
Effects of sodium substitution on properties of LiMn2O4 cathode for lithium ion batteries
GUO Hua-jun(郭华军)1, LI Xiang-qun(李向群)2, HE Fang-yong(何方勇)1,
LI Xin-hai(李新海)1, WANG Zhi-xing(王志兴)1, PENG Wen-jie(彭文杰)1
1. School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 11 December 2009; accepted 8 April 2010
Abstract: Na-doped Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes were synthesized using a sol-gel process. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffractometry (XRD), cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and charge-discharge measurements. The results show that all the samples exhibit the same cubic spinel phase structure without impurity. The lattice constant and unit cell volume decrease with increasing the sodium dopant amount. As the molar ratio of sodium to manganese (x=n(Na)/n(Mn)) increases from 0 to 0.03, the initial discharge capacity of the Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes decreases from 119.2 to 107.9 mA?h/g, and the discharge capability at large current rate and the storage performance decline dramatically, while cycling performance at room temperature and 55 ℃ are improved. The CV and EIS studies indicate that reversibility of Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes decreases and the electrochemical impedance increases with increasing the sodium dopant amount.
Key words: lithium ion battery; cathode; LiMn2O4; sodium; substitutio
1 Introduction
Layered LiCoO2 has been widely used in commercial lithium ion batteries, but Co is relatively expensive and toxic. Spinel LiMn2O4 is considered as one of the most promising alternative cathode materials and investigated widely because of its low cost, good safety and environmentally benign nature[1-2].
However, LiMn2O4 requires further improvement before it can act as a cathode material in commercial lithium ion batteries. The material has severe capacity fade during storage and cycling at elevated temperature [3-4]. Although the rationale behind the capacity loss is not completely understood, several contributing factors could include Jahn-Teller distortion, manganese dissolution, lattice instability, electrolyte decomposition and particle disruption[5-7]. Many efforts have been made to improve the elevated temperature performance by substituting O with F[8-10], coating the spinel with Li2O, B2O3, Al2O3, MgO, ZnO, SnO2 and ZrO2[4, 9-10], and doping with metal ions such as Cr3+[11-12], Al3+[13], La3+[1], Nd3+[14] and Mg2+[15-16].
Electrolytic manganese dioxide (EMD) has been widely used as manganese compound precursor for synthesis of LiMn2O4 powders. However, the EMD precursors usually have a large amount of impurities such as Na+ and SO42-. Nowadays, the commercial EMD is primarily produced by electrodeposition from manganese sulfate. The deposit consists of manganese hydroxide and/or manganese dioxide with low crystallinity, loose structure and abounding micro cavities, which results in serious absorption and sandwich inclusion of SO42- and sodium impurities. Many efforts have been made to eliminate these impurities but little effect is achieved. Therefore, LiMn2O4 cathode made from EMD contains a large amount of those impurities, which may be the important causes to the failure of the LiMn2O4 cathode in the lithium ion batteries. But, there is no research on the effects of sodium reported yet.
The amount of sodium in the commercial EMD is usually larger than 0.25% by mass fraction, which means molar ratio of sodium to manganese (x=n(Na)/n(Mn)) is above 0.01. As the residue, sodium in the manganese dioxide is usually not considered in determining the molar ratio of Li to Mn for synthesis of manganese spinel cathode, and the amount of sodium is much lower than that of lithium and manganese. In this work, we fixed the molar ratio of lithium to manganese as 1.05:2 and added sodium acetate in the starting materials with molar ratios (x= n(Na)/n(Mn)) of 0, 0.01, 0.02 and 0.03, respectively, and then Na-doped spinels were synthesized using a sol-gel process. The effects of the sodium substitution on the structure and performances of Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes were investigated.
2 Experimental
Analytical reagent-grade CH3COOLi·2H2O, CH3COONa, Mn(CH3COO)2·4H2O and citric acid were dissolved in distilled water at a molar ratio of 0.525:x:1: 0.75, where x is 0, 0.01, 0.02 and 0.03, respectively. Analytical reagent-grade ammonium hydroxide was added slowly to the solution with constant stirring until pH 8 was achieved. The resultant solution was evaporated at 80 ℃, during which a sol was obtained and then it transformed into a gel. To remove water, the gel was dried at 140 ℃ for 12 h in a vacuum oven. The resulting gel precursors were calcined at 700 ℃ for 24 h in air to obtain the spinel phase. The structure of the samples was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis using a Rigaku diffractometer.
The Li1.05Mn2O4 spinel, acetylene black and poly-vinylidene difluoride (PVDF) were mixed in a mass ratio of 8:1:1 and emulsified in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone. The cathode was prepared by spreading the resulting slurry on an aluminum foil and dried overnight at 120 ℃. The coin cell was prepared in an Ar atmosphere glove box using Li foil as an anode and UP 3025 porous membrane as a separator. The electrolyte was 1 mol/L LiPF6 dissolved in a mixture of ethylene carbonate (EC), dimethyl carbonate (DMC) and methyl-ethyl carbonate (EMC) with a volume ratio of 1:1:1. The cell was charged and discharged from 3.0 to 4.3 V at different current rates.
An accelerated measurement of storage performance for the Li1.05Mn2O4 spinels was carried out by storing the cells at 55 ℃. The cells were charged and discharged for 3 cycles at 0.5C current rate at room temperature, and then they were fully charged and stored at 55 ℃ for 7 d. The cells were discharged at 0.5C current rate at room temperature after the storage. The self-discharge was determined by the difference between the discharge capacity before the storage and that after the storage, and then the self-discharge ratio (ratio of the self-discharge capacity to the discharge capacity before the storage) of the cathodes was obtained.
Cyclic voltammetery (CV) was carried out on a CHI660A electrochemical workstation between 3.0 and 4.5 V at a scan rate of 0.2 mV/s and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was measured between 0.001 and 100 kHz
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Crystal structure and morphology
Fig.1 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of Li1.05Mn2O4 spinels doped with different amounts of sodium. All the four materials exhibit single-phase diffraction patterns, which can be indexed to the cubic spinel structure of Fd3m space group. In the pristine LiMn2O4 spinel, lithium and manganese occupy the tetrahedral (8a) and the octahedral sites (16d), respectively, and the oxygen ions are located at the (32e) sites. As the Na-doped manganese spinels are concerned, there are three possible sites for the sodium ions: 1) the tetrahedral (8a) sites; 2) the octahedral (16d) sites, which are fully occupied by manganese ions in LiMn2O4; and 3) the octahedral (16c) sites, which are unoccupied in the LiMn2O4 and are vital in the lithium diffusion process. In another study, HE[17] simulated the possible sites of sodium in the spinel by Carine crystallography program, carried out the Rietveld refinement on the XRD data of the Na-doped spinels by Fullprof program, and found that the sodium ions primarily occupied the tetrahedral (8a) sites and caused part of the lithium ions to move from the (8a) sites to the (16d) sites by partially replacing the manganese ions.
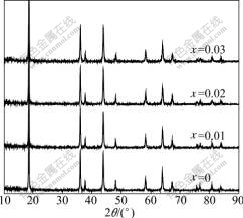
Fig.1 XRD patterns of Li1.05Mn2O4 spinels doped with different amounts of sodium
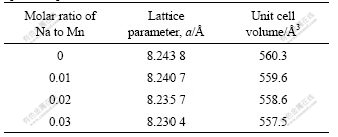
As shown in Fig.1, the intensity of the diffraction peaks becomes lower and broader after doping, indicating lower crystallinity and smaller crystal size. The lattice parameters and volume of the unit cell were calculated and the results are summarized in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the increasing sodium doping amount decreases the lattice parameters and the lattice volume. As discussed above, the sodium doping results in part of the lithium ions replacing manganese ions in the (16d) sites, which in turn causes twice amounts of Mn3+ ions oxidized to Mn4+ ions in order to keep electrical neutralization of the spinel compounds. Since the radium of the Mn4+ ion (0.53 ?) is much smaller than that of the Mn3+ ion (0.65 ?)[18], the volume of the spinel shrinks with increasing sodium dopant amount though the radium of sodium ion is larger than that of lithium ion and manganese ion. The shrinkage of the lattice crystal provides less lattice space for lithium intercalation and deintercalation, which will in turn affect the electro- chemical performances of the Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes.
Table 1 Lattice parameters and unit cell volume of Li1.05Mn2O4 spinels doped with different amounts of sodium
3.2 Charge-discharge characteristics
Fig.2 shows the initial discharge curves for the Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes doped with different amounts of sodium. All the four samples present two discharge shoulders around 4.1 and 3.95 V, which are the typical characteristic of manganese spinels. The discharge capacity decreases with increasing sodium dopant amount. The pristine Li1.05Mn2O4 delivers a large initial discharge capacity of 119.2 mA?h/g (80.5% of the theoretical value), while the Li1.05Mn2O4 cathode with a molar ratio (x=n(Na)/n(Mn)) of 0.03 shows a much smaller initial discharge capacity of 107.9 mA?h/g. As mentioned above, introduction of sodium ion into the manganese spinel crystal will accompany the oxidation of Mn3+ to Mn4+. However, the capacity of the manganese spinel depends on the Mn3+ that can be oxidized to Mn4+ during the deintercalation of lithium ions. In addition, the sodium ions at the (8a) sites in the crystal cannot deintercalate as lithium ions do, so the capacity of Li1.05Mn2O4 cathode decreases with increasing sodium dopant amount.
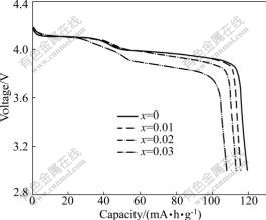
Fig.2 Initial discharge curves for Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes doped with different amounts of sodium at current density of 62.5 mA/g (0.5C)
Fig.3 shows cycling performances for the Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes doped with different amounts of sodium at 0.5C rate at room temperature and 55 ℃. Both the cycling stability at room temperature and that at 55 ℃ are improved with increasing sodium dopant amount. With the molar ratio of sodium to manganese increasing from 0 to 0.03, the capacity retention ratios for the Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes charged and discharged for 25 cycles at room temperature are 93.1%, 95.0%, 96.1% and 97.0%, respectively, while those at 55℃ are 82.7%, 83.6%, 89.2% and 91.0%, respectively. In the Na-doped Li1.05Mn2O4 spinels, the sodium ions in the lattice will act as a pillar to prevent the collapse of the crystal during the cycling. Furthermore, the improvement on strength of Mn—O band due to the increase of Mn4+ also facilitates stability of the spinel crystal.
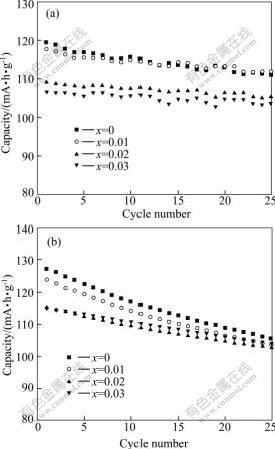
Fig.3 Cycling performances for Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes doped with different amounts of sodium at 0.5C rate at room temperature (a) and 55 ℃ (b)
The cells with different Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes were fully charged and then stored at 55 ℃ for 7 d to investigate the capacity loss during the storage. The discharge curves of the Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes before storage and those after storage are shown in Fig.4. As the molar ratio of sodium to manganese increases from 0 to 0.03, the discharge capacity before storage for the Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes decreases from 118.2 to 108.1 mA?h/g, while that after storage decreases from 86.4 to 44.6 mA?h/g, thus the self-discharge ratio increases from 26.9% to 58.7%, indicating the storage performance decreases dramatically with increasing sodium dopant amount. It may be due to the decrease in crystallinity and increase in mess degree of the cations arrangement resulted from the sodium substitution.
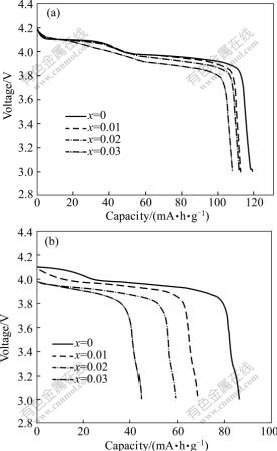
Fig.4 Discharge curves for Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes doped with different amounts of sodium at current density of 62.5 mA/g (0.5C): (a) Before storage; (b) After storage
Fig.5 shows discharge curves for the LiMn2O4 cathodes doped with different amounts of sodium at 0.2C and 2C current rate. With increasing the molar ratio of sodium to manganese from 0 to 0.03, the discharge capacity of Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes at 0.2C current rate decreases from 119.2 to 110.4 mA?h/g, while that at 2C current rate declines from 114.8 to 99.5 mA?h/g, so ratio of the discharge capacity at 2C rate to that at 0.2C rate decreases from 96.31% to 90.12% with increasing sodium dopant amount. Since some lithium ions are replaced by sodium ions at the (8a) sites, the deintercalation of lithium ions may be hampered by sodium ions, and the shrinkage of the lattice crystal provides less lattice space for lithium ions intercalation and deintercalation. So, the discharge capability at large current rate decreases with the increasing sodium dopant amount.
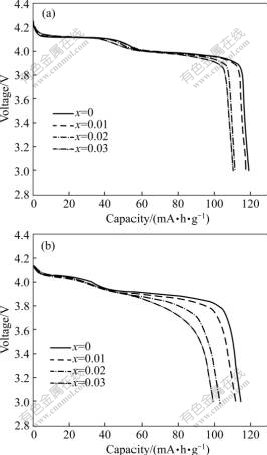
Fig.5 Discharge curves for Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes doped with different amounts of sodium at 0.2C (a) and 2C (b) current rate
3.3 Cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
Fig.6 shows the cyclic voltammograms of Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes doped with different amounts of sodium at a scan rate of 0.2 mV/s. The CV pattern shows two anodic peaks around 4.1 and 4.2 V as well as the corresponding cathodic peaks around 3.9 and 4.05 V. The two symmetrical couples of redox peaks are associated with the two voltage shoulders observed in the charge- discharge tests. CV curves of pristine Li1.05Mn2O4 have two redox peaks which are narrow and well separated. With increasing sodium dopant amount, both the anodic and cathodic peaks become low and broad. The anodic peaks shift toward high potential and the cathodic ones shift toward low potential. As a result, the difference between them increases, suggesting the reversibility of the cathodes decreases. The sodium dopant increases mess degree of the cations in the crystal and hampers the diffusion of lithium ion in the solid, thus the polarity of the cathode increases and the reversibility decreases, which will in turn decrease the performance of the spinel.
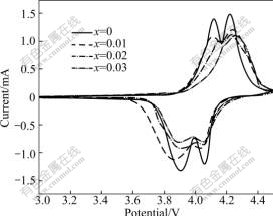
Fig.6 Cyclic voltammograms of Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes doped with different amounts of sodium at scan rate of 0.2 mV/s
AC impedance measurement was carried out after the cells had been charged and discharged at 0.2C current rate for a cycle, and the results are shown in Fig.7. The impedance plot consists of a depressed semicircle and an inclined line. The intercept at the Z′ axis in high frequency corresponds to the ohmic resistance (Re), which represents the resistance of the electrolyte. The semicircle in the middle frequency range indicates the charge transfer resistance (Rct). The inclined line in the low frequency represents the Warburg impedance (Zw) [19], which is associated with lithium ion diffusion in the cathode Li1.05Mn2O4 particles. In this work, the Re values are almost the same throughout the experiments due to the same electrolyte and fabrication parameters, and they are around 5 Ω and much smaller than the Rct values. The Rct values for Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes with the molar ratio (x=n(Na)/n(Mn)) of 0, 0.01, 0.02 and 0.03 can be evaluated to be about 80, 113, 124 and 152 Ω, respectively, indicating the Rct values increase obviously with increasing sodium dopant amount. It can be attributed to the shrinkage of lattice crystal which results in less lattice space for lithium ions intercalation and deintercalation as well as the hindrance of sodium ions in the spinel.
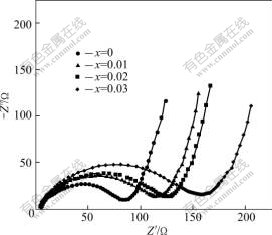
Fig.7 Nyquist impedance spectra of Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes doped with different amounts of sodium
4 Conclusions
1) Na doped Li1.05Mn2O4 spinels were synthesized using a sol-gel process. The sodium substitution does not change the basic spinel structure, but slightly affects the lattice parameters. All the materials exhibit the same cubic spinel phase structure without impurity. The lattice parameter and unit cell volume decrease with increasing sodium dopant amount.
2) The sodium substitution decreases the initial discharge capacity, discharge capability at large current rate and storage performance of the Li1.05Mn2O4 cathodes, while improves the cycling stability at room temperature and 55 ℃. As the molar ratio of sodium to manganese increases from 0 to 0.03, the initial discharge capacity decreases from 119.2 to 107.9 mA?h/g, the self-discharge ratio increases from 26.9% to 58.7%, the ratio of discharge capacity at 2C to that at 0.2C declines from 96.31% to 90.12%, and the capacity retention ratio after 25 cycles at 55 ℃ rises from 82.7% to 91.0%. The CV and EIS results indicate that the reversibility decreases and the electrochemical impedance increases with increasing sodium dopant amount.
References
[1] Arumugam D, Kalaignan G P, Manisankar P. Development of structural stability and the electrochemical performances of “La” substituted spinel LiMn2O4 cathode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries [J]. Solid State Ionics, 2008, 179: 580-586.
[2] GUO Hua-jun, XIANG Kai-xiong, CAO Xuan, LI Xin-hai, WANG Zhi-xing, LI Li-ming. Preparation and characteristics of Li2FeSiO4/C composite for cathode of lithium ion batteries [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(1): 166-169.
[3] Wang X, Yagi Y, Lee Y S, Yoshio M, Xia Y, Sakai T. Storage and cycling performance of stoichiometric spinel at elevated temperatures [J] J Power Sources, 2001, 97/98: 427-429.
[4] Lee C W, Kim H S, Moon S I. Effects on surface modification of spinel LiMn2O4 material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2005, 123: 234-237.
[5] Pasquier A, Blyr A, Cressent A, Lenain C, Amatucci G, Taraseon J M. An update on the high temperature ageing mechanism in LiMn2O4-based Li-ion cells [J]. J Power Sources, 1999, 81/82: 54-59.
[6] Aoshima T, Okahara K, Kiyohara, Shizuka K. Mechanisms of manganese spinels dissolution and capacity fade at high temperature [J]. J Power Sources, 2001, 97/98: 377-380.
[7] TAmatucci G G, Pereira N, Zheng T, Tarascon J M. Failure mechanism and improvement of the elevated temperature cycling of LiMn2O4 compounds through the use of the LiAlxMn2-xO4-zFz solid solution [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2001, 148: A171-A182.
[8] LI Xin-hai, HE Fang-yong, GUO Hua-jun, WANG Zhi-xing. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of LiMn2O4 doped with F- [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008,18(1): 54-58. (in Chinese)
[9] Fu L J, Liu H, Li C, Wu Y P, Rahm E, Holze R, Wu H Q. Surface modifications of electrode materials for lithium ion batteries [J]. Solid State Sciences, 2006, 8: 113-128.
[10] TPark S B, Shin H C, Lee W G, Cho W I, Jang H. Improvement of capacity fading resistance of LiMn2O4 by amphoteric oxides [J]. J Power Sources, 2008, 180: 597-601.
[11] Thirunakaran R, Kim K T, Kang Y M, Lee J Y. Cr3+ modified LiMn2O4 spinel intercalation cathodes through oxalic acid assisted sol-gel method for lithium rechargeable batteries [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2005, 40: 177-186.
[12] TYoshio M, Xia Y, Kumada N, Ma S. Storage and cycling performance of Cr-modified spinel at elevated temperatures [J]. J Power Sources, 2001, 101: 79-85.
[13] TLee Y S, Kumada N, Yoshio M T. Synthesis and characterization of lithium aluminum-doped spinel (LiAlxMn2-xO4) for lithium secondary battery [J]. J Power Sources, 2001, 96: 376-384.
[14] TSinghal R, Das S R, Tomar M S, Ovideo O, Nieto S, Katiyar R S. Synthesis and characterization of Nd doped LiMn2O4 cathode for Li-ion rechargeable batteries [J]. J Power Sources, 2007, 164: 857-861.
[15] THayashi N, Ikuta H, Wakihara M T. Cathode of LiMgyMn2-yO4 and LiMgyMn2-yO4-delta spinel phases [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1999, 146: 1351-1354.
[16] Takahashi M, Yoshida T, Ichikawa A, Kitoh K, Katsukawa H, Zhang Q, Yoshio M. Effect of oxygen deficiency reduction in Mg-doped Mn-spinel on its cell storage performance at high temperature [J] Electrochimica Acta, 2006, 51: 5508-5514.
[17] He Fang-yong. Study on preparation and performance of impure LiMn2O4 cathodes [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2007: 35-51. (in Chinese)
[18] Shannon R D. Crystal physics, diffraction, theoretical and general crystallography [J]. Acta Cryst, 1976, 32: 751-767.
[19]Gao F, Tang Z Y. Kinetic behavior of LiFePO4/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53: 5071-5075.
Foundation item: Project(2007CB613607) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China, Projects(2009FJ1002, 2009CK3062) supported by the Science and Technology Program of Hunan Province, China
Corresponding author: GUO Hua-jun; Tel: +86-731-88836633; E-mail: ghj.csu @163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60255-7
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)