文章编号:1004-0609(2013)11-3127-08
钨和H13钢的耐铝液腐蚀-磨损性能与机理
陈维平1,方思聪1,曾 勇1,吴 晶1,罗洪峰1, 2
(1. 华南理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,广州 510640;
2. 海南大学 机电工程学院,海口 570228)
摘 要:通过铝液中的静态腐蚀,高温下的摩擦磨损和铝液中的腐蚀-磨损试验,对钨和H13钢的耐铝液腐蚀-磨损性能和机理进行研究。结果表明:钨在铝液中的平均腐蚀速率约为H13钢的1/14,在高温下的摩擦磨损性能与H13钢的相当,在腐蚀-磨损条件下钨的材料损失率仅约为H13钢的1/24,远远优于H13钢的耐铝液腐蚀-磨损性能。在腐蚀-磨损过程中,试验材料均发生了磨粒磨损,而钨的腐蚀-磨损表面生成的产物起到了很好的保护基体材料的作用。腐蚀和磨损的交互作用是造成试验材料在腐蚀-磨损条件下材料损失急剧增大的主要原因。
关键词:钨;H13钢;铝液;腐蚀;磨损
中图分类号:TG172.6;TH117.1 文献标志码:A
Corrosion-wear resistant performance and mechanisms of tungsten and H13 steel in molten aluminum
CHEN Wei-ping1, FANG Si-cong1, ZENG Yong1, WU Jing1, LUO Hong-feng1, 2
(1. School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China;
2. Institute of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China)
Abstract: The corrosion-wear resistant performance and mechanisms of tungsten and H13 steel in molten aluminum were investigated through static corrosion in molted aluminum, friction-wear tests in air at high temperature, and corrosion-wear experiments in molten aluminum. The results show that the average corrosion rate of tungsten in molten aluminum is about 1/14 of H13 steel’s, and the performances of these two materials at high temperature friction-wear condition are nearly the same. The loss rate of tungsten under corrosion-wear condition is only about 1/24 of H13 steel’s, demonstrating that the corrosion-wear resistance of tungsten is much superior to that of H13 steel. Abrasive wear occurs in the corrosion-wear tests of these two experimental materials. In addition, the matrix is well protected by reaction products of tungsten on the corrosion-wear surface. The interaction behavior of corrosion and wear under corrosion-wear condition is the main reason for the rapid increment mass loss of the test materials.
Key words: tungsten; H13 steel; molten aluminum; corrosion; wear
铝及其合金由于质轻、性价比优良、综合性能好等优点,广泛应用于机械、交通、能源、电子等领域。然而,在铝合金的熔炼、铸造成形及热浸镀、连铸连轧等生产过程中,活泼的高温铝液极易造成直接接触材料的腐蚀破坏[1-3],尤其在同时存在摩擦磨损的情况下,与铝液接触的零部件的使用寿命更是急剧缩短。例如,铝合金压铸中的压射冲头和压室,挤压铸造中压头、压套在高温、高压下与铝液接触,不仅发生物理化学蚀损,而且因压射冲头(压头)与压室(压套)之间的相对运动,造成材料表面的磨损[4]。中国科学院金属研究所研究证明了钨与Al2O3/SiC陶瓷组成的滑动摩擦副具有良好的抗熔融锌铝合金腐蚀性能,并探索出一条钨的成型和焊接工艺新途径,使宝钢热镀锌生产线上稳定辊和沉没辊轴套的使用寿命提高了一倍,每年可多为宝钢创造产值近四千万元[5]。可见,研究熔融铝液中的腐蚀-磨损过程,对解决腐蚀-磨损失效问题,延长在熔炼、成形及热浸镀铝等过程中使用的坩埚、充液料筒、模具等零部件的使用寿命,降低铝液污染,提高经济效益等均具有现实意义。
目前,国内外对于金属熔体中的腐蚀-磨损的相关研究主要集中在锌液中的腐蚀-磨损[6-9]。然而,与锌液相比,铝液的温度更高,腐蚀性更强,对试验设备与条件的要求也更高。因此,与单一的耐铝液腐蚀材料的研究相比,材料的耐铝液腐蚀-磨损性能与机理的研究还十分缺乏。铁基材料作为铝及铝合金铸造工业中应用最广泛的模具及坩埚材料,目前已有不少研究者对铸铁、铸钢等材料在铝液中的腐蚀行为进行了研究。研究表明,铁基材料在铝液中易于在基体表面反应生成Fe2Al5和FeAl3两种金属间化合物[10-12],这两种脆性产物的生长和剥落造成铁基材料不断被铝液腐蚀。虽然通过各种表面处理可以提高材料的耐铝液腐蚀性能[13-16],但在高温铝液的腐蚀-磨损条件下,有限的表面层厚度并不一定能起到有效的保护作用。因此,许多研究人员都在积极寻找和开发具有良好耐铝液腐蚀-磨损性能的新材料[17-20]。
难熔金属钨及钨合金具有高熔点、高密度、高强度以及良好的抗腐蚀性能,其耐铝液腐蚀-磨损性能具有重要的研究意义。ZHU等[21]针对铝压铸成型时模具的工况条件,对几种先进金属材料的抗铝液焊合、冲刷和热疲劳性能进行了对比研究,结果表明Anviloy1150钨基合金表现出最佳的性能。陈维平等[22]对91W-6Ni-3Fe难熔合金、TiAl合金和铁基合金在熔铝中的耐腐蚀行为的研究也表明91W-6Ni-3Fe合金具有最优的耐铝液腐蚀性能。
单一的高温铝液腐蚀失效或单一的高温磨损失效试验较容易实现,然而,高温腐蚀-磨损工况并不是腐蚀与磨损效果的简单叠加,该工况下高温金属液的腐蚀失效与摩擦磨损失效是相互影响、相互促进的过程[23-25]。为了研究材料在熔融铝液中腐蚀-磨损失效的过程和机理,本课题组自主研发了一台新型高温金属腐蚀-磨损试验机[26],用于模拟材料在熔融金属中同时承受腐蚀和磨损的行为。本文作者选取耐腐蚀性能良好的钨以及广泛应用于铝及铝合金铸造工业中的H13钢,分别进行铝液中的静态腐蚀试验、高温下的摩擦磨损试验以及熔融铝液中的腐蚀-磨损试验。
1 实验
1.1 静态腐蚀试验方法
试验材料加工成尺寸为d 10 mm×30 mm的试样棒,表面经砂纸打磨,丙酮除油,去离子水清洗,空气中干燥。腐蚀试验前采用精度为0.1 mg的电子天平称量不同试样的质量。将不同成分的试样分别静置于750 ℃的熔融纯铝液中进行24 h的腐蚀试验,试验后试样置于空气中冷却,用质量分数为10%的NaOH溶液去除试样表面的覆铝层,称量腐蚀后试样的质量。
试样的腐蚀量用平均腐蚀率来评定,计算公式如下:
K=(m1-m2)/(Sρt) (1)
式中:m1为试样腐蚀前的质量,g;m2为试样腐蚀后的质量,g;S为试样腐蚀表面积,mm2;ρ为试样的密度,g/mm3;t为腐蚀时间,h;K为腐蚀的线速率,mm/h。
1.2 腐蚀磨损试验方法
试验在自行研制的高温金属腐蚀-磨损试验机(ZL201010526678.5)上进行[26],其主要结构如图1所示。试验机采用环块式摩擦磨损方式,其中块状试样为试验材料,环形配副为96Al2O3陶瓷,具体尺寸如图2所示。
试验分为两部分,分别是在750 ℃高温下的干磨损试验和在750 ℃纯铝液中的腐蚀-磨损试验。试验参数为:摩擦环转速60 r/min,加载载荷10 N,测试时间60 min。考虑到材料在高温下的氧化,在高温干磨损试验中,将尺寸相同的同种试样置于坩埚中进行氧化,以测定氧化增质量。试验材料为市场上供应的工业纯钨和H13钢,两者硬度分别为55HRA和37HRA。
试验前采用精度为0.1 mg的电子天平称量块状试样的质量。干磨损试验后,试样直接称量质量;腐蚀-磨损试验后,将试样置于质量分数为10%的NaOH溶液中除去试样表面的覆铝层后再称重。高温干磨损条件下,由下式计算材料损失的线速率:
K=(m1-m2+m3)/(Sρt) (2)
式中:m1为试样磨损前的质量,g;m2为试样磨损后的质量,g;m3为试样氧化所增加的质量,g;S为试样磨损面的面积,mm2;ρ为试样的密度g/mm3;t为磨损时间,h;K为磨损的线速率,mm/h。在腐蚀-磨损条件下,材料损失的线速率(mm/h)可由式(1)计算得到(其中S用腐蚀-磨损表面的面积代入)。
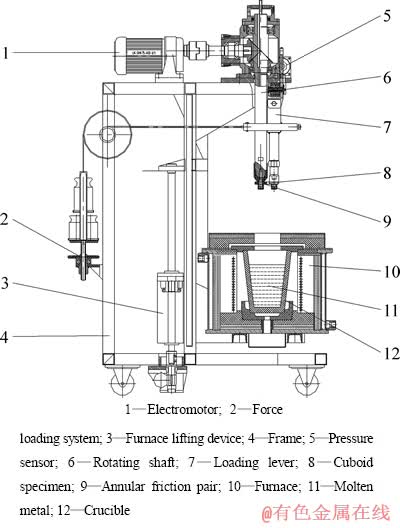
图1 高温金属腐蚀-磨损试验机示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of high temperature test rig for corrosion-wear in molten metal
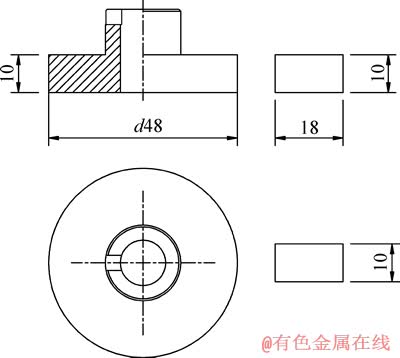
图2 摩擦副的形状及尺寸
Fig. 2 Shape and dimension of friction pair (Unit: mm)
2 结果与讨论
对钨和H13钢分别进行铝液中的腐蚀试验,高温下的干磨损试验以及铝液中的腐蚀-磨损试验所得到的结果如表1所示。
表1 静态腐蚀、干磨损及腐蚀-磨损试验结果
Table 1 Test results of static corrosion, friction-wear and corrosion-wear
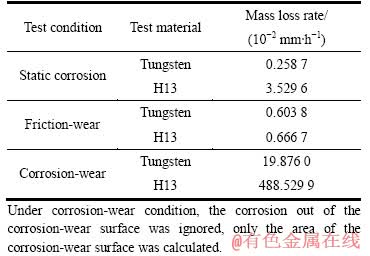
从表1中可得出,钨的耐铝液腐蚀性能远优于H13钢的,其腐蚀的线速率约为H13钢的1/14。在高温干磨损条件下,试验材料的损失率均较小,都表现出良好的耐摩擦磨损性能;在750 ℃铝液中的腐蚀-磨损条件下,两种材料的损失率差别增大,其中H13钢的材料损失非常严重,而钨的损失率仅约为H13钢的1/24,表现出远远优于H13钢的耐铝液腐蚀-磨损性能。
为了观察试样在铝液中腐蚀界面的微观形貌,重复一次腐蚀试验,试样取出后空冷,沿横截面切开,经镶嵌、打磨和抛光后,使用Quanta200型扫描电子显微镜对其进行观察和分析。如图3所示,试验材料在铝液中腐蚀过后的界面组织由表面层、过渡层和基体3部分组成。表面层主要是试验中所用的铝,基体为试验材料,过渡层则是试验材料和铝液反应所生成的产物。对比发现,钨试样中的过渡层呈条带状,且与基体材料的结合界面平整,可见,铝液对钨的腐蚀主要停留在暴露于铝液中的试样表面;H13钢试样中的过渡层呈舌状结构,且深入到基体中,表明铝液对H13钢的腐蚀已经渗透到基体内部。这也进一步验证了钨的耐铝液腐蚀性能远优于H13钢的试验结果。对腐蚀试样横截面上基体与腐蚀产物的结合界面进行XRD物相分析的结果(见图4)表明:钨在铝液中反应生成的产物主要有WAl5和WAl12,而H13钢在铝液中腐蚀的产物主要是Fe2Al5。
图5所示为钨和H13钢的干磨损和腐蚀-磨损后的微观组织形貌。图5(a)和(e)表明:高温干磨损条件下,两种材料的主要流失机制均为塑性流变,高温条件下材料的硬度降低,试样磨损表面的微凸体在摩擦磨损过程中产生极大的应力集中,从而产生塑性变形,并在剪切力作用下发生转移。图5(c)和(f)表明,在腐蚀-磨损条件下,钨的腐蚀-磨损表面上存在较多沿运动方向延伸、深浅不等、宽窄不一的连续犁沟;而H13钢的腐蚀-磨损表面上则出现了明显的推碾形貌,且残留少量磨屑,显然,两者均发生了磨粒磨损。进一步观察图5(d)和(g)发现,钨的腐蚀-磨损面表层有许多裂纹,且大部分裂纹互相连接成了网格,此外,还可看到大小、深度不一的不规则剥落坑;而H13钢的表面上则布满了微裂纹。
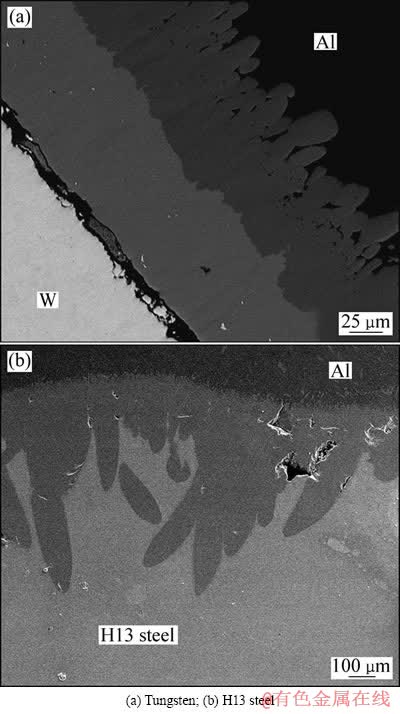
图3 钨和H13钢在铝液中腐蚀后的界面组织形貌
Fig. 3 Cross-section morphologies after corrosion test in molten aluminum
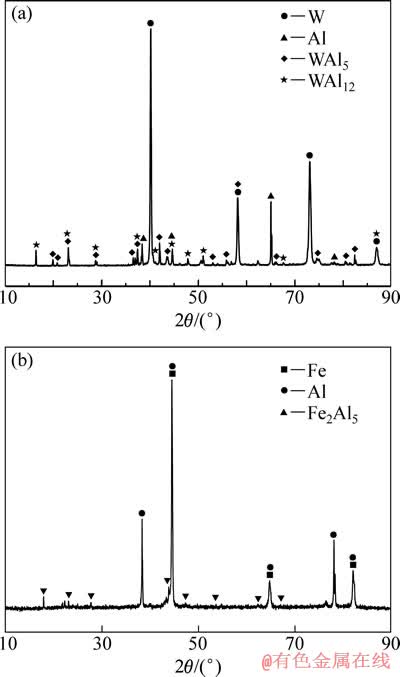
图4 钨和H13钢的铝液腐蚀界面XRD谱
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of interface between molten aluminum and tungsten (a) or H13 steel (b)
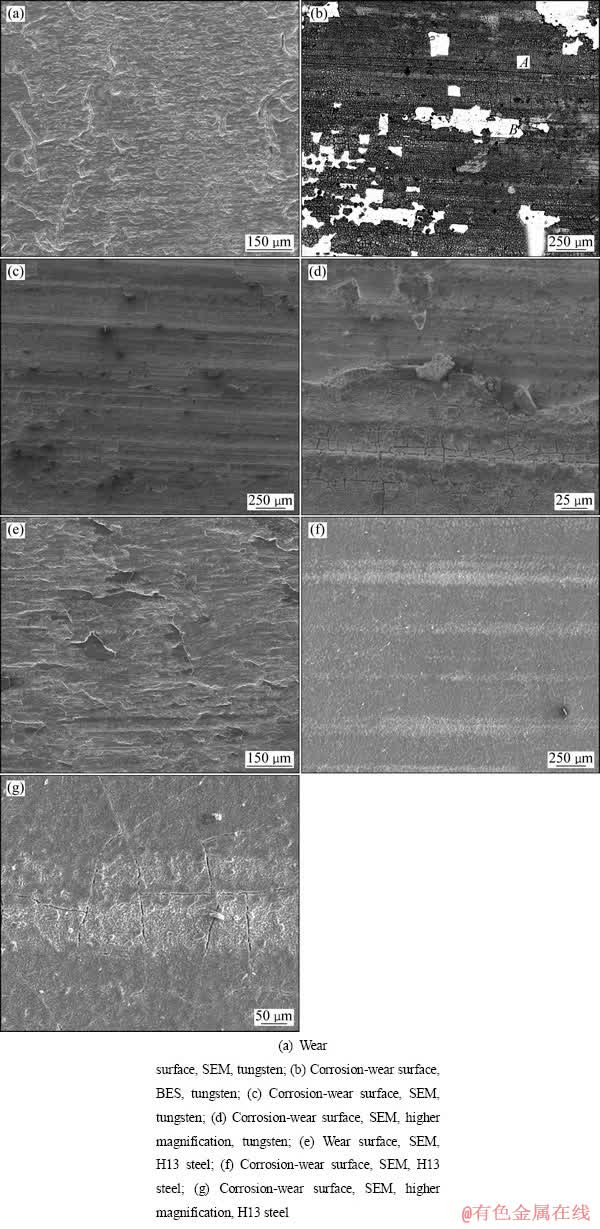
图5 钨和H13钢的干磨损和腐蚀-磨损形貌
Fig. 5 Wear surface and corrosion-wear surface morphologies of tungsten and H13 steel
可见,两种材料的腐蚀-磨损机理并不相同。H13钢在腐蚀-磨损过程中,试样表面受到压应力、剪切应力以及化学反应的交互作用,腐蚀产物不断被剥落而形成磨粒,加之高温下材料软化,磨粒经过处的材料表面将发生塑性变形,并且被推碾至碾沟的两边,从而使基体表面不断地暴露出来。磨粒在表面运动时还可能形成很高的局部应力集中,此时磨粒前沿的材料中将产生很高的剪切应力和拉应力,随着磨损过程的进行,形成微裂纹。由纯腐蚀试验可知,H13钢在与铝液接触的表面上生成的化合物呈舌状。因此,在腐蚀-磨损条件下,铝液将极易沿显微裂纹与基体反应,从而加速了对试样的腐蚀;同时,铝液在裂纹尖端的腐蚀又加速了裂纹的扩展与繁殖,最终导致试样磨损的加剧。从图5(b)可以看出,钨的腐蚀-磨损表面上有白色和暗灰色两种区域,其中大部分区域为暗灰色的区域(区域A),少量为白色区域(区域B)。对这两种不同的区域分别进行EDS能谱分析,结果表明,暗灰色区域为钨在铝液中所生成的产物,白色区域为表层产物剥落后裸露出的钨基体。这说明钨在铝液中的腐蚀-磨损过程中,材料表面所生成的腐蚀产物具有耐磨性高、与基体材料结合性良好的特点,从而很好地起到了保护基体材料的作用。此外,腐蚀-磨损表面的裂纹表明腐蚀-磨损产物脆性较大。由纯腐蚀试验可知,钨试样在铝液环境中形成条带状过渡层。在腐蚀-磨损过程中,平整而又耐磨的腐蚀产物避免了基体材料直接暴露在铝液中进行磨损,在腐蚀和磨损的交互作用下,磨损面上应力集中的部位将首先产生裂纹,由于腐蚀产物脆性较大,裂纹将随着腐蚀-磨损过程的进行迅速扩展和延伸,一部分腐蚀产物从基体上脱落而成为磨粒,同时在磨损面上形成剥落坑,裸露出的基体材料又与铝液反应生成耐磨的腐蚀产物。因此,钨表现出更优异的耐铝液腐蚀-磨损性能。
图6所示为钨和H13钢分别与96Al2O3陶瓷配副在750 ℃空气中进行干磨损和在熔融铝液中进行腐蚀-磨损的摩擦因数与时间的关系曲线。由图6可以看出,钨和H13钢在腐蚀-磨损条件下的摩擦因数均比干磨损条件下的小;腐蚀-磨损条件下钨的摩擦因数的波动比H13钢的小得多。这表明铝液的存在以及磨损面上腐蚀产物的生成,起到了润滑的作用,从而降低了摩擦因数。腐蚀-磨损过程中,H13钢的腐蚀产物不断生成和剥落,使表面粗糙度增大,腐蚀和磨损的交互作用造成磨损面受力状况更加复杂,摩擦因数的波动更大;而钨的表面腐蚀产物平整耐磨,且结合较牢固,更不易脱落,所以钨在腐蚀-磨损过程较平稳,摩擦因数的波动较小。
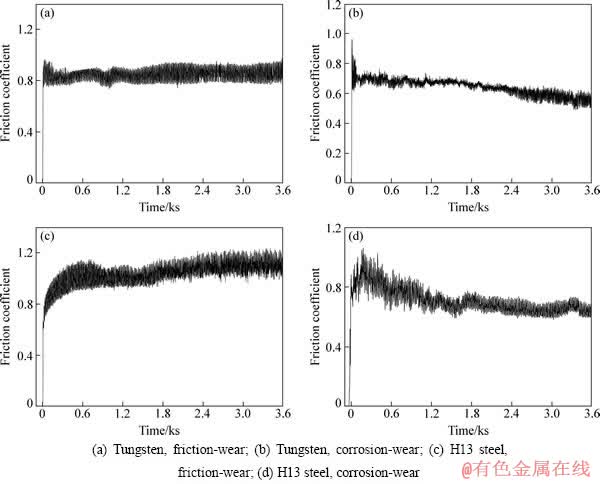
图6 摩擦因数与时间的关系
Fig. 6 Relation between friction coefficient and time
试验结果表明,腐蚀-磨损造成的材料损失远远大于单纯的磨损或单纯的腐蚀所造成的材料损失。显然,在腐蚀-磨损条件下,腐蚀与磨损的交互作用是材料破坏的主要原因,即腐蚀加速磨损的同时磨损也加速了腐蚀。
腐蚀加速磨损作用的原因在于:铝液的腐蚀作用破坏材料表面的晶界、相界或其他组织的完整性,降低了材料的结合强度,使材料表面更容易被磨损;试验材料在铝液中生成的腐蚀产物基本上是脆性的化合物(如前文提到的WAl5、WAl12和Fe2Al5等),会造成材料表面粗糙,并且腐蚀产物在随后铝液的冲刷和其他微凸体的作用下容易从材料表面脱落而形成磨粒,从而加速材料的磨损。
磨损加速腐蚀的原因在于:磨损加速了试样表面腐蚀产物的剥落,使得基体材料不断暴露于高温铝液中,促进腐蚀的发生和发展。试验材料在压应力和剪切应力的交互作用下容易在磨痕位置、腐蚀产物与基体结合位置产生裂纹,使材料表面变得疏松,增加铝液侵蚀材料的通道而加速腐蚀。在静态腐蚀条件下,随着腐蚀反应的进行,有部分试验材料会溶解到铝液中,一些腐蚀产物也会从表面脱落进入铝液中,造成铝液的浓度降低,使得腐蚀反应速率减慢。但是在腐蚀-磨损过程中,试样表面的铝液不断受到机械搅拌作用,从而加速了传质过程,不断补充铝液,促进腐蚀过程的进行。
在高温干磨损条件下,钨并没有表现出比H13钢更优越的性能;而从材料损失率的倍数关系上看,腐蚀-磨损条件下两种材料的性能差异从静态腐蚀时的14倍增大到了24倍。其原因可能在于,钨更耐铝液腐蚀,同时表面腐蚀产物层平整耐磨,更能起到保护基体的作用,腐蚀速率的减小极大地抑制了腐蚀与磨损间交互作用的进行,从而使钨在腐蚀-磨损条件下表现出更大的优越性。钨优异的耐铝液腐蚀-磨损性能不仅为工程应用提供了一种材料选择,也为解决材料在熔融铝液中的腐蚀-磨损失效问题提供了一种思路,即将腐蚀或磨损两者之一控制在较低水平,从而抑制腐蚀与磨损间交互作用的进行。
3 结论
1) 在铝液中腐蚀和腐蚀-磨损的试验条件下,钨都表现出比H13钢更好的性能,尤其是在腐蚀-磨损条件下,钨的材料损失率仅约为H13钢的1/24。钨的高温干磨损性能与H13钢的相当。
2) 试验材料在腐蚀-磨损过程中均发生了磨粒磨损,但H13钢在铝液腐蚀和冲刷作用下,腐蚀-磨损表面的犁沟槽被大大弱化;而在钨的腐蚀-磨损表面则能观察到较多的平行犁沟磨痕。
3) 钨在腐蚀-磨损过程中生成的表面产物层起到了很好的保护基体的作用,这也是钨具有良好的耐铝液腐蚀-磨损性能的重要原因。
4) 在铝液中腐蚀-磨损的过程中,腐蚀和磨损的交互作用是造成材料流失急剧增大的主要原因。
REFERENCES
[1] 刘树勋, 李培杰, 曾大本. 液态金属腐蚀的研究进展[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2001, 13(5): 275-278.
LIU Shu-xun, LI Pei-jie, ZENG Da-ben. Research progress of liquid metal induced corrosion[J]. Corrosion Science and Technology Protection, 2001, 13(5): 275-278.
[2] YAN M, FAN Z. Durability of materials in molten aluminum alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2001, 36(2): 285-295.
[3] WANG D, SHI Z, ZOU L. A liquid aluminum corrosion resistance surface on steel substrate[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2003, 214(1/4): 304-311.
[4] SUMANTH S, DIRAN A. Die soldering: Mechanism of the interface reaction between molten aluminum alloy and tool steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2002, 33(3): 465-476.
[5] 黄须强. 在熔融锌铝合金中与陶瓷滑动配副抗磨蚀材料和轴套的研究[D]. 沈阳: 中国科学院金属研究所, 2000: 73-96.
HUANG Xu-qiang. Study on materials with corrosive wearing resistance to ceramics in molten zinc-aluminum alloy[D]. Shenyang: Institute of Metal Research Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2000: 73-96.
[6] ZHANG K, TANG N Y. On the wear of a cobalt-based superalloy in zinc baths[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2003, 34(10): 2387-2396.
[7] ZHANG K. Effects of test conditions on the tribological behaviour of a journal bearing in molten zinc[J]. Wear, 2005, 259(7/12): 1248-1253.
[8] 张丽敏, 曹晓明, 马瑞娜. 氧化铝配对摩擦副在锌液中的摩擦磨损性能研究[J]. 表面技术, 2006, 35(1): 22-24.
ZHANG Li-min, CAO Xiao-ming, MA Rui-na. Sliding wear performance of several materials in molten-zinc against Al2O3[J]. Surface Technology, 2006, 35(1): 22-24.
[9] 曹晓明, 马瑞娜, 王 岩, 范永哲. 钴基合金在液锌中的腐蚀磨损性能[J]. 天津大学学报, 2008, 41(12): 1485-1491.
CAO Xiao-ming, MA Rui-na, WANG Yan, FAN Yong-zhe. Corrosive wear performance of cobalt-based alloys in molten zinc[J]. Journal of Tianjin University, 2008, 41(12): 1485-1491.
[10] HOU Hua, YANG Rui-feng. Study on stainless steel electrode based on dynamic aluminum liquid corrosion mechanism[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21: S170-S173.
[11] BALLOY D, TISSIER J C, GIORGI M L, BRIANT M. Corrosion mechanisms of steel and cast iron by molten aluminum[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2010, 41(9): 2366-2376.
[12] 余 岩, 谢海东. 不锈钢在熔融铝液中的高温腐蚀[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2012, 33(3): 216-217.
YU Yan, XIE Hai-dong. Corrosion of stainless steels in melting aluminum alloy[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2012, 33(3): 216-217.
[13] WANG De-qing, SHI Zi-yuan, ZOU Long-jiang. A liquid aluminum corrosion resistance surface on steel substrate[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2003, 214(1/4): 304-311.
[14] HO W Y, HUANG D H, HUANG L T, HSU C H, WANG D Y. Study of characteristics of Cr2O3/CrN duplex coatings for aluminum die casting applications[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004, 177/178: 172-177.
[15] 王 荣, 闵永安, 吴晓春. H13钢经不同表面处理后的静态抗铝热熔损性能比较[J]. 金属热处理, 2003, 28(12): 5-8.
WANG Rong, MIN Yong-an, WU Xiao-chun. Comparison of static anti-melting-loss ability of H13 steel with different surface treatment[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2003, 28(12): 5-8.
[16] 吴晓春, 邬天荣, 杨浩鹏, 王庆芳. H13钢低温等离子体渗硼层的热熔损性能[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2011, 32(1): 97-102.
WU Xiao-chun, WU Tian-rong, YANG Hao-peng, WANG Qing-fang. Melting-loss resistance of H13 steel with low temperature plasma boride layer in liquid aluminium[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2011, 32(1): 97-102.
[17] KOMAROV S, KUZNETSOV D. Erosion resistance and performance characteristics of niobium ultrasonic sonotrodes in molten aluminum[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2012, 35: 76-83.
[18] TANAKA M, KASHIWAGI K, KAWASHIMA N, KITAOKA S, SAKURADA O, OHYA Y. Effect of grain boundary cracks on the corrosion behaviour of aluminium titanate ceramics in a molten aluminium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2012, 54: 90-96.
[19] IBARRA CASTRO M N, ALMANZA ROBLES J M, CORTES HERNANDEZ D A, ESCOBEDO BOCARDO J C, TORRES TORRES J. The effect of SrSO4 and BaSO4 on the corrosion and wetting by molten aluminum alloys of mullite ceramics[J]. Ceramics International, 2010, 36(4): 1205-1210.
[20] 陈维平, 杨少锋, 肖华强, 罗洪峰, 吴 晶. 耐高温铝液腐 蚀-磨损材料的研究进展[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金,2012, 32(4): 324-329.
CHEN Wei-ping, YANG Shao-feng, XIAO Hua-qiang, LUO Hong-feng, WU Jing. Process in materials in molten aluminium tribocorrosion environment[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2012, 32(4): 324-329.
[21] ZHU Yu-long, SCHWAM D, WALLACE J F, BIRCEANU S. Evaluation of soldering, washout and thermal fatigue resistance of advanced metal materials for aluminum die-casting dies[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 379(1/2): 420-431.
[22] XIAO Hua-qiang, CHEN Wei-ping, LIU Zhe. Corrosion resistance of 91W-6Ni-3Fe refractory metal, TiAl compound and iron based alloys in molten aluminum[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(9): 2320-2326.
[23] 卢书媛. 湿磨衬板新材质开发及冲击腐蚀磨损机理的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2003: 28-42.
LU Shu-yuan. The development of new materials and the behavior of corrosion-abrasion of the liner of wet-grinding machine in metallurgical industry[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2003: 28-42.
[24] ZIOMEK-MOROZ M, MILLER A, HAWK J, CADIEN K, LI D. An overview of corrosion-wear interaction for planarizing metallic thin films[J]. Wear, 2003, 255(7/12): 869-874.
[25] SHIBLI S M A, CHACKO F, DIVYA C. Al2O3-ZrO2 mixed oxide composite incorporated aluminium rich zinc coatings for high wear resistance[J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(2): 518-525.
[26] 陈维平, 吴 晶, 罗洪峰. 新型高温金属腐蚀-磨损试验机及其应用[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2012, 32(10): 883-885.
CHEN Wei-ping, WU Jing, LUO Hong-feng. A new high temperature test rig for corrosion-wear in molten metal and its application[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2012, 32(10): 883-885.
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51271080);广东省自然科学基金资助项目(S20110100002227);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助项目(20100172110033)
收稿日期:2012-12-13;修订日期:2013-04-18
通信作者:陈维平,教授,博士;电话:020-87113832;E-mail:mewpchen@scut.edu.cn