文章编号:1004-0609(2013)S1-s0134-05
铌元素对铸造纯钛显微组织和性能的影响
刘时兵,娄延春,谢华生,赵 军,刘宏宇
(沈阳铸造研究所,沈阳 110022)
摘 要:通过熔配5种成分(w(Nb)=15%,20%,25%,30%,35%)的钛铌合金,采用石墨铸型浇注成棒状试样,并进行固溶处理,研究铌元素对铸造纯钛组织和性能的影响。结果表明:铌可以显著降低铸造纯钛的硬度、弹性模量和线膨胀系数,并提高强度。在铌含量为15%~35%范围内,Ti-20%Nb合金具有最低的硬度(HRC=5)和最低的弹性模量(E=56 GPa);当铌含量约为25%时合金具有最小的平均线膨胀系数(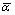 =6.6×10-6/℃(20~100 ℃))。固溶后合金抗拉强度为520~660 MPa,伸长率为19%~32%。TN系列合金固溶组织由基体相β和针状析出相α″、α′和α相组成,α″和β相是造成铸造纯钛硬度、弹性模量和线膨胀系数降低的主要原因。
=6.6×10-6/℃(20~100 ℃))。固溶后合金抗拉强度为520~660 MPa,伸长率为19%~32%。TN系列合金固溶组织由基体相β和针状析出相α″、α′和α相组成,α″和β相是造成铸造纯钛硬度、弹性模量和线膨胀系数降低的主要原因。
关键词:铌元素;钛合金;硬度;弹性模量;线膨胀系数
中图分类号:TG146.23; TG294 文献标志码:A
Effect of element Nb on microstructure and properties of cast pure titanium
LIU Shi-bing, LOU Yan-chun, XIE Hua-sheng, ZHAO Jun, LIU Hong-yu
(Shenyang Research Institute of Foundry, Shenyang 110022, China)
Abstract: Five kinds of Ti-Nb alloys (w(Nb)=15%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%) were prepared, melted into rod with graphite mould, and solution-treated to investigate the effect of single Nb addition on the microstructure and properties of cast pure titanium. The results shows that Nb element can significantly decrease the hardness, elastic modulus and linear expansion coefficient, and increase the strength of cast pure titanium. In the Nb mass frachion range of 15%~35% the Ti-20% Nb alloy has the lowest Rockwell hardness (HRC=5) and the lowest elastic modulus (E=56 GPa); and the Ti-25% Nb alloy has the lowest linear expansion coefficient (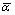 =6.6×10-6/℃, 20~100 ℃). The tensile strength and elongation of the Ti-Nb alloys are in the ranges of 520~660 MPa and 19%~32%, respectively. The microstructures of the solution-treated Ti-Nb alloys all are composed of matrix β-phase and acicular precipitated phases α′ and α″ and phase α. Phase α″ and β-phase are the main reasons of low Rockwell hardness, low elastic modulus and low linear expansion coefficient for the Ti-Nb alloys.
=6.6×10-6/℃, 20~100 ℃). The tensile strength and elongation of the Ti-Nb alloys are in the ranges of 520~660 MPa and 19%~32%, respectively. The microstructures of the solution-treated Ti-Nb alloys all are composed of matrix β-phase and acicular precipitated phases α′ and α″ and phase α. Phase α″ and β-phase are the main reasons of low Rockwell hardness, low elastic modulus and low linear expansion coefficient for the Ti-Nb alloys.
Key words: element Nb; titanium alloy; hardness; elastic modulus; linear expansion coefficient
钛合金是现代装备制造业的重要结构材料。钛及其合金从其发现到现在成为大多数领域不可或缺的重要应用材料仅仅经历了60多年,与钢、铝等传统结构材料相比,钛完全是一颗“新星”,但其优异的物理、化学、力学性能使其在关系国家经济民生、安全发展领域发挥了不可替代的重要作用。随着航空、航天、舰船及现代化工、医疗技术的快速发展,近年来钛合金材料发展也趋向于功能化、高性能化,特种新钛合金材料不断得到开发和应用[1-3],如高温领域应用的耐高温钛合金[4]、低温领域应用的超低温钛合金[5]、高强度钛合金[6]和高损伤容限钛合金等。上述新材料中,一个十分突出的特征是都含有金属元素Nb。Nb元素在改善钛合金组织,提高性能方面发挥了重要作用。但对于Nb 元素对纯钛的单一影响方面,相关研究报道较少。为此,本文作者开展单一Nb元素对铸造纯钛组织和性能的影响研究。
1 实验
共设计了5种不同铌含量的钛铌合金,铌的质量分数分别为15%、20%、25%、30%和35%。为保证合金成分纯净,试验用金属材料选用0级海绵钛,Nb1铌片(长260 mm、宽10 mm、厚2 mm)。先将铌片用丙酮溶液清洗,去除表面杂质和油污、晾干,经真空加热干燥后备用。按设计成分比例配制合金,并放入自制金属模具中采用液压机压制成约d80 mm圆形铸锭,与钛电极头焊接成自耗电极,然后采用真空自耗凝壳炉熔化,经切割成块,清洗干燥后组焊成电极,再次重熔2~3次,以促进成分均匀,最后采用刷涂料的石墨铸型重力浇注成分析试样。随后在850 ℃行固溶处理1 h并水淬获得最终试样。分别取样进行成分分析和性能测试,化学分析采用等离子体发射直读光谱仪和N、H、O联合分析仪,拉伸性能测试采用CSS-1120电子万能试验机,硬度测试采用TH301洛氏硬度计,热膨胀系数测试采用Wetzlar光学线膨胀仪。金相试样采用线切割取样,进行表面抛光处理后,用腐蚀剂(m(HF):m(HNO3): m(H2O)=10:5:85)进行腐蚀,采用光学显微镜ZEISS AXIOWordert.AE进行显微组织观察,采用X射线衍射仪D/max 2500pc进行相组成分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 合金的化学成分
表1所列为熔配合金最终浇注成环形试样的化学分析结果。从表1中可看出,杂质元素含量较低,达到了国标GB/T 3620.1—2007规定的ELI级水平,且波动范围较小;而主合金化元素Nb的波动范围则较大,且与设计值(名义值)有不同程度的偏差。从分析数据来看,Nb元素含量越高,偏差趋势越大。经分析,这种偏差是由Nb元素与Ti元素的密度偏析以及配料方式引起的。总体来看,各合金成分能够代表设计值,符合实验要求。
2.2 合金的热物理性能及力学性能
通过对合金的热物理性能参数和室温力学性能进行测试,得到如表2所列结果。
表1 Ti-Nb合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of Ti-Nb alloys
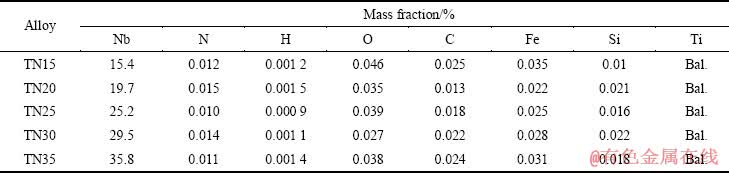
表2 Ti-Nb合金的主要性能参数
Table 2 Main property parameters of Ti-Nb alloys

2.2.1 Nb元素对铸造纯钛线膨胀系数的影响
从表2中数据可以看出,Nb含量对铸造纯钛的平均线膨胀系数具有一定的影响。随Nb含量的逐渐增加,合金的平均线膨胀系数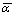 呈先降低而后上升的趋势。在Nb含量达到约25%时,该系列合金具有最小的平均线膨胀系数,即6.6×10-6/℃;在Nb含量达到约35%时,平均线膨胀系数
呈先降低而后上升的趋势。在Nb含量达到约25%时,该系列合金具有最小的平均线膨胀系数,即6.6×10-6/℃;在Nb含量达到约35%时,平均线膨胀系数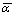 具有最大值,并接近于单质纯钛的。
具有最大值,并接近于单质纯钛的。
2.2.2 Nb元素对铸造纯钛硬度的影响
从3次测量的平均洛氏硬度值来看,添加Nb进行合金化并固溶处理后,与纯钛相比,硬度值出现明显降低,TN15~TN35系列合金的硬度值均低于20。且随Nb含量增加,硬度值(HRC)先降低、后升高、再降低,最高的是TN30合金,为19.5,最低的是TN20,仅为5。该变化趋势与其线膨胀系数变化趋势相似,但不同的是硬度值最后再次随Nb含量增加出现降低,且最低点从TN25合金迁移到TN20合金。在上述合金范围内,硬度值最大降低幅度为84.4%,最小幅度为39.1%。可以看出,Nb对铸造纯钛具有强烈的软化效应。
2.2.3 Nb元素对铸造纯钛弹性模量的影响
对于弹性模量,从表2中数据来看,与纯钛相比,TN系列合金的弹性模量有了大幅度降低,基本都处于50~80 GPa之间,其中1个数据在60 GPa以下,2个数据在60~70 GPa之间。Nb元素对铸造纯钛的弹性模量影响明显。弹性模量最低的是TN20合金,为56 GPa,约为未合金化纯钛的53%;最高的是TN30合金,为76.8 GPa,约为未合金化纯钛的73%。随Nb含量增加,合金的弹性模量同样呈先降低、后增加、再降低趋势,与硬度值的变化趋势完全相同,其最低点和趋势转变点均为TN20合金和TN30合金。
2.2.4 Nb元素对铸造纯钛拉伸性能的影响
由表2可知,铸造纯钛在未合金化时具有较低的室温拉伸强度,其抗拉强度为450 MPa,但经Nb元素合金化后,拉伸强度有了显著提高,其抗拉强度提高到520~660 MPa。其中,TN15、TN25、TN30和TN35合金的抗拉强度在固溶状态下都处于(635±25) MPa以内,随Nb含量的变化波动较小,基本处于同一水平。但TN20合金相对于其他合金,抗拉强度较低,这与该合金的硬度、弹性模量具有极小值一致。从塑性指标来看,上述合金都有较好塑性,伸长率很大,为19%~32%。
2.3 显微组织
如图1(a)~(e)所示分别为TN15~TN35的显微组织,图2(a)和(b)所示分别为TN15和TN20的X射线衍射分析结果。通过观察合金组织及衍射分析结果可知,TN系列合金固溶后组织中有马氏体组织α″和α′相生成。其中TN15合金组织由白色基体相β和大量黑色短针状α′相及少量α″相组成,α′和α″相由淬火所得,α′相针具有一定的位向排列,各针相呈平行或斜交关系分布,见图1(a)。TN20合金组织则由白色的析出相α″、α′和残余相β组成,其中α″相呈粗针状正交析出,且长度较短,α′相则呈长针状分布,其余为未转变的残余β相,见图1(b)。TN25合金组织由大量呈正交析出的白色针状α″相和残余β相组成。与TN20合金相比,α″相长度明显增加、宽度变窄,并且α′相完全消失,见图1(c)。TN30合金组织与TN25合金比较相近,大部分由长针状析出的α″相和残余β相组成,但不同的是TN30合金平行析出的α″相数量增多,且α″相针束宽度明显增加,而正交析出的α″相数量明显减少,并有α相出现,该α相由高温β相直接转变生成,见图1(d)。TN35合金组织与上述合金组织明显不同,大部分为白色的基体相β,在β相基体上杂乱的分布着大量黑色短棒状α′相,并少量析出长条状α相。
2.4 讨论
对于纯钛来说,Nb属于β相稳定化元素,其获得全β相的临界浓度值(wK)为36%[7]。因此,在钛中加入Nb元素将阻碍β相向α相的转变。在本研究中,Nb的含量(质量分数)范围为15%~35%,因此,在固溶后淬火过程中,不可避免地要发生高温β相向α相的转变。随Nb含量的增加,Nb元素的阻碍效应越来越明显。在图1中,当Nb含量较低(15%)时,阻碍效应较弱,高温β相除保留至室温部分外,大部分转变为马氏体α′组织。但随着Nb含量的逐步增加,其稳定化效应越来越大,高温β相逐渐不能直接生成α′相,部分β相只能先转变成过渡相α″,因此出现了TN20和TN25组织中的大量α″相。Nb含量进一步增加,高温β相转变为α″相的难度也进一步增加,只有少量β相转变为α″相,部分高温β相于是直接转变为α′相或α相。为此,出现了图1中的TN30和TN35合金组织。
一般来说,α相的硬度比α″相的硬度高,但较α′相的硬度低 [8-10]。在本研究中,TN20合金具有最低硬度值,其组织由β+α″相组成,与该结论一致,即Nb元素添加导致马氏体相α″的生成是铸造纯钛硬度软化的主要原因。从弹性模量来看,其变化趋势与硬度完全一致,因此,Nb元素添加导致马氏体相α″的生成也是弹性模量降低的主要原因。此外,β相也是具有较低弹性模量的相,β相和α″相共同造成较低的弹性模量。Nb元素对铸造纯钛的硬度和弹性模量影响效果基本相同。对于平均线膨胀系数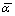 ,不含α相的TN15、TN20和TN25合金比含α相的TN30和TN35合金有一定程度的降低,尤其是含α″相较多的TN25合金,平均线膨胀系数最低,因此可推出,α″相是导致合金低膨胀系数的主要原因。但对于α″相导致铸造纯钛硬度、弹性模量,以及线膨胀系数降低的作用机理还有待进一步研究解决。
,不含α相的TN15、TN20和TN25合金比含α相的TN30和TN35合金有一定程度的降低,尤其是含α″相较多的TN25合金,平均线膨胀系数最低,因此可推出,α″相是导致合金低膨胀系数的主要原因。但对于α″相导致铸造纯钛硬度、弹性模量,以及线膨胀系数降低的作用机理还有待进一步研究解决。

图1 不同铌含量钛合金固溶后的显微组织
Fig. 1 Microstructures of Ti-Nb alloys with different Nb contents after solution treatment
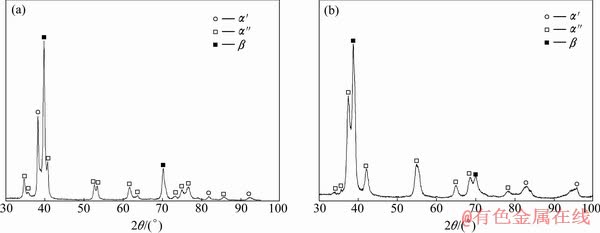
图2 TN15和TN20合金的XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of TN15 (a) and TN20 (b) alloys
3 结论
1) Nb元素对铸造纯钛的平均线膨胀系数具有一定影响,随Nb含量增加,平均线膨胀系数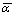 先降低而后增加,具有最小平均线膨胀值的合金是TN25合金,其值约为6.6×10-6/℃。
先降低而后增加,具有最小平均线膨胀值的合金是TN25合金,其值约为6.6×10-6/℃。
2) Nb元素对铸造纯钛具有明显的硬度软化作用,随Nb含量增加,洛氏硬度先降低、后增加、再降低,最低的为TN20合金,其硬度值HRC为5。
3) Nb元素对铸造纯钛的弹性模量影响较大,TN系列合金具有较低的弹性模量,是铸造纯钛弹性模量的56%~73%,随Nb含量的增加,铸造纯钛的弹性模量先降低、后增加、再降低,与硬度值变化趋势一致,TN20合金的弹性模量最低,为56 GPa。
4) Nb元素对铸造纯钛拉伸性能影响明显,合金化后抗拉强度从450 MPa提高到520~660 MPa,但在Nb含量为15%~35%的范围内,合金拉伸性能变化幅度不大;TN系列合金具有较好的塑性,伸长率较大,为19%~32%。
5) TN系列合金固溶显微组织由基体相β和针状马氏体析出相α″、α′相及α相组成,α″相和β相是造成合金硬度低、弹性模量低和低膨胀系数小的主要原因。
REFERENCES
[1] 黄 旭. 航空用钛合金发展概述[J]. 军民两用技术与产品, 2012(7):12-14.
HUANG Xu. Development of titanium alloys in aviation [J]. Dual Use Technologies & Products, 2012(7): 12-14.
[2] 朱康平, 祝建雯, 曲恒磊. 国外生物医用钛合金的发展现状[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(11): 2058-2063.
ZHU Kang-ping, ZHU Jian-wen, QU Heng-lei. Development and application of biomedical Ti alloys abroad [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(11): 2058-2063.
[3] 张文毓. 钛合金技术发展现状及趋势[J]. 中国有色金属, 2010(1): 76-77.
ZHANG Wen-yu. Development and trend of titanium alloys technologies [J]. China Nonferrous Metals, 2010(1): 76-77.
[4] ZHAO Er-tuan, KONG Fan-tao, CHEN Yu-yong, LI Bao-hui. Interfacial reaction between Ti-1100 alloy and ceramic mould during investment casting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011(S2): s348-s352.
[5] 刘清华, 惠松骁, 叶文君, 王 国, 胡光山. 初生α相含量对TC4 ELI钛合金动态应力应变行为的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(10): 2749-2755.
LIU Qing-hua, HUI Song-xiao, YE Wen-jun, WANG Guo, HU Guang-shan. Effect of primary α phase cotent on dynamic stress—strain behavior of TC4 ELI titanium alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(10): 2749-2755.
[6] 王鼎春. 高强钛合金的发展与应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): s958-s963.
WANG Ding-chun. Development and application of high- strength titanium alloys [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): s958-s963.
[7] 王金友, 葛志明, 周彦邦. 航空用钛合金[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1985: 118-122.
WANG Jin-you, GE Zhi-min, ZHOU Yan-bang. Aeronautical titanium alloy [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Press, 1985: 118-122.
[8] Е А 鲍利索娃. 钛合金金相学[M]. 陈石卿, 译. 北京: 工业出版社, 1986: 35-141.
БОРИСОВА E A. Titanium alloys metallography [M]. CHEN Shi-qing, transl. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 1986: 135-141.
[9] 邓安华. 钛合金的马氏体相变[J]. 上海有色金属, 1999(12): 193-199.
DENG An-hua. Martensitic transformation of titanium alloys [J]. Shanghai Nonferrous Metals, 1999(12): 193-199.
[10] 毛彭龄. 两相钛合金的相变特征和热处理规范[J]. 上海钢研, 1995(3): 50-57.
MAO Peng-ling. The features of phase transformation and heat treatment in two-phase titanium alloys [J]. Shanghai Steel & Iron Research, 1995(3): 50-57.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51375318)
收稿日期:2013-07-28;修订日期:2013-10-10
通信作者:刘时兵,高级工程师;电话:024-89354095;E-mail:ls-b@163.com