SiC颗粒粒径和相对密度对泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料压缩性能的影响
罗彦茹1,于思荣2,朱先勇1,刘家安3
(1. 吉林大学 机械科学与工程学院,吉林 长春,130022;
2. 中国石油大学 机电工程学院,山东 青岛,266555;
3. 吉林大学 材料科学与工程学,吉林 长春,130022)
摘要:采用CaCO3作为发泡剂用熔体发泡法制备泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料,用CMT5205电子万能试验机对该材料压缩性能进行测试,并分析泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料在外力作用下的破坏机理及SiC颗粒粒径和相对密度对该材料压缩性能的影响规律。研究结果表明:泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料受轴向压缩时由于孔壁发生弯曲和横向拉伸而呈脆性逐层破坏或沿斜截面断裂的特征;当SiC颗粒粒径由28 μm减小到5 μm时,泡沫5% SiCp/ZL104(体积分数)复合材料的屈服应力由5 MPa增至11 MPa;当其相对密度由0.16增至0.32时,对应的屈服应力由5 MPa增至10 MPa。
关键词:金属基复合材料;泡沫金属;破坏机理;SiC颗粒;相对密度
中图分类号:TB331 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)06-1599-05
Effects of SiC particle size and relative density on
compressive properties of SiCp/ZL104 composite foams
LUO Yan-ru1, YU Si-rong2, ZHU Xian-yong1, LIU Jia-an3
(1. Institute of Mechanical Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China;
2. College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, China University of Petroleum, Qingdao 266555, China;
3. Institute of Material Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China)
Abstract: The SiCp/ZL104 composite foams were fabricated by the melt foaming process using CaCO3 as blowing agent. The compressive properties were tested by CMT5205 electron universal testing machine. The failure mechanism and the effects of SiC particle size and relative density on compressive properties of SiCp/ZL104 composite foams were investigated under loading condition. The results show that, under axial compression, the failure mechanism of SiCp/ZL104 composite foams display brittle crack characteristics layer by layer or along the sloping section due to the bending and landscape orientation stretching of SiCp/ZL104 composite as cell wall material. The yield stress of 5% SiCp/ZL104 (volume fraction) composite foams changes from 5 to 11 MPa with the decrease of the SiC particle size from 28 to 5 μm and changes to 10 MPa from 5 MPa with the increase of relative density from 0.16 to 0.32.
Key words: metal matrix composite; metal foams; failure mechanism; SiC particle; relative density
在航空航天及汽车业中,要求吸收性材料具有高强度、高能量,泡沫材料正是具有这种性能的新型功能材料。在泡沫材料的诸多性能中,压缩性能尤为重要,因此,对泡沫金属压缩行为的研究,成为近年来力学、材料科学及其他应用领域中非常活跃的研究课题[1-3]。为了揭示泡沫金属的压缩性能与结构特征参数的关系,许多科研工作者对泡沫金属压缩时的压缩行为与变形机制开展了一系列的研究工作,但大部分工作都集中在Alulight和Alporas等闭孔结构的商业化泡沫铝上[4-6]。陶瓷颗粒增强复合材料中由于SiC颗粒的加入改变了原有复合材料的性能[7-10],对闭孔泡沫铝基复合材料变形机制、压缩性能及其与结构参数之间的关系的研究较少。Gui等[11]研究了泡沫20% SiCp/A356(体积分数)的应力-应变特征,但并未提及其压缩过程中的变形机制和能量吸收特性。Elbir等[12]对用粉末冶金法制备的SiC体积分数为8.6%的泡沫铝基复合材料进行了压缩性能的测试,也只研究了相对密度对其屈服强度的影响。基于Luo等[13]的前期研究,本文作者主要研究SiC颗粒粒径和相对密度对闭孔泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料压缩性能的影响规律。
1 实验材料和方法
1.1 泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料的制备
基体材料选用ZL104合金,增强材料选用平均粒径分别为5,10和28 μm的α-绿SiC颗粒,发泡剂选用粒度小于44 μm的CaCO3,采用熔体发泡法在700~720 ℃时保温发泡制备出泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合 材料。
1.2 实验方法
将制备好的块状泡沫材料(见图1和图2)加工成15 mm×15 mm×35 mm的试样。压缩试验在CMT5205电子万能试验机上进行,压缩速率为4 mm/min。载荷及位移通过传感器输入计算机,处理后得到不同泡沫复合材料的压缩应力-应变曲线。
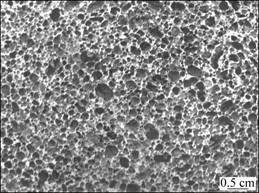
图1 泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料的截面图
Fig.1 Cross section of SiCp/ZL104 composite foams
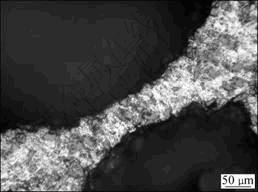
图2 泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料的孔壁截面图
Fig.2 Cell wall cross section of SiCp/ZL104 composite foams
2 实验结果与讨论
2.1 泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料在外力作用下的变形机制
图3所示为相对密度相同的泡沫5% SiCp/ZL104复合材料(SiC颗粒的粒径为28 μm)和泡沫ZL104的应力-应变曲线。从图3可以看出:这2种不同泡沫金属其应力(σ)-应变(ε)曲线都表现出明显的“三阶段”特征,即由线弹性变形段、屈服平台段和压实段组成。由图3可知:2种材料的线弹性变形段都很小,在 ε<0.03的范围内;当弹性应变增大到一定值后出现一个应力平台,这时,随着应变的增大,应力几乎保持不变。2种材料的平台段应变均在ε=0.03~0.65范围内(图3)。
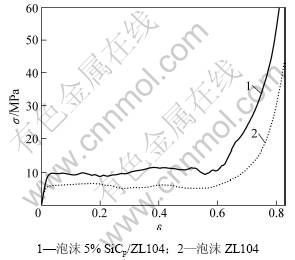
图3 泡沫5% SiCp/ZL104复合材料和泡沫ZL104的应力-应变曲线
Fig.3 Stress-strain curves of 5%SiCp/ZL104 composite foams and ZL104 foams
泡沫5% SiCp/ZL104复合材料的屈服应力几乎是泡沫ZL104的2倍(图3)。造成这种差异的原因是泡沫5% SiCp/ZL104复合材料中SiC颗粒的存在导致在平台区泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料与泡沫ZL104的变形机制不同,如图4所示(以平行泡孔为例)。由于泡沫材料制备过程不可避免地出现孔壁厚度不均匀现象,闭孔泡沫金属受压时,变形机制主要为孔壁材料的弯曲和横向拉伸。当材料承受载荷时,破坏首先出现在最弱的泡孔壁处,孔壁的材料首先由弹性弯曲转变为塑性弯曲直至断裂,泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料属于弹脆性泡沫材料,SiC颗粒本身具有的脆性导致了孔壁的整体塑性下降,一旦外力破坏了最弱泡孔,就会发生其所在的整层泡孔的破坏。如图4(a)所示,孔壁发生断裂导致含有此泡孔且与外力垂直的平面内产生应力集中,破坏随后在此层中扩展,导致此层的泡孔壁逐渐被破坏,从而使部分能量在变形过程中被耗散掉,但其余层面上的泡孔仍处于弹性变形后的等待阶段。随着应力进一步增加,泡孔的破坏又在孔壁较薄的其他未被破坏的泡孔层中产生。如此反复进行,最终材料被压实。当某层泡孔发生破坏时,作用在泡沫材料上的应力瞬间变小;当该层泡孔被压实后,应力又开始增大,直到把其他层泡孔破坏,应力才又瞬间变小。如此反复,泡沫材料逐层被压实。因此,其应力-应变曲线呈锯齿状波动。泡沫ZL104中孔壁发生的是塑性变形(图4(b)),因而,其应力-应变曲线的平台段相对光滑(图3);由于泡沫金属材料在制备过程中难免会产生泡沫不均匀现象,即孔壁薄厚在微观尺度上分布不均,所以,实际变形中泡孔并不完全是整行的破裂最后导致压实。由于力是垂直加载到试样上,因此,变形仍旧会首先出现在泡孔壁最薄的横断面处,但一旦一系列孔壁较薄的泡孔位于与横截面成较大角度的斜截面上时,便会产生切向力,致使在加压过程中可能发生沿斜截面方向的坍塌(图5(a)),所以,即使整行的泡孔中偶尔有几个壁薄的泡孔,变形也未必从这一行开始,关键还是看泡孔和孔壁分布的均匀度,由于实验制备的泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料厚度分布比较均匀,大部分试样变形时都发生逐层破坏(见图5(b))。由以上分析可知:无论泡沫ZL104还是泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料,变形特征都是逐层破坏的。泡沫材料被压实后,应变越来越多地由基体材料本身所提供,导致压缩应力随应变的增加而迅速增大。
2.2 SiC颗粒粒径对泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料压缩性能的影响
SiC颗粒粒径对泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料压缩性能的影响主要表现在对基体材料性能的增强上。对于相同结构特征的泡沫材料,增强材料占泡沫体的体积分数越大,对基体材料的增强效果越明显,从而压缩性能越好。这一结论已在作者的前期研究工作中得到证实[13]。而对于相同体积分数的复合材料,增强颗粒粒径对其强度也有一定的影响。图6所示为SiC颗粒粒径对泡沫5% SiCp/ZL104复合材料压缩性能的影响。从图6可见:随SiC颗粒粒径的减小,泡沫5% SiCp/ZL104复合材料的屈服强度逐渐增大,当SiC颗粒粒径由28 μm减小到10 μm时,材料的屈服强度增大仅约1 MPa;而SiC颗粒粒径由10 μm减小到5 μm时,材料的屈服强度却增加了4 MPa。这说明增强颗粒的粒径越小对泡沫复合材料屈服强度的影响越大,颗粒粒径越小,泡沫复合材料的屈服强度越大。颗粒增强金属基复合材料的位错强化说增强机制认为可以用Orowan理论来解释颗粒强化的机理[14-15]:
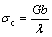 (1)
(1)
式中:σc为屈服应力;G为复合材料基体的剪切模量;b为位错的柏氏矢量;λ为平均颗粒间距。当增强相粒子所占体积分数一定时,颗粒半径越小,颗粒数量就越多,颗粒间距也越小,位错绕过颗粒所需的切应力越大,强化作用越大。
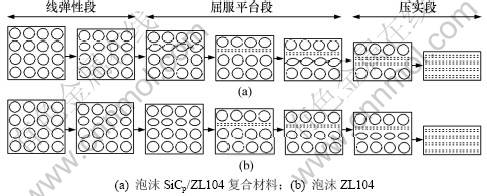
图4 泡沫材料压缩变形示意图
Fig.4 Sketch map of compressive deformation of foams

图5 泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料变形的不同截面
Fig.5 Different deformation sections of SiCp/ZL104 composite foams
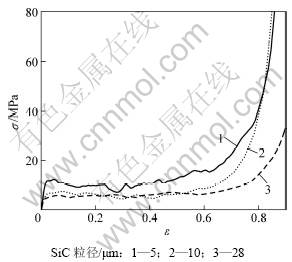
图6 SiC颗粒粒径对泡沫5% SiCp/ZL104复合材料压缩性能的影响(相对密度ρ/ρs=0.16)
Fig.6 Effect of SiC particle size on compressive property of 5% SiCp/ZL104 composite foams when ρ/ρs is 0.16
用上述理论可以解释本实验中泡沫5% SiCp/ ZL104复合材料中含不同粒径SiC颗粒的压缩行为。当增强相SiC颗粒所占体积分数一定时,随SiC颗粒粒径的减小,所得泡沫材料的强度增大,这与实验结果相符。
2.3 相对密度对泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料压缩性能的影响
图7所示为不同相对密度泡末10% SiCp/ZL104复合材料的应力-应变曲线。由图7可知:随着相对密度的增大,泡沫10% SiCp/ZL104复合材料的屈服应力与流动应力也相应增加,但压缩至压实段的最大应变量εD减小。这一结论也可从图3和图6的对比得出。相对密度ρ/ρs是0.16的泡沫5% SiCp/ZL104复合材料的屈服应力小于相对密度为0.32的泡沫体屈服应力,前者为5 MPa,后者则为10 MPa。相对密度越大,在垂直于加载方向的截面内泡孔的数目越少,孔壁越厚,引起的应力增量越大。在研究有关闭孔泡沫材料的应力与相对密度的关系方面,Gibson-Ashby等建立了二维闭孔泡沫体受压时的理论模型[16],认为当闭孔泡沫材料受压时,孔棱的变形引起孔面的变形,并得出如下方程式:
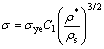 (2)
(2)
式中:σ 为泡沫材料的屈服应力;σys为孔壁材料的屈服应力;C1为常数。由式(2)可知:随着泡沫材料相对密度的增大,材料的屈服应力逐渐增大,这与实验结果相吻合。

图7 不同相对密度泡沫10% SiCp/ZL104复合材料的应力-应变曲线
Fig.7 Stress-strain curves of 10% SiCp/ZL104 foams with different relative densities
3 结论
(1) 泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料在外加载荷作用下孔壁材料发生弯曲和横向拉伸的变形,由于SiC颗粒的加入,使得该材料受压时呈脆性逐层破坏或沿某斜截面断裂的特征,这导致其应力-应变曲线上出现较长的带锯齿状的屈服平台段;泡沫SiCp/ZL104复合材料的压缩性能较好,压缩变形过程经历线弹性段、屈服平台段和压实段3个阶段。
(2) 对于SiC颗粒体积分数和相对密度相同的泡沫5% SiCp/ZL104复合材料,当SiC颗粒粒径由28 μm减小到5 μm时,其屈服应力由5 MPa增至11 MPa,利用Orowan理论可以解释SiC颗粒的强化机理;而对于SiC颗粒粒径和体积分数相同的该材料,其相对密度由0.16增至0.32时对应的屈服应力则由5 MPa增至10 MPa,这一结论与Green的二维闭孔泡沫体受压时的理论模型相符。
参考文献:
[1] Mohamed S A. Behavior of closed cell aluminium foams upon compressive testing at elevated temperatures: Experimental results[J]. Materials Letters, 2007, 61(14/15): 3138-3141.
[2] Asavavisithchai K S, Kennedy A R. The effect of compaction method on the expansion and stability of aluminium foams[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2006, 8(9): 810-815.
[3] Ito K, Kobayashi H. Production and fabrication technology development of aluminum useful for automobile lightweighting[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2006, 8(9): 828-835.
[4] Kitazono K, Sato E, Kuribayashi K. Novel manufacturing process of closed-cell aluminium foam by accumulative roll-bonding[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 50(4): 495-498.
[5] Gibson L J. Mechanical behavior of metallic foams[J]. Annual Review of Materials Science, 2000, 30(1): 191-227.
[6] Paul A, Ramamurty U. Strain rate sensitivity of a closed-cell aluminum foam[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 281(1/2): 1-7.
[7] ZHU De-zhi, WU Gao-hui, CHEN Guo-qin, et al. Dynamic deformation behavior of a high reinforcement content TiB2/Al composite at high strain rates[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 487(1/2): 536-540.
[8] 王日初, 毕豫, 黄伯云, 等. SiC颗粒表面处理对6066Al基复合材料力学性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2005, 36(3): 369-374.
WANG Ri-chu, BI Yu, HUANG Bai-yun, et al. Effect of surface treatment of SiC particle on mechanical properties of SiCp/6066 Al composites[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2005, 36(3): 369-374.
[9] WANG De-qing, SHI Zi-yuan. Effect of ceramic particles on cell size and wall thickness of aluminum foam[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 361(1/2): 45-49.
[10] Kok M. Production and mechanical properties of Al2O3 particle-reinforced 2024 aluminium alloy composites[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2005, 161(3): 381-387.
[11] GUI Man-chang, WANG Dian-bin, WU Jie-jun. Deformation and damping behaviors of foamed Al-Si-SiCp composite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 286(2): 282-288.
[12] Elbir S, Yilmaz A, Tolosoy A K, et al. SiC-particulate aluminum composite foams produced by powder compacts: Foaming and compression behavior[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2003, 38(23): 4745-4755.
[13] LUO Yan-ru, YU Si-rong, LI Wen, et al. Compressive behavior of SiCp/AlSi9Mg composite foams[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 460(1/2): 294-298.
[14] 魏建锋, 宋余九. 颗粒增强纯铝基复合材料的增强机制[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 1994, 23(3): 17-22.
WEI Jian-feng, SONG Yu-jiu. The strengthening mechanism of particulate reinforced pure aluminium composites[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1994, 23(3): 17-22.
[15] Orowan E. Symposium on internal stress in metals and alloys[M]. London: Institute of Metals, 1948: 451.
[16] Kathryn A D, James L Jr. High strain rate compression of closed-cell aluminum foams[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 293(1/2): 157-164.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2010-05-14;修回日期:2010-08-19
基金项目:吉林省科技发展计划项目(20100550)
通信作者:罗彦茹(1979-),女,吉林松原人,博士,讲师,从事复合材料研究;电话:13843119744;E-mail:luoyr@jlu.edu.cn