DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.04.16
Co基合金在熔融NaCl-52%MgCl2中的腐蚀机理
周红霞1, 2,孟小焕2,王军伟1, 2
(1. 青海大学 青海省高性能轻金属合金及深加工国家地方联合工程研究中心,西宁 810016;
2. 青海大学 青海省新型轻合金重点实验室,西宁 810016)
摘 要:通过纯Co及代表性的Co基合金GH5188和GH6159在520 ℃熔融NaCl-52%MgCl2(摩尔分数)中的腐蚀行为研究,揭示Co基合金在熔融氯化盐中的腐蚀机理。结果表明:3种试样的腐蚀动力学曲线近似满足线性规律。腐蚀20 h后的扫描电镜分析表明,纯Co试样表面形成了壳层结构;EDS及XRD分析表明,壳层成分主要为MgO,这在一定程度上起到了减缓腐蚀的作用。GH6159表面也出现类似壳层结构,GH5188表面有孔洞出现;腐蚀160 h后,GH5188表面出现大量互相连通的腐蚀孔洞。横截面EDS分析表明,Co和Cr的含量均明显降低。因此,Co基合金的腐蚀机理主要源于合金元素Cr 、Fe和Co等的氧化、溶解和挥发。
关键词:熔融盐;腐蚀;Co基合金;NaCl-52%MgCl2
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-04-0774-08 中图分类号:TG172 文献标志码:A
在太阳能光热利用中,为了应对太阳能的间断性,储能技术应运而生[1-2]。其中,无机盐储能作为一种有效储能方式,受到广泛关注。无机盐高温相变储热装置能够延长太阳能热发电装置的工作稳定性[3-4]。当阳光辐射充足时,封装在储热腔内的无机盐熔化,将富裕热量储存;阳光辐射不足时,熔化的无机盐凝固,释放结晶潜热,为设备补充热量[5]。与硝酸盐、碳酸盐等含氧酸盐相比,氯化盐熔点更高、性能更稳定,尤其是NaCl-52%MgCl2的混合氯化盐(熔点520 ℃,单位质量潜热值最高达430 J/g)作为中高温相变储热介质具有很好的发展潜力[6]。然而,熔盐中含有的氯离子高温下具有较强的腐蚀性,其对于蓄热装置的腐蚀不可忽视[7-8]。
高温合金是以Fe、Co、Ni为基体的一类高温结构材料,通常可以在较高温度环境下工作,且具有表面稳定性,能够承受较复杂的应力[9]。Co基高温合金的高温强度、抗热腐蚀性能、热疲劳性能和抗蠕变性能均较好[10-11],但其在高温熔融氯化盐中的腐蚀数据缺乏,腐蚀机理尚不明确。因此,本实验中采用两种代表性的高温Co基合金,通过研究其在520 ℃熔融NaCl-52%MgCl2中的腐蚀行为,探讨其腐蚀机理。
1 实验
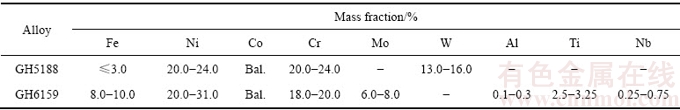
在高纯氩气保护下,用中频感应熔炼炉制备纯Co及两种合金,合金成分如表1所列。用电火花线切割机将试样切割成10 mm×10 mm×5 mm的小块,采用1200 ℃保温1 h、900 ℃保温8 h、空冷热处理后,依次在600号、1200号、2000号金相砂纸打磨并抛光,最后在蒸馏水和酒精中超声清洗。
为了尽量减少熔盐中氧的含量,配盐时进行如下操作:将NaCl在150 ℃下烘干5 h,然后按照12:13摩尔比称量NaCl和MgCl2,混合均匀后装入刚玉坩埚,并放入马弗炉中加热至520 ℃,待混合盐熔化后,将纯Co和两种合金的4块平行试样浸入混合熔融盐中,开始腐蚀实验。腐蚀20 h后,取出坩埚,试样在熔融盐保护下冷却至室温。将其中一个试样采用水浸处理方法去除表面残盐,采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,JSM-6610LV)观察其表面形貌。其余试样分别在蒸馏水和酒精中超声清洗15 min,冷风干燥后,用精度为0.1 mg电子天平称量并记录数据。以上操作循环8次,依据前7次实验数据绘制腐蚀动力学曲线和平均质量损失图。最后一次腐蚀结束后,保留试样表面残盐,作如下处理:第一个试样同腐蚀20 h的试样处理方式一样,水浸去除残盐观察表面形貌;第二个试样采用干抛法(不添加水溶性抛光剂)磨出试样横截面,用SEM观察试样横截面形貌特征,用扫描电镜附带的能谱(EDS)分析腐蚀层附近元素分布;第三个试样用X射线衍射仪(XRD,Rigaku D/max-2500/PC,Cu Kα,λ=0.1541 nm)分析腐蚀层不同深度上的物相成分。
表1 Co基合金试样的名义化学成分
Table 1 Nominal chemical composition of Co-based alloys
2 结果与分析
2.1 腐蚀动力学曲线
3种试样在20 h内的平均质量损失如图1所示,GH5188的平均质量损失量最大为6.7 μg/mm2 ,而纯Co的平均质量损失量最小为0.2 μg/mm2。3种试样腐蚀动力学曲线如图2所示,近似满足线性规律。其中,纯Co的腐蚀速率最小,GH5188的腐蚀速率最大,与平均质量损失结果一致。
2.2 腐蚀微观形貌
图3所示为纯Co、GH5188和GH6159腐蚀20 h 后的表面形貌及局部EDS分析结果。从图3(a)可以看出,纯Co试样表面存在出现壳层结构,EDS分析表明底层为Co基体,表层为损坏的富Mg的壳层,GH6159(见图3(c))表面亦出现类似现象。GH5188(见图3(b))试样腐蚀20 h后表面变疏松,EDS表明表面主要元素为合金基体成分Co、Fe、Ni等。图4所示为3种试样腐蚀160 h后的表面形貌。由图4可以看出,3种试样表面均比较松散,其中GH5188表面腐蚀比较严重,呈现镂空状结构,出现大量孔洞。
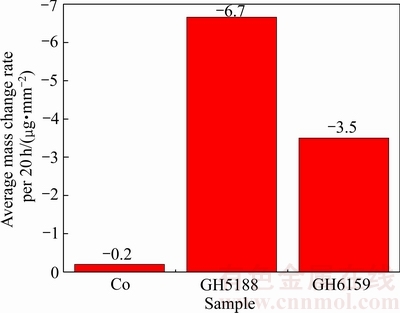
图1 3种试样的平均质量损失
Fig. 1 Average mass loss rate of three samples
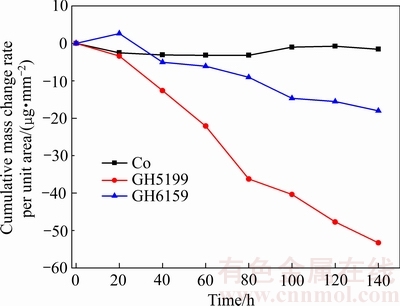
图2 3种试样的腐蚀动力学曲线
Fig. 2 Corrosion kinetics curves of three samples
图5所示为纯Co、GH5188和GH6159腐蚀20 h和160 h后的表面XRD分析结果。由图5可以看出,纯Co腐蚀20 h和160 h后,试样表面均以MgO和(Mg,Co)O为主。其他两种试样腐蚀20 h和160 h后,试样表面均以Co为主。
图6所示为3种试样腐蚀160 h后横截面SEM像及对应的EDS分析结果。纯Co试样没有形成明显的腐蚀层;GH5188在横截面附近约5μm处出现大量腐蚀孔洞,附近Co和Cr的含量均明显降低,Ni含量相对升高。GH6159也没有形成明显的腐蚀层,表层Cr、Co和Ni含量均出现下降。
2.3 腐蚀残盐及不同深度的腐蚀产物分析
图7所示为3种试样腐蚀20 h后残盐的XRD谱。残盐中主要存在NaCl、Na2MgCl4、NaMgCl3、MgO、MgCl2-(H2O)6等物质,并没有发现Ni、Fe、Cr和Co等金属化合物。图8所示为3种试样腐蚀160 h后不同腐蚀深度上的XRD谱。从图8可以看出,3种试样表现出相似的结果,即最表层(第一层)上残存大量腐蚀残盐:NaMgCl3、Na2MgCl4、NaCl及MgO,有些试样表面也存在一定量的MgCl2-(H2O)6;第二层和第三层上残盐成分减少,试样基体Co成分增大,但纯Co试样在第二层中MgO含量仍然较高,这与腐蚀20 h及160 h后表面的EDS分析结果一致。
3 讨论
3.1 Co基合金的腐蚀机理
由于熔融NaCl-MgCl2是强电解质,3种试样的腐蚀将按照电化学-化学联合腐蚀机制进行。合金中含量较多的元素Cr、Fe、Co、Ni在电解质作用下,容易失去电子变成相应的金属离子。且4种元素电负性排序从小到大的顺序依次为Cr、Fe、Co、Ni,由于GH5188和GH6159中Ni元素含量差别不大,因此,Cr、Fe、Co元素含量的差异造成了这两种合金腐蚀程度的差异。Cr和Fe在熔融氯化盐中的腐蚀过程可描述为:在熔融盐的电解作用下,Cr、Fe和Co首先被电解成Cr3+、Fe2+和Co2+,并被溶解于熔融盐中的O2氧化,形成Cr2O3、Fe2O3和CoO。图9所示为几种常见金属氧化物在熔融NaCl-KCl中的溶解度[12-13]。由图9可见,这3种氧化物在熔融氯化盐中的溶解程度均较大,因此,生成的氧化物溶于熔盐中,并与熔盐中的Cl-反应生成极易挥发的金属氯化物,逃逸系统[14],残盐的XRD中没有出现这3种金属也证明了这一点。其腐蚀机理见图10所示,相关的化学反应方程式如下(M代表金属Cr、Fe、Co、Ni,n代表失电子数目):
M-ne→Mn+ (1)
2Mn++nO2→2nMO (2)
MO+Cl-→MCl (3)

图3 纯Co、GH5188和GH6159腐蚀20 h后表面形貌及局部EDS分析结果
Fig. 3 Morphologies and EDS analysis results of pure Co, GH5188 and GH6159 alloys after being corroded for 20 h
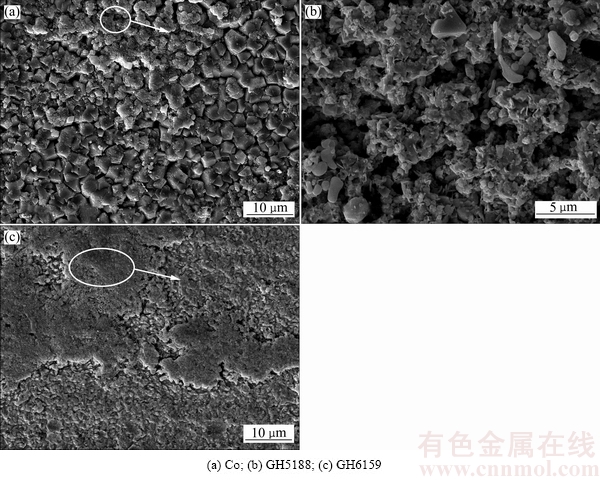
图4 纯Co、GH5188和GH9159腐蚀160 h后表面形貌
Fig. 4 Surface morphologies of alloys after being corroded for 160 h
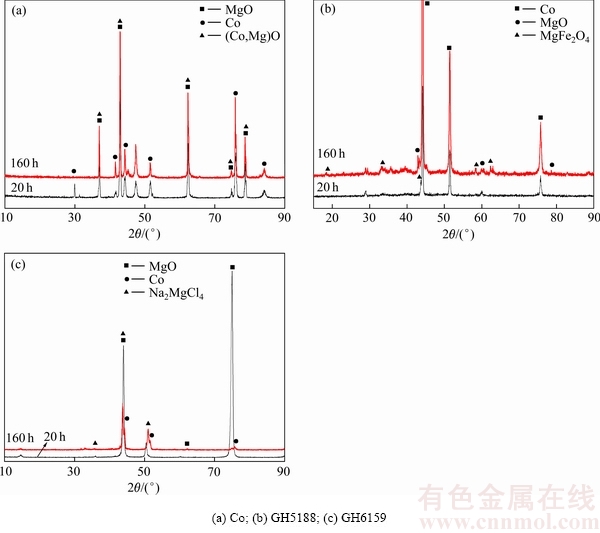
图5 纯Co、GH5188和GH9159腐蚀20h和160 h后的表面XRD谱
Fig. 5 XRD patterns of pure Co, GH5188 and GH9159 alloys after being corroded for 20 h and 160h
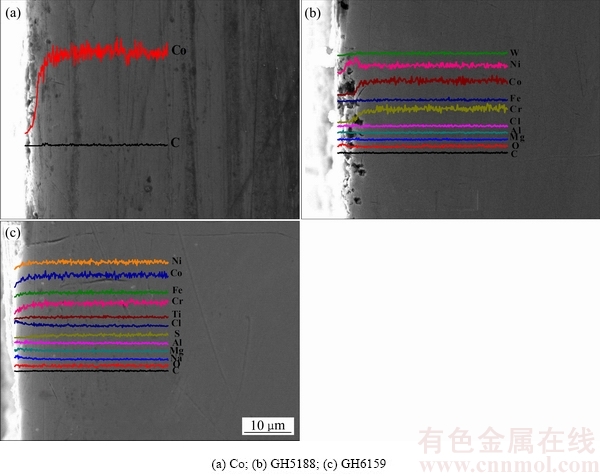
图6 纯Co、GH5188和GH9159腐蚀160 h干抛试样横截面SEM像及对应的EDS线扫描结果
Fig. 6 Cross section morphologies of pure Co, GH5188 and GH9159 alloys and EDS analysis results near corrosion layer after being corroded for 160 h

图7 纯Co、GH5188和GH9159腐蚀20 h后腐蚀残盐的XRD谱
Fig. 7 XRD patterns of residual salt after pure Co, GH5188 and GH9159 alloys being corroded for 20 h
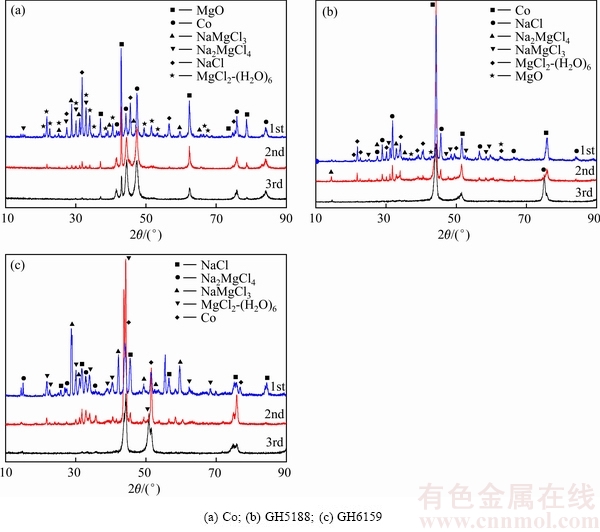
图8 纯Co、GH5188和GH9159腐蚀160 h后腐蚀层不同深度处的XRD谱
Fig. 8 XRD patterns of pure Co, GH5188 and GH9159 alloys after being corroded for 160 h at various depths
从组成来看,由于GH5188中Cr含量最高,因此,腐蚀最严重。虽然GH6159的Fe含量比GH5188中的高,但Cr含量比GH5188中的低,因此,腐蚀速率较后者的低。且另一方面,耐蚀合金元素Mo、Al、Ti、Nb的添加在一定程度上也起到了减缓腐蚀速率的作用,但其作用机理有待进一步研究。从图6中腐蚀160 h后的横截面形貌也可以看出,GH6159没有形成明显的腐蚀层,腐蚀后形成的孔隙也比较少。
3.2 纯Co表面壳层结构的形成分析
由于纯Co试样不含易腐蚀的Cr、Fe等元素,因此在3种试样中,腐蚀程度最小。关于纯Co试样腐蚀20 h后表面MgO壳层的生成,如3.1节分析,推测是由于被电解的Co失去的电子被熔盐中的Mg2+捕获,形成Mg原子,由于520 ℃下O2与Mg反应生成MgO的吉布斯自由能(约为-1032.384 kJ/mol)比O2与Co反应生成CoO的吉布斯自由能(约为-355.926 kJ/mol)小很多,因此,Mg原子还原CoO形成MgO和Co,它们在试样表面形核并长大。可能的化学反应方程式如下:
Co–2e→Co2+ (4)
Co2++O2→CoO (5)
Mg2++2e→Mg (6)
CoO+Mg→Co+MgO (7)
反应过程中被还原的Co容易被再次氧化为CoO,因此在试样表面形成含CoO的MgO壳层,这在一定程度上可以抑制O2和熔融盐向金属/氧化膜界面扩散,也可以阻碍电子从该界面向熔融盐中传输。推测其他3种合金在腐蚀初期也形成了MgO壳层,只是随着合金元素Cr、Fe、Co及Ni的氧化、溶解和挥发,导致壳层失去支撑而破碎和脱落,从而带来腐蚀损失质量的增大。从图4中也可以看出,腐蚀160 h后,纯Co和GH6159试样表面还存在残留的MgO壳层(红圈部位),而GH5188表面已被严重腐蚀,出现大量腐蚀孔洞。由此,从微观结构角度也可以证明GH5188在熔融氯化盐中的耐蚀性最差。
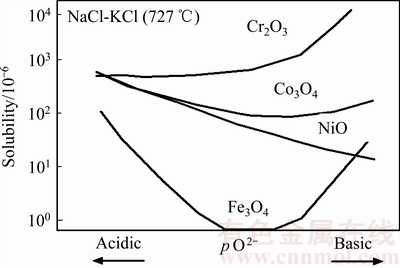
图9 几种常见金属氧化物在熔融NaCl-KCl中的溶解度[12-13]
Fig. 9 Common metal solubility in molten NaCl-KCl[12-13]
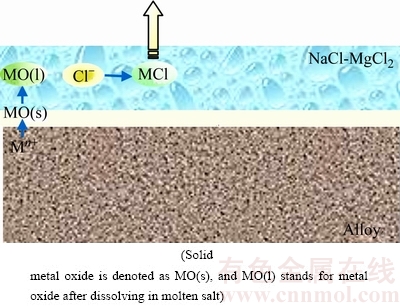
图10 Co基合金在熔融NaCl-52%MgCl2中的腐蚀机理
Fig. 10 Corrosion mechanism of Co-based alloys
3.3 残盐的成分分析
腐蚀后的残盐中检测到Na2MgCl4和NaMgCl3,这是在该比例混合盐熔化后所形成的两个新物相。MgCl2(H2O)6是极易吸潮的MgCl2在配盐的称量过程及熔化过程中形成的,从NaCl-MgCl2相图可知(见图11[15]),MgCl2吸潮导致该部分混合盐成分点左移,因此,腐蚀残盐中检测到数量可观的NaCl。关于MgO来源,除前文所述Mg原子还原Co等金属氧化物外,还有两个可能的途径:1) 吸潮后的MgCl2(H2O)6高温下分解形成MgO;2) 熔融盐中溶解的微量O2将与还原得到的Mg发生反应生成MgO,尽管O2在熔融盐中的溶解度很低,但这个原因也不可排除。
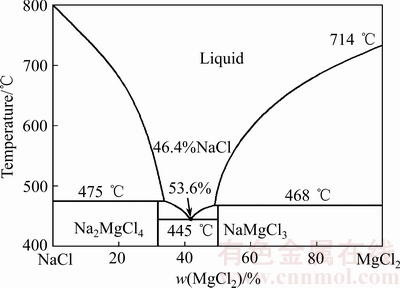
图11 NaCl-MgCl2相图[15]
Fig. 11 Phase diagram of NaCl-MgCl2[15]
4 结论
1) 纯Co、GH5188和GH6159合金在熔融NaCl- 52%MgCl2中的腐蚀动力学曲线遵循线性规律,纯Co的腐蚀速率最低,而GH5188的腐蚀速率最高。
2) 腐蚀20 h后,纯Co试样表面有壳层结构形成,EDS和XRD结果表明主要成分为MgO。GH5188表面出现腐蚀孔洞;腐蚀160 h后,纯Co和GH6159表面有残留的壳层,而GH5188试样发生严重腐蚀,表面出现镂空结构。
3) 3种试样的腐蚀机理主要是电化学-化学联合作用过程。两种合金试样的腐蚀是由于所含合金元素Cr、Fe和Co等的氧化、溶解和挥发;纯Co试样表面的MgO壳的生成是由于CoO 与的被还原的 Mg之间的置换反应及MgCl2(H2O)6的分解;生成的MgO壳及GH6159中所含的Mo、Al、Ti、Nb等耐蚀元素在一定程度上起到了延缓腐蚀的作用。
REFERENCES
[1]  A S, BRUCE P, SCROSATI B, TARASCON J M, SCHALKWIJK W V. Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices[J]. Nature Materials, 2005, 4(5): 366-77.
A S, BRUCE P, SCROSATI B, TARASCON J M, SCHALKWIJK W V. Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices[J]. Nature Materials, 2005, 4(5): 366-77.
[2] KENISARIN M M. High-temperature phase change materials for thermal energy storage[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2010, 14(3): 955-970.
[3] 路 阳, 成 波, 王军伟, 王智平, 李文生, 董洪峰. 不锈钢在熔融NaCl中的电化学-化学-稀释模型[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2015, 23(2): 75-80.
LU Yang, CHENG Bo, WANG Jun-wei, WANG Zhi-ping, LI Wen-sheng, DONG Hong-feng. Electrochemical-chemical- dilution corrosion model of stainless steel in molten NaCl[J]. Materials Science & Technology, 2015, 23(2): 75-80.
[4] ZHAO C Y, WU Z G. Thermal property characterization of a low melting-temperature ternary nitrate salt mixture for thermal energy storage systems[J]. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, 2011, 95(12): 3341-3346.
[5] XU E, YU Q, WANG Z, YANG C. Modeling and simulation of 1MW DAHAN solar thermal power tower plant[J]. Renewable Energy, 2011, 36(2): 848-857.
[6] 马宏芳, 朱 明, 赵云苗, 夏 瑾. 两种合金在氯化物熔盐中腐蚀行为研究[J]. 材料导报, 2014, 28(14): 109-113.
MA Hong-fang, ZHU Ming, ZHAO Yun-miao, XIA Jin. Corrosion behaviors of two kinds of alloys in chloride molten salts[J]. Materials Review, 2014, 28(14): 109-113.
[7] 成 波. 合金在熔融卤化盐高温相变储热介质中的腐蚀机理研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2014.
CHENG Bo .Corrosion mechanism of alloy in high-temperature phase change molten halide salt thermal storage medium[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2014.
[8] CUI C W, HUANG J L, XIU J. Study on metal corrosion caused by chlorine dioxide of various purities[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology (New Series), 2004, 11(6): 593-596.
[9] 鲍庆煌, 叶 兵, 蒋海燕, 谢超英, 丁文江. 镍基高温合金耐腐蚀性能的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2015, 29(17): 128-134.
BAO Qing-huang, YE Bing, JIANG Hai-yan, XIE Chao-ying, DING Wen-jiang. Research progress on the corrosion resistance of Nickel-based superalloy[J]. Materials Review, 2015, 29(17): 128-134.
[10] 黄乾尧, 李汉康. 高温合金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2000.
HUANG Qian-yao, LI Han-kang. High-temperature alloy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press,2000.
[11] 邵卫东, 严 彪, 毛彭龄. 新型钴基高温合金的组织结构与力学性能[J]. 上海有色金属, 2005, 26(4): 160-163.
SHAO Wei-dong, YAN Biao, MAO Peng-ling. Structure and mechanical properties of newly developed Co-based superalloys[J]. Shanghai Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 26(4): 160-163.
[12] ISHITSUKA T, NOSE K. Solubility study on protective oxide films in molten chlorides created by refuse incineration environment[J]. Materials & Corrosion, 2000, 51(3): 177-181.
[13] SHORES D A, MOHANTY B P. Role of chlorides in hot corrosion of a cast Fe-Cr-Ni alloy. Part II: thermochemical model studies[J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46(12): 2909-2924.
[14] LI Y, ALOMARY M, NIU Y, ZHANG K. The Corrosion of various materials under chloride deposits at 623-723 K in pure oxygen: High temperature materials and processes[J]. High Temperature Materials and Processes, 2002, 21(1/2): 11-24.
[15] WILLIAMS D F. Assessment of candidate molten salt coolants for the NGNP/NHI heat-transfer loop[J]. High Temperature Materials and Processes, 2002, 21(1/2): 11-24.
Corrosion behavior of Co-based alloys in molten NaCl-52%MgCl2
ZHOU Hong-xia1, 2, MENG Xiao-huan2, WANG Jun-wei1, 2
(1. Qinghai Provincial Engineering Research Center of High Performance Light Metal Alloys and Forming, Qinghai University, Xining 810016, China;
2. Qinghai Provincial Key Laboratory of New Light Alloys, Qinghai University, Xining 810016, China)
Abstract: In order to explore the corrosion mechanism, the corrosion behaviour of two common Co-based alloys GH5188 and GH6159 immersed in high temperature NaCl-52%MgCl2 (mole fraction) molten salt for 160 h was measured. The results show that the corrosion kinetics curves are approximately linear. After being corroded for 20 h, there is a shell emerging on the surface of pure Co as well as GH6159 samples, which slows down the corrosion rate to some extent. Meanwhile, a lot of pores form on the surface of GH5188. And after being corroded for 160 h, these pores grow up and link together. The cross-section EDS analysis of GH5188 shows a decrease of Cr and Co content in the corrosion layer. Therefore, the mechanism of Co-based alloys is oxidation and dissolution of Cr, Fe and Co followed by volatilization of metal chloride.
Key words: molten salt; corrosion; Co-based alloy; NaCl-52%MgCl2
Foundation item: Project(51441003) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2017-ZJ-Y17) supported by Qinghai Provincial Science and Technology Department, China; Project (2015-QGY-7) supported by the Young and Middle-aged Research Fund of Qinghai University, China
Received date: 2017-01-19; Accepted date: 2017-06-17
Corresponding author: WANG Jun-wei; Tel: +86-971-5310440; E-mail: Wangjw86@163.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51441003);青海省科技项目资助(2017-ZJ-Y17);青海大学中青年科研基金资助项目(2015-QGY-7)
收稿日期:2017-01-19;修订日期:2017-06-17
通信作者: 王军伟,副教授;电话:0971-5310440;E-mail: Wangjw86@163.com