Treatment of oil/water emulsion by polyethylene glycol ultrafiltration membrane①
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2005年第5期
论文作者:何德文 肖羽堂 李雄 金艳
文章页码:542 - 545
Key words:oil/ water emulsion; ultrafiltration membrane; permeate flux; chemical oxygen demand
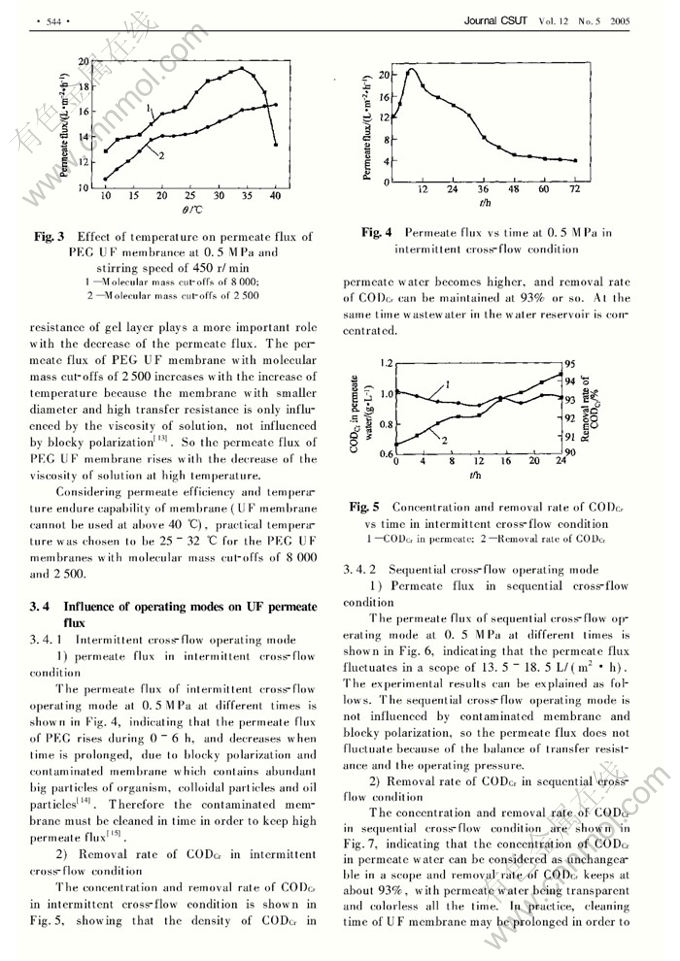
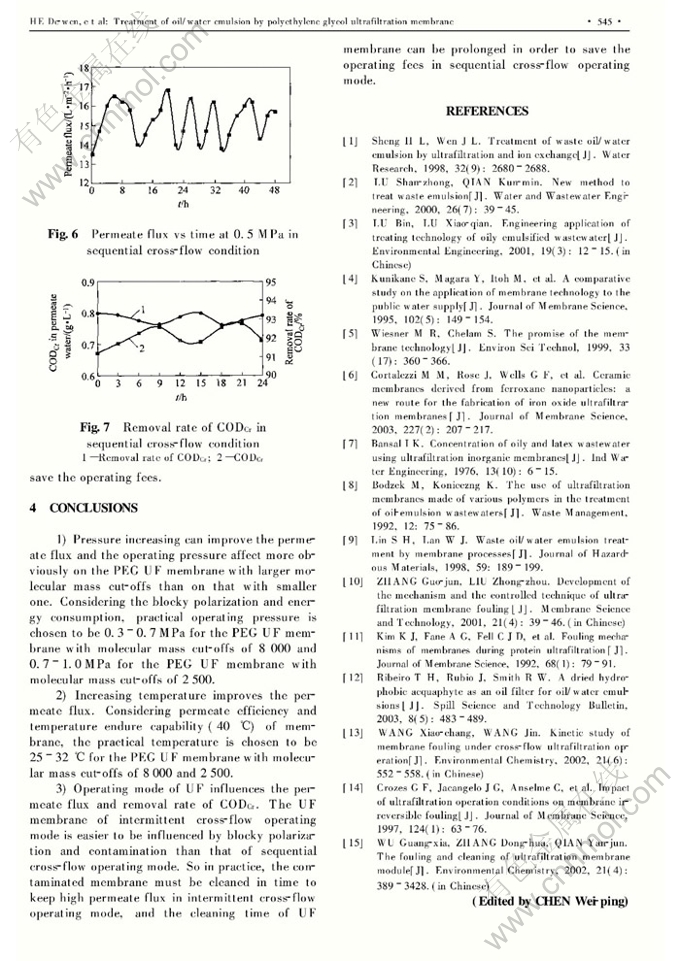
Abstract: Polyethylene glycol (PEG) membranes with different molecular mass cut-offs were used to treat oil/water emulsion, and the effects of experimental conditions including pressure, temperature and different operating modes on permeate flux and removal rate of chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) were studied. The results show that the permeate flux of ultrafiltration membrane is influenced by pressure and temperature; practical pressure is chosen to be 0.3 0.7 MPa for the PEG with molecular mass cut-offs of 8 000 and 0.7 1.0 MPa for the PEG with molecular mass cut-offs of 2 500; and the practical temperature is chosen to be 25 32℃. Different operating modes of ultrafiltration also influence the permeate flux and removal rate of CODCr. The ultrafiltration membrane of intermittent cross-flow operating mode is easier to be influenced by blocky polarization and contamination than that of sequential cross-flow operating mode. Removal rate of CODCr in intermittent cross-flow and sequential cross-flow condition can be maintained at about 93%.