后的组织形貌,与等温锻造GH4169合金相比,合金的晶粒尺寸略有减小,其尺寸为5~7 mm,仍具有孪晶的变形特征,其中,不同晶粒存在不同取向的孪晶,如图1(b)中箭头所示。
采用不同工艺制备的GH4169合金的TEM像如图2所示。等温锻造(ITF)合金中的晶界如图2(a)中黑色箭头所示,由于等温锻造期间发生塑性变形,合金中有明显的变形孪晶存在,其中,孪晶呈阶梯状形态,并终止于晶界,如图2(a)中白色长箭头所示。与等温锻造工艺相比,合金在热连轧期间发生的塑性变形程度较大,除发生孪晶变形外(如图2(b)中白色长箭头所示),在孪晶内存在大量位错缠结(见图2(b)中的暗色区域),并有明显的位错滑移迹线,如图2(b)中白色短箭头所示。图2(b)中A区域位错迹线的放大形貌如图2(c)所示。如果认为合金在制备变形期间产生的孪晶和位错具有形变强化作用,则等温锻造期间仅发生孪晶变形,而热连轧期间,合金既发生孪晶变形,在孪晶内又发生位错滑移。这表明经热连轧变形后合金的形变强化作用增强。
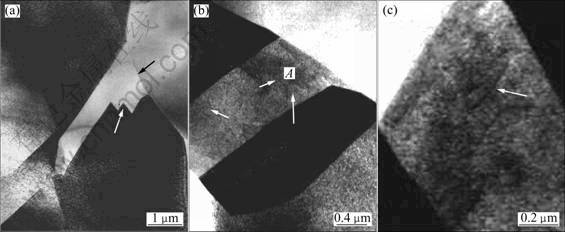
图2 采用不同工艺制备的合金的微观组织形貌
Fig.2 Microstructures of alloy prepared by different technologies: (a) Twining in ITF alloy; (b) Twining and dislocations in HCR alloy; (c) Magnified microstructure of dislocation trace in region A in (b)
2.2 制备工艺对合金蠕变性能的影响
在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下,测定等温锻造+直接时效和热连轧+直接时效GH4169合金的蠕变曲线,结果如图3所示。图3中曲线1为等温锻造合金经直接时效处理后测定的蠕变曲线,其稳态蠕变期间的应变速率为0.011 6 %/h,蠕变寿命为60 h;曲线2为热连轧合金经直接时效处理后测定的蠕变曲线,且具有较低的应变速率、较小的形变量和较长的蠕变寿命,其稳态蠕变期间的应变速率为0.004 2 %/h,稳态蠕变阶段的时间约为80 h,蠕变寿命达126 h。
2.3 蠕变期间合金的变形特征
等温锻造合金经直接时效处理后,在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下蠕变60 h断裂后的微观组织形貌如图4所示。可以看出,合金中晶界形貌如图4(a)中黑色箭头所示,合金中同一晶粒内有多组孪晶,且孪晶大多具有相互平行的特征(孪晶具有相同取向),其宽度细小,并终止于晶界处,如图4(a)白色箭头所示。图4(b)所示为该孪晶的衍射斑点标定。可以看出,形成的孪晶面为(111)面。
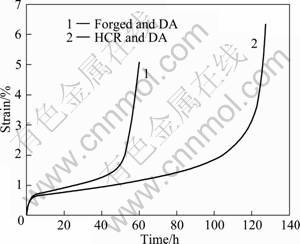
图3 采用不同工艺制备的GH4169合金在660 ℃、 700 MPa条件下的蠕变曲线
Fig.3 Creep curves of GH4169 alloy prepared by different technologies at 660 ℃ and 700 MPa
热连轧合金经直接时效后,在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下蠕变126 h断裂后的微观组织形貌如图5所示。可以看出,合金中存在两种不同取向的交叉孪晶A和B,如图5中箭头所示,其中,竖直方向的孪晶A,宽度较大,其尺寸约为1.2 μm,其孪晶衍射斑点及指数标定如图5(b)所示。可以确定,孪晶A的孪晶面为
 ,而近似水平方向的孪晶B与孪晶A相交,孪
,而近似水平方向的孪晶B与孪晶A相交,孪
晶B的宽度约为0.8 μm,孪晶B的衍射斑点及指数标
定如图5(c)所示,可以确定,孪晶B的孪晶面为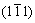 。
。
此外,孪晶A内存在高密度位错塞积于近孪晶B区域,如图5(a)中C所示。由此可推断,合金在蠕变期间的机制为孪晶变形,且孪晶的取向各异,孪晶面均为{111}面。

图4 ITF合金经直接时效后在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下蠕变60 h断裂后的微观组织形貌
Fig.4 Microstructures of ITF-DA-alloy crept for 60 h up to fracture under applied stress of 700 MPa at 660 ℃: (a) Twinnings; (b) SAD patterns of twinning
HCR合金经直接时效后,在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下蠕变126 h断裂后的微观变形特征如图6所示。在蠕变期间,基体中发生孪晶变形及孪晶内位错的双取向滑移,其中,孪晶的形态如图6(a)中黑色箭头所示,且位错在孪晶内发生的双取向滑移,如图6(a)中白色箭头所示。在样品的另一局部区域,晶界的形貌如图6(b)中白色箭头所示,孪晶形貌如图6(b)中白色长箭头所示,随着蠕变的进行,在合金的晶粒内发生位错的双取向滑移,在晶界左下方的晶粒中,位错的双取向滑移方向如图6(b)中黑色箭头所示,其中,位错的主滑移方向为近似于竖直方向,而在晶界的右上方,位错发生双取向滑移的方向如图6(b)中交叉箭头所示,其中,向下方滑移的位错终止于晶界处,如图6(b)中D所示,同时,沿左斜上方滑移的位错终止于孪晶界,如图6(b)中E所示。
随着蠕变的进行,形变位错的数量与密度逐渐增加,当形变位错滑移至孪晶和晶界交接处时,由于晶界和孪晶皆可阻碍位错滑移,故导致形变位错在近晶界区域塞积,具有形变强化作用。随着蠕变的进行,位错塞积的数量增多,并产生应力集中。集中应力的作用致使位错在孪晶内发生滑移,其滑移方向如图6(b)中的白色短箭头所示。这表明晶界和孪晶可有效阻碍位错的滑移,从而提高合金的蠕变抗力。根据图4、5及6可知,合金在蠕变期间的主要变形机制是孪晶及孪晶内的位错滑移。
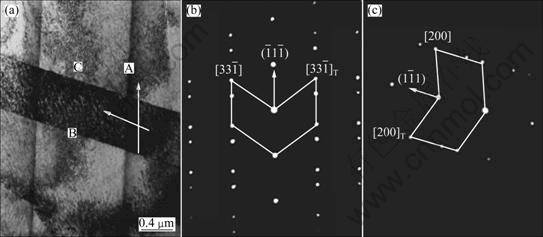
图5 HCR合金经直接时效后在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下蠕变126 h断裂后的微观组织形貌
Fig.5 Microstructures of HCR-DA-alloy crept for 126 h up to fracture under applied stress of 700 MPa at 660 ℃: (a) Twinnings A and B with different orientations; (b), (c) SAD patterns of twinnings A and B in (a)

图6 HCR合金经直接时效后在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下蠕变126 h断裂后的变形特征
Fig.6 Deformation characteristics of DA-HCR-alloy after crept for 126 h to fracture under applied stress of 700 MPa at 660 ℃: (a) Dislocation slipping within twinning region; (b) Double orientations of denser dislocations piled up near boundary region
3 讨论
等温锻造GH4169合金经直接时效处理后具有较均匀的晶粒尺寸,同时具有明显的孪晶变形特征,如图1(a)所示,且在孪晶内无位错滑移迹线,如图2(a)所示。与等温锻造合金相比,合金在热连轧期间发生较大的塑性变形,具有细化晶粒的效果,经直接时效后,仍使合金中的晶粒尺寸减小到5~7 μm,如图1(b)所示, 在变形合金中保留了孪晶及孪晶内的位错滑移,如图2(b)所示,其形变强化作用可提高合金的蠕变抗力。
等温锻造合金经直接时效处理后,在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下蠕变60 h断裂后,合金中的孪晶数量明显增多,但孪晶内无位错滑移迹线,如图4所示。蠕变期间合金发生5.1%的变形量,仅为孪晶变形的贡献。在蠕变期间,合金首先发生孪晶变形,随着蠕变进行,在晶内不发生位错滑移,故在晶界区域易产生应力集中,并促使裂纹沿晶界萌生,直至发生沿晶断裂,因此,合金具有较低的蠕变抗力和较短的蠕变寿命。
而热连轧合金经直接时效处理后,在合金中除有孪晶外,孪晶内还存在高密度位错的单取向或双取向滑移,如图2(b)所示。该合金在660 ℃、700 MPa条件下蠕变126 h断裂后,合金中存在不同取向的孪晶变形特征,且孪晶内发生位错的双取向滑移,如图6所示。图6表明,合金在蠕变期间发生孪晶及孪晶内的位错滑移两种变形机制。其中,在热连轧期间产生的位错,作为预存留位错,可促进蠕变位错的滑移,并协调晶粒间的变形,蠕变期间可延缓或减小形变产生的应力集中。研究表明,在等温锻造态合金中无位错滑移,在蠕变期间也不发生位错滑移变形,并具有较低的蠕变抗力和较短的蠕变寿命;而热连轧合金中存在位错滑移迹线,蠕变期间孪晶内可发生位错的单取向或双取向滑移,使合金具有较强的蠕变抗力和较长的蠕变寿命。因此,合金在热连轧蠕变期间形成的位错促进孪晶内发生位错的单取向或双取向滑移,减缓应力集中,是使合金具有较强蠕变抗力和较长蠕变寿命的主要原因。
4 结论
1) 与等温锻造合金相比,热连轧合金具有较小的晶粒尺寸;合金在等温锻造期间仅发生孪晶形变,而在热连轧期间,合金的变形特征是孪晶及位错在孪晶内的双取向滑移。采用不同工艺制备的合金中发生孪晶变形的孪晶面均为{111}面。
2) 与等温锻造合金相比,热连轧直接时效合金具有较强的蠕变抗力和较长的蠕变寿命;合金在热连轧蠕变期间形成的位错可促进孪晶内发生位错的单取向或双取向滑移,减缓应力集中,是合金具有较强蠕变抗力和较长蠕变寿命的主要原因。
REFERENCES
[1] TIAN S G, LI Z R, ZHAO Z G, CHEN L Q, LIU X H. Influence of direct aging treatment on creep behaviors of hot continuous rolled GH4169 superalloy[C]//Proceedings of EPD(Extraction and Processing Division) Congress. Warrendale: TMS, 2010: 455-462.
[2] HAN W B, ZHANG K F, WANG B, WU D Z. Superplasticity and diffusion bonding of IN718 superalloy[J]. Acta Metallurgic Sinica, 2007, 20(4): 307-312.
[3] 王 岩, 林 琳, 邵文柱, 甄 良, 张新梅. 固溶处理对GH4169合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2007, 28(S): 176-179.
WANG Yan, LIN Lin, SHAO Wen-zhu, ZHEN Liang, ZHANG Xin-mei. Effect of solid-solution treatment on microstructure and performance of GH4169 superalloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2007, 28(S): 176-179.
[4] RAO G A, KYMAR M, SRINIVAS M, SARMA D S. Effect of standard heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of hot isostatically pressed superalloy Inconel 718[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 355(1/2): 114-125.
[5] TIAN S G, ZHAO Z G, LIU Y, BAO X Y, CHEN L Q, LIU X H. Microstructure and creep behavior of casting and rolling GH4169 superalloy after long-term aged[C]//Proceedings of EPD (Extraction and Processing Division) Congress. San Francisco: TMS, 2009: 353-359.
[6] 何玉怀, 于慧臣, 郭伟林, 沈莉莉, 苏 彬. 直接时效GH4169高温合金疲劳裂纹扩展性能试验[J]. 航空动力学报, 2006, 21(2): 349-353.
HE Yu-huai, YU Hui-chen, GUO Wei-lin, SHEN Li-li, SU Bing. Experimental study on fatigue crack growth behavior of direct aging GH4169 superalloy[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2006, 21(2): 349-353.
[7] 刘 芳, 孙文儒, 杨树林, 李 战, 郭守仁, 杨洪才, 胡壮麒. Al含量对GH4169镍基合金组织及稳定性的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2008, 44(7): 791-797.
LIU Fang, SUN Wen-ru, YANG Shu-lin, LI Zhan, GUO Shou-ren, YANG Hong-cai, HU Zhuang-qi. Effects of Al content on microstructure and stability of GH4169 nickel base alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2008, 44(7): 791-798.
[8] 曹美华, 陈国胜, 周奠华, 庞克昌. 变形速度及晶粒度对GH4169合金高温拉伸性能和组织的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2003, 15(7): 361-365.
CAO Mei-hua, CHEN Guo-sheng, ZHOU Dian-hua, PANG Ke-chang. Influences of deformation speed and grain size on high temperature properties and microstructures of superalloy GH4169[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 15(7): 361-365.
[9] TIAN S G, ZHAO Z G, LIU Y, BAO X Y, CHEN L Q, LIU X H. Creep behaciors of DA casting and rolling GH4169 superalloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(S3): 20-23.
[10] 李荣斌, 姚 枚, 刘文昌, 张伟红, 何贤昶. 直接时效工艺对Inconel 718合金组织的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2002, 27(2): 21-22.
LI Rong-bin, YAO Mei, LIU Wen-chang, ZHANG Wei-hong, HE Xian-chang. Effects of direct aging treatment on structure of Inconel 718 alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2002, 27(2): 21-22.
[11] 宁永权, 姚泽坤, 郭鸿镇, 田军强, 虢迎光. 等温锻造对IN718合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2007, 36(21): 65-67.
NING Yong-quan, YAO Ze-kun, GUO Hong-zhen, TIAN Jun-qiang, GUO Ying-guang. Effect of isothermal forging on microstructure and mechanical properties of IN718 alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2007, 36(21): 65-67.
[12] MA X F, DUAN Z, SHI H J, MURAI R, YANAGISAWA E. Fatigue and fracture behavior of nickel based superalloy Inconel 718 up to the very high cycle regime[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science A, 2010, 11(10): 727-737.
[13] 陈国胜, 王庆增, 张玩良, 李 伟, 王资兴, 刘丰军, 王世普. GH4169合金细晶棒材的连轧工艺及其组织与性能[J]. 材料工程, 2010(4): 18-21.
CHEN Guo-sheng, WANG Qing-zeng, ZHANG Wan-liang, LI Wei, WANG Zi-xing, LIU Feng-jun, WANG Shi-pu. Microstructure and properties of fine grain GH4169 alloy bar rolled by continuous roller[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2010(4): 18-21.
[14] 田素贵, 赵忠刚, 陈礼清, 于慧成, 刘 洋, 包宪宇, 刘相华. 直接时效处理对热连轧GH4169合金蠕变行为的影响[J]. 航空材料学报, 2010, 30(S) : 14-18.
TIAN Su-gui, ZHAO Zhong-gang, CHEN Li-qing, YU Hui-chen, LIU Yang, BAO Xian-yu, LIU Xiang-hua. Influence of direct aged treatment on creep behaviors of hot continuous rolling GH4169 superalloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2010, 30(S): 14-18.
[15] 孔永华, 李 龙, 陈国胜, 朱世根. 不同热处理工艺对GH4169合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010, 39(S): 472-475.
KONG Yong-hua, LI Long, CHEN Guo-sheng, ZHU Shi-gen. Effect of different heat treatment on microstructures and properties of GH4169 alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(S): 472-475.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金重点项目(50634030)
收稿日期:2010-10-20;修订日期:2011-04-09
通信作者:田素贵,博士,教授;电话:024-25494089;E-mail:tiansugui2003@163.com