J. Cent. South Univ. (2016) 23: 2156-2164
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3272-0

Simulation of solidification microstructure of Fe-6.5%Si alloy using cellular automaton-finite element method
SONG Wei(宋炜), ZHANG Jiong-ming(张炯明), WANG Shun-xi(王顺玺), WANG Bo(王博), HAN Li-lei(韩立磊)
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Abstract: 3D microstructures of Fe–6.5%Si (mass fraction) alloys prepared under different cooling conditions were simulated via finite element-cellular automaton (CAFE) method. The simulated results were compared to experimental results and found to be in accordance. Variations in the temperature field and solid-liquid region, which plays important roles in determining solidification structures, were also examined under various cooling conditions. The proposed model was utilized to determine the effects of Gaussian distribution parameters to find that the lower the mean undercooling, the higher the equiaxed crystal zone ratio; also, the larger the maximum nucleation density, the smaller the grain size. The influence of superheat on solidification structure and columnar to equiaxed transition (CET) in the cast ingot was also investigated to find that decrease in superheat from 52 K to 20 K causes the equiaxed crystal zone ratio to increase from 58.13% to 65.6%, the mean gain radius to decrease from 2.102 mm to 1.871 mm, and the CET to occur ahead of schedule. To this effect, low superheat casting is beneficial to obtain finer equiaxed gains and higher equiaxed dendrite zone ratio in Fe–6.5%Si alloy cast ingots.
Key words: finite element-cellular automaton; Fe–6.5%Si alloy; microstructure; temperature field; Gaussian distribution parameters
1 Introduction
Fe–6.5%Si (mass fraction) alloy is a crucial component of the high-performance electromotor and transformer often utilized in the high frequency field [1]. The material is favored over conventional silicon steel for its excellent soft magnetic properties such as high permeability, high electrical resistance, low magnetocrystalline anisotropy, and almost zero magnetostriction [2]. As Si content increases, unfortunately, the alloys become more brittle and extremely difficult to produce by conventional rolling processes. To date, several fabrication methods [3-6] have been developed in effort to minimize high Si alloy brittleness, including chemical vapor deposition (CVD), rapid solidification, and special rolling. These methods feature several notable constraints, however [5], such as the expense of the equipment, high maintenance rate, environmental pollution, and low yield.
Fe–6.5%Si alloy cannot be made by traditional processes mainly due to the bulky and developed columnar crystals in the alloy ingot, which results in intercrystalline cracks and corrugate defects during subsequent rolling. Accordingly, controlling the solidified structures in the alloy in order to obtain finer equiaxed structures has considerable practical significance in terms of manufacturing Fe–6.5%Si alloy. NARITA and ENOKIZONE [7] found that the Fe–6.5%Si alloy casting structure can be refined by adding alloy elements Al, Ni, or B, though the adjustment comes at the expense of magnetic properties and mechanical properties. LIU et al [8] investigated the initial microstructure and texture of strip-cast Fe–3%Si, and ZHENG et al [9] studied the formation mechanism of columnar structures of directionally solidified Fe-6.5%Si alloy. Though there have been many valuable contributions to the literature, the influence of casting parameters on the solidification structures of Fe-6.5%Si alloys cast under special cooling conditions have not yet been investigated in detail.
The traditional method of determining solidification structures is expensive in regards to both manpower and time, and yields fairly limited data. In recent decades, as computation power and speed (as well as solidification theory itself) have improved, there has been rapid advancement in solidification microstructure simulation technologies; simulation is now a very useful approach to study the solidification of metallic materials. Microstructure formation can be simulated numerically via deterministic model, stochastic model, or phase field model [10-13]. The stochastic model takes into account the random factors of the solidification process including the random distribution of nucleation sites and random selection of crystallographic orientation [14], and has been widely used to study the nucleation and growth of grains. RAPPAZ et al [15-16] also built a macro-micro model by coupling cellular automaton (CA) and finite element (FE) analyses that is now well-accepted and often employed among researchers in this field [17-21].
The primary goal of this work was to shed light on the solidification microstructures of Fe–6.5%Si alloy via CAFE method. The said solidification structures (as well as the temperature field and solid-liquid region during solidification) were examined in alloys prepared under different cooling conditions by both simulation and experiment. Based on the results, the influence of superheat and Gaussian distribution parameters on the solidification structures were examined and discussed, and a series of statistics were also established for the simulation results.
2 Model and methods
2.1 Macroscopic thermal transport
Neglecting convection in the liquid zone, the temperature field obeys the following nonstationary heat flow equation:

 (1)
(1)
where T is temperature, λ is thermal conductivity, cp is specific heat, L is the volumic latent heat of fusion, and fs is the solid fraction.
The release of latent heat during metal solidification is a significant characteristic that distinguishes the solidification process from other heat conduction processes; it also represents the bond between macroscopic and microscopic factors during solidification. The release of latent heat is derived from nucleation and dendritic growth in the microscopic field, while latent heat released from dendritic growth is fed back to calculate the temperature field. Therefore, enthalpy can serve as a variable (rather than temperature) for computing latent heat [22]:
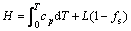 (2)
(2)
Equation (1) can then be rewritten as follows:
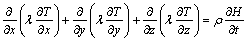 (3)
(3)
2.2 Cellular automaton (CA) model
2.2.1 Heterogeneous nucleation model
There are two ways to treat the heterogeneous nucleation for the purposes of microstructure simulation: Instantaneous nucleation and continuous nucleation [11]. Continuous nucleation distribution function was adopted for the CAFE method, assuming that instantaneous nucleation may occur in the range of possible sites. If there are no nucleation sites in a cell, nucleation does not occur regardless of how low the temperature is. Conversely, new nucleation forms randomly in the bulk volume as the result of drop in local temperature of the nucleating cell below the critical temperature in the given time step. At any undercooling temperature, the number of nucleation sites in the liquid steel is expressed by the following equation:
 (4)
(4)
where nmax is the maximum nucleation density which integrates from 0 to ∞ according to normal distribution; nucleation at the mould wall is in m-2 units whereas that in the volume of the melt is in m-3. △Tn is mean nucleation undercooling temperature (K) and △Tσ is nucleation undercooling temperature for the standard deviation (K). Therefore, the number of nucleation sites can be expressed at any undercooling temperature by the following equation:
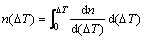 (5)
(5)
2.2.2 Dendrite tip growth kinetics model
During the casting process, the total undercooling of the dendrite tip (△T) is generally the sum of four contributions:
 (6)
(6)
where △Tc, △Tt, △Tr and △Tk are the undercooling contribution associated with solute diffusion, thermal diffusion, solid-liquid interface curvature and attachment kinetics, respectively. For most metallic alloys, the last three contributions that appear in Eq. (6) are small and solute undercooling predominates. Thus, the growth kinetics of both columnar and equiaxed morphologies can be described by the KGT model [23]. To accelerate the velocity of computation, the KGT model is fitted to form the following equation [14]:
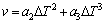 (7)
(7)
where a2 and a3 are the fitting polynomial coefficients of dendrite tip growth kinetics parameters, in m/(s·K).
2.3 Calculation procedure
A flowchart of the simulation process is shown in Fig. 1. The 3D grid model was first established in Pro/E software, then the thermal field was calculated in ProCAST, and finally the solidification structure was simulated by CAFE calculation. The CAFE calculationwas carried out on the basis of calculating the temperature field, which requires mass fraction, liquidus slope, partition coefficient, mass transfer coefficients, and Gibbs–Thompson coefficient. The final results were then extracted after the CAFE calculation was complete.

Fig. 1 Flowchart of numerical simulation model
A schematic diagram of octahedron cellular growth is shown in Fig. 2. At the beginning of CAFE calculation, the temperature of the alloy is supra-liquidus temperature and each cell is flagged by a state index I=0. In some time-steps, the supercooling satisfies grain nucleation, the state index I converts to a nonzero integer, and the cell (I≠0) begins nucleation. The cell growth is based on the growth of the octahedron bounded by the (111) face and applied to each cell which has a nonzero state index and at least one neighboring liquid cell. The octahedron- associated cells ν (Iν≠0) then capture the cell center of one of their neighbors μ (Iμ=0) during the growth process, then the state index of the cell μ is switched to that of the parent cell ν (Iν= Iμ) and a new octahedron associated with cell μ grows later. As soon as a cell is fully surrounded by mushy cells, the growth of its associated octahedron stops. The main diagonals of the octahedron correspond to the <100> crystallographic orientations and are parallel to the axis. This algorithm can directly reflect the competitive mechanism of dendrite growth [16].
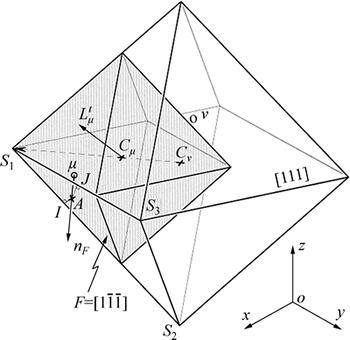
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of octahedron cellular growth [16]
2.4 Coupling FE and CA model
In the CAFE model, interpolation coefficients are defined between nodal points of the FE mesh and CA cells and the influence of the latent heat release of the grains is introduced into the calculated thermal history in order to ensure micro-structure development as a function of the thermal field (Fig. 3). The CA cell ν, with its center in the finite element I, has non-zero interpolation coefficients Φνi, Φνj, and Φνk with FE nodes i, j and k, respectively. These interpolation coefficients allow the determination of the temperature at the cell locations at the FE nodal points. At the nodal points, the same coefficients are adopted and summed, then latent heat is released by nucleation, growth, and thickening of the dendritic microstructure, updating the temperature at the FE nodal points [24].
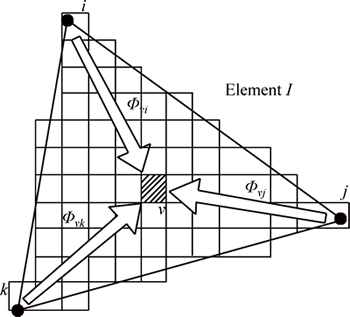
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of relationship between FE nodes and CA nodes [24]
3 Simulating 3D-microstructures in Fe- 6.5%Si alloy
The simulation model with mesh parameters is shown in Fig. 4. The casting material of the actual ingot is Fe-6.5%Si alloy, the compositions of which are listed in Table 1. The casting material was smelted in a 10 kg vacuum induction furnace under protective argon, and then molded in a steel mould. Of the two ingots we produced, one was cooled by natural convection and the other by forced water cooling. All simulated conditions were in keeping with the experiments.
In the simulation, the mould was filled with the melt instantaneously. The molten steel pouring temperature was 1773 K. In the FE model, the calculated coefficient of thermal conductivity under air cooling was 110 W/(m2·K), was 5020 W/(m2·K) under water cooling, and was 15 W/(m2·K) under slow cooling, all as-derived from the JMatPro thermodynamics database.

Fig. 4 Simulation model and mesh parameters
Table 1 Chemical composition of high silicon steel (mass fraction, %)

Maximum nucleation density nV,max, about 4.65×107 m-3, was calculated according to the ASTM standard algorithm (nV=0.8 n3/2 S). The metallograph statistics of the casting are shown in Fig. 5 (nS,max, about 1.5×105 m-2). The Gaussian distribution parameters, e.g., surface nucleation parameter △TS,n=0.5 K, the surface nucleation undercooling for the standard deviation △TS,σ=0.1 K, volume nucleation parameter △TV,n=10 K, and the volume nucleation undercooling for the standard deviation △TV,σ=0.1 K, were utilized for CAFE calculation.
In this work, the alloy was decomposed into Fe-X binary alloy systems. The liquidus and solidus temperature of Fe-6.5%Si alloy were obtained according to the Fe-Si binary phase diagram: 1721 K and 1675 K, respectively. The coefficients of dendrite tip growth kinetics were calculated based on the data given in Table 2 [19-20]: a2=2.183×10-7 and a3=1.440×10-7. The solidification structure section and temperature measurement locations are shown in Fig. 6.
4 Simulation results and discussion
4.1 Effect of cooling condition on solidification structure
The simulated and experimental results of solidification structures under air and water cooling conditions are shown in Fig. 7. The simulated results, including both columnar dendrite zones and equiaxed dendrite zones, were in close agreement with the experimental results.
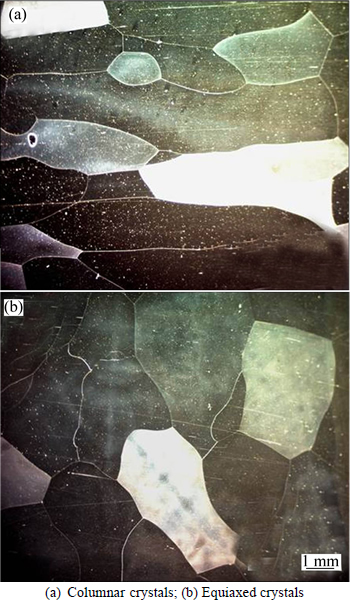
Fig. 5 Metallographs of cast Fe-6.5%Si alloy:
Table 2 Composition C0, solute partition coefficient k, liquidus slope m and diffusion coefficient DL of binary Fe-based alloy

The simulated results of the alloy solidification structures under both cooling conditions are shown in Fig. 8, and the relevant statistics are provided in Table 3. The equiaxed dendrites developed more extensively as the cooling intensity decreased from water cooling to air cooling to slow cooling; consequently, the equiaxed crystal ratio increased from 15.12% to 83.56% and the mean gain radius decreased from 3.508×10-3 m to 0.173×10-3 m. This can be mostly attributed to the lower thermal gradient at the solidified front and the larger solid-liquid region during solidification under slow cooling, which are beneficial to equiaxed grain growth. In addition, the dendrite tip was smashed by the fluid flow when there was a larger solid-liquid region, which transported fragments of the equiaxial dendrite to the bulk melt and formed a number of nucleation cores. In short, weaker cooling facilitated the formation of finer and greater quantity of equiaxed grains.

Fig. 6 Location of temperature measurement points and solidification structure calculation section

Fig. 7 Experimental and simulated microstructure results of Fe-6.5%Si ingot:

Fig. 8 Simulation results of solidification structure under different cooling conditions:
Table 3 Solidification structures statistics under different cooling conditions

4.2 Simulated temperature field results and discussion
Figure 9 shows the temperature curves at locations a-e in Fig. 6. At the beginning of the casting process, the temperature decreased rapidly due to the high temperature gradient between the melt and the mould wall and the cooling rate at the surface layer of the casting (point a) was quicker than at other points in the ingot. As soon as temperature dropped below the liquidus temperature, the melt was undercooled and nucleation and solidification began. This took place from the casting surface regions toward the casting center (i.e., from point a toward point e). During the initial stage of solidification, temperature curves remained basically invariable because the release of the latent heat of crystallization was equal to the thermal release. As solidification progressed, less latent heat of crystallization was released than the thermal release, so solidification occurred throughout a continuous temperature-fall and the temperature curves rapidly decreased after solidification was complete. The temperature field under slow cooling was more uniform than that under air cooling or water cooling during the entire solidification process (Fig. 9).
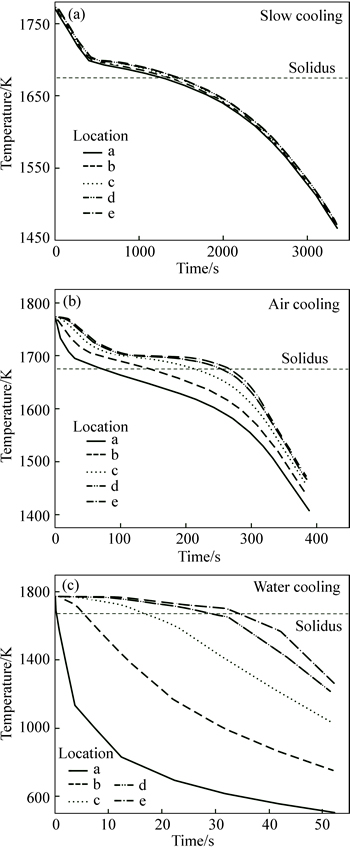
Fig. 9 Simulation results of cooling curves under different cooling conditions
Figure 10 shows the changes in the solid-liquid region under different cooling conditions. As shown in Figs. 10(b) and 10(c), under air cooling and water cooling, there was a narrow solid-liquid region in the initial stage due to the high thermal gradient ahead of the solidification front; as solidification progressed,however, the solid-liquid region expanded considerably due to the slower heat transfer through the solidified metal layer. The mushy zone, under slow cooling (Fig. 10(a)) remained effectively invariable due to the lower heat transfer and extended local solidification time during solidification. As a result, equiaxed grains readily formed in the mushy zone.

Fig. 10 Simulation results of solid-liquid region changes under different cooling conditions
4.3 Effect of Gaussian distribution parameters on solidification microstructure
In order to study the effects of Gaussian distribution parameters on the microstructure simulation, volume nucleation undercooling (△TV,max) and maximum nucleation density (nV,max) were used to represent the undercooling, which activate the heterogeneous nucleus and the number of heterogeneous cores, respectively. The simulated nucleation parameters for each specimen are listed in Table 4.
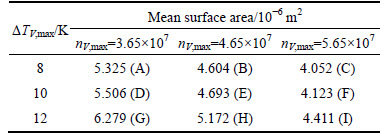
The simulation results are shown in Fig. 11 and the statistical results are listed in Table 5. The equiaxed dendrite zone grew larger gradually as the meanundercooling temperature decreased from 12 K to 8 K, suggesting that the mean undercooling mainly controlled equiaxed dendrite zones in the CAFE model: The lower the mean undercooling, the larger the equiaxed dendrite zones. The mean surface area also decreased considerably as the maximum nucleation density increased from 3.65×107 to 5.65×107 at same mean undercooling level. In effect, the maximum nucleation density mainly controlled the grain size: The larger the maximum nucleation density, the smaller the grains.
Table 4 nV,max and △TV,max values
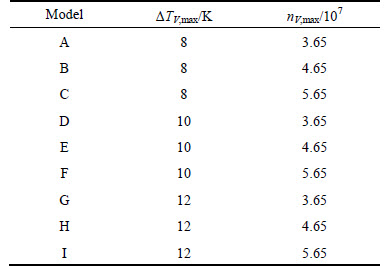
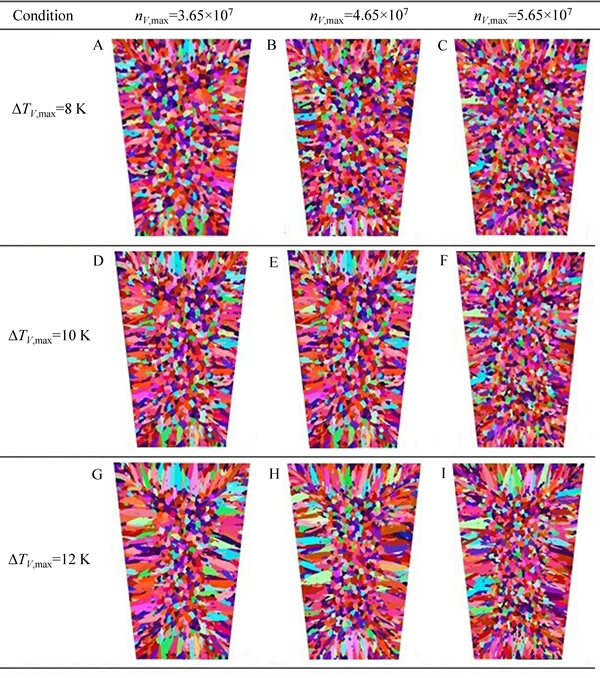
Fig. 11 Simulation results of solidification structure under different nucleation conditions
Table 5 Statistical results of mean surface area in model A-I
4.4 Effect of superheat on solidification microstructure and CET (columnar to equiaxed transition)
Superheat is one of the key parameters in determining casting quality. In this segment, the model of air cooling was employed to investigate the effect of superheat on solidification microstructures by changing the initial temperature. The simulated solidification structures under various superheats are shown in Fig. 12 and the relevant statistics are listed in Table 6. As superheat temperature decreased from 52 K to 20 K, the equiaxed dendrite zone ratio increased from 58.13% to 65.6%, the number of grains increased from 1969 to 2125, and the mean gain radius decreased from 2.102 mm to 1.871 mm. When the molten steel solidified from liquid to solid during the casting process, the atoms in the molten steel were initially unstable before transforming from messy clusters to orderly atomic crystals; low superheat decreased the degree of atomic disorder in the molten steel and helped to promote the nucleation. Low superheat also benefitted 1) the formation of a low thermal gradient ahead of the solidification front, 2) a large number of nucleation embryos, and 3) a high equiaxed grain ratio in the cast alloy.

Fig. 12 Simulation results of solidification structure under different superheat conditions:
Table 6 Solidification structure statistics under different superheat conditions
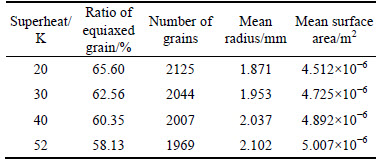
Figure 13 shows the CET results of the alloys cast under different superheats. The CET was not abrupt but instead formed gradually during solidification; the transition took place ahead of schedule at lower superheats. This phenomenon can be attributed to the fact that the CET mechanism in the CAFE model is characterized by thermal interaction: When the superheat decreased, the thermal gradient decreased and the undercooling in the liquid region ahead of the columnar dendrite tip increased, which promoted the development of nucleation embryos and inhibited columnar grain growth.
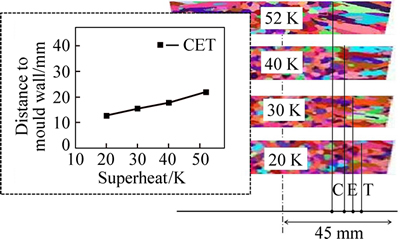
Fig. 13 CET simulation results under different superheats
5 Conclusions
1) The 3D microstructures of Fe–6.5%Si cast alloy ingots were simulated via CAFE method and compared to experimental results. The simulated solidification structures, including both equiaxed dendrite zones and various sizes of grains were consistent with the experimental observations. Finer and larger quantity of equiaxed grains was obtainable when the cooling conditions were weaker.
2) The temperature field under slow cooling was more uniform and stable than that under air or water cooling; moreover, the solid-liquid region stayed basically invariable during solidification due to the lower heat transfer compared to the other two cooling conditions.
3) The effects of Gaussian distribution parameters on the microstructures were observed in detail to find that the lower the mean undercooling, the higher the equiaxed dendrite zone ratio; also the larger the maximum nucleation density, the smaller the grain size.
4) As the superheat decreased from 52 K to 20 K, the equiaxed zone ratio increased from 58.13% to 65.6%, the mean gain radius decreased from 2.102 mm to 1.871 mm, and the columnar to equiaxed transition (CET) occurred farther ahead of schedule. In short, low superheat casting was beneficial in terms of obtaining finer equiaxed grains and higher equiaxed dendrite zone ratio in the Fe–6.5%Si alloy ingot.
References
[1] HAIJI H, OKADA K, HIRATANI T, ABE M, NINOMIYA M. Magnetic properties and workability of 6.5% Si steel sheet [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 1996, 160: 109-114.
[2] HE Zhi-zhong, ZHAO Yu, LUO Hai-wen. Electrical sheet [M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 2008: 976. (in Chinese)
[3] FANG Xian-shi, LIANG Yong-feng, YE Feng, LIN Jun-pin. Effect of rolling reduction on the texture of 6.5% Si electric steel during warm rolling [J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2012, 24: 3346-3350. (in Chinese)
[4] YANG Jin-song, XIE Jian-xin, ZHOU Cheng. Preparation technology and prospect of 6.5% Si steel [J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2003, 34(3): 244-246. (in Chinese)
[5] ZHENG Xin, YAN Biao. Properties and preparation techniques of Fe-6.5%Si high silicon steel [J]. Materials Review, 2012(S1): 392-396.
[6] LIN Jun-pin, YE Feng, CHEN Guo-liang. Fabrication technology, microstructures and properties of Fe-6.5% Si alloy sheets by cold rolling [J]. Frontier Science, 2007, 2(2): 18-26. (in Chinese)
[7] NARITA K, ENOKIZONO M. Effect of nickel and manganese addition on ductility and magnetic properties of 6.5% silicon-iron alloy [J]. IEEE Trans Magn, 1978, 14(4): 258-262.
[8] LIU Hai-tao, LIU Zhen-yu, LI Chen-gang, CAO Guang-ming, WANG Guo-dong. Solidification structure and crystallographic texture of strip casting 3% Si non-oriented silicon steel [J]. Materials Characterization, 2011, 62(5): 463-468.
[9] ZHENG Zhi-lin, YE Feng, LIANG Yong-feng, LIN Jun-pin, CHEN Guo-liang. Formation of columnar-grained structures in directionally solidified Fe-6.5% Si alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19(2): 165-168.
[10] SPITTLE J A, BROWN S G R. Computer simulation of the effects of alloy variables on the grain structures of castings [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1989, 37(7): 1803-1810.
[11] WANG S L, SEKERKA R F, WHEELERh A A, MURRAY B T, CORIELL S R, BRAUN R J. Thermodynamically-consistent phase-field models for solidification [J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1993, 69(1): 189-200.
[12] NATUME Y, OHSASA K, NARITA T. Phase-field simulation of transient liquid phase bonding process of Ni using Ni-P binary filler metal [J]. Materials Transactions, 2003, 44(5): 819-823.
[13] ZHAO Yu-zhen, SHI Yao-wu, SHI Li-feng. Current research status of computer simulation of casting solidification structure [J]. Metal Forming Technology, 2002, 20(6): 53-56. (in Chinese)
[14] RAPPAZ M, GANDIN C A. Probabilistic modelling of microstructure formation in solidification processes [J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1993, 41(2): 345-360.
[15] GANDIN C A, RAPPAZ M. A 3D cellular automaton algorithm for the prediction of dendritic grain growth [J]. Acta Materialia, 1997, 45(5): 2187-2195.
[16] GANDIN C A, DESBIOLLES J L, RAPPAZ M. A three- dimensional cellular automation-finite element model for the prediction of solidification grain structures [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1999, 30(12): 3153-3165.
[17] PANG Rui-peng, WANG Fu-ming, ZHANG Guo-qing, LI Chang- rong. Study of solidification thermal parameters of 430 ferrite stainless steel based on 3D-CAFE method [J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2013, 49(10): 1234-1242. (in Chinese)
[18] LUO Yan-zhao, ZHANG Jiong-ming, WEi Xiao-dong. Numerical simulation of solidification structure of high carbon SWRH77B billet based on the CAFE method [J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2012, 39(1): 26-30.
[19] JING Cai-liang, WANG Xin-hua, JIANG Min. Study on solidification structure of wheel steel round billet using FE-CA coupling model [J]. Steel Research International, 2011, 82(10): 1173-1179.
[20] WANG Jin-long, WANG Fu-ming, ZHAO Yan-yu, ZHANG Jiong- ming, REN Wei. Numerical simulation of 3D-microstructures in solidification processes based on the CAFE method [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2009, 16(6): 640-645.
[21] HOU Zi-bing, JIANG Fang, CHENG Guo-guang. Solidification structure and compactness degree of central equiaxed grain zone in continuous casting billet using cellular automaton-finite element method [J]. ISIJ International, 2012, 52(7): 1301-1309.
[22] THEVOZ P, DESBIOLLES J L, RAPPAZ M. Modeling of equiaxed microstructure formation in casting [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1989, 20(2): 311-322.
[23] KURZ W, GIOVANOLA B, TRIVEDI R. Theory of microstructural development during rapid solidification [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1986, 34(5): 823-830.
[24] GANDIN C A, RAPPAZ M. A coupled finite element-cellular automaton model for the prediction of dendritic grain structures in solidification processes [J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1994, 42(7): 2233-2246.
(Edited by YANG Bing)
Foundation item: Project(2012AA03A505) supported by the High-Tech Research and Development Program of China; Project(51474023) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2015-04-07; Accepted date: 2015-09-24
Corresponding author: ZHANG Jiong-ming, Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-10-82376597; E-mail: jmz2203@sina.com