DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.03.14
磁制冷材料Ni-Mn-Ga合金的连续马氏体相变与奇异热膨胀特性
魏生贤1,何禧佳1,曹义明1,李 哲1,张清清1,时有明2,陶 昌2
(1. 曲靖师范学院 磁性材料及器件研究中心,曲靖 655011;
2曲靖师范学院 物理与电子工程学院,曲靖 655011)
摘 要:为深入解磁制冷材料Ni-Mn-Ga合金的热膨胀特性,利用SEM、XRD、DSC及PPMS系统分别对合金Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 (x=0.2,0.6,1.0)的组分、结构、相变及热膨胀特性进行实验测试。结果表明:随着Ni含量的增加,合金的马氏体相变温度逐渐增加。当x从0.2增至1.0时,合金正反马氏体相变峰温分别从274、282 K增至300、309 K,且存在7~10 K的热滞后。在升降温过程中,x为0.2和0.6的合金出现两个连续的马氏体相变、x=1.0的合金发生磁-结构耦合转变,相变温区分别为33.5 K、35.1 K、27.5 K。零场热应变曲线表明,合金具有各向同性的热膨胀特性。马氏体相与奥氏体相的热膨胀系数分别为5.02×10-6~10.31×10-6 K-1和3.74×10-6~7.72×10-6 K-1之间。马氏体相变过程中合金出现正热膨胀行为和奇异的负热膨胀行为,最大的负热膨胀系数约为-139.84×10-6 K-1。结合实验数据,从微观的角度对Ni-Mn-Ga的负热膨胀效应进行初略讨论。
关键词:磁制冷;Ni-Mn-Ga合金;马氏体相变;热膨胀特性;负热膨胀行为
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-03-0549-10 中图分类号:TG132.1 文献标志码:A
与气体压缩式制冷技术相比,固态磁制冷技术因其结构紧凑、低噪声、高效率(效率可达卡诺循环的30%~60%,压缩式制冷效率只有卡诺循环的5%~ 10%[1])、节能(比压缩式制冷节能20%~30%[2])、绿色环保[3-4]等优点而备受关注。因此,磁制冷技术被认为是压缩式制冷技术的替代技术[2, 4-5]。磁制冷技术是一种基于磁性材料在磁化和退磁过程中自身温度升高或降低的磁热效应的制冷技术。典型的磁制冷材料有Gd-Si-Ge[6-7]、La-Fe-Si[8-9]、La-Fe-Si-H[10]、Mn-Fe- P-As[11]、Ni-Mn-Ga[12-13]等化合物,它们发生一级磁-结构相变(即磁性转变与结构转变同时发生)时具有较大的磁热效应。比较而言,这些磁制冷材料的制冷性能基本相当。但Gd-Si-Ge、La-Fe-Si及La-Fe-Si-H系列化合物中含有稀土元素,价格昂贵;Mn-Fe-P-As中含有剧毒元素(As);而Ni-Mn-Ga合金无毒无害、生物相容性强,制备简单、成本相对低廉[14-15],是近年来磁制冷技术的重点研究对象之一。
研究表明,Ni2MnGa合金在降温过程中会发生两个分离的相变:在376 K附近发生二级磁转变(或称为居里转变);在202 K附近发生一级马氏体相变(或称为结构转变)[16]。通过组分调节可实现Ni-Mn-Ga合金一级磁-结构转变,此时合金具有较大的磁热效应[12-14]。受组分、热处理工艺、内应力等的影响,Ni-Mn-Ga合金在马氏体相变前后会出现分离的预马氏体相变[17-18]或中间马氏体相变[19-20]。连续的马氏体相变有利于拓宽合金相变的温度区间、提高材料的制冷性能。但对于Ni-Mn-Ga合金连续的马氏体相变报道较少,深入开展此方面的研究是非常必要的。
此外,在无外加磁场的条件下,Ni-Mn-Ga合金发生马氏体相变时,合金热应变曲线的斜率会发生改变或突变。即发生马氏体相变时,合金热应变曲线的斜率有的为正[21-23]、有的为负[23-27]。然而,上述研究中合金热应变曲线斜率正负(或大小)的变化主要用于表征马氏体相变是结构上的相变。很少有研究者关注热应变曲线斜率正负的含义及其产生的机制。事实上,热应变曲线斜率的正负代表的是在该温度区间材料具有正热膨胀或负热膨胀效应。热应变曲线斜率发生改变、尤其是突变,意味着合金热膨胀系数的突变,即合金的体积突然增大或减小。例如,Ni54.75Mn20.25Ga25单晶在马氏体相变附近(330~333.5 K)的线膨胀系数达到了12×10-4 K-1 [27],即约4 K的温差内合金体积膨胀了1.44%。工程应用中,这种现象的发生会严重降低材料的抗热冲击性,缩短材料的使用寿命[28],对磁制冷腔体或装置造成严重损坏、降低系统的总体性能,甚至导致系统瘫痪。因此,在磁制冷腔体的设计中须预留足够的空间,以防磁性材料体积突变导致系统瘫痪。为确定合适的预留空间,对Ni-Mn-Ga合金的热膨胀系数进行实验测试是非常必要的。为解决此问题,本文对Ni54+xMn19-xGa27(x=0.2,0.6,1.0)合金的结构、相变及热膨胀特性进行了实验测试与分析。结果显示,x=0.2和0.6的合金出现了两个连续的马氏体相变,x=1.0的合金出现了磁-结构转变。3个合金在马氏体相变附近出现了奇异的负热膨胀行为。此负热膨胀效应很可能是马氏体变体的成核、重取向与磁态、热膨胀相互竞争的结果。研究结果对全面了解Ni-Mn-Ga合金的热膨胀特性及磁制冷腔体预留空间大小的设计具有较好的指导意义。
1 实验
实验选用高纯金属单质镍Ni、锰Mn、镓Ga(纯度分别为99.98%、99.98%、99.999%)为原料,采用 WK2 型非自耗高真空电弧炉,在高纯氩气保护下制备名义组分为Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 (x=0.2,0.6,1.0) 的多晶样品。为使样品成分均匀化, 所有样品均反复熔炼4次,但样品未做任何热处理。扫描电子显微镜(Scanning electron microscope,SEM)测试显示,实际组分与名义组分基本一致。室温下样品的晶体结构采用Rigaku D/max-Ultima IV多功能X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffraction,XRD)加以表征。样品的相变温度由差示扫描热分析仪(Differential scanning calorimetry,DSC)加以测定,测试速率为10 K/min。利用物性测量系统(Physical properties measurement system,PPMS,美国Quantum Design 公司)的振动样品磁强计(Vibrating sample magnetometer,VSM)测量样品低磁场(500 Oe)下磁化强度(Magnetization,M)与温度(T)之间的热磁曲线[M(T)],以便确定样品的磁转变;升降温测试速率为1.5 K/min。样品在零磁场下的热应变采用标准应变仪接入PPMS系统进行测试:温度范围为50~360 K,加热/冷却速率为3 K/min,试样为2 mm×5 mm×10 mm的长方体。
2 结果与分析
2.1 合金的相变特性
Ni54+xMn19-xGa27(x=0.2,0.6, 1.0)合金的DSC曲线及热磁曲线M(T)如图1所示。图1中Ms、Mf和As、Af分别表示正、反马氏体相变开始与结束的温度;Mi与Ai分别为合金中间马氏体态的温度;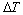 与
与 分别表示马氏体相变和中间马氏体相变的热滞后。正、反马氏体相变峰值温度由TM≈(Ms+Mf)/2,TA≈(As+Af)/2近似计算。所有合金的相变温度及其峰值温度如表1所列。
分别表示马氏体相变和中间马氏体相变的热滞后。正、反马氏体相变峰值温度由TM≈(Ms+Mf)/2,TA≈(As+Af)/2近似计算。所有合金的相变温度及其峰值温度如表1所列。
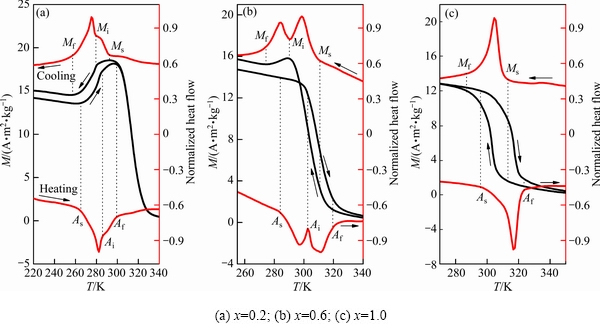
图1 Ni54+xMn19-xGa27合金的DSC曲线与热磁曲线M(T)
Fig. 1 DSC and M(T) curves of Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 alloys
表1 Ni54+xMn19-xGa27合金的马氏体转变温度与热滞后
Table1 Martensitic transformation temperatures and thermal hysteresis of Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 alloys
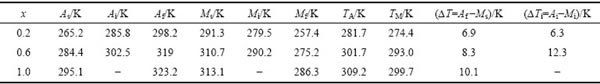
由图1和表1可知:1) 合金相变温度及其峰值温度随x的增大而单调地增大。即随着Ni部分替代Mn,Ni54+xMn19-xGa27合金马氏体相变温度单调地增加。这一结果与前期关于Ni50+xMn25-xGa25的研究结果基本一致[29]。马氏体相变温度增大是由于Ni部分替代Mn致使合金晶胞体积减小而导致的[30]。2) 当x从0.2增至1.0时,合金正、反马氏体相变峰值温度分别由274、282 K增至 300、309 K;升降温过程存在7 ~ 10 K的热滞后。3)对于x为0.2和0.6的合金,马氏体相变过程中各存在一个中间马氏体转变;中间马氏体转变的温度Mi和Ai分别约为280、290 K与286、303 K,存在6 K与12 K的热滞后。
图1(a)的热磁曲线M(T)显示:对于x=0.2的合金,从340 K降温至Ms点过程中,合金的磁化强度迅速增大、合金从顺磁奥氏体态转变成铁磁的奥氏体态(属于二级磁相变)。随着温度进一步降低,磁化强度在Ms与Mi处出现了缓慢降低和迅速减小,意味着合金在上述两点处发生了马氏体相变和中间马氏体相变;当温度达到Mf时,磁化强度基本趋于稳定,此时相变完成。这种连续的马氏体相变较为少见,但它有利于扩大相变温区、提高材料的制冷性能。在随后的升温过程中,磁化强度在As处急剧升高、Ai处缓慢增大、Af处趋于稳定,意味着连续的反马氏体相变的开始与结束。随着温度的进一步升高,磁化强度出现急剧降低,合金发生二级磁相变。
图1(b)所示的DSC曲线与M(T)曲线显示:对于x=0.6的合金,在降温过程中,合金在Ms与Mi之间发生了一个磁转变、在Mi与Mf之间发生了一个马氏体相变。在随后的升温过程中,合金在As与Ai间发生了一个反马氏体相变、在Ai与Af间发生了一个磁转变。结合表1的数据,Ms与Af间存在8 K的热滞后,意味着合金在Ms与Mi间及Ai与Af间发生的是磁-结构相变。对于x=0.6的合金,在升降温过程中同样存在两个连续的马氏体相变。
图1(c)显示,在降温和升温过程中,x=1.0的合金正、反马氏体相变与磁转变同时发生,达到了磁-结构耦合转变。
由上述分析可知:1) 对于x=0.2和0.6的合金,在升降温过程中存在两个连续的马氏体相变,整个相变的温区(用((Af-As)+(Ms-Mf))/2表示)分别为33.5 K与35.1 K。2) 对x=1.0的合金,升降温过程合金发生了磁-结构耦合转变,相变温区为27.5 K。3) 连续马氏体相变及较大的相变温区很可能是由于样品制备中引入的内应力所导致的。
2.2 合金的X射线衍射分析
图2所示为Ni54+xMn19-xGa27合金粉末在室温下的XRD谱。XRD谱表明:1) 当x=0.2时,合金的主要衍射峰显示,室温下此合金为立方奥氏体结构,其晶格常数为0.58155 nm。其(220)峰出现了一个小的劈裂(见标“*”的峰位),这可能是由于此样品的马氏体相变温度接近室温,以至于室温下出现了少量的马氏体相[31]。2)当x=0.6时,XRD谱表明,此样品主要是7M调制马氏体结构,并残留少量的非调制马氏体结构[13]。依据正交晶体结构给出了此合金的晶格参数a=0.84855 nm, b=0.56487 nm,c=0.51429 nm。分析发现,7M调制马氏体结构(222)峰分裂成(220), (202)和(022) 3个峰,在其它Ni-Mn-Ga合金中已有类似的报道[13-14]。3) 当x=1.0时,室温下为非调制的四方马氏体结构,晶格常数a=b=0.76814 nm , c=0.67085 nm。以上分析表明,在Ni54+xMn19-xGa27合金中,随着Ni含量的增加,马氏体相变温度逐渐增大,相变温度的变化趋势与DSC测试结果一致。
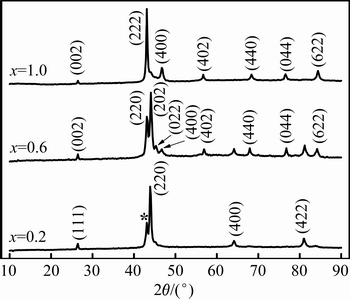
图2 Ni54+xMn19-xGa27合金粉末室温下的XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 alloy powder at room temperature
2.3 合金的热膨胀特性
2.3.1 合金的热应变
为了研究Ni54+xMn19-xGa27合金的热膨胀特性,本研究对合金在零磁场下的应变(ΔL/L293 K)(293 K表示室温)随温度的变化行为进行了测试,结果如图3~5所示。由图3可知:1) 在奥氏体相和马氏体相,随着温度的升高、合金热应变逐渐增大,呈现出近似线性的正膨胀行为;而且,在升降温过程中合金的热应变基本重合在一起,无热滞后现象。2) 在马氏体相变附近,x=0.2和0.6的合金热应变随温度的降低出现了跳跃式的减小再增大的趋势;而在反马氏体相变过程中,合金热应变随温度的升高则出现跳跃式的减小再增大的趋势,如图5(a)和(b)所示。热应变的上述变化趋势与图1(a)和(b)的两个连续马氏体相变相对应。而且在第二个马氏体相变过程中,随着温度的降低、合金的热应变逐渐增大,即合金出现了明显的、奇异的负热膨胀行为。在升降温过程中合金的热应变曲线不重合,存在6 K和12 K的热滞后。3)对于x=1.0的合金,马氏体相变附近,随着温度的降低和升高合金热应变出现跳跃式增大和减小,展现出非常明显的负热膨胀行为(存在10 K的热滞后)。热应变变化量远大于x=0.2和0.6合金的热应变变化量(如图5所示),这可能是由于x=1.0的合金具有较强的磁-结构耦合相互作用而引起的。
2.3.2 合金在马氏体相与奥氏体相的热膨胀特性
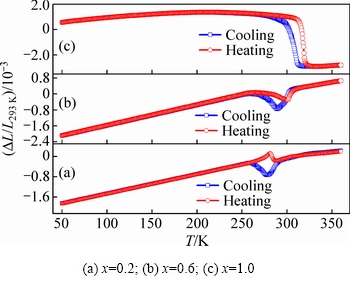
图3 合金Ni54+xMn19-xGa27的热应变曲线
Fig. 3 Thermal strain curves of Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 alloys
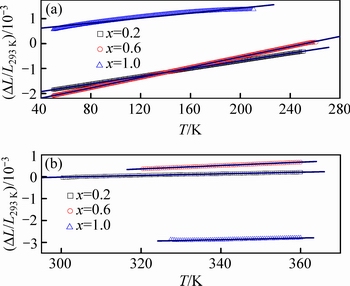
图4 合金在马氏体相与奥氏体相的热应变曲线
Fig. 4 Thermal strain curves of alloys at pure martensitic (a) and austenitic (b) states
因合金在马氏体相与奥氏体相的热应变曲线与温度基本成线性关系,现将合金升温过程的热应变数据做线性拟合(见图4),用拟合曲线的斜率代表合金的线膨胀系数α,如表2所示。表2的数据表明:1) 对于所有的合金,线性拟合的相关系数R均大于0.97,说明合金热应变与温度相关性较强;2) 随着Ni含量的增加,合金热膨胀系数变化不大,马氏体相与奥氏体相的热膨胀系数分别为5.02×10-6~10.31×10-6 K-1与3.74×10-6~7.72×10-6 K-1。两相的热膨胀系数与Ni含量基本上无直接关系,很可能是Ni含量变化太小的缘故;3) 对比两相的热膨胀系数可知,马氏体相的热膨胀系数约为奥氏体相的1.34~2.05倍。
2.3.3 马氏体相变附近的热膨胀特性
表2 合金Ni54+xMn19-xGa27在马氏体相和奥氏体相的平均热膨胀系数
Table 2 Average thermal expansion coefficients of Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 alloys at martensite and austenite phases
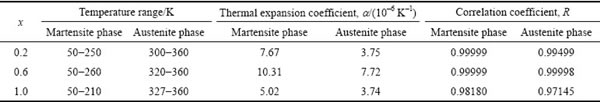
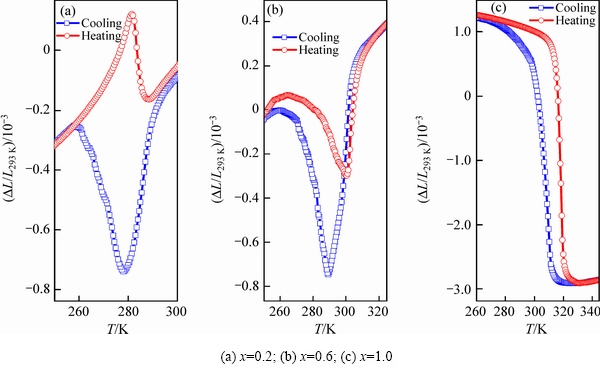
图5 合金Ni54+xMn19-xGa27在马氏体相变附近的应变曲线
Fig. 5 Strain curves of alloys Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 near martensitic transformation
图5所示为合金在马氏体相变附近的热应变曲线。对于相变附近的平均负热膨胀系数,本文取热应变曲线最高点和最低点对应的应变值和温度值加以估算,结果如表3所列。
表3 马氏体相变附近合金的平均热膨胀系数
Table 3 Average thermal expansion coefficients of Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 near martensitic transformation
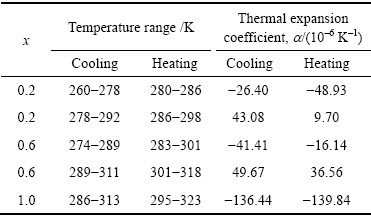
由表3的数据可知:1) 对于x=0.2和0.6的合金,在两个连续的马氏体相变过程中,合金的平均热膨胀系数分别由43.08×10-6与49.67×10-6 K-1转变为-26.40×10-6与-41.41×10-6 K-1;在随后连续的反马氏体相变过程中,合金的平均热膨胀系数分别由-48.93×10-6与-16.14×10-6 K-1转变为9.70×10-6与36.56×10-6 K-1。2) 降温与升温过程中,合金x=1.0的平均热膨胀系数均为负值;其数值较大、分别约为-136.44与-139.84×10-6 K-1。如此大的负热膨胀系数很可能是由于x=1.0的合金具有磁-结构耦合相变所致的。
2.3.4 合金热膨胀的各向同性实验
为验证Ni-Mn-Ga合金热膨胀是各向同性的,以x=0.2的合金为研究对象,将应变片沿相互垂直的两个方向(AB与BC方向)贴于样品上分别进行热应变测试,结果如图6(a)和(c)所示。由图6(a)和(c)可知,两个方向上的热应变曲线基本相同。为精确判定两方向上合金热膨胀特性的差别,将升温过程两相的应变数据分别做线性拟合,结果如图6(b)和(d)所示。结果显示:1) 在马氏体相,AB与BC方向的负热膨胀系数分别为7.6705×10-6 K-1与7.6683×10-6 K-1;2) 对于奥氏体相,两方向对应的热膨胀系数分别为3.7512×10-6 K-1与3.7751×10-6 K-1。在连续反马氏体相变过程(图6未给出)中,合金的热膨胀系数分别为-48.934与9.703×10-6 K-1(AB方向)和-48.893与9.754×10-6 K-1(BC方向)。由此可知,Ni-Mn-Ga合金在任意两个垂直方向上的热膨胀系数近似相等,这说明此类合金的热膨胀是各向同性的。
2.3.5 合金负热膨胀机理的讨论
从目前的研究来看,负热膨胀效应的机理主要可分为振动效应、铁电相变机制、阳离子迁移机制和磁容积效应等。其中,1) A2M3O12(A为碱土金属、M为过渡金属)[32]、ZrV2O7[33]、TiF3[34]、Ag3[Co(CN)6][35]等材料的负膨胀效应源于振动效应,主要由桥氧原子的横向低能热振动或刚性多面体热摆动耦合作用所驱动;2) PbTiO3基钙钛矿结构材料的负热膨胀效应主要源于铁电转变[36];3) LaCu3Fe4O12[37]和BiNiO3[38]的负热膨胀则源于温度引起的阳离子迁移;4) 锰氮化合物[39]及LaFe13-xMx(M为Si,Al等)金属间化合物[9]的负热膨胀效应源于磁容积效应。除上述四类材料以外,具有热弹性马氏体相变的材料,如Ni-Ti[40]、Ni-Fe[41]、Mn-Co-Ge基化合物[42]等,在马氏体相变过程中同样呈现出显著的负热膨胀效应。其中,Ni-Ti与Ni-Fe的负热膨胀效应被归因于其晶体结构的转变(高温立方B2结构→马氏体单斜B19′结构)[40, 43]。与之类似,Mn-Co-Ge基合金的负热膨胀效应亦可理解为晶体结构上的变化所致。
Ni-Mn-Ga合金的热弹性马氏体相变属于结构转变(高温立方L21结构→低温调制/非调制四方马氏体结构)。变温XRD与中子衍射均表明,高温立方相到低温马氏体相的转变过程中,合金的晶胞体积略有减小[16, 20, 44]。尽管Ni-Mn-Ga合金在马氏体相变过程中的负热膨胀效应是由结构相变所引起的,但此效应不可归因于两相晶胞体积的变化。Ni-Mn-Ga合金在温度诱导下发生马氏体相变时伴随磁态的变化,如图1所示。磁态的变化对合金负热膨胀效应亦存在一定的影响,如图5所示。结合表3的数据,对比图1与5可知,与x=0.2的合金(铁磁奥氏体→铁磁马氏体)相比,马氏体相变过程中x=1.0的合金(顺磁奥氏体→铁磁马氏体)的负热膨胀效应更为显著。前期研究显示,孪晶界移动所引起的马氏体变体的重取向会导致合金微观体积的变化[45-46]。而且,马氏体相变过程中结构相变与磁性变化存在较强的耦合作用,有利于孪晶界的移动。基于上述分析,本研究初略推测该合金体系在马氏体相变过程中的奇异负热膨胀行为很可能是马氏体变体的成核、重取向与磁态、热膨胀相互竞争的结果;其背后所隐含的物理机制目前尚不清楚,是个值得进一步深入研究的课题。
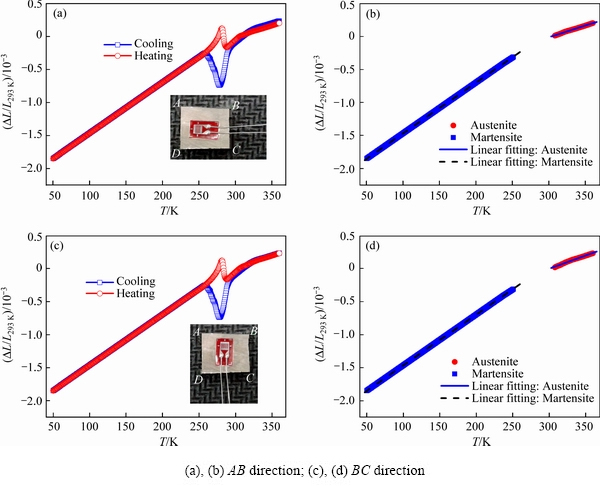
图6 x=0.2合金沿AB、BC方向的热应变
Fig. 6 Thermal strain of alloy with x=0.2 measured along AB, BC directions
3 结论
1) 随着Ni含量的逐渐增大,Ni54+xMn19-xGa27合金的马氏体相变温度逐渐增大。当x从0.2增至1.0时,合金正、反马氏体相变峰值温度分别由274、282 K增至 300、309 K,且存在7~10 K的热滞后。
2) 对于x=0.2和0.6的合金,在升降温过程中出现了两个连续的马氏体相变,整个相变温区分别为33.5 K与35.1 K。对x=1.0的合金,升降温过程合金发生了磁-结构耦合转变,相变温区为27.5 K。连续马氏体相变及较大的相变温区很可能是由于样品制备中引入的内应力所导致的。
3) XRD分析显示:随着Ni含量的增加,合金室温下的结构由立方奥氏体结构(x=0.2)过渡到7M调制马氏体结构(x=0.6)、最后转变为四方马氏体结构(x=1.0)。即随着Ni含量的增加,马氏体相变温度逐渐增大,XRD定性分析与DSC定量测试结果一致。
4) 零场热应变曲线表明:Ni-Mn-Ga合金具有各向同性的热膨胀行为。在马氏体相和奥氏体相,合金呈现出正膨胀行为,热膨胀系数分别位于5.02×10-6~10.31×10-6 K-1与3.74×10-6~7.72×10-6 K-1之间。马氏体相的热膨胀系数约为奥氏体相的 1.34 ~2.05倍。
5) 对于x=0.2和0.6的合金,在连续马氏体相变过程中均存在一个热膨胀行为和一个负热膨胀行为。对于x=1.0的合金,在磁-结构相变中存在明显的、异常的负热膨胀行为,且其最大负热膨胀系数约为-139.84×10-6 K-1,远大于前两者的热膨胀系数。该合金体系的负热膨胀行为,很可能是马氏体变体的成核、重取向与磁态、热膨胀相互竞争所引起的。
REFERENCES
[1] Yu B f, Liu M, Peter W E, Andrej K. A review of magnetic refrigerator and heat pump prototypes built before the year 2010[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2010, 33 (6): 1029-1060.
[2] Velázquez D, Estepa C, Palacios E, Burriel R. A comprehensive study of a versatile magnetic refrigeration demonstrator[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2016, 63: 14-24.
[3] 李振兴, 李 珂, 沈 俊, 戴 巍, 高新强, 郭小惠, 公茂琼. 室温磁制冷技术的研究进展[J]. 物理学报, 2017,66(11): 110701.
Li Zhen-xing, Li Ke, SHEN Jun, Dai Wei, Gao Xin-qiang, Guo Xiao-hui, Gong Mao-qiong. Progress of room temperature magnetic refrigeration technology[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017,66(11): 110701.
[4] 郑新奇, 沈 俊, 胡凤霞, 孙继荣, 沈保根. 磁热效应材料的研究进展[J]. 物理学报, 2016,65(21): 217502.
Zheng Xin-qi, Shen Jun, Hu Feng-xia, Sun Ji-rong, Shen Bao-gen. Research progress in magnetocaloric effect materials[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65 (21): 217502.
[5] Romero G J, Ferreiro G R, Carbia C J, Romero G M. A review of room temperature linear reciprocating magnetic refrigerators[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013, 21: 1-12.
[6] Pecharsky V K, Gschneidner K A. Giant magnetocaloric effect in Gd5(Si2Ge2)[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1997, 78 (23): 4494-4497.
[7] James D M, Morrison K,Perkins G K,Deborah L S, Lograsso T A, Gschneidner K A, Pecharsky V K,Cohen L F. Metamagnetism seeded by nanostructural features of single-crystalline Gd5Si2Ge2[J]. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(37): 3780-3783.
[8] Fujita A, Fujieda S, Hasegawa Y, Fukamichi K. Itinerant-electron metamagnetic transition and large magnetocaloric effects in La(FexSi1-x)13 compounds and their hydrides[J]. Physical Review B, 2003, 67 (10): 104416.
[9] Hu F X,Shen B G, Sun J R,Cheng Z H,Rao G H,Zhang X X. Influence of negative lattice expansion and metamagnetic transition on magnetic entropy change in the compound LaFe11.4Si1.6[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 78 (23): 3675-3677.
[10] Lyubina J, Nenkov K, Schultz L, Gutfleisch O. Multiple metamagnetic transitions in the magnetic refrigerant La(Fe, Si)13Hx [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 101(17): 177203.
[11] Tegus O, Brück E, Buschow K H J, de Boer F R. Transition-metal-based magnetic refrigerants for room- temperature applications[J]. Nature, 2002, 415(6868): 150-152.
[12] Li Z B, Zhang Y D, Sánchez-Valdés C F, Sánchez L J L, Esling C, Zhao X, Zuo L. Giant magnetocaloric effect in melt-spun Ni-Mn-Ga ribbons with magneto-multistructural transformation[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(4): 044101.
[13] Li Z, Xu K, Zhang Y L, Tao C, Zheng D, Jing C. Two successive magneto-structural transformations and their relation to enhanced magnetocaloric effect for Ni55.8Mn18.1Ga26.1 Heusler alloy[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 15143.
[14] Babita I, Gopalan R, Manivel R M, Chandrasekaran V, Ram S. Magnetostructural transformation, microstructure, and magnetocaloric effect in Ni-Mn-Ga Heusler alloys[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102(1): 013906.
[15] Duan J F, Long Y, Bao B, Zhang H, Ye R C, Chang Y Q, Wan F R, Wu G H. Experimental and theoretical investigations of the magnetocaloric effect of Ni2.15Mn0.85-xCuxGa (x=0.05,0.07) alloys[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 103(6): 063911.
[16] Webster P J, Ziebeck K R A, Town S L, Peak M S. Magnetic order and phase transformation in Ni2MnGa [J]. Philosophical Magazine Part B, 1984, 49(3): 295-310.
[17] Liu J Y, Wang J M, Zhang H B, Jiang C B, Xu H B. Effect of directional solidification rate on the solidified morphologies and phase transformations of Ni50.5Mn25Ga24.5 alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 541: 477-482.
[18] Cui Y T, Chen J L, Liu G D, Wu G H, Wang W L. Characteristics of the premartensitic transition strain in ferromagnetic shape memory Ni50.5Mn24.5Ga25 single crystals[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2004,16 (18): 3061-3069.
[19] 敖 玲, 王文洪, 陈京兰, 高淑侠, 吴光恒. 郝斯勒合金Ni-Mn-Ga中间马氏体相变研究[J]. 物理学报, 2001,50(4): 793-796.
Ao Ling, Wang Wen-hong, Chen Jing-lan, Gao Shu-xia, Wu Guang-heng. Investigation on intermartensitic transformation in Ni-Mn-Ga alloy [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2001, 50(4): 793-796.
[20] Li Z B, Yang B, Zhang Y D, Esling C, Zou N F, Zhao X, Zuo L. Crystallographic insights into the intermartensitic transformation in Ni-Mn-Ga alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 74: 9-17.
[21] Rudajevová A. Analysis of the thermal expansion characteristics of Ni53.6Mn27.1Ga19.3 alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 430: 153-157.
[22] Rudajevová A, Sroub J, Lang V. Influence of heat transfer on determination of transient temperatures for Ni53.6Mn27.1Ga19.3 shape memory alloy from dilatometric data[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 2009, 30(3): 969-975.
[23] Kourov N I, Pushin V G, Korolev A V, Marchenkov V V, Marchenkova E B, Kazantsev V A, Kuranova N N, Popov A G. Crystal structure and physical properties of magnetic shape memory alloys Ni50–xCuxMn29Ga21[J]. Physics of the Solid State, 2013, 55(12): 2471-2478.
[24] Pushin V G, Kourov N I, Korolev A V, Marchenkov V V, Marchenkova E B, Kazantsev V A, Kuranova N N, Popov A G. Effect of cobalt doping on thermoelastic martensitic transformations and physical properties of magnetic shape memory alloys Ni50–xCoxMn29Ga21[J]. Physics of the Solid State, 2013, 55(12): 2413-2421.
[25] Sakon T, Nagashio H, Sasaki K, Susuga S, Numakura D, Abe M, Endo K, Yamashita S, Nojiri H, Kanomata T. Thermal strain and magnetization of the ferromagnetic shape memory alloy Ni52Mn25Ga23 in a magnetic field[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2013, 74 (1): 158-165.
[26] Sakon T, Otsuka K, Matsubayashi J, Watanabe Y, Nishihara H, Sasaki K, Yamashita S, Umetsu R Y, Nojiri H, Kanomata T. Magnetic properties of the ferromagnetic shape memory alloys Ni50+xMn27-xGa23 in magnetic fields[J]. Materials, 2014, 7(5): 3715-3734.
[27] Vasil’ev A N, Estrin E I, Khovailo V V, Bozhko A D, Ischuk R A, Matsumoto M, Takagi T, Tani J. Dilatometric study of Ni2+xMn1-xGa under magnetic field[J]. International Journal of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics, 2002, 12(1): 35-37.
[28] 马 骁,祝 星,赵仲勋,曹姗姗,柯常波,张新平. 显微组织不均匀性对富Ti 含量Ti-Ni合金负热膨胀行为的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报,2018,28(3): 446-456.
MA Xiao, ZHU Xing, ZHAO Zhong-xun, CAO Shan-shan, KE Chang-bo, ZHANG Xin-ping. Influence of anisotropic microstructure on negative thermal expansion behavior of Ti-rich Ti-Ni alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018,28(3): 446-456.
[29] 柳祝红, 胡凤霞, 王文洪, 陈京兰, 吴光恒, 高书侠, 敖 玲. 哈斯勒合金Ni-Mn-Ga的马氏体相变和磁增强双向形状记忆效应[J]. 物理学报, 2001, 50(2): 233-238.
Liu Zhu-hong, Hu Feng-xia, Wang Wen-hong, Chen Jing-lan, Wu Guang-heng, Gao Shu-xia, Ao Ling. Investigation on martensitic transformation and field-induced two-way shape memory effect of Ni-Mn-Ga alloy[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2001, 50(2): 233-238.
[30] 蔡培阳, 冯尚申, 薛双喜, 陈卫平, 周 英, 吴建波, 王古平. 定向凝固Ni47Mn32Ga21多晶合金的结构、相变及磁特性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(11): 2869-2974.
CAI Pei-yang, FENG Shang-shen, XUE Shuang-xi, CHEN Wei-ping, ZHOU Ying, WU Jian-bo, WANG Gu-ping. Structure, phase transformation and magnetic properties in polycrystalline Ni47Mn32Ga21 directionally solidified alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(11): 2869-2974.
[31] Panda A K, Ghosh M, Arvind K, Mitra A. Magnetic transitions and structure of a NiMnGa ferromagnetic shape memory alloy prepared by melt spinning technique[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2008, 320 (17): L116 - L120.
[32] Evans J S O, Mary T A, Sleight A W. Negative thermal expansion in a large molybdate and tungstate family [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1997, 133(2): 580-583.
[33] Khosrovani N, Sleight A W, Vogt T. Structure of ZrV2O7 from -263 to 470 ℃[J] Journal of Solid State Chemistry,1997,132(2): 355-360.
[34] Wang L, Yuan P F, Wang F, Sun Q, Liang E J, Jia Y, Zheng X G. Negative thermal expansion in TiF3 from the first-principles prediction[J]. Physics Letters A, 2014,378 (38/39): 2906-2909.
[35] Goodwin A L, Calleja M, Conterio M J, Dove M T, Evans J S O, Keen D A, Peters L, Tucker M G. Colossal positive and negative thermal expansion in the framework material Ag3[Co(CN)6][J]. Science, 2008, 319(5864): 794-797.
[36] CHEN J, NITTALA K, FORRESTER J S, JONES J L, DENG J X, YU R B, XING X R. The role of spontaneous polarization in the negative thermal expansion of tetragonal PbTiO3-based compounds[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(29): 11114-11117.
[37] Long Y W, Hayashi N, Saito T, Azuma M, Muranaka S, Shimakawa Y. Temperature-induced A–B intersite charge transfer in an A-site-ordered LaCu3Fe4O12perovskite[J]. Nature, 2009, 458: 60-63.
[38] Azuma M, Chen W T, Seki H, Czapski M, Olga S, Oka K, Mizumaki M, Watanuki T, Ishimatsu N, Kawamura N, Ishiwata S, Tucker M G, Shimakawa Y, Attfield J P. Colossal negative thermal expansion in BiNiO3induced by intermetallic charge transfer[J]. Nature Communications, 2011, 2: 347.
[39] Takenaka K, Takagi H. Giant negative thermal expansion in Ge-doped anti-perovskite manganese nitrides [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 87: 261902.
[40] Mavoori H, Jin S. Low-thermal-expansion copper composites via negative CTE metallic elements[J]. Journal of the Minerals, 1998, 50(6): 70-72.
[41] SCHILFGAARDE M V, ABRIKOSOV I A, JOHANSSON B. Origin of the Invar effect in iron–nickel alloys [J]. Nature, 1999, 400: 46-49.
[42] Zhao Y Y, Hu F X, Bao L F, Wang J, Wu H, Huang Q Z, Wu R R, Liu Y, Shen F R, Kuang H, Zhang M, Zuo W L, Zheng X Q, Sun J R, Shen B G. Giant negative thermal expansion in bonded MnCoGe-based compounds with Ni2In-type hexagonal structure[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(5): 1746-1749.
[43] Uchil J, Mohanchandra K P, Kumara K G, Mahesh K K, Murali T P. Thermal expansion in various phases of nitinol using TMA [J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 1999, 270(3/4): 289-297.
[44] Yao J, Zheng X D, Cai W, Sui J H. Characterization of free-standing nanocrystalline Ni55.2Mn24.7Ga19.9 Gd0.2high temperature shape memory thin film[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 661: 43-48.
[45] Ullakko K, Huang J K, Kantner C, Handley R C O, Kokorin V V. Large magnetic-field-induced strains in Ni2MnGa single crystals[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1996, 69(13): 1966-1969.
[46] Chmielus M, Zhang X. X, Witherspoon C, Dunand D C, Mullner P. Giant magnetic-field- induced strains in polycrystalline Ni-Mn-Ga foams[J]. Nature Materials, 2009, 8(11): 863-866.
Successive martensitic phase transformations and abnormal thermal expansion in Ni-Mn-Ga magnetic refrigeration materials
Wei Sheng-xian1, He Xi-jia1, Cao Yi-ming1, Li Zhe1, Zhang Qing-qing1, Shi You-ming2, Tao Chang2
( 1. Center for Magnetic Materials and Devices, Qujing Normal University, Qujing 655011, China;
2. College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Qujing Normal University, Qujing 655011, China)
Abstract: The magnetic refrigeration materials Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 (x=0.2, 0.6, 1.0) with nominal composition were prepared to reveal the thermal expansion properties of Ni-Mn-Ga alloys. The actual compositions, crystal structures, martensitic transformation temperatures, magnetic transition and zero field thermal strain of the alloys were experimentally investigated by scanning electron microscope equipped with energy-dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS), X-ray diffractometer (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) and standard strain-gauge connected with physical properties measurement system (PPMS), respectively. The results show that the nominal composition of these alloys agree with the actual composition. The results from DSC and magnetic transition measurements show that the martensitic transformation temperatures gradually increase with Ni content increasing. Moreover, the peak temperatures of direct and reverse martensitic transformations increase from 274 K, 282 K (x=0.2) to 300 K, 309 K (x=1.0), respectively, and they have a distinct thermal hysteresis of about 7 ~ 10 K. Two successive martensitic transformations and magnetic-structural coupling transition are observed in alloys x=0.2, 0.6, and x=1.0, respectively, during cooling and heating cycles. The temperature window of phase transformations is about 33.5 K, 35.1 K and 27.5 K for x=0.2, 0.6 and 1.0. Zero field thermal strain curves illustrate that the alloys studied exhibit an isotropic thermal expansion property. The thermal expansion coefficients range from 5.02 to 10.31×10-6 K-1 and 3.74 to 7.72×10-6 K-1 at martensite and austenite phases, respectively, for Ni54+xMn19-xGa27 alloys. More importantly, the alloys exhibit an obvious and abnormal negative thermal expansion behavior in the vicinity of the martensitic transformation. The maximal negative thermal expansion coefficient occurs in alloy with x of 1.0 is about -139.84×10-6 K-1. This abnormal negative thermal expansion behavior may well be related to the nucleation and orientation of martensitic variants during the martensitic transformation. Based on the experimental data, the negative thermal expansion effect of Ni-Mn-Ga alloys was discussed briefly from microcosmic point of view.
Keywords: magnetic refrigeration; Ni-Mn-Ga alloy; martensitic transformation; thermal expansion property; negative thermal expansion behavior
Foundation item: Projects(31760341, 51661029) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017FH001-054) supported by the Yunnan Local Colleges Applied Basic Research Projects of Yunnan Province, China; Project(201710684007) supported by the National Students’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program, Ministry of Education, China
Received date: 2018-01-16; Accepted date: 2018-06-10
Corresponding author: WEI Sheng-xian; Tel: +86-874-8987852; E-mail: wsx_8600@163.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(31760341,51661029);云南省地方本科高校联合专项-面上项目(2017FH001-054);2017年地方高校国家级大学生创新创业训练计划项目(201710684007)
收稿日期:2018-01-16;修订日期:2018-06-10
通信作者:魏生贤,教授,博士;电话:0874-8987852;E-mail:wsx_8600@163.com