文章编号:1004-0609(2015)-09-2558-07
高通量测序技术分析不同温度下赞比亚低品位铜矿生物浸出过程中的微生物多样性
郝晓东1,曾伟民1, 2,彭堂见1,胡 琪1,梁伊丽1, 2,尹华群1, 2,邱冠周1, 2,刘学端1, 2
(1. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 教育部生物冶金重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:与传统微生物生态学分析方法相比,近几年高通量测序以速度快、通量高、低成本等特征在微生物多样性检测方面得到了充分应用,并采用此方法研究温度对微生物浸出赞比亚一种低品位铜矿的效率和群落生态的影响。结果表明:在30 ℃和45 ℃浸出条件下,铜浸出率分别为64.2%和69.4%,45 ℃条件下获得了较高铜浸出率。采用高通量Illumina Miseq测序技术分析30 ℃和45 ℃浸出条件下微生物群落结构及其动态变化,当浸出温度为30℃,Acidithiobacillus caldus和Acidiphilium sp.是主要浸矿菌;当浸出温度为45℃时,Sulfobacillus sp.和Acidithiobacillus caldus是优势种群。
关键词:铜矿;温度;生物浸出;群落动态;Illumina Miseq测序
中图分类号:TF 18 文献标志码:A
Analysis of microbial diversity during bioleaching of low grade copper ore from Zambia using high-throughput sequencing technology at different temperatures
HAO Xiao-dong1, ZENG Wei-min1, 2, PENG Tang-jian1, HU Qi1, LIANG Yi-li1, 2,
YIN Hua-qun1, 2, QIU Guan-zhou1, 2, LIU Xue-duan1, 2
(1. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Biometallurgy, Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The main features of high-throughput sequencing are high speed, high-throughput and low cost compared with the traditional microbial ecology analysis method. In recent years, the high-throughput sequencing technology gets full uses in the investigation of microbial diversity. The effects of temperature on bioleaching of low grade copper ore and the dynamics of microbial community from Zambia were studied. The results show that, at 30 ℃ and 45 ℃, the copper leaching rates are 64.2% and 69.4%, respectively. The rise of temperature results in higher copper leaching rate at 45 ℃. The shift of microbial community at 30 ℃ and 45 ℃ during bioleaching process was analyzed by Illumina Miseq sequencing platform. The results show that Acidithiobacillus caldus and Acidiphilium sp. are the main microorganisms at 30 ℃. While at 45 ℃, Sulfobacillus sp. and Acidithiobacillus caldus dominate in the microbial community.
Key words: copper ore; temperature; bioleaching; microbial community dynamics; Illumina Miseq sequencing
目前,生物浸出作为一种新型的具有吸引力的冶金方法,已在低品位铜、钴、镍矿等[1]重要金属资源的有效回收方面取得了较大成功。截止到2010年,全球约20%的铜产量来源于生物冶金技术。生物堆浸是应用最为广泛的一种微生物浸出工艺,其过程受许多物理化学因素的影响,比如温度、pH、氧化还原电位、金属离子浓度和溶氧浓度[2]。
在生物堆浸过程中,微生物自身生长代谢和硫化矿分解释放的热量会改变矿堆内部的温度。堆中心温度可达到50~60 ℃以上,而矿堆表面的热量扩散较快,其堆面温度与周围环境温度相近。矿堆不同位置温度的变化对微生物的氧化活性和矿相的改变有很大的影响。温度在矿体中分布的不均匀性直接导致浸矿菌的群落多样性,有研究表明,在生物堆浸体系中已检测到14个属包括多达33种浸矿微生物的存在[3],并有实验表明生物富集物相比于纯菌在分解硫化矿物的效率上更快速、更高效[4]。因此,选择和优化不同生长温度下的高效微生物菌群用于生物堆浸显得尤为重要。
生物学技术的革新对微生物生态学的发展至关重要。自20世纪80年代以来,以分子系统发育分析为基础的微生物生态学分析手段逐渐建立起来,如RFLP、DGGE、RT-PCR等。但是这些检测方法得到的数据信息量有限,一般只能检测到环境样品中的优势种群的存在,从而制约了在环境微生物多态性分析中的大规模应用。而高通量测序技术的问世完全改变了过去的研究模式,该测序方法由于通量高、产生的数据量大、测序周期短、准确率高以及成本低等优点在微生物生态学的研究中具有优越性。LAUBER等[5]首次应用高通量测序技术在对美国88个土壤样品的微生物种群结构多样性研究中,发现不同土壤微生物群落多样性及系统发育多样性与土壤pH存在显著的相关性。LIU等[6]和KUANG等[7]运用高通量测序技术分别对尾矿堆和AMD环境中微生物的群落结构进行了分析,探讨微生物多样性与生境中地球化学参数之间的相关性。应用高通量测序对微生物物种和结构多样性研究,可以准确获得更多的信息,使研究者深入探明样品中微生物群落结构多样性。
本文作者在30 ℃和45 ℃两个浸出温度下,研究一种富集物对赞比亚低品位铜矿浸出的影响,同时采用高通量Illumina Miseq测序技术测定浸出过程中浸矿微生物群落结构,旨在探讨温度对赞比亚低品位铜矿生物浸出过程和浸矿微生物群落动态变化的影响,为阐明温度对铜矿物生物浸出的影响提供参考基础。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
1) 浸矿微生物的获得和培养。本实验中所用菌种是从江西德兴铜矿酸性矿坑水中富集得到。水样用0.22 μm的微孔滤膜通过真空抽滤机抽滤处理。滤膜置于无菌pH值为2.0的无机盐培养基中,在室温、170 r/min下震荡1 h。无机盐培养基成分如下:(NH4)2SO4 3 g/L,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g/L,KCl 0.1 g/L,Ca(NO3)2 0.01 g/L,K2HPO4 0.5 g/L。将50 mL滤膜震荡后获得的菌液接入到250 mL pH值为2.0的无机盐培养基中。加入硫酸亚铁(44.7 g/L)、单质硫(10 g/L)和2%粒径为74 μm的实验矿粉,培养温度分别为30 ℃和45 ℃。当溶液菌浓度超过1×108~2×108/mL时,按上述方式传代,传代3次后,将溶液中菌液在12000 r/min离心15 min收菌,作为最终生物浸矿试验的富集物。
2) 实验矿样。本实验中所用矿样来自非洲赞比亚卢安夏铜带省。矿样磨至粒径小于74 μm,各元素及含量(质量分数)如下:1.40% Cu,5.65% Fe,0.23% S,0.20% P,5.63% K,8.85% Al,2.8% Mg;铜物相分析结果如下:自由氧化铜0.4%,结合氧化铜0.41%,次生硫化铜0.35%,原生硫化铜0.23%(质量分数)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 实验流程
本研究以500 mL锥形瓶作为浸出反应器,准确称取10 g粒径<74 μm赞比亚低品位矿粉置于体积为200 mL的pH值为2.0的无机盐培养基中,反应温度为30 ℃和45 ℃,恒温摇床转速为170 r/min。浸出过程持续14 d,第一天每隔3 h监测浸出液中铁、铜离子浓度、pH值、φ,其余13 d每天测定一次,在浸出过程中稳定浸出液pH值为2.0。
1.2.2 实验理化参数测定
定期取2 mL浸出液,测定其中各项理化参数,并用无菌去离子水补充取样后浸出液的损失。Fe2+浓度通过邻菲罗啉比色法测定;总铁、Cu2+浓度通过ICP-AES测定;Fe3+浓度通过总铁和Fe2+浓度的差值确定。浸出结束的矿渣通过化学方法测定铜物相。浸出体系菌浓度在光学显微镜下通过血球计数板每天计数得到。
1.2.3 基因组DNA提取、16S-rRNA基因测序及OTU生物学聚类分析
生物浸出过程中,提取初始富集物(0 d)、第4、9和14 d的浸矿微生物基因组DNA。200 mL的浸出体系(包括溶液和矿)在12000 r/min下离心15 min后去上清,用ZHOU等[8]方法提取沉淀中浸矿微生物基因组DNA,每个时间点提取3瓶。16S-rRNA基因扩增引物序列如下:515F:5’-GTGYCAGCMGCCGCGGTA-3’,806R:5’-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3’。扩增体系和程序见文献[9]。PCR产物用1%(质量分数)琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,并切胶回收用试剂盒纯化。16S rRNA基因文库构建和测序用Illumina Miseq测序仪进行。利用MOTHUR软件对原始下机序列进行优化,主要包括去除非特异性序列片段、重复序列及包含模糊碱基和单碱基高重复区的序列,最终获得高质量的序列集。上述获取的优化序列通过MOTHUR软件OTU pipeline构建OTU数据集。所有OTU序列在本地服务器上依托16s微生物序列数据库进行BLASTN比对注释(E值为1×10-5)。最后依托MEGAN软件并利用原始OTU序列文件及相应的注释文件对样本的OTU进行生物学聚类分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 温度对赞比亚低品位铜矿生物浸出的影响
图1所示为在不同温度下浸出液中Cu2+离子浓度的变化。由图1可看出,30 ℃和45 ℃时,浸出液Cu2+离子浓度先是快速的增加,随后增加的速率变慢;且45 ℃实验组Cu2+离子浓度高于30 ℃实验组的。在第12 h,Cu2+浸出率分别为46.6%和53.3%;实验结束时,浸出率分别为64.2%和69.4%。在浸出初始阶段,Cu2+离子浓度增加速率较快,这是因为氧化铜矿最先溶解,并且受温度的影响,高温能够加速这一化学反应过程[10]。随后,浸出速率的降低是因为浸矿微生物对硫化矿物的氧化较缓慢,加之浸出后期溶液中金属离子浓度的增加和有机物质的累积[11],致使浸矿微生物氧化活性降低,导致铜浸出效率变低。

图1 不同温度下浸出液中Cu2+离子浓度的变化
Fig. 1 Variation of Cu2+ ion concentration in leachate at different temperatures
图2所示分别为溶液中总铁和Fe3+浓度的变化趋势。由图2可知,两者先急剧地升高,随后至第156 h时,离子浓度保持稳定,最后总铁和Fe3+浓度分别呈现缓慢下降和快速下降的趋势。当浸出温度为30 ℃,溶液中总铁和Fe3+浓度均分别高于45 ℃下的含量,文献[12]中报道,Fe3+离子浓度的减少可能是因为浸出液中形成了黄钾铁矾沉淀,铁沉淀的形成是化学反应,较高温度能促进此反应的快速进行[13],因此,30 ℃时溶液中的Fe3+浓度较高。
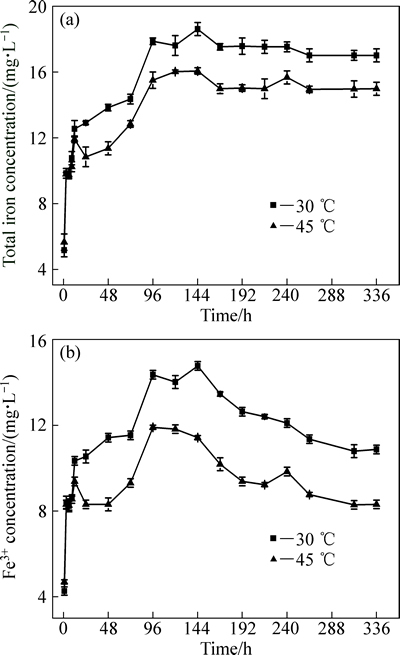
图2 不同温度下浸出液中总铁、Fe3+浓度的变化
Fig. 2 Concentration variation of total ferrous iron (a) and ferric iron (b) in leachate at different temperatures
图3所示为不同温度下浸出液中微生物数量的变化。初始浸矿微生物浓度为1×107/mL,富集物加入到浸出体系中会吸附在矿表面,并适应新的生长环境,致使前48 h菌浓度处于较低值。第48 h至120 h时,浸矿微生物处于对数生长期,45℃比30℃时的微生物生长速率更快,菌浓度更高,这是因为在浸出初期,较高温度可以更快地浸出Fe2+等物质,为浸矿微生物提供更多的能源物质促进体系中微生物的生长。120~264 h为稳定期,264 h后,菌浓度开始降低,可能是能源物质的减少和浸出环境的改变抑制了浸矿微生物的生长[12]。
表1所列为原矿和矿渣中铜物相结果。结果显示,当浸出过程结束后,30 ℃和45 ℃下氧化铜矿所占比例分别为0.189%和0.115%,其含量随反应温度升高而降低,由于高温能够加速氧化铜矿与浸出液氢离子酸碱中和反应的进行。硫化铜矿在30 ℃和45 ℃下均有较高的浸出率,且两者之间差别不大,分别为93.97%和92.24%。有研究[14]表明,中度嗜热微生物(45~60 ℃)具有高酶活性和对金属离子高抗性等特点,能有效溶解硫化矿。而本实验中两个实验组硫化铜矿浸出率差别不大原因可能是,在45 ℃下,溶液中Fe3+浓度低于30 ℃的,生成了较多黄钾铁矾沉淀,其会覆盖在矿表面[15],阻碍矿颗粒与浸矿微生物的能量传递和物质交换[9],抑制了硫化铜矿的浸出效率。

图3 不同温度下浸出液中浸矿微生物数量变化
Fig. 3 Variation of cell density in leachate at different temperatures
2.2 高通量测序技术分析生物浸出过程中群落结构及动态变化
基于16S rRNA基因PCR扩增,采用Illumina Miseq测序技术测定了30 ℃和45 ℃生物浸出过程中微生物的群落结构和动态变化(见图4)。由图4(a)中可看出,Acidithiobacillus caldus、Leptospirillum ferriphilum、Ferroplasma acidiphilium和Acidiphilium sp.存在于初始浸矿富集物中。初始浸矿菌中还含有其他微生物,但由于所占比例很低,没有被检测到。尽管如此,Acidithiobacillus caldus、Leptospirillum ferriphilum、Ferroplasma acidiphilium和Acidiphilium sp.这4种菌既包含铁氧化菌又包含硫氧化菌,既有自养微生物也有兼性异养微生物,在生物浸出过程中功能可以相互促进、相互补充[16]。从图4(b)和(c)可以看出,浸出温度为30℃时,Acidithiobacillus caldus、Sulfobacillus sp.、Leptospirillum ferriphilum和Acidiphilium sp.成为浸矿体系中的主要菌种;除了30 ℃下的4种浸矿菌外, 45 ℃下Ferroplasma acidiphilium也能在整个浸出过程中检测到。Sulfobacillus sp.在初始富集物中丰度很低没有被检测到,但在30 ℃和45 ℃浸出过程中的丰度越来越高。
图4(b)和(c)中显示,Acidithiobacillus caldus在群落中的比例随浸矿过程的进行而降低。在30 ℃和45 ℃时,Acidithiobacillus caldus在第4 d的丰度为91.3%和93.45%,随后在第9 d分别降至73.5%和38.71%,最后在第14 d降至41.38%和14.47%;而铁氧化菌Leptospirillum ferriphilum在不同温度的浸出过程中的比例先升高后降低,分别为1.1%、6.5%、3.45%和1.26%、2.1%、0.74%。生物浸出过程中,矿物分解产生的元素硫和Fe2+能为浸矿菌的生长提供能源,但铁氧化菌氧化Fe2+获得能量的速率较硫氧化菌氧化元素硫获得能量速率更快,因此,Leptospirillum ferriphilum比例升高,Acidithiobacillus caldus比例下降。Leptospirillum ferriphilum在浸出过程中的丰度较低,但在30~45 ℃条件下具有较强的氧化活性,对溶解硫化矿有重要的作用。Leptospirillum ferriphilum只能以Fe2+作为能源,且对Fe3+有较强的耐受能力,但是其他微生物尤其是在生物搅拌反应器中的菌群对Fe3+浓度变化较敏感[17]。Leptospirillum ferriphilum与Fe3+浓度变化有关(见图2(b)),对Fe3+浓度有较高的耐受性,因此,在第9 d时,Leptospirillum ferriphilum比例较第4和14 d要高。
在30 ℃条件下,Sulfobacillus sp.的丰度(第4、9、14 d分别为1.08%、2.5%、3.6%)比在45 ℃条件下要低(2.3%、32.26%、78.62%)。Sulfobacillus sp.适宜生长条件为45~50 ℃,并且能够利用元素硫、Fe2+和酵母浸出物等多种物质,这些特性使得其丰度在45 ℃条件下要高于30 ℃。JOHNSON等[18]报道Sulfobacillus spp.具有较为多样的生理生长机制,能够形成芽孢更好地适应多变的环境条件。
表1 原矿和矿渣中铜物相
Table 1 Copper phase composition in raw ore and leaching residues
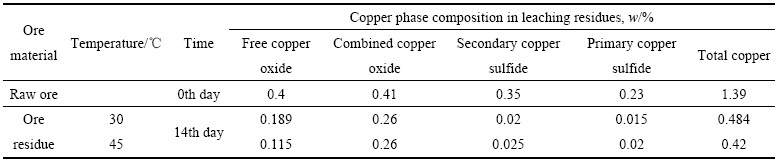
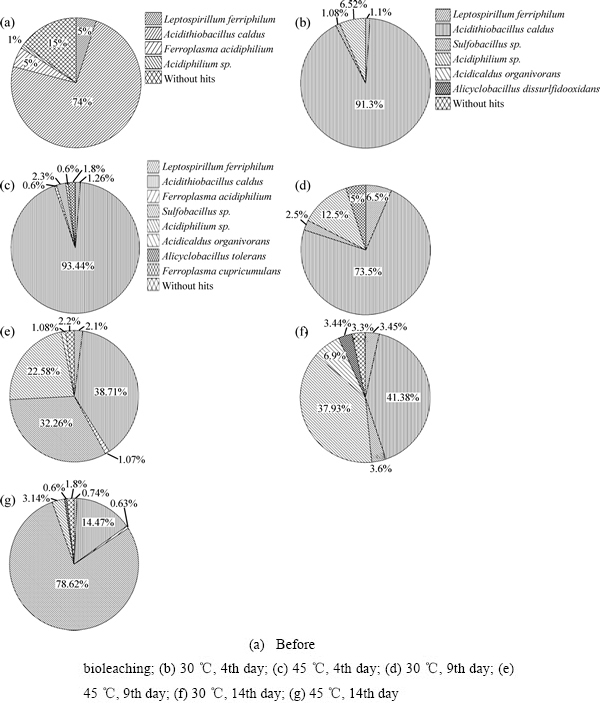
图4 群落结构分析
Fig. 4 Analysis of microbial community structures
在初始富集物中Acidiphilium sp.含量很低,但是随着浸出时间的延长,其占的比例越来越高,并且在30 ℃浸出条件下的丰度高于在45 ℃浸出条件下的。Acidiphilium sp.不仅能够利用自养菌如Acidithiobacillus caldus、Leptospirillum ferriphilum和Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans等代谢产生的有机物作为能源,而且在生长过程中会产生有机酸等代谢物,此类产物的生成对硫化铜矿的溶解有重要的作用[19]。许多文献报道大量古菌共存在于AMD及相关环境中[20]。在45 ℃浸出条件下,Ferroplasma acidiphilium在初始富集物和浸出过程中均被检测到,而Ferroplasma cupricumulans仅在45 ℃浸出条件下的第4 d出现。Ferroplasma acidiphilum能够以Fe2+作为唯一能源并以无机碳作为唯一碳源来生长[21];Ferroplasma cupricumulans能够在Fe2+和酵母浸出物中生长,在只有酵母浸出物环境下不能生长[22]。Ferroplasma sp.的生长需要较高的生长温度和较低的生长pH值,然而本实验设计的浸出条件(pH 2.0、30 ℃或45 ℃)导致Ferroplasma acidiphilium和Ferroplasma cupricumulans在浸出过程中只占有较低的丰度。
当浸出温度为30 ℃时,Acidiphilium sp.所占比例逐渐增加(6.52%、12.5%、37.93%),并在浸出后期成为优势种群;浸出温度为45℃时,Acidiphilium sp.所占比例仅为0.6%、22.58%、3.14%,Ferroplasma acidiphilium所占比例仅为0.6%、1.08%、6.3%,两者都可以利用有机物生长并在一定程度上减轻有机物对自养浸矿菌的抑制作用[16],但45 ℃下自养菌丰度较低,对有机物代谢能力有限,导致在30 ℃温度下硫化矿也具有较高的浸出效率。
Illumina Miseq高通量测序与传统微生物多样性分析手段相比,具有通量高、读长长且准确率高等特点,因此,能在测定浸矿微生物群落结构多样性上检测到丰度较低的微生物。在30 ℃下Tumebacillus permanentifrigoris在第9 d被检测到,有文献报道[23],此菌株能够生长的温度范围为5~37 ℃,此菌为异养菌,能够在混合碳基质并以无机硫化合物如亚硫酸盐和硫代硫酸盐作为电子供体而生长。在30 ℃条件下,Alicyclobacillus disulfidooxidan和Acidicaldus organivorans在第14 d被检测到。Alicyclobacillus disulfidooxidans能在葡萄糖、谷氨酸盐和有机硫物质等有机物基质上生长,其适宜生长pH为1.5~2.5,利用不同底物时,其生长温度范围为4~40 ℃,适宜生长温度为35 ℃[24];比较基因组学研究发现,Acidicaldus organivorans拥有相对较简单的硫氧化途径,和许多异养硫氧化菌一样,Acidicaldus organivorus没有直接氧化亚硫酸盐酶的编码基因,但是可以氧化元素硫至硫酸,此外,Acidicaldus organivorus能够催化Fe3+的还原。在45 ℃条件下,Alicyclobacillus tolerans在第14 d被检测到,此菌可以Fe2+、S2-/S0或硫化矿作为电子供体,此菌生长温度为37~42 ℃、pH值范围为1.5~5.0、适宜生长pH值为2.5~2.7。上述微生物所占比例较低,在浸出过程中不能总被检测到。在生物浸出过程的后期,有机物质的增加不利于自养微生物的生长,而上述微生物多为异养菌,异养微生物的存在在一定程度上能够消除有机物对自养微生物的抑制作用。
3 结论
1) 45 ℃时铜的浸出效率高于30 ℃的。45 ℃浸出温度加速并提高氧化铜矿的溶解,两个温度下的硫化铜矿浸出率相近,在45 ℃条件下获得较高最终铜浸 出率。
2) 生物浸出体系群落动态变化受温度影响显著,不同微生物在不同温度下所占比例有很大差异:浸出温度为30 ℃时,Acidithiobacillus caldus和Acidiphilium sp.是主要浸矿菌;浸出温度为45 ℃时,Sulfobacillus sp.和Acidithiobacillus caldus是优势种群。生物浸出中后期,异养微生物多样性和丰度逐渐增加。
REFERENCES
[1] 郭朝晖, 程 义, 邱冠周, 刘学端, 潘凤开. Pb/Zn冶炼废渣中有价金属生物浸出条件优化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(5): 924-929.
GUO Zhao-hui, CHENG Yi, QIU Guan-zhou, LIU Xue-duan, PAN Feng-kai. Optimization on bioleaching of metal values from Pb/Zn smelting slag[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(5): 924-929.
[2] CHEN B W, LIU X Y, LIU W Y, WEN J K. Application of clone library analysis and real-time PCR for comparison of microbial communities in a low-grade copper sulfide ore bioheap leachate[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2009, 36(11): 1409-1416.
[3] OJUMU T V, PETERSEN J. The kinetics of ferrous ion oxidation by Leptospirillum ferriphilum in continuous culture: The effect of pH[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 106 (1/2): 5-11.
[4] ZHOU H B, ZHANG R B, HU P L, ZENG W M, XIE Y J, WU C B, QIU G Z. Isolation and characterization of Ferroplasma thermophilum sp. nov., a novel extremely acidophilic, moderately thermophilic archaeon and its role in bioleaching of chalcopyrite[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2008, 105(2): 591-601.
[5] LAUBER C L, HAMADY M, KNIGHT R, FIERER N. Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(15): 5111-5120.
[6] LIU J, HUA Z S, CHEN L X, KUANG J L, LI S J, SHU W S, HUANG L N. Correlating microbial diversity patterns with geochemistry in an extreme and heterogeneous environment of mine tailings[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(12): 3677-3686.
[7] KUANG J L, HUANG L N, CHEN L X, HUA Z S, LI S J, HU M, LI J T, SHU W S. Contemporary environmental variation determines microbial diversity patterns in acid mine drainage[J]. The ISME Journal, 2013, 7(5): 1038-1050.
[8] ZHOU J Z, BRUNS M, TIEDJE J. DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1996, 62(2): 316-322.
[9] MUYZER G, DE W E, UITTERLINDEN A. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction—Amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1993, 59(3): 695-700.
[10] DIXON D G. Analysis of heat conservation during copper sulphide heap leaching[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 58(1): 27-41.
[11] XIA L X, LIU J S, XIAO L, ZENG J, LI B M, GENG M M, QIU G Z. Single and cooperative bioleaching of sphalerite by two kinds of bacteria—Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(1): 190-195.
[12] 马鹏程, 杨洪英, 佟琳琳, 韩战旗, 宋 言. 黄铜矿生物浸出过程中Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)的行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(6): 1694-1700.
MA Peng-cheng, YANG Hong-ying, TONG Lin-lin, HAN Zhan-qi, SONG Yan. Behaviour of Fe(Ⅱ)and Fe(Ⅲ) in chalcopyrite bioleaching process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(6): 1694-1700.
[13] PRADHAN N, NATHSARMA K C, RAO K S, SUKLA L B, MISHRA B K. Heap bioleaching of chalcopyrite: A review[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2008, 21(5): 355-365.
[14] GERICKE M, GOVENDER Y, PINCHES A. Tank bioleaching of low-grade chalcopyrite concentrates using redox control[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 104(3): 414-419.
[15] 杨洪英, 潘颢丹, 佟琳琳, 刘媛媛. 黄铜矿表面生物氧化膜的形成过程[J]. 金属学报, 2012, 48(9): 1145-1152.
YANG Hong-ying, PAN Hao-dan, TONG Lin-lin, LIU Yuan-yuan. Formation process of biological oxide film on chalcopyrite crystal surface[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(9): 1145-1152.
[16] 余润兰, 石丽娟, 周 丹, 邱冠周, 曾伟民. 生物浸出过程中微生物协同作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(10): 3007-3015.
YU Run-lan, SHI Li-juan, ZHOU Dan, QIU Guan-zhou, ZENG Wei-min. Research development of microorganism synergy mechanisms during bioleaching[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(10): 3007-3015.
[17] YU R L, SHI L J, GU G H, ZHOU D, YOU L, CHEN M, QIU G Z, ZENG W M. The shift of microbial community under the adjustment of initial and processing pH during bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate by moderate thermophiles[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 162: 300-307.
[18] JOHNSON D B. Biodiversity and interactions of acidophiles: Key to understanding and optimizing microbial processing of ores and concentrates[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(6): 1367-1373.
[19] ZENG W M, QIU G Z, ZHOU H B, PENG J H, CHEN M, TAN S N, CHAO W L, LIU X D, ZHANG Y S. Community structure and dynamics of the free and attached microorganisms during moderately thermophilic bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(18): 7068-7075.
[20] SCHIPPERS A, BREUKER A, BLAZEJAK A, BOSECKER K, KOCK D, WRIGHT T L. The biogeochemistry and microbiology of sulfidic mine waste and bioleaching dumps and heaps, and novel Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 104(3): 342-350.
[21] GOLYSHINA O V, PIVOVAROVA T A, KARAVAIKO G I,  T F, MOORE E R, ABRAHAM W,
T F, MOORE E R, ABRAHAM W,  , TIMMIS K N, YAKIMOV M M, GOLYSHIN P. Ferroplasma acidiphilum gen. nov., sp. nov., an acidophilic, autotrophic, ferrous-iron-oxidizing, cell-wall-lacking, mesophilic member of the Ferroplasmaceae fam. nov., comprising a distinct lineage of the Archaea[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2000, 50(3): 997-1006.
, TIMMIS K N, YAKIMOV M M, GOLYSHIN P. Ferroplasma acidiphilum gen. nov., sp. nov., an acidophilic, autotrophic, ferrous-iron-oxidizing, cell-wall-lacking, mesophilic member of the Ferroplasmaceae fam. nov., comprising a distinct lineage of the Archaea[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2000, 50(3): 997-1006.
[22] REBECCA B, HAWKES P D, FRANZMANN G O, JASON J P. Ferroplasma cupricumulans sp. nov., a novel moderately thermophilic, acidophilic archaeon isolated from an industrial-scale chalcocite bioleach heap[J]. Extremophiles, 2006, 10(6): 525-530.
[23] STEVEN B, CHEN M Q, GREER C W, WHYTE L G, NIEDERBERGER T D. Tumebacillus permanentifrigoris gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic, spore-forming bacterium isolated from Canadian high Arctic permafrost[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2008, 58(6): 1497-1501.
[24] DUFRESNE S, BOUSQUET J, BOISSINOT M, GUAY R. Sulfobacillus disulfidooxidans sp. nov., a new acidophilic, disulfide-oxidizing, gram-positive, spore-forming bacterium[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 1996, 46(4): 1056-1064.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2010CB630901);国家自然科学青年科学基金资助项目(31200382);国家自然科学基金面上项目(31470230);国家自然科学基金国际合作重大项目(51320105006)
收稿日期:2015-01-21;修订日期:2015-05-05
通信作者:刘学端,教授,博士;电话:0731-88830546;E-mail:xueduanliu@yahoo.com