以改性聚酯颗粒为碳源去除饮用水中高氯酸盐
何芳1,李富生2,周海红1,牛玲玲1
(1. 济南大学 资源与环境学院,山东 济南,250022;
2. 日本国立岐阜大学 流域圈科学研究中心,岐阜 501-1193,日本)
摘要:以改性淀粉基聚酯(S-PBS)颗粒为固体碳源和生物膜载体,研究其去除饮用水中高氯酸盐的特性。研究结果表明:S-PBS颗粒仅在微生物作用下分解并为高氯酸盐降解菌(PRB)提供碳源,9 h内可将进水中2 mg/L的ClO4-降低到检测限以下。存在于该生物反应器中的ClO4-和NO3-可同步去除,高质量浓度硝酸盐的存在会影响高氯酸盐的降解速率。水温对高氯酸盐的生物降解有较大影响。生物膜发育后聚合物在2 849,2 923及3180~3 430 cm-1处峰值减弱,说明材料中的甲基和羟基官能团呈比例下降,颗粒单体组分可以持续被PRB用作碳源。微生物附着生长后,S-PBS颗粒表面会形成孔洞结构,进一步扩大微生物的附着面积,有利于形成更加稳定致密的生物膜,对PRB形成保护作用。
关键词:高氯酸盐;降解;固体碳;生物反应器
中图分类号:X171 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)12-4452-06
Removal of perchlorate from drinking water using modified polyester particles as carbon source
HE Fang1, LI Fusheng2, ZHOU Haihong1, NIU Lingling1
(1. School of Resources and Environment, University of Jinan, Jinan 250022, China;
2. River Basin Research Center, Gifu University, Gifu 501-1193, Japan)
Abstract: Modified starch-based polyester particles were used as solid carbon source and biofilm carrier to remove perchlorate from drinking water. The results show that S-PBS can be only decomposed in the present of the microbes in bioreactor and provide carbon source for PRB. Influent perchlorate (2 mg/L) can be reduced to below the detection limit. Simultaneous perchlorate and nitrate degradation occurs when perchlorate and nitrate concentrations correspond to a typical perchlorate-contminated site. Effluent concentrations of perchlorate vary positively with temperature. With the development of biofilm, absorption bands at 2 923, 2 849, 3 180-3 430 cm-1 are weak, which suggests that the content of methyl or hydroxyl group in particles decreases slightly. The monomer of S-PBS can be utilized as carbon source by perchlorate reducing bacteria (PRB). The cavity can be formed on the particle surface, which increases the area for microbes to be attached. The formation of the cavity structure on the S-PBS surface is beneficial to further development of biofilm, which can protect PRB within the biofilm.
Key words: perchlorate; degradation; solid carbon; bioreactor
高氯酸盐(ClO4-)是环境污染物之一,过高浓度的高氯酸盐会影响正常的甲状腺机能,扰乱体内正常的荷尔蒙分泌平衡。高氯酸盐易溶于水,并在环境中迁移,由于其性质稳定,不易分解,可在环境中存在数十年,这使得高氯酸盐污染具有广泛性和持久性,且处理难度极大[1]。我国存在大量以高氯酸盐为直接产品的化工厂,ClO4-污染不容忽视。国内饮用水中的监测也显示,部分水厂的源水和出厂水中高氯酸盐含量较高[2-3]。但我国相关研究仍处于起步阶段。在各种高氯酸盐去除方法中[4-5],微生物还原高氯酸盐法因成本低、效率高而在实际工程处理中有广阔的应用前景。但饮用水中有机物供体不足,目前生物降解高氯酸盐常用的有机碳源包括醋酸盐、乳酸盐、乙醇等,但这些外部投加的有机电子供体易存在投加不足或过量的风险,需要复杂的工艺控制系统,尤其在进水高氯酸盐有波动情况下,有机电子供体投放的调控更加困难,影响出水水质。1992年,Muller等采用可生物降解聚合物(BDPs)作为固体碳源去除饮用水中的硝酸盐,并取得良好效果[6]。Chu等[7-8]采用聚己内酸酯等人工合成的BDPs材料进行饮用水源水反硝化的研究并取得成功。BDPs不溶于水,仅在微生物代谢作用下才得以分解,解决了碳源投加过程中的不足或者过量的问题;且可同时作为微生物的碳源和生物膜载体。研究证实,反硝化细菌可以像高氯酸盐还原酶一样利用异养硝酸盐还原酶降解高氯酸盐,绝大多数的高氯酸盐降解菌也能降解硝酸盐[9-10]。因此反硝化技术中的BDPs材料很有可能成为一种非常有潜力的生物降解高氯酸盐的电子供体,但相关研究尚未见报道。本研究将2种具有不同生物降解性能的聚合物(淀粉和聚丁二酸丁二醇酯)进行共混、挤出技术处理,将获得的共混聚合物颗粒作为碳源和生物膜载体进行高氯酸盐去除试验研究,并探讨其生物降解机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
实验室自制淀粉基可生物降解颗粒为将易于生物降解的淀粉和相对难以生物降解的聚丁二酸丁二醇酯进行共混、挤出技术处理所得;得到的改性聚酯颗粒中单体间不是简单的共混,而是经过处理和反应后的最终相溶产品,产品不溶于水,长时间浸泡在水中不会失去其机械强度。随着易降解淀粉在反应器内微生物作用下进行降解,载体颗粒表面会相应产生微孔或丝状结构,这有利于微生物在载体表面附着、生长并发育成生物膜,从而有利于高氯酸盐的去除。表1所示为该自制可生物降解共聚物颗粒物(称作S-PBS颗粒)的主要性能参数。
表1 S-PBS聚酯颗粒的主要性能参数
Table 1 Main characteristics of S-PBS polymer particles
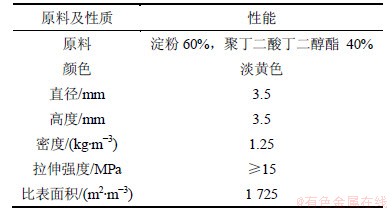
高氯酸钠(NaClO4·H2O)为纯度(质量分数)>99.0%;试验配水的制备方法为在地下水中加入高氯酸钠,使ClO4-的质量浓度保持在2 mg/L。
试验中所用的污泥取自济南市某污水处理厂曝气池,采泥点位于曝气池出口处,可避免存在于污水处理厂进水且易于被活性污泥降解的有机物存在。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 实验装置
反应器为250 mL锥形瓶,瓶口用橡胶塞密封,橡胶塞上有排气管通过乳胶管导入水中,在排出厌氧、去除高氯酸盐作用产生氧气的同时,保持反应器内缺氧环境。
1.2.2 高氯酸盐降解菌的驯化与生物膜培养
在250 mL 的锥形瓶中加入30 g S-PBS颗粒(干质量)和100 mL配水,然后加入活性污泥,污泥质量浓度控制在800 mg/L左右,放入恒温振荡培养箱,对高氯酸盐降解菌进行驯化。每天测定ClO4-质量浓度,当ClO4-质量浓度低于检测限时,补加高氯酸盐。当配水中2 mg/L的高氯酸盐在1 d内完全去除时,换水以排除未附着在聚酯颗粒上的微生物及污泥杂质,只保留生长有生物膜的S-PBS颗粒。当ClO4-质量浓度低于检测限时换水。反复驯化,继续培养高氯酸盐降解菌生物膜,培养20 d左右,高氯酸盐去除效果稳定,挂膜结束。实验温度为25 ℃,振荡速度为80 r/min,通过氮气吹脱控制溶液中的溶解氧(DO),进水DO质量浓度控制在2.0 mg/L以下。
1.2.3 生物降解试验
将挂膜成熟的S-PBS颗粒30 g用配水配制成一定浓度的水样100 mL,放入250 mL锥形瓶中,再放入振荡式培养器内。为了使反应在完全厌氧的条件下进行,在试验开始时先用振荡培养器搅拌同时通入湿润氮气30 min后,再加入ClO4-(初始质量浓度为2 mg/L)开始试验,定时取样分析。
1.3 测试分析方法
1.3.1 水样
对于不同时间从反应器中取出的水样(约6 mL),经3 000 r/min离心分离3 min后,取上清液用孔径为0.45 μm醋酸纤维滤膜过滤。滤液经C18小柱进一步萃取去除残余有机物后通过0.2 μm微孔膜过滤,以备离子色谱分析所用。
ClO4-测定方法:仪器采用离子色谱仪(Dionex, ICS1000),AG20+AS20(4×250 mm)柱,300 μL大体积定量环进样,淋洗液KOH浓度为35 mmol/L,抑制电流为100 mA。分析软件采用Dionex Chromeleon 6160 chromatography workstation。
Cl-,NO2-和NO3-的测定条件为AG23 + AS23(4×250 mm)柱,10 μL定量环进样,淋洗液为4.5 mmol/L Na2CO3和0.8 mmol/L NaHCO3。
1.3.2 S-PBS颗粒和生物膜形貌
从反应器中取生长有生物膜的S-PBS颗粒,用蒸馏水轻微冲洗,放入密闭试管,用蒸馏水淹没后,超声波剥离生物膜,然后用蒸馏水冲洗干净,在50 ℃下烘干10 min。将S-PBS原材料、脱膜后的S-PBS颗粒分别制作切片,在扫描电镜下观察其表面形态。用刀片切取S-PBS原材料、脱膜后S-PBS颗粒的表面薄层,采用薄膜法进行红外光谱分析。所用仪器为扫描电镜JSM-6460LV和傅里叶变换红外光谱仪NICOLET560。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 以改性聚酯颗粒为固体碳源去除ClO4-特征
分别在S-PBS改性聚酯颗粒挂膜过程中和挂膜成熟后,对受污染饮用水源水进行高氯酸盐去除试验研究,结果见图1。
试验配水溶液的溶解氧(DOC)质量浓度约为2.1 mg/L,加入S-PBS颗粒和活性污泥进行驯化挂膜时,溶液中DOC上升至7 mg/L左右;当颗粒表面形成稳定的生物膜后,溶液中的DOC质量浓度稳定在4.5~5.8 mg/L。驯化挂膜阶段ClO4-的去除情况见图1(a),可见活性污泥中的高氯酸盐降解菌易于附着在聚酯颗粒表面。在微生物作用下S-PBS颗粒分解出溶解性的小分子有机物,进入反应溶液后被高氯酸盐降解菌用作碳源去除ClO4-。在7 h内,进水2 mg/L的高氯酸盐降低至检测限以下。在没有投加聚酯颗粒的对照组反应溶液中,进水中的ClO4-几乎没有减少,溶液中DOC质量浓度为2~4 mg/L,变化不大,期间可能会有微生物个体发生自溶现象,造成该反应器溶液中的DOC稍有提高。说明驯化挂膜期间正是由于S-PBS颗粒在微生物作用下分解出小分子有机物,为高氯酸盐降解菌提供碳源。当S-PBS颗粒表面的生物膜发育成熟后,聚合物表面分解的小分子有机物被生物膜内高氯酸盐降解菌利用,致密的生物膜阻碍了S-PBS分解形成的部分小分子有机物进入溶液,因此,颗粒表面形成稳定的生物膜后,溶液中的DOC质量浓度有所降低但较稳定;高氯酸盐降解仅在生物膜内部进行,去除速率比挂膜期间低。S-PBS颗粒表面的高氯酸盐降解菌生物膜可以在9 h内将进水中2 mg/L的ClO4-降低到检测限以下。
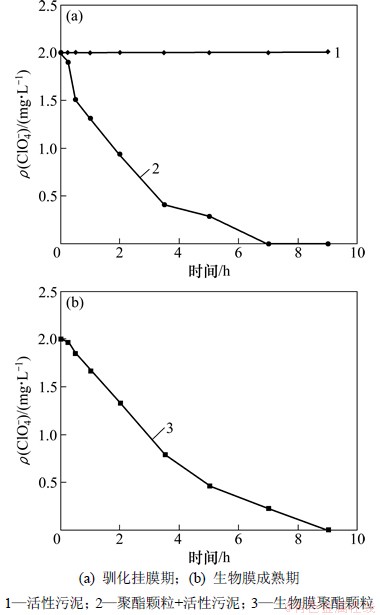
图1 改性聚酯颗粒作为碳源去除高氯酸盐特征
Fig. 1 Perchlorate removal characteristics using modified polyester particles
2.2 共存NO3-的影响
研究发现实际环境中94%受高氯酸盐污染的水体中均存在硝酸盐共污染问题[11-13]。而共存的硝酸盐是否抑制高氯酸盐的生物降解,一直没有得到合理解释。本实验研究了NO3-共存情况下高氯酸盐的降解效果,结果如图2所示。
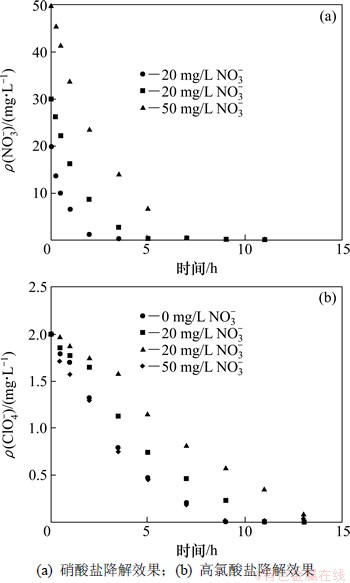
图2 共存NO3-对高氯酸盐降解影响
Fig. 2 Effect of coexistence of NO3- on perchlorate removal
由图2可见:在NO3-质量浓度为20 mg/L时,高氯酸盐的去除速率与不存在NO3-干扰情况下几乎相同。说明在S-PBS颗粒生物反应器溶液中,当ClO4-和NO3-质量浓度水平与典型受污染水源水环境中质量浓度相当时,ClO4-和NO3-可同步去除。当NO3-浓度上升至30和50 mg/L时,出水中ClO4-质量浓度分别提高至233和571 μg/L。说明尽管影响不是非常显著,但提高进水中NO3-质量浓度的确能影响高氯酸盐的降解。说明当环境中碳源充足时,ClO4-和NO3-可同步从S-PBS反应器水溶液中去除,该结论与Tan等报道吻合[14]。同时,在该ClO4-和NO3-共存的生物反应器中,完全的反硝化过程可以快速地进行,且反应过程中没有检测到NO2-的积累。
2.3 温度的影响
微生物细胞的生长和还原降解反应是在各种酶的催化下进行的,温度是保证细胞中酶活性的重要条件之一。保持其他条件不变,考察了温度分别为13,20和30 ℃时聚酯颗粒生物反应器中高氯酸盐降解速率的变化,结果如图3所示。
由图3可见:温度越低,反应液中残留的高氯酸盐质量浓度越高。在水温分别为13,20和30 ℃时,进水中2 mg/L的ClO4-在S-PBS颗粒反应器中反应5 h后,出水中质量浓度依次降低至1.1,0.7 和0.2 mg/L,即反应温度为13℃时,出水中残留高氯酸盐质量浓度分别是水温为20和30 ℃时的1.6和5.5倍。反应6 h后,在水温为30℃的反应器中,ClO4-质量浓度低至检测限以下。
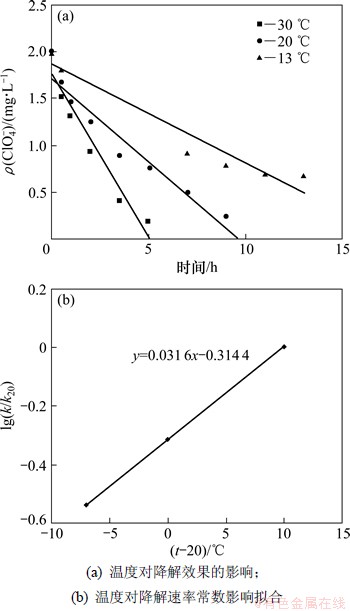
图3 温度对高氯酸盐降解的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of temperature on perchlorate removal
温度对生物降解高氯酸盐的影响可以用Arrhenius方程或其修改式(1)来描述:
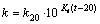 (1)
(1)
式中:k为t温度下的高氯酸盐降解速率;k20为20 ℃时的高氯酸盐降解速率;Kt为温度常数。对式(1)进行变形得到:
 (2)
(2)
利用式(2)对S-PBS颗粒反应器中不同温度下高氯酸盐降解速率常数进行拟合,结果见图3,可以用Arrenius公式修改式来描述:
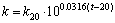 (3)
(3)
得到Kt=0.031 6,表明环境水温对S-PBS颗粒反应器系统高氯酸盐的生物降解有较大影响。
2.4 S-PBS颗粒IR谱图特征
改性聚酯S-PBS颗粒原材料以及培养约3月,脱去表面生物膜的颗粒红外光谱图见图4。
从图4可见:1 700 cm-1处的峰为羰基吸收峰,2 923 cm-1和2 849 cm-1附近的2个尖锐吸收带可归因为CH3,CH2,CH基团的贡献,反映了C—H的面内对称和反对称伸缩振动,表明甲基为S-PBS的优势官能团之一,这些基团处在脂链或者饱和脂环中[15]。经过生物膜生长后,2 849 cm-1和2 923 cm-1处吸收峰出现较大比例下降,说明在高氯酸盐降解菌去除ClO4-过程中,聚合物所含甲基中的碳被用作碳源,并消耗利用。
波数3 180~3 430 cm -1处存在的宽峰表明在聚合物中存在不同形式的羟基,羟基谱带的位置由3 180 cm-1移至3 430 cm-1,表明羟基是以多聚的缔合结构形式存在,而经过生物膜生长后,介于3 180~3 430 cm-1波数内吸收峰下降,结合波数402和 1 109 cm-1附近吸收峰下降,表明羟基官能团在S-PBS中的数量下降。应该是单体淀粉被高氯酸盐降解菌用做碳源的结果。在其他波数范围内,生物膜生长前后,聚合物材料的吸收峰变化甚微。
2.5 S-PBS颗粒表面形貌和生物膜变化特征
图5(a)所示为S-PBS颗粒表面生物膜结构,可以看出:高氯酸盐降解菌能够在颗粒表面附着并发育成致密的生物膜,以球菌和杆菌为主,生物密度非常大。
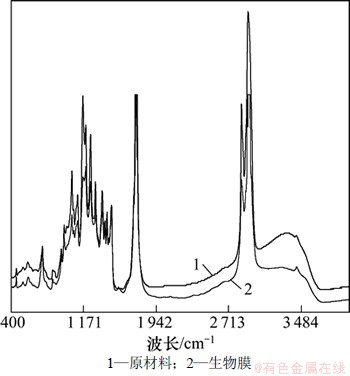
图4 改性聚酯颗粒原材料与发育生物膜后的红外光谱图
Fig. 4 Infrared spectra of raw material and developed material with biofilm of polyester particles
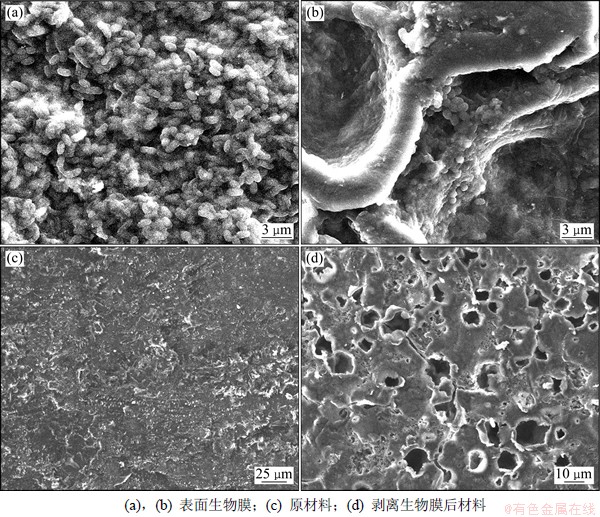
图5 聚酯颗粒表面生物膜及原材料和剥离生物膜后材料表面形貌
Fig. 5 Biofilm morphologies of polymer surface, raw material and used polymer material after cultivation
利用扫描电镜观察了S-PBS颗粒原材料(图5(c))和剥离生物膜后的颗粒表面形貌(图5(d))。原材料表面相对较光滑,基本没有孔隙,而经过生物膜生长后,其表面出现密集的孔洞,表明颗粒表面的易生物降解部分被生物膜里面的微生物分解充当碳源。在驯化挂膜过程中,溶液中DOC质量浓度始终维持在很低值,表明S-PBS颗粒难溶于水,只有在微生物体内酶作用下分解并为高氯酸盐还原菌提供碳源的结论相吻合。
挂膜期间在颗粒表面高氯酸盐降解菌密集附着的位点,聚合物被微生物迅速利用后会形成部分孔隙,而这些孔隙的存在会增大微生物的附着面积,使得高氯酸盐降解菌更加容易附着生长,致使聚合物的消耗速率提高,最终导致这些孔隙不断扩大,形成孔洞结构(图5(b))。孔洞利于形成更加致密、发育良好的生物膜,对其内部的高氯酸盐还原菌形成很好的保护作用,保证聚合物颗粒在不利环境条件下顺利去除水中高氯酸根。
3 结论
1) 改性聚酯S-PBS颗粒仅在微生物作用下分解,可以同时作为生物膜载体和高氯酸盐降解菌碳源去除水中的ClO4-,在9 h内可将进水中2 mg/L的ClO4-质量浓度降低到检测限以下。
2) 当环境中碳源充足、ClO4-和NO3-质量浓度与典型受污染水源水环境中质量浓度相当时,存在于S-PBS颗粒生物反应器中的ClO4-和NO3-可同步去除。水温对该反应器中高氯酸盐的生物降解有较大影响,可用Arrenius修改式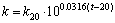 描述。
描述。
3) 聚酯颗粒中单体淀粉和聚丁二酸丁二醇酯均可被高氯酸盐降解菌当作碳源。随着高氯酸盐降解反应的进行,颗粒表面会形成大量孔洞结构,进一步扩大微生物的附着面积,有利于微生物在其表面形成更加稳定致密的生物膜。
参考文献:
[1] Blount B C, Rich D Q, Valentin-Blasini L, et al. Perinatal exposure to perchlorate, thiocyanate, and nitrate in New Jersey mothers and newborns[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2009, 43: 7543-7549.
[2] 张萍, 史亚利, 蔡亚岐, 等. 改进的离子色谱法测定环境水样中的高氯酸盐[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(7): 1246-1250.
ZHANG Ping, SHI Yali, CAI Yaqi, et al. An improved ion chromatography method for determination of trace level perchlorate in environmental water[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(7): 1246-1250.
[3] 刘勇建, 牟世芬, 林爱武, 等. 北京市饮用水中溴酸盐、卤代乙酸及高氯酸盐的研究[J]. 环境科学, 2004, 25(2): 51-55.
LIU Yongjian, MU Shifen, LIN Aiwu, et al. Investigation of bromate, haloacetic acids and perchlorate in beijing’s drinking water[J]. Environmental Science, 2004, 25(2): 51-55.
[4] Srinivasan R, Sorial G A. Treatment of perchlorate in drinking water: A critical review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2009, 69: 7-21.
[5] Ghosh A, Pakshirajan K, Ghosh P K, et al. Perchlorate degradation using an indigenous microbial consortium predominantly Burkholderia sp.[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 187(1/3): 133-139.
[6] Muller W R, Heinemann A, Schafer C, et al. Aspects of PHA (poly-e-hydroxy-butyric-acid) as an H-donor for denitrification in water treatment processes[J]. Water Supply, 1992, 10: 79-90.
[7] Chu L B, Wang J L. Comparison of polyurethane foam and biodegradable polymer as carriers in moving bed biofilm reactor for treating wastewater with a low C/N ratio[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 83: 63-68.
[8] Zhou H H,Zhao X,Wang J L. Nitrate removal from groundwater using biodegradable polymers as carbon source and biofilm support[J]. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 2009, 38(3): 339-348.
[9] Li X, Upadhyaya G, Yuen W, et al. Changes in the structure and function of microbial communities in drinking water treatment bioreactors upon addition of phosphorus[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(22): 7473-7481.
[10] Nerenberg R, Rittmann B E. Hydrogen-based, hollow-fiber membrane biofilm reactor for reduction of perchlorate and other oxidized contaminants[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2004, 49(11/12): 223-230.
[11] Mamie N I, Scow K M, Rolston D E. Reduction of perchlorate and nitrate by microbial communities in vadose soil[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(7): 3928-3934.
[12] Nozawa-Inoue M, Scow K M, Rolston D E. Reduction of perchlorate and nitrate by microbial communities in Vadose soil[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(7): 3928-3934.
[13] 彭银仙, 吴春笃, 宁德刚, 等. 氯酸盐去除方法研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2009, 32(2): 87-90.
PENG Yinxian, WU Chundu, NING Degang, et al. Development of perchlorate removal method[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 32(2): 87-90.
[14] Tan K, Anaerson T A, Jackson W A. Degradation kinetics of perchlorate of perchlorate in sediments and soils[J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 2004, 151(1/4): 245-259.
[15] 冯杰, 李文英, 谢克昌. 傅里叶红外光谱法对煤结构的研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2002, 31(5): 362-366.
FENG Jie, LI Wenying, XIE Kechang. Research on coal structure using FT-IR[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2002, 31(5): 362-366.
(编辑 何运斌)
收稿日期:2013-12-10;修回日期:2014-04-23
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(21107031);济南市科技发展计划项目(201202261)(Project (21107031) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (201202261) supported by the Project of Jinan Science and Technology Board)
通信作者:何芳(1975-),女,山东济南人,博士,副教授,从事饮用水源水微污染防治研究;电话:0531-82769233;E-mail:chm_hef@ujn.edu.cn