DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.09.009
基于元胞自动机的Haynes230动态再结晶组织演变
朱宁远1,夏琴香1,程秀全2
(1. 华南理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,广东 广州,510640;
2. 广州民航职业技术学院 机务工程系,广东 广州,510403)
摘要:采用元胞自动机(CA),通过Matlab编程实现不同温度、不同应变速率下Haynes230镍基高温合金动态再结晶微观组织演变的动态观测,获得微观组织、位错密度、动态再结晶体积分数等微观层次的演变规律及宏观层次的流变应力-应变变化规律。研究结果表明:随着温度的升高和应变速率减小,动态再结晶分数增加、流变应力减小,因此,较高温度及较小的应变速率有利于Haynes230难变形金属热成形中动态再结晶的发生。Haynes230合金动态再结晶分数随着应变的增加而增大,其增长经历缓慢-快速-缓慢3个过程。CA模拟获得的再结晶分数与已有试验规律一致,最大相对误差为14.6%。
关键词:元胞自动机;动态再结晶;微观组织演变;Haynes203合金
中图分类号:TG14;TG113.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2017)09-2316-08
Dynamic recrystallization microstructure evolution of Haynes230 alloy based on cellular automata
ZHU Ningyuan1, XIA Qinxiang1, CHENG Xiuquan2
(1. School of Mechanical and Automobile Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China;
2. Department of Aircraft Maintenance Engineering, Guangzhou Civil Aviation College, Guangzhou 510403, China)
Abstract: The dynamic observation of dynamic recrystallization (DRX) microstructure evolution of Ni-based high temperature alloy Haynes230 under hot compression at various strain rates and temperatures was realized by means of the cellular automata (CA) simulation by the programming based on Matlab software. Dislocation density and RDX volume fraction were obtained as well as the macro-level variation of the flow stress-strain the micro-level evolution of the microstructure. The results show that the DRX volume fraction increases and the flow stress decreases with the increase of the temperature and the decrease of the strain ratio. Therefore, the reasonable high temperature and low strain ratio are beneficial to the occurrence of DRX and the plastic forming of the difficult-to-deform metal. The DRX volume fraction of Haynes230 alloy increases with the increase of strain, and the increase of the DRX volume fraction follows the law of slow-shape-slow. The simulation results conform well to the experiment ones, and the maximum error is 14.6%.
Key words: cellular automata; dynamic recrystallization; microstructure evolution; Haynes230 alloy
Haynes230镍基高温合金因具有良好的高温强度、抗氧化性、耐腐蚀性及热稳定性,广泛应用于航空航天、舰船等领域[1]。常温下,该合金变形抗力大、塑性差,难以进行塑性成形,属于难变形金属[2]。热强旋成形是将坯料加热到再结晶温度以上再进行旋压成形的方法,具有变形抗力小、可旋性好、成形工具简单、材料利用率高等特点,是制造难变形金属筒形件最有效的方法之一[3-4]。杜军等[5]采用热强旋方法获得了成形精度较高的304不锈钢筒形件;徐文臣等[6]对BT20钛合金旋压件热强旋的成形缺陷进行了研究,获得了合理的热强旋工艺。目前关于热强旋成形的研究主要针对旋压件的宏观成形质量方面。然而微观组织是决定产品性能的关键[5]。以往多采用金相显微镜(OM)、X线衍射(XRD)、电子背散射电子衍射(EBSD)等方法对组织进行试验研究。SHAN等[7-8]采用OM及XRD研究了TA15和BT20钛合金筒形件热强旋后的微观组织形态,指出滑移变形是主要的变形机制,孪晶起到协调变形的作用;ROMERO等[9]采用EBSD对铝合金热强旋后的微观组织进行了研究,指出成形过程中动态再结晶的发生使位错迁移并阻碍了亚晶的形成及晶粒的变形。但由于试验手段的局限性,无法实现微观组织的动态观察,凭经验又很难进行预测以及控制,因此微观组织演变的数值模拟技术正成为研究材料热加工组织演变的重要工具[10]。目前微观组织演变模拟方法主要有相场(PF)法、Mote Carlo (MC)法、元胞自动机(CA)法等。PF法中各物理变量拥有实际的物理意义,但需要求解偏微分方程,计算量非常大,可模拟的区域小;MC法运算量大,运算速度慢,未能充分考虑晶粒生长过程的物理机制[11];CA法是一种时间、空间和状态都离散的网格动力学模型,其计算效率高,是对物理模型的离散,考虑了物理机制[12]。如:ZHANG等[13]采用CA法对镍钛形状记忆合金热压缩变形动态再结晶进行了模拟,研究表明,位错密度随变形温度的增加而减小,随应变速率的增加而增加。位错运动是塑性变形的微观本质,而目前对位错密度变化规律及分布的模拟研究较少。本文作者以难变形金属Haynes230镍基高温合金为对象,采用CA法对热压缩过程中动态再结晶组织演变过程进行模拟,以获得不同温度和应变速率下,Haynes230高温合金的组织、位错密度等微观层次的演变规律及宏观层次的流变应力-应变变化规律,为热强旋成形过程的形/性一体化研究提供依据。
1 动态再结晶模型建立
1.1 位错密度演变
金属热成形过程是加工硬化、动态回复及动态再结晶相互竞争的过程,其微观本质为位错密度的聚集和湮灭,本文采用如式(1)所示的Kocks-Mecking (KM)物理模型[14]描述位错密度的演变。
 (1)
(1)
式中: 为晶粒i的位错密度;
为晶粒i的位错密度; 为应变;h和r分别为硬化、软化系数,
为应变;h和r分别为硬化、软化系数, ,
, ;
; 为材料线性硬化率,可通过流变应力-应变曲线获得;b为柏氏矢量;
为材料线性硬化率,可通过流变应力-应变曲线获得;b为柏氏矢量;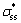 为稳态流变应力;G为剪切模量,
为稳态流变应力;G为剪切模量, ;G0为常温下剪切模量;T为成形温度;Tm为材料熔点温度。
;G0为常温下剪切模量;T为成形温度;Tm为材料熔点温度。
1.2 再结晶形核
根据位错理论,当位错密度达到再结晶临界值后,优先在位错密度较高的晶界处以一定形核率 形核,Roberts and Ahlblom指出动态再结晶临界位错密度
形核,Roberts and Ahlblom指出动态再结晶临界位错密度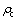 可表示为[15]:
可表示为[15]:
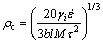 (2)
(2)
式中: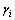 为晶界能;
为晶界能;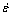 为应变速率;l为运动位错平均自由程,
为应变速率;l为运动位错平均自由程, ,
, 为流变应力;M为晶界迁移率,
为流变应力;M为晶界迁移率,
 (3)
(3)
δD0b为晶界扩散系数;Qb为晶界扩散激活能,k为Boltzmann常数;R为理想气体常数; 为平均位错线能量,
为平均位错线能量, ;a为位错几何结构常数,一般取0.5。DING等[16]提出形核率
;a为位错几何结构常数,一般取0.5。DING等[16]提出形核率 为
为
 (4)
(4)
其中:C为常数;Qact为变形激活能;m为应变速率指数。
1.3 再结晶晶粒长大
动态再结晶晶粒的长大驱动力主要有晶体缺陷及晶界能,因此,在CA模型中再结晶晶粒i的长大速率Vi可表达为[17]:
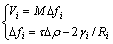 (5)
(5)
其中:M为晶界迁移率; 为晶粒i长大驱动力;
为晶粒i长大驱动力;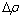 为原基体晶粒的位错密度
为原基体晶粒的位错密度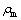 与再结晶晶粒位错密度
与再结晶晶粒位错密度 之差,
之差,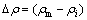 ;
;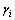 为晶界能;Ri为再结晶晶粒直径。
为晶界能;Ri为再结晶晶粒直径。
2 CA模拟及条件
2.1 初始组织模拟
初始组织模型是动态再结晶组织模拟的基础,为获得符合原始组织的初始组织模型,通过对Haynes230镍基高温合金取样、镶嵌、打磨、抛光后,采用HNO3与HCl体积比为1:3的溶液对金相试样进行侵蚀,利用MJ-42金相显微镜获得原始金相组织(见图1),通过能谱分析获得主要成分(见表1)。由图1可知:原始金相组织中存在着退火孪晶,并在晶粒内存在着M6C型碳化物,在晶界处分布着M23C6型碳化物[1],原始金相组织为均匀的等轴晶,采用截线法[18],求得平均晶粒粒径D0=15 μm。
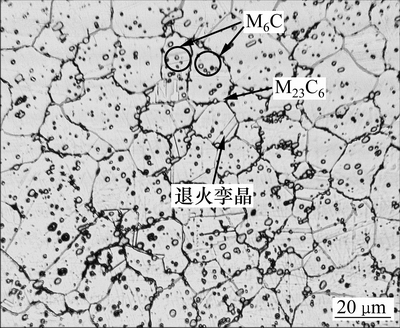
图1 Haynes230合金原始金相组织
Fig. 1 Original microstructure of Haynes230 alloy
表1 Haynes230合金主要成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Composition of Haynes230 alloy %

图1所示为0.15 mm×0.15 mm的实际区域,故将元胞空间划分为300×300的四边形网格,元胞边长为0.5 μm,则整个元胞空间代表0.15 mm×0.15 mm的实际样品。采用周期性边界和Moore邻居类型。模拟时设定相邻的同一取向元胞集合为晶粒,设定元胞取向取值范围为0~Q的整数,为方便与实际取向数对应,模拟中Q=180,因此,模拟中数值1即代表实际取向1°。在模拟过程中,元胞的状态变量包括:1) 取向变量,用于存储元胞取向数;2) 晶粒识别变量,对相邻同一取向元胞进行唯一标识;3) 晶界识别变量,用于识别处于晶界的元胞,形成虚拟晶界;4) 再结晶识别变量,识别再结晶晶粒。每完成1个模拟步后,对相关状态变量进行更新。
试验材料为铸造后经热处理的等轴晶组织,为获得更加符合其制备过程物理机制及形貌的初始组织,采用凝固过程晶核等概率长大及热处理过程中晶粒正常长大的CA模拟,以获得等轴初始组织。首先采用位置过饱和形核机制在元胞空间中随机散布具有取向数的晶核,再经过等概率长大及曲率驱动长大,直到达到实际所需晶粒粒径D0,采用如式(6)所示的等效圆直径方法计算晶粒直径。本文对动态再结晶过程的模拟暂不考虑弥散碳化物及退火孪晶的影响,模拟所得初始组织如图2所示,其为与图1所示的原始金相组织相符的平均等效粒径为15.02 μm的均匀等轴晶组织。
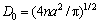 (6)
(6)
其中:n为晶粒的元胞数;a为元胞边长。

图2 Haynes230初始组织模拟
Fig. 2 Simulation of initial structure of Haynes230 alloy
2.2 动态再结晶CA模拟流程
在初始组织基础上,进行动态再结晶组织演变模拟,模拟中采用的Haynes230参数如表2所示,模拟流程如图3所示。
CA模拟过程中动态再结晶形核条件为[19]:1) 元胞处于晶界处;2) 位错密度大于临界位错密度ρc;3) 形核概率p≥随机数r1。再结晶长大条件为[17]:1) 元胞处于晶界处;2) 再结晶次数大于其邻居元胞再结晶次数;3) 当前模拟步长大距离LCA≥元胞边长a,LCA=Vi× ,
, 为模拟步对应的实际时间;4) 长大概率i/4大于等于随机数r2。每一模拟步对应的应变增量
为模拟步对应的实际时间;4) 长大概率i/4大于等于随机数r2。每一模拟步对应的应变增量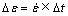 ,相同再结晶次数晶粒相遇方向停止长大,当应变量达到设定值时模拟完成。
,相同再结晶次数晶粒相遇方向停止长大,当应变量达到设定值时模拟完成。
表2 Haynes230合金CA模拟参数
Table 2 Parameters of CA simulation of Haynes230 alloy
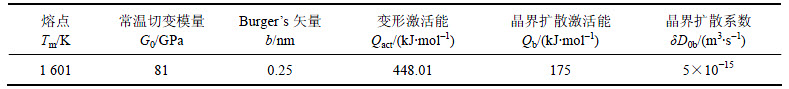
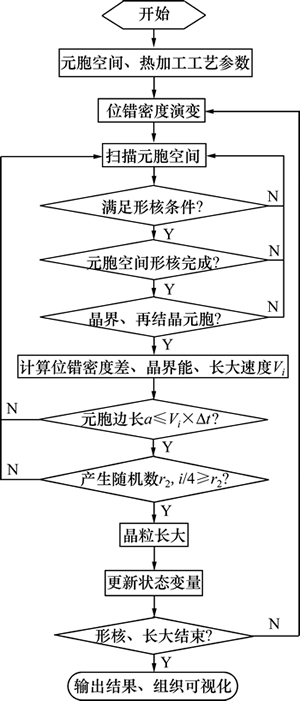
图3 动态再结晶模拟流程
Fig. 3 Flow of DRX simulation
3 模拟结果及分析
对温度为1 000,1 100,1 150和1 200 ℃,应变速率为0.01,0.1,1 s-1时的动态再结晶过程进行CA模拟。通过式(7)[16]所示的流变应力与位错密度之间的关系获得1 150 ℃时流变应力-应变曲线,如图4所示。由图4可知:CA模拟所得流变应力-应变曲线与文献[1]中同一条件下的流变应力-应变曲线的变化趋势一致,在应变速率为0.01,0.1和1 s-1时,最大相对误差分别为7.88%,10.59%和14.6%,表明本文CA模拟结果准确性较好。
 (7)
(7)
其中: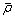 为平均位错密度,
为平均位错密度,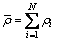 ;N为元胞空间中晶粒数;
;N为元胞空间中晶粒数; 为晶粒i的位错密度;
为晶粒i的位错密度;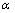 为位错交互作用强度参数,一般取0.5。
为位错交互作用强度参数,一般取0.5。
图5~7所示为当温度为1 000 ℃、应变速率 = 0.01 s-1时,模拟所得应力-应变曲线及对应的再结晶组织与位错密度。在热成形中,加工硬化(WH)、动态回复(DRV)、动态再结晶(DRX)同时存在并处于相互竞争状态。由图5可知流变应力主要分为3个阶段:
= 0.01 s-1时,模拟所得应力-应变曲线及对应的再结晶组织与位错密度。在热成形中,加工硬化(WH)、动态回复(DRV)、动态再结晶(DRX)同时存在并处于相互竞争状态。由图5可知流变应力主要分为3个阶段:
1) 加工硬化与动态回复阶段(WH+DRV),该阶段以WH和DRV为主,且WH硬化作用比DRV的软化作用大,宏观表现为流变应力以硬化速率减小的趋势快速上升。这主要是由于WH导致位错密度的急剧聚集使流变应力快速上升,同时由于DRV过程中位错密度的相互抵消使上升的速率减小。
2) 动态回复及动态再结晶阶段(DRV+ DRX),该阶段主要是DRV与DRX相互竞争阶段,表现为流变应力达到一定值(峰值流变应力)后平稳缓慢下降。
3) 动态再结晶阶段(DRX),该阶段主要以DRX为主,流变应力进入平稳的稳态流变应力阶段。

图4 流变应力-应变对比
Fig. 4 Comparison of flow stress-strain

图5 CA动态再结晶模拟应力-应变曲线(1 000 ℃、 =0.01 s-1)
=0.01 s-1)
Fig. 5 Flow stress-strain obtained by CA simulation of DRX at 1 000 ℃,  =0.01 s-1
=0.01 s-1

图6 CA模拟所得再结晶组织(1 000 ℃,  =0.01 s-1)
=0.01 s-1)
Fig. 6 Structure of DRX obtained by CA simulation at 1 000 ℃,  =0.01 s-1
=0.01 s-1

图7 CA模拟所得位错密度(1 000 ℃,  =0.01 s-1)
=0.01 s-1)
Fig. 7 Dislocation density obtained by CA simulation at 1 000 ℃,  =0.01 s-1
=0.01 s-1
图6和图7所示分别为图5中对应位置的再结晶组织及位错密度。在图5中d处,晶界处出现了少量的再结晶晶粒(如图6(a)所示,d,e,f和g处再结晶次数分别为1,2,2和3);组织中出现了少量位错密度较低的再结晶区域(如图7所示)。随着应变的增大,在晶界处再结晶增多,且再结晶晶粒长大,位错密度中再结晶区域增多。
图8所示为不同温度和应变速率下CA模拟所得平均位错密度曲线。由图8可见:在变形开始阶段,由于加工硬化导致位错急剧积聚,随后由于动态回复及动态再结晶的启动导致位错湮灭,模拟结果与典型的动态再结晶过程吻合。

图8 位错密度模拟结果
Fig. 8 Simulation results of dislocation density
图9所示为不同条件下模拟所得DRX体积分数。由图9可见:DRX体积分数随着应变的增加而增大,在变形初始阶段增长较缓。这主要是由于再结晶初始阶段由于动态回复的存在使位错湮灭导致作为动态再结晶驱动力的畸变能降低,再结晶缓慢;随后再结晶分数进入快速增长阶段,这主要是由于随着应变的增大,给动态再结晶提供了足够的驱动力。

图9 DRX体积分数对比
Fig. 9 Comparison of DRX volume fraction
由图9还可以看出:达到同一应变量时,应变速率越小,再结晶分数越大,且上升梯度越大。主要是由于较小的应变速率给动态再结晶的进行提供了充足的时间,这表明应变速率的减小有利于动态再结晶。同时,温度越高,达到同一再结晶分数所需的应变量越小,再结晶的发生越容易,达到完全再结晶所需的应变量越小。
图10所示为不同条件下模拟所得微观组织。再结晶晶粒首先在晶界处形成,形成了典型的“链状”组织,如图10(c)所示;随着应变速率的减小和温度的增高,动态再结晶次数增加,且再结晶晶粒长大。

图10 CA模拟动态再结晶微观组织
Fig. 10 CA simulation of DRX microstructures
4 结论
1) 通过Matlab编程,采用CA法模拟了Haynes230合金在不同温度和应变速率时动态再结晶过程,获得了Haynes230合金热变形过程中的组织、位错密度等微观层次的演变规律及宏观层次的流变应力-应变变化规律,实现了金属热变形过程组织演变的动态观测。
2) 在应变速率为0.01,0.1和1 s-1时,流变应力-应变CA模拟最大相对误差分别为7.88%,10.59%和14.6%,模拟结果准确性较好,后续将通过试验进一步验证。
3) 应变速率的减小有利于发生动态再结晶,温度越高,越容易发生再结晶,达到完全再结晶所需的应变越小。因此,较高温度及较小的应变速率有利于Haynes230之类的难变形金属热强旋成形中动态再结晶的发生。
4) Haynes230合金动态再结晶分数随着应变的增加而增大,可分为初期缓慢增长、中期快速增长、接近完全再结晶时缓慢增长3个时期。
参考文献:
[1] LIU Yi, HU Rui, LI Jinshan, et al. Characterization of hot deformation behavior of Haynes230 by using processing maps[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(8): 4020-4026.
[2] XIA Qinxiang, ZHU Ningyuan, CHENG Xiuquan, et al. The classification and a review of hot power spinning of difficult-to-deform metals[J]. International Journal of Materials and Product Technology, 2017, 54(1): 212-235.
[3] XIA Qinxiang, XIAO Gangfeng, LONG Hui, et al. A review of process advancement of novel metal spinning[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2014, 85: 100-121.
[4] 朱宁远, 夏琴香, 肖刚锋, 等. 难变形金属热强旋成形技术及研究现状[J]. 锻压技术, 2014, 39(9): 42-47.
ZHU Ningyuan, XIA Qinxiang, XIAO Gangfeng, et al. Technology and research status of difficult-to-deform metal in hot power spinning[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2014, 39(9): 42-47.
[5] 杜军, 夏琴香, 朱宁远, 等. 304不锈钢管热强旋成形试验研究[J]. 锻压技术, 2015, 40(6): 24-28.
DU Jun, XIA Qinxiang, ZHU Ningyuan, et al. The experiment research of 304 stainless steel in hot power spinning[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2015, 40(6): 24-28.
[6] 徐文臣, 单德彬, 陈宇, 等. 钛合金薄壁筒形件热旋成形技术研究[J]. 锻压技术, 2008, 33(3): 56-59.
XU Wenchen, SHAN Debin, CHEN Yu, et al. Study on hot spinning technology of tubular workpieces for TA15 titanium alloy[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2008, 33(3): 56-59.
[7] SHAN Debin, YANG Guoping, XU Wenchen. Deformation history and the resultant microstructure and texture in backward tube spinning of Ti-6Al-2Zr-1Mo-1V[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(17): 5713-5719.
[8] CHEN Yong, XU Wenchen, SHAN Debin, et al. Microstructure evolution of TA15 titanium alloy during hot power spinning[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(2): 323-328.
[9] ROMERO P, OTERO N, CABRERA J M, et al. Laser assisted conical spin forming of dual phase automotive steel. Experimental demonstration of work hardening reduction and forming limit extension[J]. Physics Procedia, 2010, 5(1): 215-225.
[10] JANG Y S, KO D C, KIMC B M. Application of the finite element method to predict microstructure evolution in the hot forging of steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2000, 101(1/2/3): 85-94.
[11] 李殿中, 杜强, 胡志勇, 等. 金属成形过程组织演变的Cellular Automaton模拟技术[J]. 金属学报, 1999, 35(11): 1201-1205.
LI Dianzhong, DU Qiang, HU Zhiyong, et al. Simulation of the microstructure evolution in metal forming by using cellular automaton method[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1999, 35(11): 1201-1205.
[12] 罗伯D. 计算材料学[M]. 项金钟, 吴兴惠, 译. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2002: 234-259.
RAABE D. Computational Materials Science[M]. XIANG Jinzhong, WU Xinghui, trans. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002: 234-259.
[13] ZHANG Yanqiu, JIANG Shuyong, LIANG Yulong, et al. Simulation of dynamic recrystallization of NiTi shape memory alloy during hot compression deformation based on cellular automaton[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2013, 71: 124-134.
[14] KOCKS U F. Laws for work-hardening and low-temperature creep[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1976, 98(1): 76-85.
[15] TOMOHIRO T, CHIHIRO Y, AKINORI Y, et al. Multiscale modeling of hot-working with dynamic recrystallization by coupling microstructure evolution and macroscopic mechanical behavior[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2014, 52: 105-116.
[16] DING R, GUO Z X. Coupled quantitative simulation of microstructural evolution and plastic flow during dynamic recrystallization[J]. Acts Materialia, 2001, 49(16): 3163-3175.
[17] JIN Zhaoyang, CUI Zhenshan. Investigation on dynamic recrystallization using a modified cellular automaton[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2012, 63: 249-255.
[18] GB/T 6394—2002, 金属平均晶粒度测定法[S].
GB/T 6394—2002, Measurement of average grain size for metal[S].
[19] KROC J. Application of cellular automata simulations to modelling of dynamic recrystallization[J]. Computational Science, 2002, 2329: 773-782.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2016-09-12;修回日期:2016-12-25
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51375172);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助项目(20130172110024) (Project(51375172) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(20130172110024) supported by Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education)
通信作者:夏琴香,博士,教授,从事精密成形及模具技术研究;E-mail: meqxxia@scut.edu.cn