热加工对电子束焊接TC11/Ti2AlNb双合金接头组织和性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2014年第11期
论文作者:秦 春 姚泽坤 李誉之 宁永权 郭鸿镇
文章页码:3500 - 3508
关键词:热加工;钛合金;力学性能;热稳定性;电子束焊接
Key words:hot working; titanium alloy; mechanical properties; thermal stability; electron beam welding
摘 要:研究热加工对电子束焊接TC11/Ti2AlNb双合金接头显微组织的影响,对焊接件热暴露前后的室温拉伸性能进行测试。结果表明:电子束焊接TC11/Ti2AlNb双合金熔合区主要由β相组成;经过变形和热处理后,熔合区主要由β、α2和α相组成,同时原始铸态的晶界在变形过程中破碎。在拉伸试验中,熔合区是薄弱区域;在不同的变形条件下,试样(热暴露前后)在此区域发生断裂。热处理后试样的最大室温拉伸强度达到1190 MPa;锻后水冷试样具有较好的塑性,其伸长率达到4.4%。相比较而言,经过(500 °C,100 h)的热暴露后,试样的室温拉伸强度略有上升,但塑性变化较小。拉伸断口SEM观察显示,在不同变形条件下穿晶断裂为主要的断裂机制。
Abstract: The influence of hot working on the microstructures of TC11/Ti2AlNb dual-alloy joints welded by electron beam welding (EBW) process was investigated. The tensile tests were performed at room temperature for specimens before and after thermal exposure. The results show that the fusion zone of TC11/Ti2AlNb dual-alloy joint welded by EBW is mainly composed of β phase. After deformation and heat treatment, the grain boundaries of the as-cast alloy are broken and the fusion zone mainly consists of β, α2 and α phases. The fusion zone performs poor property in the tensile test. Specimens before and after thermal exposure all fail in this area under different deformation conditions. The ultimate tensile strength of specimens after heat treatment is up to 1190 MPa at room temperature. The joints by water quenching after deformation have better plasticity with an elongation up to 4.4%. After thermal exposure at 500 °C for 100 h, the tensile strength of the specimen slightly rises while the ductility changes a little. SEM observation shows that the fracture mechanism is predominantly transgranular under different deformation conditions.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 3500-3508
Chun QIN, Ze-kun YAO, Yu-zhi LI, Yong-quan NING, Hong-zhen GUO
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
Received 8 January 2014; accepted 30 April 2014
Abstract: The influence of hot working on the microstructures of TC11/Ti2AlNb dual-alloy joints welded by electron beam welding (EBW) process was investigated. The tensile tests were performed at room temperature for specimens before and after thermal exposure. The results show that the fusion zone of TC11/Ti2AlNb dual-alloy joint welded by EBW is mainly composed of β phase. After deformation and heat treatment, the grain boundaries of the as-cast alloy are broken and the fusion zone mainly consists of β, α2 and α phases. The fusion zone performs poor property in the tensile test. Specimens before and after thermal exposure all fail in this area under different deformation conditions. The ultimate tensile strength of specimens after heat treatment is up to 1190 MPa at room temperature. The joints by water quenching after deformation have better plasticity with an elongation up to 4.4%. After thermal exposure at 500 °C for 100 h, the tensile strength of the specimen slightly rises while the ductility changes a little. SEM observation shows that the fracture mechanism is predominantly transgranular under different deformation conditions.
Key words: hot working; titanium alloy; mechanical properties; thermal stability; electron beam welding
1 Introduction
TC11 alloy is an α+β titanium alloy similar to Russian alloy BT9, which is widely used in compressor blades and discs in aerospace for its attractive properties such as high specific strength, fracture toughness and good formability [1,2]. Intermetallics based on Ti2AlNb are expected to operate at temperatures of 600-700 °C in the aircraft engine for their outstanding properties including high specific strength, good creep and corrosion resistance [3,4]. Owning to technical and economic problems, it is difficult to apply intermetallics [5]. The requirements for bore and rim mechanical properties of engine compressor discs are different. Some works about dual-property disc have been done [6-8]. If the Ti2AlNb intermetallics are joined with widely used TC11 alloy, the combination might meet different kinds of property needs of compressor discs, making use of each material efficiently [9].
Electron beam welding (EBW) is a fusion welding process and can be applied to joining different kinds of titanium alloys with little defects. Some researches have been done about the Ti-Al-Nb intermetallics jointed with Ti alloys using EBW technology [10-14]. The resistance to solidification cracking was good and the grain size affected the tensile strength critically. According to these studies, it could also be found that isothermal deformation and heat treatment had important influence on the microstructure and properties of dissimilar joints.
Up to now, there have been rare reports on the effect of thermal exposure on the mechanical properties of Ti-Al-Nb/Ti alloy joints welded by EBW. The aeroengine works in abominable and complicated environment operating at high temperature. So, the research of thermal stability for the microstructure at high temperature seems to be particularly important. The aim of the present study is to investigate the influence of hot working on the microstructure and mechanical properties of TC11/Ti2AlNb joints welded by EBW process and to characterize the mechanical property change of welds after thermal exposure.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
The nominal compositions of TC11 alloy and Ti2AlNb based alloy used in this work were Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si (mass fraction, %) and Ti-22Al-27Nb (molar fraction, %), respectively. Two alloys were both forged to the required dimension and spark machined to cuboid specimens (20 mm × 25 mm × 35 mm for EBW and 20 mm×25 mm surface for welding). The microstructures of base metals of two alloys for welding are shown in Fig. 1. The parent TC11 alloy presents typical bimodal microstructure consisting of the equiaxed α phase with the average grain size of 5 μm, transformed β phase and an lamellar α phase with a thickness of 0.6 μm (Fig. 1(a)). The microstructure of Ti2AlNb alloy is composed of large grains with α2 phase distributed at the grain boundary and fine O phase precipitated in the grains (Fig. 1(b)).
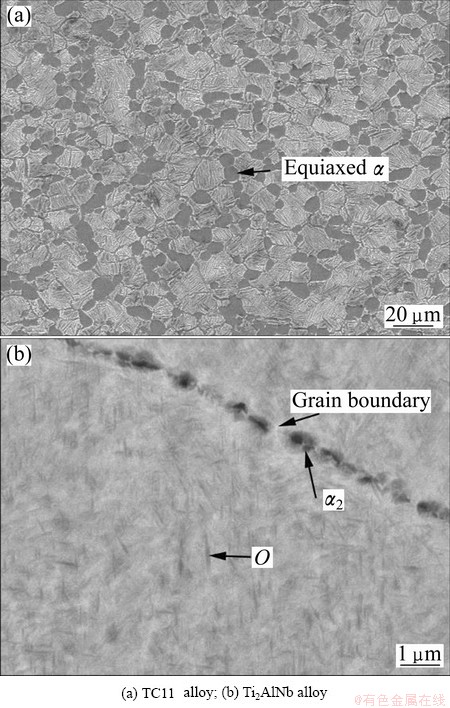
Fig. 1 Microstructures of base alloy for EBW process
2.2 Experimental procedures
The welded surfaces were polished and cleaned before welding. Welding experiments were conducted using a KS55-G150 model EBW machine. The specimens were welded on both sides by EBW. Only welding current was changed during the both sides welding. Welding current on one side was 14 mA and that on the other side was 10 mA. Other parameters adopted in the EBW process are as follows: accelerating voltage 150 kV, focusing current 2250 mA and welding speed 8 mm/s.
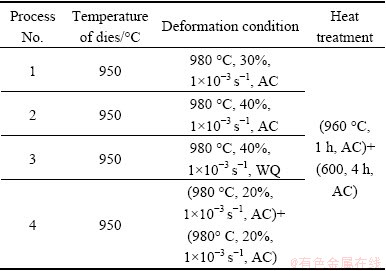
After welding, nearly isothermal deformation was carried out on a THP-630A model hydraulic machine which allowed the specimens to be deformed at a constant strain rate. During the deformation process, the temperature of dies was kept at 950 °C. The specimens were heated to 980 °C and held for 18 min in the box heat treatment furnace. A borosilicate glass lubricant was spread on the surface of the specimens. The deformation direction was parallel to the welding interface. The experimental scheme is given in Table 1. The process No. 4 was forged twice. The first forged processing was similar to the other and the second processing was carried out with the specimen being turned 90°. The heat treatment of specimens was (960 °C, 1 h, AC)+(600, 4 h, AC). After heat treatment, the specimens were thermally exposed at 500 °C for 100 h. Tensile tests were carried out at room temperature with drawing direction perpendicular to the weld interface. The microstructure was observed on an OLYMPUSPM-G3 microscope. The fracture surfaces of specific specimens were observed on an SUPRA55 SEM.
Table 1 Experimental scheme
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure evolution
Figure 2(a) shows a macrophotograph of the cross-section of electron beam welded dissimilar joint for TC11 alloy and Ti2AlNb alloy. The fusion zone is an hourglass shape that is big at both ends and small in the middle, unlike other electron beam welded joint, which looks like a burette [10,11]. The reason for this is that the EBW processes in this experiment are both sides resulting two weld pools. In order to identify the phases of the weld metal, X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used. According to XRD pattern of the weld (Fig. 2(b)), it can be confirmed that the fusion zone is composed of single β phase. According to the research of TAN et al [11], the microstructure of fusion zone consists of β, O and α2 phases when TC11 alloy and Ti2AlNb alloy are welded by EBW, which was different from the results in this work. The reason is that the residence time for the microstructure of fusion zone is short in high temperature region as the cooling speed is quick during the EBW process. Meanwhile, the content of β-stable element Nb is higher, resulting in the inhibition of the β phase transformation.
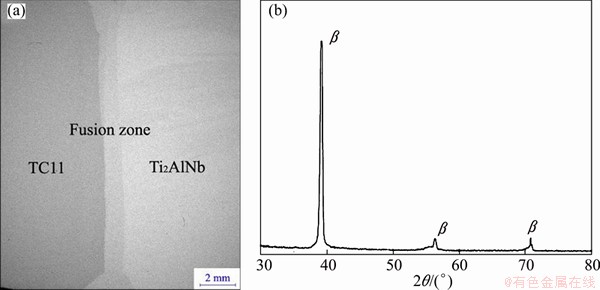
Fig. 2 Macrophotograph of cross-section of TC11/Ti2AlNb dual-alloy joint (a) and XRD pattern of fusion zone (b)
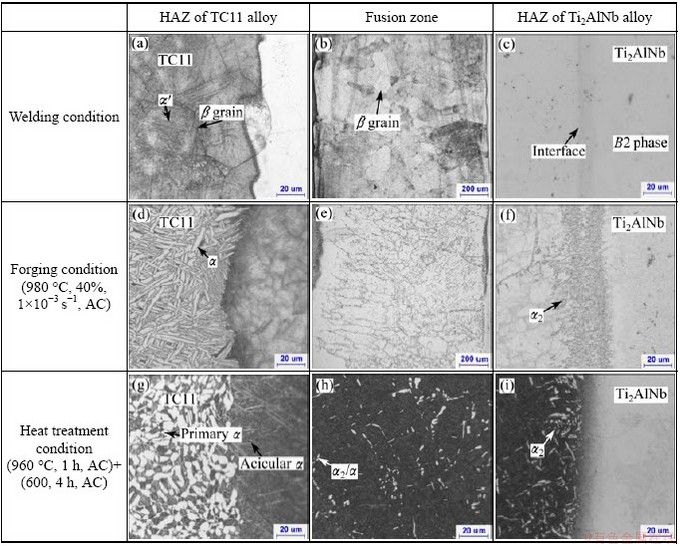
Fig. 3 Microstructures of welding zones under different conditions
The microstructures of the welding zone under different conditions are shown in Fig. 3. Figures 3(a)-(c) show the microstructures of Ti2AlNb/TC11 alloys under welding condition. The near heat affected zone (HAZ) of TC11 alloy mainly consists of martensite α' phase that is arranged in a random direction. A few α phases appear in the area a little far away from the interface. The β grains are coarse (Fig. 3(a)). These results can be explained that temperature in the HAZ of TC11 alloy exceeds the transformation point, and temperature in the area nearby the interface is higher than that in the area far away from HAZ. The fusion zone is composed of β grains and solidification structure appears (Fig. 3(b)). The zone near the boundary between the fusion zone and the HAZ consists of columnar grains whose orientation is perpendicular to the boundary and the middle of fusion zone is composed of the equiaxed grains. Heat transfers along the cross direction and depth direction during the welding process. The temperature in the middle of fusion zone is greater and the solidification process begins from the interface. Consequently, the morphology as shown in Fig. 3(b) appears. Figure 3(c) shows that the HAZ of Ti2AlNb alloy predominantly contains B2 phase and the boundary between the HAZ of Ti2AlNb alloy and the fusion zone is not clear. During the EBW, the cooling rate is fast enough to suppress β to O/α2 phase transformation.
After nearly isothermal forging, the microstructures change a lot. Figures 3(d)-(f) show the microstructures of welding zone after forging under process No. 2. The HAZ of TC11 alloy consists of lamellar α phase (Fig. 3(d)). Phase transformation α′→α+β occurs during the heating and forging processes and more α phases precipitate during the cooling process after forging. Grains in the fusion zone are stretched perpendicularly to the deformation direction (Fig. 3(e)). The grain boundaries become curvy and more fine phases precipitate along the grain boundaries because the defects in the boundary are more than those beneficial to the nucleation. Figure 4 shows the phase diagrams of the Ti-Al-Nb system. During the forging process, the Ti2AlNb alloy is in the α2+O+B2 three-phase region as the temperature of weldment is 980 °C (Fig. 4(a)) [15], so the microstructure of Ti2AlNb alloy after forging contains the α2, O and B2 phases. Along the boundary between the fusion zone and HAZ of Ti2AlNb alloy, Al and Nb contents are close to those of Ti2AlNb alloy, which benefits the precipitation of α2 phases according to Fig. 4(b) [15]. Due to the distance far from the interface, Al and Nb contents decrease, resulting in the fact that the precipitate phase is mainly β phase (Fig. 3(f)).
Figures 3(g)-(i) show the microstructures of Ti2AlNb/TC11 alloys weldment under process No. 2 followed by heat treatment with (960 °C, 1 h, AC)+(600, 4 h, AC). It can be seen that the microstructure of TC11 alloy in HAZ consists of primary α and transformed β phase. The content of primary α phase is about 50%. At the interface between the HAZ of TC11 alloy and the fusion zone, the microstructure consisting of acicular α phase is different from that in the HAZ of TC11 alloy. This result may be on account of the increase of the β-stable element Nb in this zone, which results in the decrease of the phase transformation point. The deformation temperature can exceed the phase transformation point, leading to the microstructure variation at the interface.
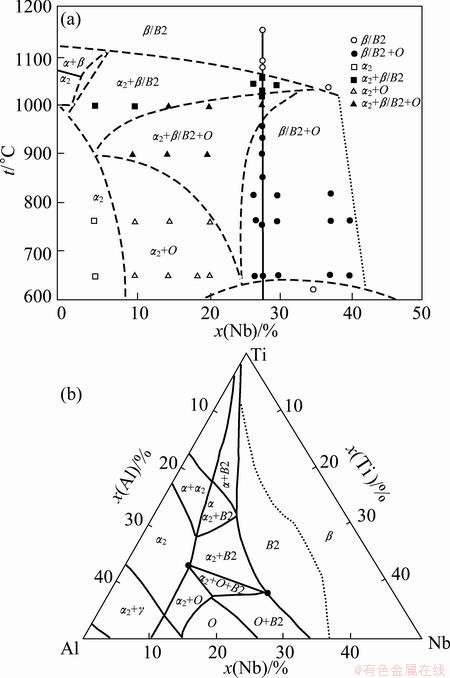
Fig. 4 Vertical interfaces of phase diagram for Ti-22Al-xNb system (molar fraction, %) (a) and isothermal section for Ti-Al-Nb system at 900 °C (b) [15]
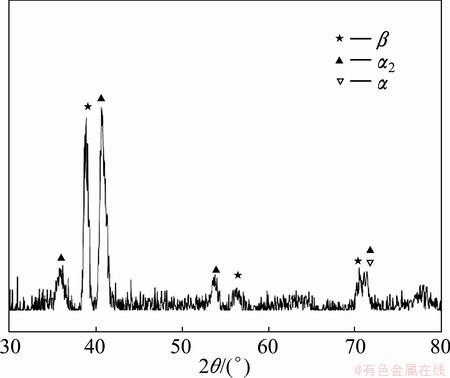
Fig. 5 XRD pattern of fusion zone after heat treatment
Figure 5 shows XRD pattern of fusion zone after heat treatment. From Fig. 5, it can be seen that after heat treatment the microstructure of the fusion zone consists of β, α2 and α phases. Meanwhile, from 900 °C isothermal section for Ti-Al-Nb system (Fig. 4(b)), the fusion zone is in the three-phase region. According to the research of Ti-15Al-12Nb (molar fraction, %), the microstructure of the alloy after furnace cooling mainly contains α2 and β phases [16]. In this work, the chemical composition of the fusion zone is similar to that in Ref. [16]. α2 phase precipitated is more than α phase. As the element content is similar to the TC11 alloy, more α phase precipitates in fusion zone near the TC11 alloy. Intermittent grain boundaries with α2/α phase can be seen in the fusion zone (Fig. 3(h)), which are broken by the deformation process. At the interface between the HAZ of Ti2AlNb alloy and the fusion zone, more α2 phase precipitates (Fig. 3(i)). In this area, the Al content is higher than that at the center of fusion zone, resulting in more α2 phase precipitation.
The microstructures of welding zone after heat treatment under different conditions are shown in Fig. 6. It can be seen that the microstructures of the fusion zone have different morphologies under different deformation conditions. In the HAZ of TC11 alloy, primary α phase (αp) is mainly lath with 20%+20% deformation degree (Fig. 6(g)) while αp phases are partly spheroidization under other deformation conditions (Figs. 6(a) and (d)). The possible mechanism that the lath α phase separates to short segments is the formation of sub-boundaries across α lamellar phase during hot deformation as the localized shear of the lamellar [17,18]. During the heat treatment, due to the atom diffusion β phase penetrates into α phase and separates α phase into short segments. Generally, β phase in α+β titanium alloys represents considerably lower flow stress than α phase [19], so β phase is easier to deform than α phase during forging. When the deformation degree is small in one time, main deformation occurs in β phase and little localized shear of α phase forms, so main α phase keeps the lath structure. Meanwhile, much inner-stress such as shear stress and dislocation are retained in grains after deformation due to the driving force of recrystallization during heat treatment [18]. When the deformation degree decreases, the inner-stress is less and the recrystallization degree is small, resulting in small αp of spheroidization degree. It can also be seen that the microstructures of the fusion zone are different by different cooling ways after forging. The microstructures of fusion zone under different deformation conditions are similar (Figs. 6(b) and (h)) by AC. And by WQ, obvious grain boundaries can be seen in the fusion zone and more fine phases precipitate along the grain boundaries (Fig. 6(e)). By WQ, more inner-stress retains, and during heat treatment there are more nucleation sites for the precipitating of α2 phase. As the previous instruction, at the interface between the HAZ of Ti2AlNb alloy and the fusion zone, more α2 phases precipitate. The microstructures of these areas under different deformation conditions have similar phenomenon.
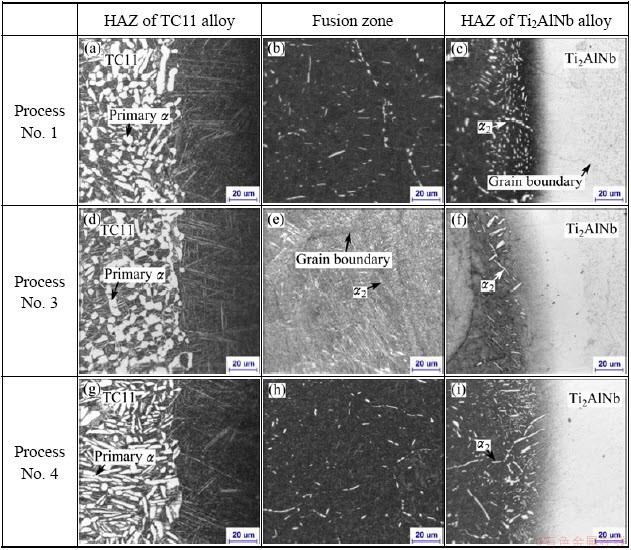
Fig. 6 Microstructures of welding zone after heat treatment under different deformation conditions
3.2 Mechanical properties
A summary of tensile tests at room temperature for welds with heat treatment is presented in Table 2. These data are the average values of at least two specimens. The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of the specimens with 20%+20% deformation is up to 1140 MPa, and that of the others is higher (up to 1190 MPa). In contrast, the specimens with twice forging have low yield strength (YS) of 1090 MPa. The elongations of all specimens are low. By comparison, specimens with WQ have better plasticity. The elongation of the specimen with WQ achieves 4.4% and the others are only 3.2%. The α2 slip remains planar, and α2/α2 cracks for continuous α2 grains are observed in Ti-Al-Nb alloys [20,21]. As the fusion zone contains more grain boundaries with α2 phase, pinning effect caused by α2 phase hinders the slip, which leads to the stress concentration at the grain boundaries. High stress concentration exists at α2/α2 grain boundaries, which is responsible for the α2/α2 grain-boundary cracks, resulting in low RT elongations.
Table 2 Mechanical properties of TC11/Ti2AlNb dual-alloy welds at room temperature under different deformation conditions

It can be noted that all the tensile specimens failed in the fusion zone regardless of the deformation conditions. This is different from the result of TAN’s work that specimens failed in TC11-base metal [12]. This is related to the welding method that results in the microstructure difference. Both-side welding could influence the properties of the weldment. The strength of the weldment is similar to the result in Ref. [12] (1180 MPa). But the elongation is much lower than that in Ref. [12] because of the specimen fracture in TC11 alloy. For Ti3Al/TC4 joints with no deformation [10], the highest tensile strength of joint reaches 831 MPa and fracture locates in the fusion zone. The properties of joints after deformation are better than those of Ti3Al/TC4 joints.
The Al and Nb contents of fusion zone are approximately 15% and 13%, respectively, which are between Al and Nb contents of TC11 and Ti2AlNb alloys. The tensile properties of the Ti-15Al-12Nb alloy are listed in Table 3 [16]. The microstructure of Ti-15Al-12Nb alloy with fewer equiaxed α2 phase produced by WQ exhibits UTS of 948 MPa and elongation of 1.3%, while microstructure with more equiaxed α2 phase produced by furnace-cooled (FC) exhibits UTS of 946 MPa and elongation of 18.47%. Meanwhile, the lamellar microstructure by FC has superior plasticity than thinner lamellar microstructure by WQ. In this work, the strength of weld is higher than the above result, but the elongation is lower. Compared with the Ti-15Al-12Nb alloy with fewer equiaxed α2 phase produced by WQ, the properties of Ti2AlNb/TC11 dual-alloy joint are better. The tensile properties of the joints are similar to some orthorhombic alloys such as Ti-22Al-24Nb [22], Ti-22Al-24Nb [23] and Ti-21Al-29Nb [24].
Table 3 Tensile properties of Ti-15Al-12Nb alloy [16]

Fractographic examination reveals different fracture mechanisms for the microstructures under different deformation conditions. In Figs. 7(a) and (b), the fracture morphologies show predominantly transgranular fracture over the fracture surface with shallow dimples and torn edges. The fracture morphology of the specimen with WQ (Fig. 7(c)) is mainly quasi-cleavage. On the fracture surface, fine and shallow dimples that benefit the plasticity of alloy can be found. Relatively, the RT elongation of specimen by WQ is better than others. In addition, secondary crack harmful to the plasticity of alloy can be found in the fracture surface. In Fig. 7(d), cleavage and faceted fracture are obvious throughout. The specimen exhibits a multilayer slip planes fracture characteristic of brittle metals.
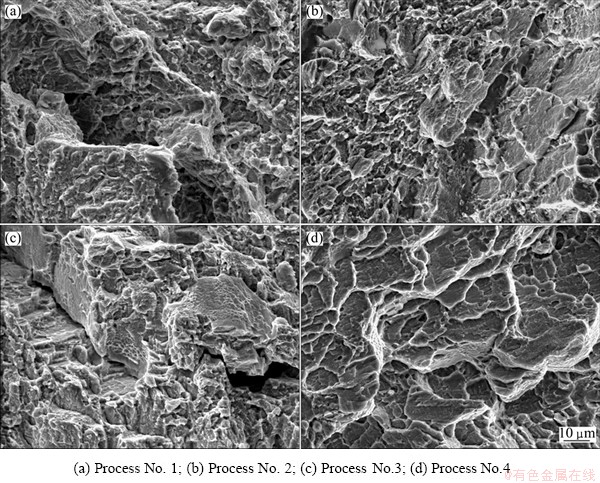
Fig. 7 Tensile fractographs of TC11/Ti2AlNb dual-alloy joints at room temperature
Table 4 Mechanical properties of TC11/Ti2AlNb dual-alloy joints under different deformation conditions after thermal exposure at room temperature
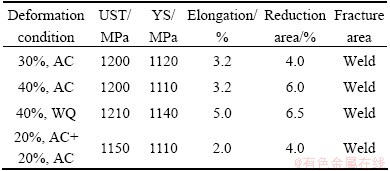
The room temperature tensile properties of Ti2AlNb/TC11 dual-alloy joints after exposure at 500 °C for 100 h are listed in Table 4. It can be seen that the ultimate tensile strength of specimens after thermal exposure is a little higher than that of the unexposed specimens and the ductility changes little. XIN et al [25] and JIA et al [26] reported the thermal exposure properties of Ti40 and Ti60 alloys, respectively. Their researches suggest that after thermal exposure, the ductility of the alloys has a decrease at room temperature as α2 phase and silicides precipitate. According to Ref. [26], the precipitation of α2 phase is the main reason for the ductility loss. However, in this work, the ductility of dual-alloy welds does not decrease. The XRD pattern of fusion zone microstructure after thermal exposure is shown in Fig. 8. Compared with Fig. 5, the phases in the fusion zone have little change. Thermal exposure of titanium alloy is a precipitation strengthening process. The fine α2 phase precipitate is responsible for the decrease of ductility and the increase of ultimate tensile strength [26]. In the fusion zone, the microstructure mainly consists of α2 and β phases, which is different from that of the two-phase titanium alloys with α and β phases. During thermal exposure, the content of precipitated α2 phase is nothing much compared with the content of primary α2 phase. So, it has little influence on the ductility of the joints. It can be concluded that thermal exposure at 500 °C has little effect on the ductility of Ti2AlNb/TC11 dual-alloy welds fractured in the fusion zone.
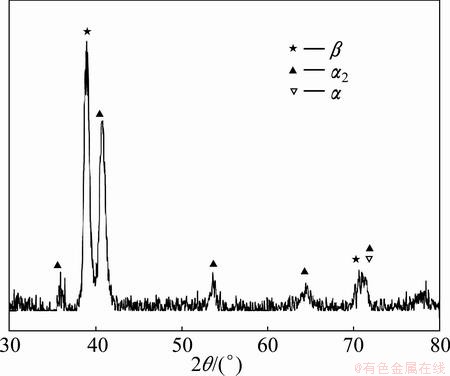
Fig. 8 XRD pattern of fusion zone after thermal exposure
4 Conclusions
1) The fusion zone of TC11/Ti2AlNb dual-alloy joint welded by EBW is composed of β phase. After deformation and heat treatment, the grain boundaries of the as-cast alloy are broken and the fusion zone mainly consists of β, α2 and α phases.
2) The fusion zone is the weak area in the tensile test. Specimens all fail in this area under different deformation conditions. The ultimate tensile strength of specimens is up to 1190 MPa at room temperature. All the joints have low elongation and SEM observation shows that the fracture mechanism is predominantly transgranular under different conditions. The joints by WQ after deformation have better plasticity than others, obtaining elongation of 4.4%.
3) After thermal exposure at 500 °C for 100 h, specimens all fail in fusion zone, and the tensile strength has slight increase, while the ductility changes little.
References
[1] LU Shi-qiang, LI Xin, WANG Ke-lu, DONG Xian-juan, FU M W. High temperature deformation behavior and optimization of hot compression process parameters in TC11 titanium alloy with coarse lamellar original microstructure [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(2): 353-360.
[2] GU Yi, QI Yan-ling, XIA Chang-qing, LI Xue-xiong, WANG Zhi-hui. Effects of thermal exposure on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC11 titanium alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(4): 997-1004. (in Chinese)
[3] WU Hong-yan, ZHANG Ping-ze, CHEN Wei, WANG Ling, ZHAO Hao-feng, XU Zhong. High-temperature tribological behaviors of Ti2AlNb-based alloys by plasma surface duplex treatment [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(5): 1121-1125. (in Chinese)
[4] ZHANG Jian-wei, LI Shi-qiong, LIANG Xiao-bo, CHENG Yun-jun. Research and application of Ti3Al and Ti2AlNb based alloys [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): s336-s341.
[5] LASALMONIE A. Intermetallics: Why is it so difficult to introduce them in gas turbine engines? [J]. Intermetallics, 2006, 14(10): 1123-1129.
[6] NISHIKIORI S, HATTORI H, NODA T, OKABE M, ISOBE S. Application of heat-resistant titanium-based compressor disk with dual structure [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996, 213(1): 124-127.
[7] GORMAN M D. Dual-property alpha-beta titanium alloy forgings: USA, 5795413 [P]. 1998-08-18.
[8] KLOTZ U E, HENDERSON M B, WILOCK I M, DAVIES S, JANSCHEK P, ROTH M, GASSER P, MCCOLVIN G. Manufacture and microstructural characterisation of bimetallic gas turbine discs [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2005, 21(2): 218-224.
[9] SUN Z, KARPPI R. The application of electron beam welding for the joining of dissimilar metals: An overview [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1996, 59(3): 257-267.
[10] ZHANG Hong-tao, HE Peng, FENG Ji-cai, WU Hui-qiang. Interfacial microstructure and strength of the dissimilar joint Ti3Al/TC4 welded by the electron beam process [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 425(1): 255-259.
[11] TAN Li-jun, YAO Ze-kun, ZHOU Wei, GUO Hong-zhen, ZHAO Yan. Microstructure and properties of electron beam welded joint of Ti-22Al-25Nb/TC11 [J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2010, 14(5): 302-306.
[12] TAN Li-jun, YAO Ze-kun, QIN Chun, GUO Hong-zhen, ZHANG Jian-wei. Effects of deformation temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded joint of dissimilar titanium alloys [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(8): 1533-1538. (in Chinese)
[13] TAN Li-jun, YAO Ze-kun, NING Yong-quan, GUO Hong-zhen. Effect of isothermal deformation on microstructure and properties of electron beam welded joint of Ti2AlNb/TC11 [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2011, 27(9): 1469-1474.
[14] LIU Ying-ying, YAO Ze-kun, GUO Hong-zhen, YANG Hang-hang. Microstructure and property of the Ti-24Al-15Nb-1.5Mo/TC11 joint welded by electron beam welding [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2009, 16(5): 568-575.
[15] ZHANG Yong-gang, HAN Ya-fang, CHEN Guo-liang, GUO Jian-ting, WAN Xiao-jing, FENG Di. Structural intermetallics [M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2001: 701-796. (in Chinese)
[16] PARADKAR A G, VARMA V K, JOSHI V, NANDY T K, GOGIA A K, KAMAT S V, KASHYAP B P. Microstructure and yield behavior of a high aluminum containing Ti-Al-Nb alloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33(8): 2763-2766.
[17] WEISS I, FROES F H, EYLON D, WELSCH G E. Modification of alpha morphology in Ti-6Al-4V by thermomechanical processing [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1986, 17(11): 1935-1947.
[18] PENG Xiao-na, GUO Hong-zhen, WANG Tao, YAO Ze-kun. Effects of β treatments on microstructures and mechanical properties of TC4-DT titanium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 533: 55-63.
[19] KIM J S, KIM J H, LEE Y T, PARK C G, LEE C S. Microstructural analysis on boundary sliding and its accommodation mode during superplastic deformation of Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 263(2): 272-280.
[20] KRISHNAMURTHY S, SMITH P R, MIRACLE D B. Preliminary evaluation of a Ti-24.5Al-17Nb/SiC composite [J]. Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1994, 31(6): 653-658.
[21] BOEHLERT C J, MAJUMDAR B S, KRISHNAMURTHY S, MIRACLE D B. Role of matrix microstructure on room-temperature tensile properties and fiber-strength utilization of an orthorhombic Ti-alloy-based composite [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1997, 28(2): 309-323.
[22] POPILLE F, DOUIN J. The dislocation microstructure in orthorhombic O Ti2AlNb deformed between RT and 800 °C [J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 1996, 73(5): 1401-1418.
[23] ROWE R G, KONITZER D G, WOODFIELD A P, CHWSNUTT J C. Tensile and creep behavior of ordered orthorhombic Ti2AlNb-based alloys [C]//JOHNSON L A, POPE D P, STIEGLER J O. High Temperature Ordered Intermetallic Alloys—IV. Pittsburgh, PA: Materials Research Society, 1991: 703-708.
[24] COWEN C J, BOEHLERT C J. Microstructure, creep, and tensile behavior of a Ti-21Al-29Nb (at.%) orthorhombic+B2 alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2006, 14(4): 412-422.
[25] XIN She-wei, ZHAO Yong-qing, ZENG Wei-dong, WU Huan. Research on thermal stability of Ti40 alloy at 550 °C [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 477(1): 372-378.
[26] JIA Wei-ju, ZENG Wei-dong, LIU Jian-rong, ZHOU Yi-gang, WANG Qing-jiang. Influence of thermal exposure on the tensile properties and microstructures of Ti60 titanium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 530: 511-518.
秦 春,姚泽坤,李誉之,宁永权,郭鸿镇
西北工业大学 材料学院,西安 710072
摘 要:研究热加工对电子束焊接TC11/Ti2AlNb双合金接头显微组织的影响,对焊接件热暴露前后的室温拉伸性能进行测试。结果表明:电子束焊接TC11/Ti2AlNb双合金熔合区主要由β相组成;经过变形和热处理后,熔合区主要由β、α2和α相组成,同时原始铸态的晶界在变形过程中破碎。在拉伸试验中,熔合区是薄弱区域;在不同的变形条件下,试样(热暴露前后)在此区域发生断裂。热处理后试样的最大室温拉伸强度达到1190 MPa;锻后水冷试样具有较好的塑性,其伸长率达到4.4%。相比较而言,经过(500 °C,100 h)的热暴露后,试样的室温拉伸强度略有上升,但塑性变化较小。拉伸断口SEM观察显示,在不同变形条件下穿晶断裂为主要的断裂机制。
关键词:热加工;钛合金;力学性能;热稳定性;电子束焊接
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (51175431) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Chun QIN; Tel: +86-29-88493744; E-mail: qinchun@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63494-4

