J. Cent. South Univ. (2017) 24: 56-61
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-017-3408-x
Mechanism of different particle sizes of quartz activated by metallic ion in butyl xanthate solution
QIN Wen-qing(覃文庆), WU Jia-jia(武佳佳), JIAO Fen(焦芬)
School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2017
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2017
Abstract: To investigate effect of metallic ion activation on different particle sizes of quartz in butyl xanthate solution, six common ions (Pb2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, Fe2+, Mg2+ and Ca2+) were introduced as activators. The approaches of micro-flotation, adsorption test and zeta potential measurement were adopted to reveal the mechanism of ion activation. The results show that Pb2+, Cu2+ and Fe3+ are effective activators for the flotation of quartz in butyl xanthate solution because of their absorption on activated quartz surface. Average recoveries of fine particles (<37 μm) are greater than those of coarser particles (37-74 μm), suggesting that the former is easier to be activated and more likely to be floated and thus entrained in sulphide concentrate. From another perspective, addition of metallic ions (Pb2+, Cu2+ and Fe3+) renders zeta potentials move positively, and addition of the same metallic ions and butyl xanthate makes zeta potential drop apparently, which support a mechanism where they adsorb onto quartz surface, resulting in an expected increase in butyl xanthate collector adsorption with a concomitant increase in the flotation recoveries.
Key words: particle size; quartz; metallic ion; activation; butyl xanthate
1 Introduction
Flotation is an important and effective mineral processing step used to achieve selective separation of minerals and gangue and to prepare raw materials for smelting. The difference of flotation performance between sulfide mineral and quartz is great enough to realize separation; however, quartz is one of the major impurities in sulfide concentrate and can not be easily removed even after repetitive cleaning processes [1, 2]. Quartz is generally thought to be entrained by froth [3-7] or as locked in composite particle with sulfide minerals [8]. Nevertheless, the inevitable metallic ions in pulp [9, 10] contribute a lot in changing the flotation behavior of quartz. Thus, mechanical entrapment is not the sole cause that quartz mingles in concentrate. In the practical mineral separations, the existence of unavoidable metal ions and ions from mineral dissolution, such as Cu2+, Fe3+, Mg2+, and Ca2+, significantly influences the flotation of minerals [11].
A considerable amount of document has been published on metallic ions activation in flotation of quartz and poses different views. ZHANG et al [12] proposed that spodumene, albite, and quartz minerals are difficult to float in the presence of NaOL alone; when Fe3+ ions were used as the activator, the flotation is dramatically improved. WANG et al [13] reported effect of precipitation of hydroxide on quartz surface. It has been concluded that precipitation of hydroxide is active component of metal ions on quartz surface. Zeta potential of quartz surface becomes positive as formation of precipitation and the corresponding pH (CR2) is the same with precipitation. Zeta potential turns into negative afterwards with pH value marked as CR3 and the range CR2≤pH≤CR3 is effective activate range of metallic ion. FORNASIERO et al [14] concerned the activation effect of Cu2+ and Ni2+. They found that quartz can be activated by them and floated with xanthate in pH region 7-10 where copper and nickel hydroxides are the stable species and by adsorbing/precipitating on the mineral surface they promote xanthate adsorption and therefore the flotation of these minerals. Numerous literature is available in this regard, including the recent ones by SHI et al [15], OU et al [16, 17], etc, who analyzed their work using two theories mentioned above. And adsorption mechanism of reagent on quartz surface in complex flotation system was learned by WANG et al [18].
On the other hand, as compositions of minerals are more complex and more finer-grained dissemination, finer particle for flotation is needed to achieve liberation and thus froth flotation. Reports on metallic ion activation of fine-grained quartz in sulfide ore flotation system have not been seen yet. So, it is necessary to study the mechanism of ion activation on different sized quartz, hoping to be utilized in promotion of sulfide concentrate standard and other fields such as flocculation, reverse flotation.
Aimed at revealing mechanism of metallic ions activation on different particle size of quartz (37-74 μm and <37 μm), six common ions (Pb2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, Fe2+, Mg2+, Ca2+) are introduced as activators. The effect of metallic ions at various concentrations and pH levels in the micro-flotation of two-sized quartz was investigated using an anionic butyl xanthate collector. The mineral surfaces in the presence of metallic ions and butyl xanthate species, responsible for the floatation of minerals, were analyzed by adsorption test and zeta-potential measurement.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Single sample and reagents
High purified quartz ores were initially hand-picked to remove impurities and then ground to finer particle using a porcelain ball mill. The product was removed to obtain <74 μm fraction by dry sieving, and followed by wet screening to receive particles of 37-74 μm and <37 μm respectively. The two powder specimens were washed using diluted hydrochloric acid and distilled water in sequence to minimize possible metallic ions contamination. No more metallic ion was involved in the preparation of single mineral and distilled water was used throughout the study. The reagents used in this study were all in chemical pure grade except terpineol was commercial pure.
Size distribution of the finer particles was determined by Mastersizer 2000 (England, Malvern Instrument Co.) and the results can be found in Fig. 1. The average size (d0.5) was 17.85 μm.
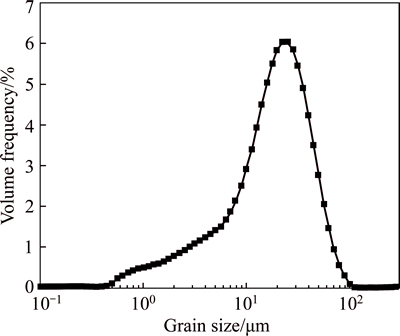
Fig. 1 Size distribution of particle size less than 37 μm
2.2 Micro-flotation test
The flotation test was carried out in a flotation cell with an effective volume of approximately 40 mL. 2.0 g sample was mixed with 40 mL distilled water. Conditioning was depending on the aim of single test and went as following order: pH regulator (HCl and NaOH), metallic ion and collectors and frother. For each reagent addition, the conditioning was taken as 2 min and flotation was conducted for 4 min. Then the concentrate samples and leftovers were collected respectively after flotation. They were filtered, dried, and the mass of the mineral, and hence the recoveries were calculated.
2.3 Adsorption test
The adsorption capacity of collector on the mineral surface was an important methodology to measure the floatability of minerals in froth flotation. Adsorption test was carried out on the basis of the principle that concentration is linearly related to the mineral surface adsorption. The suspension was made following the same procedure as micro-flotation test and then removed by centrifuging at 5000 r/min for 10 min. The supernate was run through a UV spectroscope (UV-2000 Shimadzu, Japan) at 301 nm. The equation of mineral surface adsorption is expressed as follows:
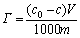
where Γ is adsorption capacity of quartz, mol/g; c0 and c are initial and residual concentrations of butyl xanthate in suspension, mol/L; V is volume of suspension, mL; m is the mass of quartz, g.
2.4 Zeta potential measurement
Zeta potentials were measured by Zetasizer Nano Zs90 (England, Malvern Instrument Co.). 40 mg <5 μm mineral sample was added to 40 mL aqueous solution with or without butyl xanthate and metallic ion butyl xanthate concentration was 1×10-5 mol/L, and concentrations of ion were the same as adsorption test. Pulp pH was adjusted to a given value using HCl or NaOH solution. After stirring the pulp for 15 min with a magnetic stirring and 2 min standing, the remaining suspension was taken for zeta potential measurement using a syringe. The results presented were the average of three independent measurements with a typical variation of ±4 mV.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Results of micro-flotation tests
3.1.1 Effect of pH value
To verify the effect of pH value on the flotation of different sized quartz particles, flotation tests were carried out at the concentration of collector and metallic ion being 1.0×10-5 mol/L and 1.0×10-4 mol/L respectively. The reagent concentrations were both within the reasonable range and can be applied to analyze the effect of pH on quartz flotation, flotation responses as shown in Fig. 2.
As seen, average recovery of finer particles (<37 μm) is higher than that of coarser particle (37-74 μm), suggesting that the coarser particle is not as easily to be activated as the finer particle, which implies that finer particle is more likely to be floated and thus entrained in concentrate due to activation by metallic ions. What’s more, alkaline environment is good for metallic ion activation. The presence of Pb2+, Cu2+ and Fe3+ metallic ions exerts positive effect on the flotation of quartz (see Figs. 2(a) and (c)), especially in pH range exceeding 8. In addition, the flotability of quartz in butyl xanthate solution with Fe2+, Mg2+ and Ca2+ is weak, and these ions can not activate quartz throughout the pH range tested even little growth for recovery of Fe2+.
To sum up, it can be safely deduced that Pb2+, Cu2+ and Fe3+are effective activators for the flotation of quartz in butyl xanthate solution, while the others are not.
3.1.2 Effect of metallic ion concentration
Concentration of metallic ion is an important factor in flotation. Flotation results of quartz as a function of different ion concentrations are illustrated in Fig. 3. The test was conducted at pH 10, butyl xanthate concentration 1.0×10-5 mol/L.
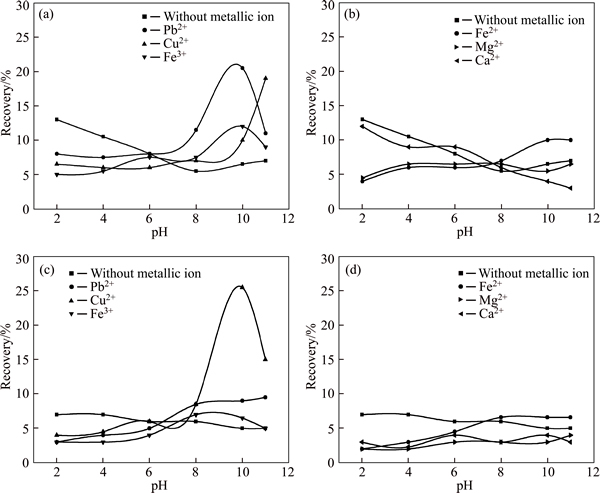
Fig. 2 Flotation recoveries of quartz particles with size of <37 μm (a, b) and 37-74 μm (c, d) as a function of pH under c(butyl xanthate)=1.0×10-5 mol/L and c(metallic ion)=1.0×10-4 mol/L
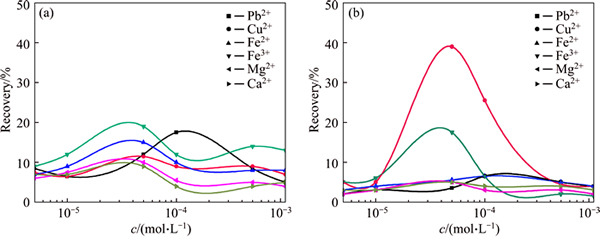
Fig. 3 Flotation recoveries of quartz particles with size of <37μm (a) and 37-74 μm (b) as a function of metallic ion under c(butyl xanthate)=1.0×10-5 mol/L
The floatability of quartz gets better with the steadily increasing concentration of metallic ion before reaching the peak, and then declines, indicating that there is an optimal concentration range to achieve the recovery. As seen, the trends of recoveries for two different sized particles are the same. 5.0×10-5 mol/L is the optimal concentration for Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Mg2+, Ca2+ while 1.0×10-4 mol/L for Pb2+. In addition, average recovery of finer particle is still higher than that of the coarser, which is in accordance with the results above.
3.2 Results of adsorption test
Before the test, the maximum adsorption peak of butyl xanthate is measured, which turns out to be 301 nm. Different concentrates of butyl xanthate were prepared to measure absorbance to draw the standard curve of butyl xanthate with results shown in Fig. 4. As shown, fit index 0.99953 is of high reliability through linear fit.
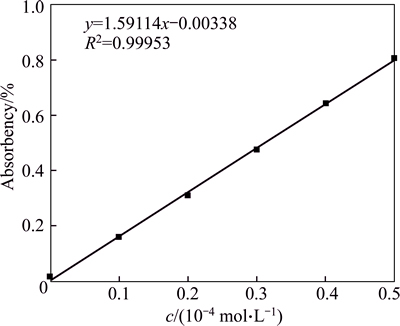
Fig. 4 Adsorption of standard curve of butyl xanthate
Quartz particles of 37-74 μm were used in adsorption measurement. The concentrations of metallic ions were determined by the usage of the highest recoveries of quartz, i.e., Pb2+ 1×10-4mol/L and the rest 5×10-5 mol/L. Then, adsorption of butyl xanthate on activated quartz was measured as a function of pH (see Fig. 5). When none metallic ion exits, pH value of solution exerts effect on absorbability of butyl xanthate and they exhibit negative correlation. Quartz liberates and Si—O bond ruptures during crushing and grinding processes [19]; its surface contacts with water molecule in solution; thus hydroxyl bonding appears and reacts with butyl xanthate further. In addition, greater growth exhibits in absorption after addition of metallic ions Pb2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+, especially in the alkaline environment. Metallic ion absorbs on quartz surface before butyl xanthate according to the experimental procedure, which makes more pathways and easier for reaction of butyl xanthate. The others are not beneficial for adsorption of butyl xanthate on quartz and thus hardly exert influence on floatability of quartz.
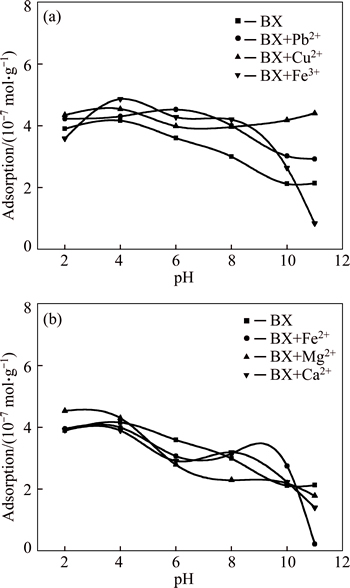
Fig. 5 Adsorption of butyl xanthate on quartz particle as a function of pH with different metallic ions (BX: Butyl xanthate)
3.3 Zeta potentials of quartz
Zeta potentials of quartz particle with or without butyl xanthate and metallic ions are measured as a function of pH value (see Fig. 6). It is carried out under the condition: concentration of butyl xanthate is 1.0×10-5 mol/L, metallic ion concentrations are 1.0×10-4 mol/L for Pb2+ and 5.0×10-5 mol/L for others. Considering the conclusions in sections 3.1.1 and 3.2, Mg2+ and Ca2+ hardly exert effect on quartz, so they are omitted here.
As shown in Fig. 6, quartz surface is negative charged, addition of butyl xanthate or metallic ion makes zeta potential move positively, on account of their adsorption on quartz surface. This is accordant with previous study [13]. What’s more, zeta potential of activated quartz declines after addition of butyl xanthate, which is attributed to butyl xanthate as a kind of anionic collector.
Considering the deviation of zeta potentials between addition of butyl xanthate alone and combination of butyl xanthate and ions, it is more significant for Pb2+, Cu2+ and Fe3+. A possible explanation therein is precipitation of hydroxide [13] or hydroxy complex of metal ion [14] forms on the surface of quartz, either can cause hydrophobic of quartz to increases floatability and decreases zeta potential. As for Fe2+ (Fig. 6(d)), there is not dramatically difference between zeta potential of activated quartz with or without collector especially in pH region 8-10, demonstrating that adsorption of butyl xanthate on quartz surface does not increase after ions are activated. So, it is not categorized as efficacious activator. However, more research on this topic needs to be undertaken before the exact product on quartz surface is conformed.
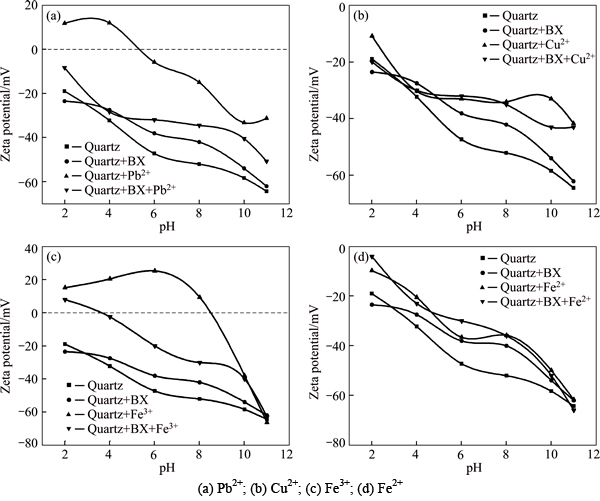
Fig. 6 Zeta potentials of quartz particle as a function of pH:
4 Conclusions
1) Results of micro-flotation tests show that Pb2+, Cu2+ and Fe3+are effective activators for the flotation of quartz in butyl xanthate solution, while the others are not. In addition, the finer particle is easier to be activated than coarser particle due to flotation results, which implies that finer particle is more likely to be floated and thus entrained in concentrate. The optimal usage is 1.0× 10-4 mol/L for Pb2+ and 5.0×10-5 mol/L for the others.
2) Through adsorption test, it is clear that pH value of solution exerts effect on absorbability of quartz, and absorption increases after adding metallic ions Pb2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+. Activation pH range is 8-10 because absorption amount is high in weak alkaline environment.
3) Zeta potential experiments shows that the addition of metallic ions except Fe2+, Mg2+ and Ca2+ reduce the negative charge on the quartz surface, addition of metallic ions above and butyl xanthate makes zeta potential drops apparently, which support a mechanism where they adsorb onto quartz surface, resulting in an expected increase in butyl xanthate collector adsorption with a concomitant increase in the flotation recoveries. But the confirmation of exact product on quartz surface needs further study.
References
[1] LIU Wen-gang, LIU Wen-bao, WANG Xin-yang, WEI De-zhou, WANG Ben-ying. Utilization of novel surfactant N-dodecyl- isopropanolamine as collector for efficient separation of quartz from hematite [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2016, 162: 188-194.
[2] ZHU Hai-ling, DENG Hai-bo, CHEN Chen. Flotation separation of andalusite from quartz using sodium petroleum sulfonate as collector [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metal Society of China, 2015, 25(4): 1279-1285.
[3] ABIDI A, ELAMARI K, BACAOUI A, YACOUBI A. Entrainment and true flotation of a natural complex ore sulfide [J]. Journal of Mining Science, 2014, 50(6): 1061-1068.
[4] YIANATOS J, VINNETT L, CARRASCO C, ALVAREZ-SILVA M. Effect of entrainment in bubble load measurement on froth recovery estimation at industrial scale [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 72: 31-35.
[5] ALBIJANIC B, OZDEMIR O, HAMPTON M A, NGUYEN P T, NGUYEN A V, BRADSHAW D. Fundamental aspects of bubble-particle attachment mechanism in flotation separation [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 65: 187-195.
[6] BASAROVA P, HUBICKA M. The collision efficiency of small bubbles with large particles [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 66-68: 230-233.
[7] VERRELLI D I, ALBIJANIC B. A comparison of methods for measuring the induction time for bubble–particle attachment [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 80: 8-13.
[8] LI Hong-qiang, FENG Qi-ming, YANG Si-yuan, OU Le-ming, LU Ying. The entrainment behaviour of sericite in microcrystalline graphite flotation [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2014, 127: 1-9.
[9] EJTEMAEI M, IRANNAJAD M, GHARABAGHI M. Role of dissolved mineral species in selective flotation of smithsonite from quartz using oleate as collector [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2012, 114-117: 40-47.
[10] ZHANG Zhi-zhen, LI Jing-sheng, LI Xiao-xia, HUANG Hou-quan, ZHOU Li-fen, XIONG Tian-tian. High efficiency iron removal from quartz sand using phosphoric acid [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2012, 114-117: 30-34.
[11] ZHU Yang-ge, ZHANG Guo-fan, FENG Qi-ming, YAN Dai-cui, WANG Wei-qing. Effect of surface dissolution on flotation separation of fine ilmenite from titanaugite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metal Society of China, 2012, 21(5): 1149-1154.
[12] ZHANG Jie, WANG Wei-qing, LIU Jing, HUANG Yang, FENG Qi-ming, ZHAO Hong. Fe(III) as an activator for the flotation of spodumene, albite, and quartz minerals [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 61: 16-22.
[13] WANG Dian-zuo, HU Yue-hua. The investigation of role of surface precipitation of meta hydroxide in flotation of quartz [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 1990, 21(3): 248-253. (in Chinese)
[14] FORNASIERO D, RALSTON J. Cu(II) and Ni(II) activation in the flotation of quartz, lizardite and chlorite [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2005, 76(1-2): 75-81.
[15] SHI Yun-liang, QIU Guan-zhou, HU Yue-hua, CHEN Chun. Surface chemical reaction of quartz in flotation [J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2001, 21(3): 43-48. (in Chinese)
[16] OU Le-ming, YE Jia-sun, ZENG Wei-wei, WAN Li. Influence and mechanism of ferric and ferrous ions on flotation of smithsonite and quartz [J]. Nonferrous Metals: Mineral Processing Section, 2012(6): 79-82. (in Chinese)
[17] OU Le-ming, HUANG Si-jie, ZHU Yang-ge. Influence of metal ions on floatability of quartz in flotation of sulfide ores [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2012, 43(2): 407-11. (in Chinese)
[18] WANG Li, SUN Wei, HU Yue-hua, XU Long-hua. Adsorption mechanism of mixed anionic/cationic collectors in muscovite-quartz flotation system [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 64: 44-50.
[19] ZHANG Kang. The study on improving the flotation performance for quartz purification [D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2013: 19-21. (in Chinese)
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Cite this article as: QIN Wen-qing, WU Jia-jia, JIAO Fen. Mechanism of different particle sizes of quartz activated by metallic ion in butyl xanthate solution [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(1): 56-61. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-017-3408-x.
Foundation item: Project(51274255) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2015CX005) supported by Innovation Driven Plan of Central South University, China; Project(2016RS2016) supported by Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Leader (Innovation Team of Interface Chemistry of Efficient and Clean Utilization of Complex Mineral Resources), China; Project supported by the Postdoctoral Research Station of Central South University, China
Received date: 2015-09-14; Accepted date: 2016-05-11
Corresponding author: JIAO Fen, PhD; Tel: +86-731-88830884; E-mail: jfen0601@126.com