DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.02.22
光电化学冶金提取半导体元素——以碲为例
刘芳洋,凡艳云,蒋良兴,赖延清,李 劼,刘业翔
(中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙410083)
摘 要:针对电化学冶金提取半导体元素存在的问题,提出采用光电化学冶金的方法来进行半导体元素的电化学沉积提取。结合半导体特性以及光电化学基本理论,阐述光电化学冶金的优势,并以碲提取为例验证光电化学冶金的优越性。结果表明:光电化学沉积过程中,半导体沉积物吸收能量大于其自身带隙宽度的光子后受激发产生光生电子-空穴对,光生电子从半导体流向电解液促进电化学还原,同时光生载流子可减小电阻率和能带弯曲,降低工作电极所分摊的电势差。与常规的电化学沉积相比,光电化学沉积可以强化电极过程、降低槽电压,以及提高沉积速率、电流效率和产能,具有良好的应用前景。最后指出光电化学冶金未来发展可能面临的问题,并对其内涵进行拓展。
关键词:半导体元素;光照;槽电压;光电化学冶金;电化学沉积
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-02-0397-09 中图分类号:O782 文献标志码:A
1 电化学冶金提取半导体元素的主要问题
半导体元素是指具有半导体性质的元素,如硅、锗、碲、硒、砷和碘等,已成为推动国民经济和社会发展和进步不可或缺的物质。因此,发展其低成本、低能耗、无污染和高产能的提取方法十分必要。电化学沉积(或称电沉积、电积)具有产品纯度高、原料适应性强、选择性良好、生产效率高、环境友好且成本低廉等优点,在金属提取和精炼领域得到广泛应用[1-3]。但是电沉积在半导体元素冶金中的应用非常有限,目前只在带隙宽度最低、导电性最好的半导体元素碲的提取(和精炼)中得到应用[4]。这主要是由于沉积物的半导体特性,导致电沉积提取半导体元素存在许多困难亟待解决。
1) 沉积速率慢,产能低。当半导体元素电沉积于阴极表面后,由于半导体元素的低导电性,电极的电阻会迅速上升;同时沉积的半导体会与其接触的电解液建立一个空间电荷区,这些都会直接导致槽电压的升高。故只能采用较低的电流密度沉积,以确保工艺尽量平稳运行。例如目前工业上电沉积碲所采用的电流密度通常为50~80 A/m2,远低于锌(350~500 A/m2)、铜(180~250 A/m2)、锡(300~400 A/m2)等[5]金属电沉积提取时常用的电流密度;而且如果采用较大的电流密度,还会很容易增大电极极化,促进副反应进行,降低电流效率,例如碲电沉积的电流密度增至160 A/m2 时,电流效率将由常用电流密度时的99%降至90%[6]。由于沉积速率低,所以碲电沉积的周期需长达150 h以上,远高于其他有色金属的电沉积周期(一般为24 h;少量为48 h,如大极板机械剥锌时),生产效率低下。对于硅的电沉积,为了获得较高质量的硅膜,电流密度需要控制在100~500 A/m2范围内(高温熔盐)[7-8],该工艺生产速率远无法和其他硅提纯工艺生产速率相竞争,是电沉积硅工艺一直未能得到实际应用的主要原因之一。
2) 工艺稳定性差。由于电沉积过程中,随着沉积层厚度的增加,阴极电阻以及槽电压均不断升高,导致电沉积过程不稳定,例如电沉积碲时,到沉积周期后期,槽电压将上升300 mV左右[9]。另一方面,由于沉积速率慢,沉积时间长,也使得电沉积反应体系的不稳定性增加。例如对于碲的电沉积,采用亚碲酸钠溶液作为电解液,随着沉积时间的延长,会使得电解液中亚碲酸钠的氧化率增加[9]。对于锗的电沉积,主要是在非水体系中进行(水溶液体系中析氢过电位极低[10]),目前报道的沉积层增厚困难,电流效率都很低,副反应严重影响了体系的稳定性,而且长的沉积时间会加速溶剂和溶质的损失[11]。硅的电沉积一般在熔盐中进行,由于硅导电性差,无法增厚且易脱落,导致固液界面不稳定,电压波动大等不足[12]。
3) 电流效率低,能耗高。半导体元素导电性差,在电沉积一定时间后电极表面易“失活”,导致电流密度分布不均匀,副反应增强,电流效率降低。从目前报道来看,除了电沉积碲的电流效率较高(能超过95%)外,锗和硅电沉积的电流效率均比较低,通常在90%以下[13-14]。并且由于半导体导电性差,随着其在电极表面沉积,电极的欧姆降增加,槽电压也随之升高,加上沉积时间往往很长,能耗也随之急剧上升,所以这对于冶金过程节能降耗是非常不利的。
上述问题一直阻碍着电沉积半导体元素技术的发展与进步。为了解决这些问题, 包括本课题组在内的众多研究机构均开展了大量的研究,但大多是常规手段的工艺优化,如沉积参数、电极材料、电解液组成、添加剂、电解槽结构等,均无法有效解决上述问题,使得电沉积在半导体元素冶金中应用非常有限。一些半导体元素的冶金,如硅和锗,宁愿选择能耗和污染排放都高得多,但产能更高、工艺稳定性更好的其他工艺(如锗采用氯化蒸馏-水解-氢还原工艺[15]、硅采用改良西门子法[16]等),也不采用电沉积的技术。即使对于碲,如何提高产能和生产效率并降低能耗也是碲冶金多年来面临的一个难题。因此, 为了促进半导体元素电沉积提取技术的进步,在碲电沉积产能提高和
节能降耗、锗和硅电沉积产业化等方面取得突破,实现半导体元素低成本、低能耗、无污染和高产能的冶金提取,必须要有新的思路和途径来突破传统电沉积的不足。
2 光电化学冶金提取半导体元素的提出
针对上述问题,并基于半导体的光电导等基本性质、半导体电极的光电化学基本原理以及半导体元素电沉积提取过程基本特征,提出了采用光电化学沉积的方法进行半导体元素的电化学冶金提取,即在半导体元素电沉积提取过程中,对阴极表面施加光照,以促进阴极还原反应的进行,并强化沉积过程。在电沉积提取半导体元素过程中,一旦沉积开始进行,电极上就会生成一层半导体膜覆盖在原始基底表面,电化学反应发生场所由导体/电解液界面转变为半导体/电解液界面。当光照射至电极表面时,半导体本身和半导体/电解液界面的性质会发生显著变化,使得电沉积过程与传统工作状态相比产生明显差异。图1所示为光电化学沉积提取半导体元素(以p型半导体为例)过程中电极/电解液的能级结构示意图,其中M为半导体元素单质还原态,M+为半导体元素的氧化态,EF为费米能级,φ为电极电势, 、
、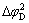 、
、 分别为暗态下的电势欧姆降、空间电荷层电势差和电极/电解液界面电势差,
分别为暗态下的电势欧姆降、空间电荷层电势差和电极/电解液界面电势差,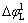 、
、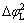 、
、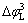 分别为光照下的电势欧姆降、空间电荷层电势差和电极/电解液界面电势差。光照下,当光子能量hv大于半导体带隙宽度Eg时,半导体被激发产生电子-空穴对,导致以下现象出现:1) 载流子浓度上升,电导率增加,欧姆降(
分别为光照下的电势欧姆降、空间电荷层电势差和电极/电解液界面电势差。光照下,当光子能量hv大于半导体带隙宽度Eg时,半导体被激发产生电子-空穴对,导致以下现象出现:1) 载流子浓度上升,电导率增加,欧姆降(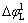 <
< )降低;2) 费米能级上升,能带弯曲减小,空间电荷区的电势分摊(
)降低;2) 费米能级上升,能带弯曲减小,空间电荷区的电势分摊(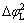 <
<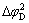 )减小;3) 光生电子从半导体流向电解液,半导体/电解液界面电势差(
)减小;3) 光生电子从半导体流向电解液,半导体/电解液界面电势差(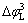 >
> )增加,促进还原反应的进行;4) 增加饱和电流,有利于采用更大的电流密度沉积。
)增加,促进还原反应的进行;4) 增加饱和电流,有利于采用更大的电流密度沉积。
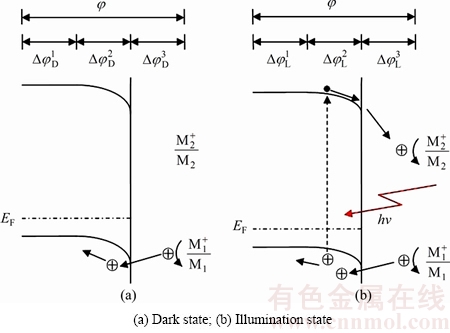
图1 p型半导体上阴极光电化学沉积过程的电极/电解液能级结构
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of band alignment at electrode/electrolyte interface during cathodic photo-electrochemical deposition on p-type semiconductor electrode
结合半导体特性以及光电化学基本理论,光电化学沉积提取半导体元素可具备以下一系列优势。
1) 降低欧姆降。半导体具有光电导效应,即当半导体吸收能量大于带隙宽度的光子以后产生光生电子-空穴对,使载流子浓度的上升,电导率增加,可以直接降低电极的欧姆降;而且半导体元素导电性差是其电沉积存在各种问题的最根本原因之一。因此,利用光电化学沉积过程中已沉积半导体的光电导效应可为解决半导体元素电沉积中半导体导电性差带来的系列问题提供有效途径。
2) 强化电极过程,改善电流效率。半导体/电解液界面实际上是一个整流结,可以起到分离光生电子-空穴对的作用[17]:对于阴极电沉积p 型半导体(碲是天然p型半导体[18];锗和硅等也很容易控制为p型,如主要杂质原子最外层电子数均小于4,呈p掺杂),将有利于光生电子流向电解液,实质上增加了阴极/电解液界面电势差,促进了还原反应的进行,强化了阴极过程,并提高了电流效率。
3) 降低槽电压。光照时载流子的重新分布(空间电荷层的载流子浓度会显著上升)会引起费米能级的上升从而减小半导体的能带弯曲[19],降低空间电荷层所分摊的电势差,也有利于降低槽电压。
4) 提高可采用的电流密度。半导体在阴极极化时,由于空间电荷区的存在,电极反应存在着饱和电流(电极反应电流密度不随过电势差的增加而增加,而是受到半导体内部载流子供应状况的限制),通过光照可以增大载流子浓度,从而增大反应的饱和电流,有利于提高沉积所用的电流密度,促进沉积速率的增加[20]。
5) 可降低反应过电势。此外,有研究发现当光照时,在半导体电极上电沉积其他金属时,光生载流子可以降低金属电化学沉积过电势并活化金属的电沉 积[21-22],这一特征可能会对半导体元素电沉积(除了最初始阶段,实际上是在半导体上同质沉积)的提高电流密度和降低槽电压等产生积极作用。
基于以上分析,光电化学冶金实际上是集光、电、化学于一体的半导体元素提取新技术,由本文作者首次在冶金提取领域提出,其实质是利用半导体的光电化学特性和光电导效应对沉积过程进行强化和节能。值得注意的是,光电化学沉积在化合物半导体功能薄膜生长制备(主要关注薄膜品质)与应用领域已经得到一定的研究,其在过程强化方面的优势也在这些化合物半导体薄膜沉积中得到充分的体现和验证,这为该法在半导体元素电沉积冶金提取提供了理论和技术的支持。MISHRA等[23]报道了光电导效应和光电化学响应对电沉积p 型CdTe 化合物半导体薄膜的影响,发现光照能促进Cd2+和HTeO2+的电化学还原反应,强化阴极沉积过程。SUGIMOTO等[24]则发现CdTe 的沉积速率与光照强度的平方根成正比。MURASE等[25]对光电化学沉积CdTe进行了细致研究,发现光照能极大地增强电化学沉积CdTe半导体薄膜的电流密度以及生长速率,还可以极大地提高电流效率,例如对于高镉离子浓度体系,施加光照后电沉积的电流效率能从30%提升至97%,相同沉积量所用时间可从2298 min降至47 min,即沉积速率能提高将近50倍。本团队[26]也首次报道了采用光电化学沉积法制备CuInSe2化合物半导体薄膜,研究发现光照不仅可明显提高CuInSe2薄膜的电流密度和沉积速率,而且能改善薄膜的形貌,使之更为均匀致密。对于半导体元素,最近本文作者团队对Se[27]和Te[28]薄膜的光电化学沉积开展了一些初步的研究,结果表明,相比如传统电化学沉积,光电化学沉积时电化学还原的法拉第阻抗显著降低,沉积电流密度显著增加。这使得采用基于电化学的方法提取Se成为可能,开辟了Se提取冶金的新途径,同时也为采用光电化学进行Te的提取提供了理论依据。本文作者将这些工作的基础上,以Te的工业电积生产溶液体系为对象,采用光电化学沉积的方法进行Te的提取,通过此例来验证光电化学冶金的优越性。
3 光电化学冶金优势的验证—以Te为例
3.1 实验
电解液为含1 mol/L Na2TeO3 (99.99%) 和2.5 mol/L NaOH的碱性溶液(模拟工业条件),电解槽为方形石英电解槽。电化学沉积及电化学行为研究均采用PARSTAT 4000型电化学工作站,实验除恒电流沉积为双电极体系外均采用常规的三电极体系,其中参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE,本研究所有电势除槽电压外均相对于此参比电极),对电极为高纯石墨片,工作电极为430不锈钢片。实验所用不锈钢片的清洗步骤为:洗衣粉水超声清洗10 min,去离子水(18.2 MΩ/cm)超声清洗10 min,无水乙醇超声清洗10 min,去离子水(18.2 MΩ/cm)超声清洗10 min,最后氮气吹干备用。光电化学沉积采用Newport 300 W光源模拟太阳光直接照射工作电极,到达电解槽处的光强用FZ-2A辐照计测定为100 mW/cm2。
循环伏安/线性伏安扫描用于研究碲的电沉积反应机制和光照对其反应机制的影响,在非搅拌的状态下进行测试,扫描速度为10 mV/s。恒电势沉积的阴极电势控制在-0.75 V (vs SCE)。恒电流沉积的电流密度分别控制在100 A/m2和200 A/m2,同时记录槽电压随时间的变化。恒电流沉积前后的不锈钢片均充分干燥后称取质量以计算沉积的碲的质量。采用荷兰FEI公司生产的Quanta-200型环境扫描电镜观察沉积物碲的形貌。
3.2 结果与讨论
对含有1mol/L Na2TeO3和2.5mol/L NaOH的电解液体系进行循环伏安测试,测试的电势范围为0.8 V到-1.0 V,结果如图2所示。从曲线上可以观察到一个明显的还原峰(标记为C)和两个氧化峰(标记为A1和A2)。结合之前的研究结果[28],此还原峰C(约为-0.75 V)对应于Te的沉积,通过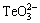 的四电子还原进行,见反应(1)。事实上在更负的电势下还会发生Te的进一步还原,见反应(2),其还原产物Te2-会与溶液中的Na2TeO3发生归中反应,形成Te单质,见反应(3)。由于本研究所采用的Na2TeO3的浓度较大,还原产物Te2-一旦形成就会立即与电解液中的Na2TeO3发生归中反应生成新的Te,故使得反应(2)所对应的还原峰没有表现出来。此外,通过仔细观察发现,在负向扫描形成还原峰C之前的-0.5 V到-0.7 V范围内,还存在一处还原特征(见图2中插图),但该还原特征对应的还原电流非常弱,这很可能对应于Te在不锈钢基底上发生Na2TeO3的四电子预还原沉积,即为碲的单层沉积[29]。
的四电子还原进行,见反应(1)。事实上在更负的电势下还会发生Te的进一步还原,见反应(2),其还原产物Te2-会与溶液中的Na2TeO3发生归中反应,形成Te单质,见反应(3)。由于本研究所采用的Na2TeO3的浓度较大,还原产物Te2-一旦形成就会立即与电解液中的Na2TeO3发生归中反应生成新的Te,故使得反应(2)所对应的还原峰没有表现出来。此外,通过仔细观察发现,在负向扫描形成还原峰C之前的-0.5 V到-0.7 V范围内,还存在一处还原特征(见图2中插图),但该还原特征对应的还原电流非常弱,这很可能对应于Te在不锈钢基底上发生Na2TeO3的四电子预还原沉积,即为碲的单层沉积[29]。
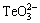 +3H2O+4e→Te+6OH- (1)
+3H2O+4e→Te+6OH- (1)
Te+2e→Te2- (2)
2 Te2-+3H2O+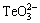 →3Techem+6OH- (3)
→3Techem+6OH- (3)
为弄清光照对电化学沉积时Te还原过程的影响,分别在光照和暗态下进行线性伏安扫描曲线测试,扫描电势范围为-0.5 V到-0.95 V,扫描速度为10 mV/S,其测试结果如图3(a)所示。由图3(a)可知,光照下碲的初始还原电位和暗态下碲的初始还原电势一致,这是因为此时基底上还没有p型半导体碲的生成,故光照对其初始沉积电位没有影响。但一旦扫描电势负于碲的初始还原电势,此时基底表面有碲的沉积,光照下的阴极还原电流密度明显大于暗态下阴极还原电流密度。这也意味着电化学沉积时如果采用相同的沉积电流密度,光照下的体系所需的沉积电势更正,槽电压会更小。图3(b)所示为含 1 mol/L Na2TeO3和2.5 mol/L NaOH电解液体系在通(on)、断(off)光状态下恒电势沉积的电流密度-时间曲线(沉积电势为-0.75 V)。由图3(b)可知,在光照的瞬间,碲的沉积电流密度迅速增大(增加的电流称为“光生电流”),但当断开光照(暗态)时,其沉积密度又立即减小,该结果与线性伏安扫描测试的结果一致。导致上述结果的原因是沉积物碲会吸收能量大于其自身禁带宽度的光子,从而激发碲价带中的电子跃迁到导带上从而产生光生电子-空穴对。一方面,光生电子-空穴对使载流子浓度的上升,电导率增加,能带弯曲较小,可以降低工作电极的欧姆降和空间电荷区的电势差分摊;另一方面,光生电子在半导体/电解液界面聚集并从半导体流向电解液参与Na2TeO3的还原。这两方面的影响均会增大电极/电解液界面电势差,促进沉积电流密度的增加,强化电极(电化学沉积)过程。以1000~1200 s这个暗态-光照循环为例,在1100 s处体系处于光照状态以后,电流密度迅速上升,由3.1 mA/cm2提高至4.5 mA/cm2,提高45%,这表明沉积速率也得到相应提高,使得碲电化学沉积提取产能的大幅提高成为可能。从图3(b)还可看到随着沉积时间的延长光生电流越来越大,这是因为沉积时间越长电化学沉积的碲也越来越厚,光照时可吸收更多的光,产生更多的光生电子-空穴对,故光电流也随之增大。
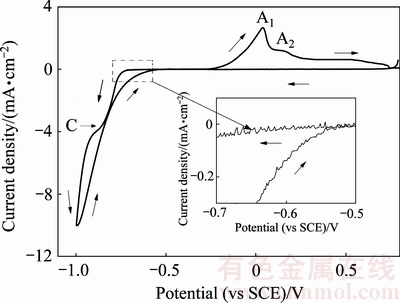
图2 不锈钢基底上Na2TeO3电解液体系的循环伏安曲线
Fig. 2 Cyclic voltammogram of Na2TeO3 electrolyte system on stainless steel substrate

图3 1 mol/L Na2TeO3+2.5 mol/L NaOH电解液体系在暗态和光照下的线性扫描伏安曲线以及在通、断光状态下电化学沉积的电流密度-时间曲线(沉积电势为-0.75 V (vs SCE))
Fig. 3 Linear sweep voltammograms of 1 mol/L Na2TeO3+2.5 mol/L electrolyte system under dark and light(a), cathodic current-time curve in 1 mol/L Na2TeO3+2.5 mol/L electrolyte system under chopped illumination (“on” and “off” stands for under light and dark, respectively) at deposition potential of -0.75 V (vs SCE)(b)
恒电流沉积是冶炼厂实际电化学沉积提取碲所采用的工艺。为了光电化学沉积冶金提取的有效性,对含1 mol/L Na2TeO3和2.5 mol/L NaOH电解液体系在光照和暗态下进行恒电流沉积,所采用的沉积电流密度为100 A/m2和200 A/m2。

图4 采用不同沉积电流密度在光照和暗态下电化学沉积碲的SEM像
Fig. 4 SEM images of electrodeposited Te with different deposition current densities under illumination and dark
沉积获得的产物碲的形貌见图4。通过对比可知光电化学沉积碲的颗粒尺寸更大。而且还可以看到,小沉积电流密度下获得产物碲的颗粒更小,枝晶或粉化现象更严重,表明当前体系下的沉积过程不完全受扩散控制(受电化学反应控制,或电化学反应/扩散混合控制)。之前在低浓度(10 mmol/L Na2TeO3+2.5 mol/L NaOH)电解液体系中的研究[28]表明,光照并不会改变碲电化学沉积初始阶段的成核与生长模式(均为三维连续成核后扩散控制生长)。本实验中由于采用的高浓度电解液体系,相比之下浓差极化将会显著降低,因此大颗粒碲的形成意味着光照促进了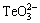 的电化学还原和颗粒的生长,这也将更有利于沉积产物碲的收集。
的电化学还原和颗粒的生长,这也将更有利于沉积产物碲的收集。
图5(a)和(b)所示为测量沉积时的槽电压-时间曲线。由图可知,对于两种沉积电流密度,光照时电解槽槽电压均明显低于暗态时的槽电压,计算可知沉积电流密度为100 A/m2时采用光照后槽电压降低了8%,而当沉积电流密度为200 A/m2时槽电压降低了13%。槽电压U主要由以下几部分组成:理论分解电压Ed,阳极过电位,阴极过电位,电解槽液的欧姆电压降IRsol,电极的欧姆电压降IRm。其中Ed是由电解反应的本身所决定,光照对其的影响可以忽略。但光照条件下由于光生电子-空穴的产生会显著增加载流子的浓度,从而显著降低工作电极(阴极)的欧姆降IRm。同时光照时载流子的重新分布(空间电荷层的载流子浓度会显著上升)会引起p型半导体碲的费米能级的上升从而减小半导体碲的能带弯曲,降低空间电荷层所分摊的电势差,也有利于降低槽电压。

图5 在不同沉积电流密度光照和暗态下电化学沉积碲的槽电压随时间的变化
Fig. 5 Cell voltage-time curves of Te electrodeposition under light and dark at different deposition current densities
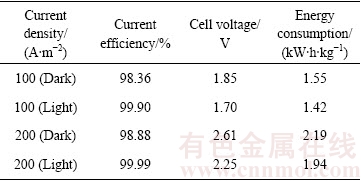
表1列出了不同条件下碲电化学沉积的电流效率 η和电能消耗W。电流效率η为沉积产物的实际产量mE与理论产量mT之比,且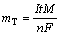 ,其中I为电流强度,t为通电时间,M为产物的分子量,n为电极反应的电子数,F为库伦常数。电能消耗W=U×I×t/mE。由表1可知,光照均提升了碲沉积体系的电流效率,这主要是因为当光照条件下碲会吸收能量较高的光子产生光生电子-空穴对,光生电子在电场的作用下会从半导体流向电解液,从而参与电解液中的
,其中I为电流强度,t为通电时间,M为产物的分子量,n为电极反应的电子数,F为库伦常数。电能消耗W=U×I×t/mE。由表1可知,光照均提升了碲沉积体系的电流效率,这主要是因为当光照条件下碲会吸收能量较高的光子产生光生电子-空穴对,光生电子在电场的作用下会从半导体流向电解液,从而参与电解液中的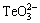 的电还原过程,所以光照条件下电沉积碲的电流效率会有所提升。同时由表1也可看出沉积电流密度为100 A/m2时暗态时的电能消耗为1.55 kWh/kg,而采用光照后其能耗值降低到1.42 kWh/kg,大约降低了8%;当沉积电流密度为200 A/m2时暗态时的电能消耗为2.19 kWh/kg,而采用光照后其能耗值降低到1.94 kWh/kg,大约降低了11%。故综上所述,光照能明显提升电流效率,降低电化学沉积碲体系的槽电压,从而降低电能消耗。但是应当说明的是,由于在实际应用时可采用自然光,此处电能消耗计算时未考虑光源的能耗。
的电还原过程,所以光照条件下电沉积碲的电流效率会有所提升。同时由表1也可看出沉积电流密度为100 A/m2时暗态时的电能消耗为1.55 kWh/kg,而采用光照后其能耗值降低到1.42 kWh/kg,大约降低了8%;当沉积电流密度为200 A/m2时暗态时的电能消耗为2.19 kWh/kg,而采用光照后其能耗值降低到1.94 kWh/kg,大约降低了11%。故综上所述,光照能明显提升电流效率,降低电化学沉积碲体系的槽电压,从而降低电能消耗。但是应当说明的是,由于在实际应用时可采用自然光,此处电能消耗计算时未考虑光源的能耗。
表1 采用不同沉积电流密度在光照和暗态下电化学沉积碲的电流效率、槽电压和电能消耗
Table 1 Current efficiency, cell voltage and energy comsuption of Te electrodeposition under illumination and dark at different deposition currents
从上述碲提取实验的结果与讨论可知,与常规的电化学沉积相比,采用光电化学沉积具有可强化电极过程,提高沉积速率、电流效率和产能,并降低槽电压等优势,是一种有良好发展潜力的冶金提取新技术。其优越性主要来源于沉积物碲能吸收量大于其自身带隙宽度的光子后受激发产生光生电子-空穴对。这一方面使载流子浓度的上升,减小了电阻率和能带弯曲,直接降低工作电极的欧姆电阻和空间电荷区所分摊的电势差;另一方面光生电子可以从半导体流向电解液促进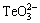 的电化学还原。
的电化学还原。
4 光电化学冶金需解决的问题及内涵拓展
虽然光电化学冶金相对于传统电化学沉积具有一系列的优势,但作为一种新技术,在未来发展过程中可能有一些问题需要解决。主要包括:1) 采用常用的人工光源,如氙灯、卤钨灯等,会增加能耗和成本,而如果引入太阳光则可能带来工艺稳定性问题。2) 光能利用率低。光源中低于沉积半导体带隙宽度的光子无法被利用,而高能光子中大于带隙宽度的部分能量也无法被利用(热化过程,“Thermolization”[29])。解决以上两个问题的可行方法是采用具有高发光效率的单色光源(其光子能量等于或略大于产物的带隙宽度即可),如LED等。3) 需要防止产生的光电子重新复合和参与副反应,即要确保产生的光电子尽可能都参与目标还原反应,而不是与空穴重新复合或者参与副反应,如析氢等。这个问题可以通过优化电解液体系和沉积参数以降低沉积产物的缺陷(减少非辐射复合中心,如深能级杂质、晶界等)来解决。此外还有一些其它问题,如溶液净化的要求可能会更高(需要更高的光学透过率)、电解槽的槽型改造(需要考虑光路)等问题在后续实际工程应用中也需要予以考虑。
最后,值得指出的是,光电化学冶金这一思路的内涵还可以进一步延伸。从前述的研究可知,光电化学冶金实质上是利用已沉积半导体的光电转换特性,即吸收大于带隙宽度的光子后激发产生光生载流子,使得电极/电解液的电学性质发生变化,同时光生载流子参与电化学沉积的反应,促进沉积的进行。这一原理实际上也可以应用于半导体矿物浸出等其他冶金过程。对于光电化学冶金,光生载流子是流入电解液促进电解液中离子的电化学还原(狭义内涵)。而如果光生载流子不是流入电解液,而是参与对自身的还原(光生电子)或氧化(光生空穴),则可以用于半导体矿物的还原或氧化浸出。因此,利用半导体元素或矿物受大于其带隙宽度光子激发产生的光生载流子参与冶金过程的氧化还原反应,来实现冶金提取过程的强化,都可以属于光电化学冶金的范畴(广义内涵)。由于大多数有色金属是以氧化物或硫化物半导体矿物形式存在于自然界,因此光电化学冶金这一原理将为这些矿物的处理提供新的途径,这将在后续研究中予以报道。
5 结论
1) 提出以光电化学沉积的新技术进行半导体元素的电化学提取,并以碲提取为例验证技术的可行性。
2) 光电化学沉积过程中,半导体沉积物能吸收能量大于其自身带隙宽度的光子受激发产生光生电子-空穴对。这一方面使载流子浓度的上升,电阻率和能带弯曲减小,降低工作电极所分摊的电势差;另一方面光生电子可以从半导体流向电解液促进电化学还原。
3) 与常规的电化学沉积相比,光电化学沉积具有可强化电极过程,提高沉积速率、电流效率和产能,并降低槽电压等优势,具有良好的发展前景。
4) 光电化学冶金的未来发展,一方面需要解决光源选择、光能利用率、光生载流子复合或参与副反应、溶液净化和光路设计等问题;另一方面其内涵还可以进一步拓展,不仅可用于半导体元素的电化学沉积,而且可以用于半导体矿物处理。
REFERENCES
[1] O’KEEFE T J. Electrodeposition in extractive metallurgy: Anemerging technology?[J]. JOM, 1992, 44(4): 30-34.
[2] 林文荣, 杨声海, 孙彦伟, 陈永明, 何 静, 唐朝波. 聚醚添加剂对Zn(Ⅱ)-NH3-NH4Cl-H2O 体系电积锌的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(8): 1738-1747.
LIN Wen-rong, YANG Sheng-hai, SUN Yan-wei, CHEN Yong-ming, HE Jing, TANG Chao-bo. Effect of polyether additive on zinc electrodeposition in Zn(Ⅱ)-NH3-NH4Cl-H2O system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(8): 1738-1747.
[3] 李 茂, 高玉婷, 白 晓, 李 远, 侯文渊, 王玉洁. 300 kA铝电解槽中氧化铝颗粒的溶解模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(2): 399-405.
LI Mao, GAO Yu-ting, BAI Xiao, LI Yuan, HOU Wen-yuan, WANG Yu-jie. Simulation of alumina particle dissolution in 300 kA aluminum electrolytic cell[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(2): 399-405.
[4] HA Y C, SOHN H J, JEONG G J, LEE C K, RHEE K I. Electrowinning of tellurium from alkaline leach liquor of cemented Te[J]. Journal of applied electrochemistry, 2000, 30(3): 315-322.
[5] 翟秀静. 重金属冶金学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2011: 74-316.
ZHAI Xiu-jing. Heavy metal metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2011: 74-316.
[6] HOFFMANN J E,KING M G,CARAPELLA S C, OLDFIELD J E,PUTNAM R D. Tellurium and tellurium compounds[M]. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2001: 6-7.
[7] RAO G M, ELWELL D, FEIGELSON R S. Electrowinning of silicon from K2SiF6-molten fluoride systems[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1980, 127(9): 1940-1944.
[8] 贾 明, 赖延清, 田忠良, 刘芳洋, 李 劼, 辛鹏飞, 刘业翔. Na3AlF6-LiF熔盐体系中硅的电沉积行为[J]. 物理化学学报, 2011, 27(5): 1108-1115.
JIA Ming, LAI Yan-Qing, TIAN Zhong-Liang, LIU Fang-Yang, LI Jie, XIN Peng-Fei, LIU Ye-Xiang. Electrodeposition Behavior of Silicon from Na3AlF6-LiF melts[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2011, 27(5): 1108-1115.
[9] 乐红春. 中和渣中碲的提取及电解制备高纯碲研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012: 36-39.
LE Hong-chun. Research on extraction of tellurium from neutralization sludge and electrolytic preparation of high purity tellurium[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012: 36-39.
[10] LIANG Xue-hai, KIM Y G, GEBERGZIABIHER D K, STICKNEY J L. Aqueous electrodeposition of Ge monolayers[J]. Langmuir, 2009, 26(4): 2877-2884.
[11] FINK C G, DOKRAS V M. Electrodeposition and electrowinning of germanium[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1949, 95(2): 80-97.
[12] MATTEI R C D, FEIGELSON R S. Growth rate limitations in electrochemical crystallization[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1978, 44(2): 115-120.
[13] SAITOU M, SAKAE K, OSHIKAWA W. Evaluation of crystalline germanium thin films electrodeposited on copper substrates from propylene glycol electrolyte[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 162(1): 101-105.
[14] BIEBER A L, MASSOT L, GIBILARO M, CASSAYRE L, TAXIL P, CHAMELOT P. Silicon electrodeposition in molten fluorides[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 62: 282-289.
[15] 梁 杰. 从含锗烟尘浸出与萃取锗研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2009: 10-11.
LIANG Jie. Research on leaching and extraction of germanium from germanium dust[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2009: 10-11.
[16] 刘 刚, 秦 榕, 刘生章, 王舒娅. 改良西门子法生产多晶硅精馏工艺的改进[J]. 有色金属: 冶炼部分, 2013, 9: 56-59.
LIU Gang, QIN Rong, LIU Sheng-zhang, WANG Shu-ya. Improvement on rectification process of polycrystalline silicon by improved Siemens process[J]. Non-ferrous Metal (Smelting Section), 2013, 9: 56-59.
[17] MICHEELS R H, DARROW A D, RAUH R D. Photoelectrochemical deposition of microscopic metal film patterns on Si and GaAs[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1981, 39(5): 418-420.
[18] WEIMER P K. A p-type tellurium thin-film transistor[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1964, 52(5): 608-609.
[19] RAJESHWAR K. Encyclopedia of Electrochemistry[M]. Chichester: John Wiley &Sons Inc, 2007: 1-52.
[20] 郭鹤桐, 谭奇贤. 电化学教程[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 2000: 219-221.
GUO He-tong, TAN Qi-xian. Course of electrochemistry. Tianjin: Tianjin UniversityPress, 2000: 219-221.
[21] ROSE T L, LONGENDORFER D H, RAUH R D. Photoelectrochemical deposition of metals onto p-silicon using an internal cell[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1983, 42(2):193-195.
[22] INOUE T, FUJISHIMA A, HONDA K. Photoelectrochemical imaging processes using semiconductor electrodes[J]. Chemistry Letters, 1978(11): 1197-1200.
[23] MISHRA K K, RAJESHWAR K. A re-examination of the mechanisms of electrodeposition of CdX and ZnX (X= Se, Te) semiconductors by the cyclic photovoltammetric technique[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1989, 273(1/2): 169-182.
[24] SUGIMOTO Y, PETER L M. Photoeffects during cathodic electrodeposition of CdTe[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 1995, 386(1): 183-188.
[25] MURASE K, MATSUI M, MIYAKE M, HIRATO T, AWAKURA Y. Photoassisted electrodeposition of CdTe layer from ammoniacal basic aqueous solutions[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2003, 150(1): C44-C51.
[26] YANG Jia, LIU Fang-yang, LAI Yan-qing, LI Jie, LIU Ye-xiang. Photoelectrochemical deposition of CuInSe2 thin films[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2012, 15(4): 19-21.
[27] FAN Y, YANG J, JIANG L, WANG Y, NG B K, SUN H, LAI Y, LI J, LIU F. Effects of illumination on the electrochemical behavior of selenium electrodeposition on ITO substrates[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(4): H225-H231.
[28] FAN Y, JIANG L, YANG J, LIU F. The electrochemical behavior of tellurium on stainless steel substrate in alkaline solution and the illumination effects[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 771: 17-22.
[29] 熊绍珍, 朱美芳. 太阳能电池基础与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 109-110.
XIONG Shao-zhen, ZHU Mei-fang. The foundmental and application of solar cell[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 109-110.
Photo-electrometallurgy for semiconductor elements extraction—taking tellurium as example
LIU Fang-yang, FAN Yan-yun, JIANG Liang-xing, LAI Yan-qing, LI Jie, LIU Ye-xiang
(School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Abstract: Photo-electrometallurgy technique was proposed for electrochemical extraction of semiconductor elements in this work aiming to solve the problems in electrometallurgy of semiconductor elements. Based on knowledge of semiconductor characters and photo-electrochemistry, the advantages of the proposed photo-electrometallurgy technique were revealed, and its superiority was experimentally confirmed by an example of tellurium (Te) electrochemical extraction. The results indicate that the semiconductor deposits can absorb the incident photons with energy larger than its band gap and be excited to generate electron-hole pair. The photon-generated electrons can flow from semiconductor electrode into electrolyte, enhancing the electrochemical reduction rate and the photon-generated-carriers can decrease the resistivity and band bending, reducing the potential drop at electrode. Compared with the traditional electrometallurgy, photo-electrometallurgy shows the advantages in intensifying process, reducing cell voltage, improving depositing rate, current efficiency and capacity, therefore exhibiting good development prospect. The issues that should be addressed in the future were also put forward and the connotation was expanded.
Key words: semiconductor element; illumination; cell voltage; photo-electrometallurgy; electrodeposition
Foundation item: Project(51774341) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2015JJ2175) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China
Received date: 2017-11-21; Accepted date: 2018-01-02
Corresponding author: LIU Fang-yang; Tel: +86-731-88830474; E-mail: liufangyang@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51774341);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(2015JJ2175)
收稿日期:2017-11-21;修订日期:2018-01-02
通信作者:刘芳洋,副教授,博士;电话:0731-88830474;E-mail: liufangyang@csu.edu.cn