文章编号:1004-0609(2011)01-0185-06
递温镁合金板轧制的数值仿真和验证实验
张丁非1, 2, 戴庆伟1, 2, 方 霖1, 2, 张钧萍1, 2
(1. 重庆大学 材料科学与工程学院, 重庆 400030;
2. 重庆大学 国家镁合金材料工程技术研究中心, 重庆 400044)
摘 要:对镁合金板材轧制过程的热量变化方程进行推导,并用有限元方法分析此热力耦合过程,并对仿真结果进行实验验证。结果表明:板材在轧制过程中有较大的温度变化,轧制过程板料的温度变化主要是由变形产热、摩擦生热和板料-轧辊热传导、以及与环境的传热情况决定,并且受板和轧辊间温度差的影响;随着板温度的下降,轧制力和等效应力线性增加,最大轧制力是最小轧制力的3倍;当温度降到210 ℃,等效应力达到160 MPa时,板料出现边裂缺陷,达到轧制成型极限;板料较佳轧制温度应高于210 ℃。
关键词:镁合金;轧制;有限元;温度梯度
中图分类号:TG335.5, TP391.9 文献标志码:A
Simulation and confirmatory experiment on rolling of magnesium alloy sheets with temperature gradient
ZHANG Ding-fei 1.2, DAI Qing-wei 1.2, FANG Lin 1.2, ZHANG Jun-ping 1.2
(1. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China;
2. National Engineering Research Center for Magnesium Alloys, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China)
Abstract: The quantity change equation of heat during the rolling of magnesium alloy was derived, and the finite element method was used to analyze the thermal-mechanical process. The simulation results were proved by confirmatory experiments. The results show that, there is a great temperature change in the rolled sheet, and the temperature change depends upon the plastic deformation heat, friction heat and heat transfer between sheet and roller, sheet and environment. The temperature difference between the sheet and roller has some effects on the change. With the temperature decreasing, the rolling force and equivalent stress increase linearly, and the maximum rolling force is 3 times as the minimum rolling force. When the temperature drops to 210 ℃, the equivalent stress is 160 MPa, and the edge cracks are generated, which is the deformation limit of AZ31 magnesium rolling. The lowest temperature of AZ31 magnesium rolling without edge cracks is 210 ℃.
Key words: magnesium alloy; rolling; finite element analysis; temperature gradient
镁合金是最轻的结构合金之一,已经在交通运输,3C等移动产品中得到了广泛应用。且镁的储量丰富,环境友好性优良,所以镁合金是非常有研究开发和应用前景的一种材料[1-2]。但是,镁合金的体积比热容较小(1781 J/(dm3·K)),且热导率较大(153 W/(m·K)),所以该合金加热升温快,散热降温也快[3-4]。在轧制过程中,镁合金板料和环境以及轧辊等发生热量传递,板料温度将发生较大的变化。同时,板料变形产生的体积功和板料与轧辊摩擦产生的摩擦热都将使板料温度升高。所以,镁合金轧制过程中温度将发生较大的变化,而温度又是影响变形抗力和板料组织变化的最重要参数之一。因此,对镁合金板材轧制过程中温度变化的研究尤为重要和迫切。
目前对镁合金的研究已经取得了很大的进展,很多镁合金的产品及零部件已经广泛用在交通、电子产品外壳等领域[5-9],但是对镁合金板材轧制过程中温度变化的研究还不够完善。汪凌云等[10]研究了AZ31镁合金板热轧+温轧+冷轧各个状态的组织和性能。陈维平等[11]研究了300、330和360 ℃下轧制AZ31镁合金板的组织和性能。目前,对镁合金轧制温度的研究多是关于某几个温度下轧制后的镁合金板的组织和力学性能,而对轧制过程温度的变化,以及变形抗力或者轧制力,板料应力分布等的研究还很少;对轧制成形性,特别是轧制板材的边裂研究亦未见文献报道。
本文作者将系统分析轧制过程中的热量产生和散失等变化,建立相应的数学模型,为了研究温度对AZ31镁合金板材轧制变形的影响,实验将以带有温度梯度的镁合金板料为研究对象,并利用大型非线性有限元软件MSC.Marc & Mentat 模拟轧制过程中温度以及应力、轧制力等的变化。
1 数学模型
轧制过程是一个复杂的热力耦合过程。由于镁合金具有体积比热容小等物理性质,其轧制过程更加复杂。其中热量的变化包括:1) 体积变形功转化为热量的部分;2) 板和轧辊摩擦生成的热量;3) 板和环境产生的热对流和辐射;4) 板和轧辊接触发生的热量传递;5) 镁合金组织变化(位错、孪晶产生和增殖等)产生的组织储能;6) 其他影响因素,例如轧辊的导热、轧制润滑、水冷、加热等。热量的变化直接影响材料的变形行为,显著体现在材料变形抗力上,进而影响轧制力。
轧制过程中板料的热量变化可以看作是有内热源的三维热传导问题,可表述为式(1)。其中,内热源就是变形功转化成热量的部分和摩擦产热。
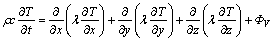 (1)
(1)
式中:ρ为密度;c为比热容;λ为热传导率;t为时间;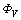 为内热源;x、y和z分别为板料的长、宽和厚度;T为板料的温度。塑性变形产生的热量可表述为
为内热源;x、y和z分别为板料的长、宽和厚度;T为板料的温度。塑性变形产生的热量可表述为
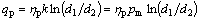 (2)
(2)
式中: qp为塑性变形发热热流;hp为塑性变形功转化热能的部分占总塑性变形功的比例,根据WERTHERIMER [12]的理论,一般取hp=0.9;pm为轧件上的平均压力;d1和d2分别为轧制前后轧件厚度。
摩擦生热用下面的方程表述:
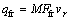 (3)
(3)
式中:qfr 为摩擦力功转化成的表面热流;M为功热转换系数;Ffr为摩擦力;vr为界面相对速度。因此,内热源可表述为
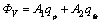 (4)
(4)
式中:A1、A2为面积。而板料和轧辊的热量传递可以表述为
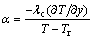 (5)
(5)
式中:α为等效热传递系数,λc为轧辊和板料的热传导率,T 和Tr 分别是板料和轧辊的温度。板料和环境的对流辐射传热可表述为
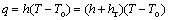 (6)
(6)
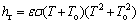 (7)
(7)
式中:ε为发散率;σ为波尔兹曼常数;To为环境温度; h和hr 都是对流换热系数。
忽略组织变化对能量的影响和其他影响小的因素,综合式(4)~(7)得到热流量表达式:
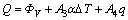 (8)
(8)
式中:A3、A4为面积;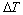 是温度差。Q能够反映主要因素引起的镁合金板轧制过程中的温度变化。式(8)为镁合金板轧制过程中的热量变化方程。
是温度差。Q能够反映主要因素引起的镁合金板轧制过程中的温度变化。式(8)为镁合金板轧制过程中的热量变化方程。
轧制过程遵守能量平衡方程和力平衡准则,故:
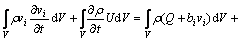
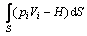 (9)
(9)
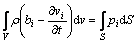 (10)
(10)
式中:vi 是速率,U是能量,Q是体积热流,bi是体积力,pi是边界上的力,H是热流密度,V是体积,S是边界的长度。又因为柯西应力准则:
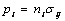 (11)
(11)
式中: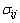 为柯西应力分量。综合式(9)~(11),得到轧制过程的热力耦合平衡方程:
为柯西应力分量。综合式(9)~(11),得到轧制过程的热力耦合平衡方程:
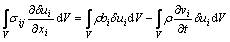 (12)
(12)
式中:ui为位移。式(12)是对轧制过程进行有限元分析的数学基础。
2 实验方法和有限元模拟
为了研究温度对AZ31镁合金板材轧制的影响规律,得到较优的轧制温度区间,采用了带有温度梯度的500 mm长的板料作为研究对象,通过加热使板料的一端到另一端呈现400 ℃到室温20 ℃的温度梯度。并且将热电偶均匀的焊接在板料上,用多通道温度巡检仪记录温度的变化,响应时间为1 s。实验用轧机为双辊轧机,辊径为170 mm,辊速为21 r/min,实验用板料的原始尺寸为10 mm×50 mm×500 mm。轧制1个道次,终轧板厚为6 mm。
实验所用材料为在420 ℃挤压成型的AZ31B镁合金,其流变应力—应变曲线如图1所示,其热导率、比热容和弹性模量随温度变化的曲线如图2所示。镁板与空气的对流换热系数为0.02 W/(m2·K),与轧辊的传热系数为35 W/(m2·K),发散系数为0.12[13]。
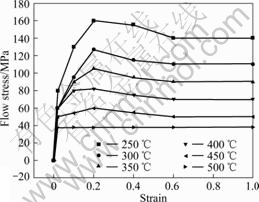
图1 AZ31镁合金流变应力—应变曲线
Fig.1 Flow stress—strain curves of AZ31[15]
有限元技术能够较好地将数学模型的结果计算和表示出来。本研究借助MSC.Marc & Mentat有限元软件来实现所建立的数学模型,并建立了相应的三维有限元模型来研究轧制过程的力-能变化,如图3所示。为了节约运算时间,模型按照实验的1/4建立,所以模型中运用两个对称面。板料温度按照原始坐标定义了400 ℃到20 ℃的温度梯度。由于辊径远大于板料厚度,轧辊温度的变化要小很多,且忽略轧辊的变形,因此轧辊定义为刚性,且温度为20 ℃。采用更新的拉格朗日方法计算,步长为0.005 s,且每隔50步记录一个数据。

图2 AZ31镁合金材料特性曲线
Fig.2 Characteristic curves of AZ31 properties: (a) Thermal conductivity[15]; (b) Specific heat capacity[15]; (c) Elastic modulus[16]
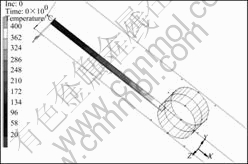
图3 轧制有限元模型
Fig.3 Finite element model of rolling
3 结果与讨论
3.1 轧制引起的板料温度变化
由于空气对流和与轧辊的接触传热以及变形功等因素,板料的温度发生了较大的变化,如图4所示。此图为板料侧面距前端125 mm处一点的温度变化曲线。在板料从加热炉出来到被咬入轧辊这段10多秒的时间里,温度下降了约10 ℃。这段时间的温度下降主要是由于板料和空气的对流辐射传热,损失了部分热量,然后是一个温度的突变。从有限元分析的结果可以看到先是一个温度的陡增,紧接着骤降。在板料经过轧辊的瞬间,热量的产生主要是由于变形功转化成的热量和摩擦生热,散失是由于板料和轧辊及周围环境的传热,其中和轧辊的接触传热起主要作用。温度陡增是由于板料刚被咬入时变形产热和摩擦生热的总和超出板料和轧辊接触导热很多,或者说是板料在短时间内还没来得及向轧辊传热,所以板料的温度快速升高。随着轧制过程的进行,此区域和轧辊的接触面积越来越大,变形也越来越小,变形产热变小,而接触散热激增,板料温度骤降。从图4可以看到,温度增加大于10 ℃,然后是温度骤降70 ℃。
实验测定结果中,轧件被咬入前后的温度下降和轧制过程中的温度陡降与有限元分析结果较吻合,但是实验测定结果没有温度的陡升。这主要是由于图4所示的有限元模拟结果的响应时间是0.05 s,而实验测定温度的巡检仪的响应时间是1s。因此,实验中很难同时测到温度的陡升和骤降。
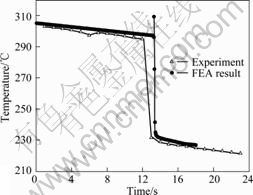
图4 板料侧边某点的温度变化
Fig.4 Temperature change of one point on edge of sheet
图5所示为板材不同位置的温度变化,数据记录间隔0.25 s。由图5可见,在被咬入之前,板料温度是降低的,根据对流辐射导热的特点,温度梯度越大,温度下降越明显,当板料温度是室温时就基本没有温度的变化了。温度的变化依然受变形产热、摩擦生热和板料-轧辊接触导热以及与环境对流辐射的影响。由于变形产热和摩擦生热,板料各处温度都会升高,由较低温度处(1/8和2/8处)的温度变化可明显得出,而热量的散失和温度梯度关系很大。这也是由于接触传热原理决定的。当温度高于150 ℃,即板料和轧辊的温度梯度大于130 ℃,散失的热量要大于产生的热量,所以经过轧制温度下降。而温度低于150 ℃时,由于板料温度梯度小,散热就少,且散热量小于产热量,因此板料温度上升。
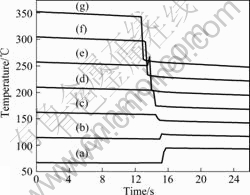
图5 板料不同位置的温度变化
Fig.5 Temperature change of different positions on sheet: (a) At 1/8 of length; (b) At 2/8 of length; (c) At 3/8 of length; (d) At 4/8 of length; (e) At 5/8 of length; (f) At 6/8 of length; (g) At 7/8 of length
3.2 温度对轧制力的影响
轧制坯料的温度直接影响着材料的变形抗力。由图1可见,温度越低,变形抗力越大,当然变形抗力越大,轧制力也会越大。图6所示为轧制力变化曲线。图6可见,当温度较高的一端(400 ℃)被咬入轧辊时,轧制力只有50 kN。随着轧制进行,温度较低的板料被咬入,轧制力变高,且板料温度越低,轧制力越高。当20 ℃的板料被咬入时,轧制力达到最大,超过140 kN,约为400 ℃的板料被咬入时的轧制力的3倍。实验所测轧制力和有限元模拟结果能够较好地吻合。
3.3 温度对应力的影响
温度不只直接影响变形抗力和轧制力,而且对等效应力的影响也非常明显。图7所示为温度梯度板料
长度方向的等效应力分布。由于是温度梯度板料,所以在长度方向的变化即温度变化。随温度的下降,等效应力直线上升。当等效应力上升到一定应力值时,达到材料的轧制极限。图8所示为板料在轧制极限时的等效应力和温度曲线。由图8可见,板料在轧制极限时的临界等效应力值为160 MPa,此时板料的温度为210℃;从0 mm到180 mm处的板料为经过轧辊的部分,由此还可以看出轧制使板料温度降低,甚至比
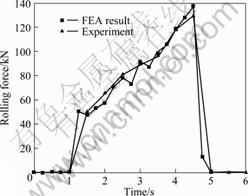
图6 轧制力的变化曲线
Fig.6 Change curves of rolling force
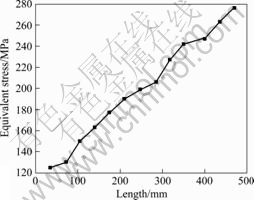
图7 温度梯度板料长度方向的等效应力分布
Fig.7 Equivalent stress of different places on sheet edge
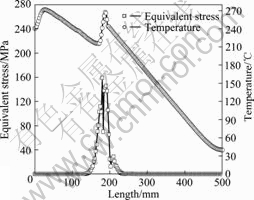
图8 板料在轧制极限时的等效应力和温度曲线
Fig.8 Equivalent stress and temperature curves of sheet at rolling limit
没经过轧辊的部分板料的温度还低。当等效应力达到材料的轧制极限时,经过轧制的板料发生边裂,且轧制时板料的温度越低,裂纹越深,如图9所示。因此,板料轧制温度应高于210 ℃。

图9 板材在轧制极限时的边裂
Fig.9 Edge cracks of sheet at rolling limit
4 结 论
1) AZ31镁合金轧制过程的温度变化主要是由变形产热、摩擦生热和板料-轧辊接触导热、与环境对流辐射决定,并且由于板料-轧辊接触导热受温度梯度的影响,所以板和轧辊之间温度差对板料温度的影响很大。
2) 在轧制过程中,AZ31镁合金板料发生较大的温度变化,最大温降为70 ℃。
3) 随着温度的下降,轧制力和等效应力线性增加。最大轧制力约为最小轧制力的3倍。
4) 当温度降到210 ℃,等效应力达到160 MPa时,轧制后的板料出现边裂缺陷,达到轧制成型极限。因此,AZ31镁合金板料的轧制温度应高于210 ℃。
References
[1] MORDIKE B L, EBERT T. Magnesium properties- applications-potential[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 302(1): 37-45.
[2] DIEM W. Magnesium in different applications[J]. Auto Technology, 2001(1): 40-41.
[3] 刘 正, 张 奎, 曾小勤. 镁基轻质合金理论基础及其应用[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2002: 16-17.
LIU Zheng, ZHANG Kui, ZENG Xiao-qin. Mg-based light-alloy theory and its application[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2002: 16-17.
[4] 陈振华, 严红革, 陈吉华, 全亚杰, 王慧敏, 陈 鼎. 镁合金[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2004: 11-16.
CHEN Zhen-hua, YAN Hong-ge, CHEN Ji-hua, QUAN Ya-jie, WANG Hui-min, CHEN Ding. Magnesium alloy[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004: 11-16.
[5] KIM W J, PARK J D, KIM W Y. Effect of differential speed rolling on microstructure and mechanical properties of an AZ91 magnesium alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 460(1/2): 289-293.
[6] HIROYUKI W, TOSHIJI M, KOICHI I. Effect of temperature of differential speed rolling on room temperature mechanical properties and texture in an AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 182(1/3): 644-647.
[7] MACKENZIE L W F, PEKGULERYUZ M. The influences of alloying additions and processing parameters on the rolling microstructures and textures of magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 480(1/2): 189-197.
[8] CHANG T C, WANG J Y, O C M, LEE S. Grain refining of magnesium alloy AZ31 by rolling[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 140(1/3): 588-591.
[9] XIA Wei-jun, CHEN Zhen-hua, CHEN Ding, ZHU Su-qing. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy sheets produced by differential speed rolling[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(1): 26-31.
[10] 汪凌云, 黄光杰, 陈 林, 黄光胜, 李 伟, 潘复生. 镁合金板材轧制工艺及组织性能分析[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(5): 910-914.
WANG Ling-yun, HUANG Guang-jie, CHEN Lin, HUANG Guang-sheng, LI Wei, PAN Fu-sheng. Rolling technology, microstructure and property analyses of magnesium alloy sheet[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(5): 910-914.
[11] 陈维平, 陈宛德, 詹美燕, 李元元. 轧制温度和变形量对AZ31 镁合金板材组织和硬度的影响[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2007, 27(5): 338-341.
CHEN Wei-ping, CHEN Wan-de, ZHAN Mei-yan, LI Yuan-yuan. Effects of rolling temperature and strain on microstructure and hardness of AZ31 magnesium sheets[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2007, 27(5): 338-341.
[12] WERTHEIMER T B. Thermal mechanically coupled analysis in metal forming processes[C]// Numerical Methods in Industrial Forming Processes. Wales, Swansea: Pineridge Press, 1982: 425-434.
[13] JI Y H, PARK J J. Analysis of thermo-mechanical process occurred in magnesium alloy AZ31 sheet during differential speed rolling[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 485(1/2): 299-304.
[14] 卢志文, 汪凌云, 潘复生, 陈 林. 变形镁合金及其成形工艺[J]. 材料导报, 2004, 18(9): 39-46.
LU Zhi-wen, WANG Ling-yun, PAN Fu-sheng, CHEN Lin. Wrought magnesium alloys and their forming processes[J]. Materials Review, 2004, 18(9): 39-46.
[15] 郭 鹏, 张兴国, 郝 海, 金俊泽. AZ31镁合金圆锭连铸过程温度场的数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(9): 1570-1576.
GUO Peng, ZHANG Xing-guo, HAO Hai, JIN Jun-ze. Temperature simulation of direct chill casting of AZ31 magnesium alloy billets[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(9): 1570-1576.
[16] 周 珂. 镁合金板材性能及轧制过程的模拟研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2007: 32-33.
ZHOU Ke. Study on the property of magnesium alloy sheet and the simulation of roll process[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2007: 32-33.
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB613700);国家“十一五”科技支撑计划重点资助项目(2007BAG06B04);重庆市科技攻关重点资助项目(CSTC,2009AB4008);国家杰出青年科学基金资助项目(50725413)
收稿日期:2009-00-00;修订日期:2010-00-00
通信作者:戴庆伟,博士;电话:023-65102821;E-mail: daiqingwei@cqu.edu.cn