文章编号:1004-0609(2012)08-2214-09
元素S对镍基合金G3在高温高压H2S/CO2气氛中腐蚀行为的影响
钱进森,陈长风,李晟伊,郑树启,翁永基
(中国石油大学 (北京) 理学院,北京 102249)
摘 要:利用美国Cortest公司高温高压反应釜模拟H2S/CO2及元素S共存环境,在流动高矿化度饱和H2S/CO2介质中进行试验,然后利用SEM、EDS及XPS等表面分析技术,探讨元素S对镍基合金G3高温高压H2S/CO2腐蚀行为的影响。结果表明:在元素S含量为0、1及10 g/L时,镍基合金G3的平均腐蚀速率变化不大,钝化膜厚度约为11 nm,其结构呈双极性,外层以Cr、Ni的氢氧化物、氧化物为主,内层以Cr、Ni的氧化物为主;当元素S含量增大到100 g/L时,腐蚀速率急剧增大,钝化膜厚度也迅速增大到约90 nm,且结构转变为外层以Cr、Ni的硫化物为主,内层以Cr、Ni的氧化物为主;钝化膜结构的转变可能是导致镍基合金G3耐蚀性能降低的最主要原因。
关键词:镍基合金;高温高压;元素S;H2S/CO2;XPS
中图分类号:TG174.2 文献标志码:A
Effect of element S on corrosion behavior of nickel-base alloy G3 in high temperature and high pressure environments containing H2S/CO2
QIAN Jin-sen, CHEN Chang-feng, LI Shen-yi, ZHENG Shu-qi, WENG Yong-ji
(College of Science, China Petroleum University, Beijing 102249, China)
Abstract: The solution immersion environments containing H2S/CO2 and element S were simulated in a high temperature and high pressure autoclave. The effect of element S on the corrosion behavior of nickel-base alloy G3 was analyzed and discussed by the following technologies, such as SEM, EDS and XPS. The results show that the average corrosion rate of nickel-base G3 changes lightly and the thickness of passive film with bipolar structure is about 11 nm under the element S contents of 0, 1 and 10 g/L. The out layer of passive film is mainly composed of oxides and hydroxides and the inner layer is mainly oxides. However, when the content of element S reaches 100 g/L, the average corrosion rate of nickel-base G3 increases rapidly, and the thickness of passive film also increases to about 90 nm. The out layer changes greatly and is mainly composed of Cr and Ni sulfide, the inner layer is still mainly Cr and Ni oxides. The transformation of passive film structure maybe is the main reason that results in the lower corrosion resistance of nickel-base G3.
Key words: nickel-base alloy; high temperature and high pressure; element S; H2S/CO2; XPS
在硫化氢环境中的油气开采和加工生产中,由于H2S的存在,不仅会导致金属管材的均匀减薄,同时还会引起HIC及SSCC脆性断裂事故,硫化氢所导致的开裂一旦发生往往是突发和灾难性的,一方面会造成巨大的经济损失;另一方面,由于H2S本身的巨毒性,严重威胁着人们的生命财产安全[1-2]。
随着全球经济对油气资源需求量的增加,使得越来越多的高含H2S/CO2酸性油气田得到开发,H2S/CO2腐蚀问题日益成为人们关注的问题。多年来,研究者试图揭示材料尤其是钢铁材料在硫化氢环境中的腐蚀行为和机理,为此进行了大量的研究工作[3-8]。但大多研究都基于低H2S分压条件下进行,对于高H2S分压,CHEN等[9-10]做了部分相关研究,取得了一定的成果,对高含H2S/CO2油气田的开发起到积极的指导作用。然而,这些研究成果对 H2S分压达到10 MPa且出现大量S沉积情况的普光气田的安全开发的指导意义较小,因此,开展高H2S分压及高含S沉积条件所使用材料的适用性研究已成为当务之急。
为确保高酸性油气田的安全开发,选用具有优良的耐蚀性、高温性能,并且兼有良好力学性能和机械加工性能的镍基合金是控制酸性油气井腐蚀的重要措施[11-13]。镍基合金的优良耐蚀性能是由于其表面形成的钝化膜,将腐蚀介质与合金隔离开来,从而提高合金的耐蚀性能。但随着腐蚀环境越来越苛刻,如 H2S/CO2分压增大、腐蚀温度升高及元素S的沉积等,镍基合金表面钝化膜的完整性将被破坏,导致镍基合金油管腐蚀破坏[13-16]。因此,研究镍基合金在高含硫化氢及元素S环境下钝化膜的结构对其腐蚀行为的影响具有重大的现实意义。在研究钝化膜的微观结构方面,X射线光电子能谱(XPS)具有相当的优势,许多研究者利用 XPS 分析方法研究不锈钢钝化膜结构,对揭示不锈钢的耐蚀机制给予了有力支持[17-20]。
本文作者利用SEM、EDS、XPS等表面分析手段,研究镍基合金 G3 在高温高压 H2S/CO2及S沉积环境下腐蚀钝化膜的结构变化特征。对 G3 钝化膜进行逐层溅射,深度剖析,分析各元素含量及其在钝化膜中化学状态的变化规律,探索G3在高温高压H2S/CO2及元素S环境中腐蚀后钝化膜的结构变化及其对材料耐蚀性的影响,为条件极其苛刻的高含硫酸性油气田的开发提供理论基础。
1 实验
本研究采用镍基合金G3的成分如表1所列。试样用SiC水砂纸逐级打磨至1000#,用蒸馏水清洗,丙酮除油。利用25 MPa哈氏合金动态高温高压反应釜开展H2S/CO2腐蚀试验,试验介质为模拟普光溶液,其离子组成如表2所列,试验温度为130 ℃,H2S分压为10 MPa,CO2分压为6 MPa,元素S含量分别为0、1、10、100 g/L,试验时间720 h。为了防止高压釜遭受严重的腐蚀,在高压釜内胆中加聚四弗乙烯衬套,试验装置示意图如图1所示。试验前室温下先通入高纯氮除氧2 h,然后先通入H2S气体达到饱和,升温至目标温度确保H2S分压为10 MPa,再降温至室温,通入CO2气体,再升温至目标温度,使得CO2分压为6 MPa,即总压为16 MPa。整个过程需要经过仔细计算,确保在目标温度下H2S、CO2气体分压准确。
试验结束后取出试样,用清水冲去腐蚀介质,用无水乙醇脱水干燥,取出其中两个试样,放入清洗液(10%(质量分数)的HCl,5 g/L六次甲基四胺)中去除腐蚀产物膜后,清水冲洗,无水乙醇脱水干燥,用FR-300MKII电子天平(精度0.1 mg)称质量,用失重法计算腐蚀速率。另外一个试样,利用FEI Quanta 200F扫描电镜观察表面腐蚀形貌,利用PHI Quantera SXM光电子能谱仪进行XPS分析;试验条件:Al Kα线(能量为1486.6 eV)为激发源,靶电压15 kV,功率25 W,真空度1.993×10-10 Pa,数据处理和光电子峰的解析使用Multipeak8.0,峰的拟合使用XPSPEAK4.1曲线拟合程序。
表1 镍基合金G3材料成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of nickel-base alloy G3 (mass fraction, %)

表2 模拟普光溶液离子浓度
Table 2 Concentration of various ions of stimulant solution (mg/L)

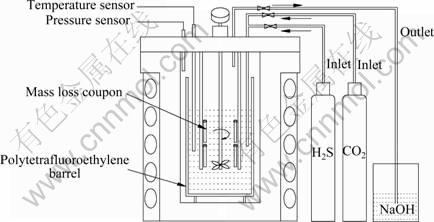
图1 腐蚀试验装置示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic illumination of corrosion apparatus
2 结果与讨论
2.1 平均腐蚀速率
图2所示为高温高压H2S/CO2及S沉积环境下元素S含量对镍基合金G3平均腐蚀速率的影响。从图2中可以看出,在仅有H2S/CO2气体而没有元素S的条件下,材料的腐蚀速率为5.4 mm/a,当腐蚀环境中分别加入1和10 g/L元素S时,腐蚀速率略微有所增大,达到5.9及8.8 μm/a,但变化并不大,当腐蚀环境中加入的元素S含量达到100 g/L时,腐蚀速率发生急剧变化,迅速增大到25.4 μm/a,是没加元素S情况的5倍,表明在该情况下,镍基合金G3表面形成的钝化膜结构和成分可能发生了变化,对基体的保护作用有所减弱。但总体来说,镍基合金G3在高温高压H2S/CO2及S沉积环境下具有很好的耐蚀性,根据NACE RP-0775—2005标准规定,即使是在100 g/L条件下腐蚀速率达到25.4 μm/a,也只属于轻度腐蚀范畴。镍基合金表面所形成的钝化膜的结构和性质对其腐蚀速率有着非常重要的影响,也许从后面对各种腐蚀条件下所形成钝化膜的结构及其性质的分析中,可以进一步揭示其腐蚀机理及腐蚀规律。
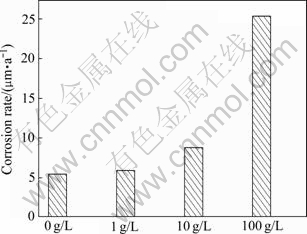
图2 元素S含量对镍基合金G3腐蚀速率的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of element S content on corrosion rate of nickel-base alloy G3
2.2 表面形貌特征
镍基合金G3在不同含量的元素S条件下经过高温高压腐蚀后,用肉眼看试样表面非常光滑,在无元素S或元素S含量相对较少的条件下,试样表面光亮如镜,几乎未腐蚀,腐蚀前打磨试样留下的划痕仍清晰可见;当元素S含量达到100 g/L时,试样表面明显变黑,在高倍电子显微镜下观察可以看到有颗粒状的腐蚀产物生成,但产物层很薄,砂纸打磨留下的划痕仍然可见;能谱分析证明这些颗粒状的物质是Cr、Ni、Fe的硫化物。在高倍扫描电子显微镜下观察试样表面微观形貌,存在许多微小的点蚀坑,点蚀坑的大小从几μm到十几μm不等,如图3所示。且从图3中还可以看出,随着元素S含量的增加,试样表面的点蚀坑的数量逐渐增多,尺寸逐渐增大,点蚀坑内存在明显的腐蚀产物,点蚀坑的局部放大扫描电镜微观形貌如图4所示。
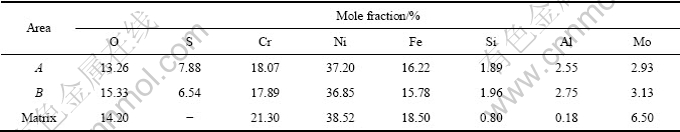
图4(a)所示为镍基合金G3在100 g/L元素S条件下腐蚀后的点蚀坑微观形貌图。从图4(a)中可以看出,点蚀坑的形状为不规则的圆形,尺寸大小约为15 μm左右,点蚀坑周围试样表面比较光滑,覆盖有一层薄薄的晶粒很细小的腐蚀产物,在点蚀坑内部腐蚀产物相对较多且晶粒相对粗大,利用EDS能谱分析得知,点蚀坑内腐蚀产物主要为Cr、Ni、Fe的氧化物及硫化物组成,其各元素的摩尔分数如表3所列。将试样表面抛光并利用浓盐酸+10%(质量分数)Fe3Cl 侵蚀以后,可以明显看出点蚀坑萌生于晶界附近,点蚀的发生明显以沿晶为主,穿晶为辅,如图4(b)所示。一般情况下,晶界是原子排列较为疏松而紊乱的区域,此区域容易富集杂质原子,产生所谓的晶界吸附和晶界沉淀,此化学不均匀性会导致晶界比晶粒化学活性高,具有更负的电极电位值,故点蚀一般从晶界开始。PAN等[21]研究发现含0.01%C(摩尔分数)的镍基合金的碳化物容易在晶界处呈薄片状连续析出,导致碳化物析出附近形成带状贫Cr区,由于Cr、Mo扩散速度慢,靠近晶粒边界附近的Cr、Mo含量远远低于耐腐蚀介质侵蚀所需的最低临界值[22]。耐蚀元素Cr和Mo在析出相中的富集导致晶界贫Cr、Mo,因此,Ni、Cr、Mo合金在晶界处容易腐蚀,形成局部腐蚀坑。表3的能谱结果表明,发生局部腐蚀的区域,Cr、Mo的含量偏低,而杂质Si、Al的含量偏高,这一点与前人的研究结果一致。
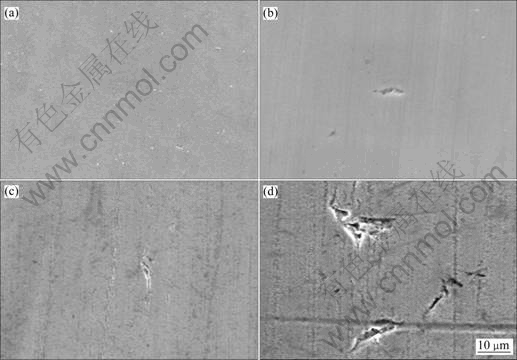
图3 镍基合金G3在不同元素S含量下腐蚀后的表面微观形貌
Fig. 3 Micrographs of nickel-base alloy G3 after corrosion under different S contents: (a) 0; (b) 1 g/L; (c) 10 g/L; (d) 100 g/L

图4 镍基合金G3在100 g/L元素S下腐蚀后的局部腐蚀特征
Fig. 4 Local corrosion characteristic of nickel-base alloy G3 after corrosion under 100 g/L element S: (a) Covered film; (b) Uncovered film
表3 局部腐蚀处腐蚀产物的化学成分
Table 3 Chemical component corrosion film in local corrosion
由于试验温度为130 ℃,高于硫的熔点(119 ℃)且硫是一种强氧化剂,在高于其熔点的温度及介质条件下吸附于表面的硫极易发生歧化反应,生成H2S和H2SO4,化学反应方程式如(1)所示。
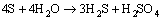 →
→
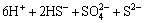 (1)
(1)
歧化反应的发生,导致钝化膜局部大量H+的电离造成局部酸化,钝化膜开始溶解。由反应式(1)生成的S2-的极性高于Cl-以及OH-的,S2-与Cl-以及OH-竞争吸附于氧空位,逐渐在钝化膜表层形成金属硫化物。进一步,膜中的S2-借助空位迁移扩散到钝化膜内层,降低了钝化膜形成的动力学因素,也破坏了钝化膜的自修复功能,从而导致了金属基体的溶解,成为点蚀的形核点,其过程如图5所示。
点蚀孔内的金属表面处于活态,电位较负;点蚀孔外的金属表面处于钝态,电位较正,于是孔内孔外构成了活态-钝态微电偶腐蚀电池,具有大阴极-小阳极的面积比结构,阳极电流密度增大,孔蚀加快。又由于孔内溶解的金属阳离子不易向外扩散,溶液中的S2-向内扩散以维持电中性。孔内形成的金属硫化物水解,酸度增加,孔口沉积不溶于水的氢氧化物,形成“闭塞电池”,“闭塞电池”内的“自催化酸化作用”使得点蚀迅速发展。
2.3 钝化膜结构特征
图6所示为镍基合金G3在130 ℃及不同元素S含量条件下腐蚀后利用氩离子轰击剥离(每分钟剥离约2.2 nm)XPS逐层分析不同条件下腐蚀后的钝化膜而得到的元素分布图。从图6中可以看出,在仅有H2S/CO2气体而没有元素S的条件下,镍基合金G3腐蚀后钝化膜表层中的O含量比较高,且随着钝化膜溅射深度的增加,内层O含量逐渐减少,最后逐渐趋于零,根据O含量的变化可以判定其钝化膜的厚度约为11 nm;Cr、Fe、Ni元素含量随着钝化膜的深度逐渐增加,最后到达基体后趋于一个相对平稳值,且Cr元素在钝化膜的外层相对富集,但S元素的含量几乎为零。在加入10 g/L元素S的条件下,钝化膜的厚度和各元素分布的情况变化不大,在钝化膜的外层有微小的S元素存在,表明钝化膜外层有微小变化,但对整个钝化膜的结构影响不大,主要还是以金属氧化物和氢氧化物为主。当加入的元素S含量达到100 g/L时,钝化膜厚度约为90 nm,钝化膜中各元素的含量分布发生了很大的变化,在钝化膜的外层O元素含量很小,而S元素含量较大,随着钝化膜溅射深度的增加,各金属元素含量逐渐增加,最后趋于平稳;在钝化膜内层,S元素含量逐渐减小至零,O元素含量先增多后减小,出现一个峰值,表明该条件下形成的钝化膜外层以金属硫化物为主,内层以金属氧化物为主。
图7所示为是镍基合金G3在不同元素S含量条件下腐蚀后钝化膜中Cr元素的价态分析及拟合曲线。从钝化膜的成分分布来看,在仅有H2S/CO2气体而没有元素S的条件下腐蚀后,钝化膜表层中氧含量较高,在钝化膜内层,氧含量降低,Ni、Cr 的含量增高,钝化膜中的Ni 含量较Cr 含量高。XPS 分析结果显示,钝化膜表面主要是Ni、Cr,由氢氧化物和氧化物构成,而钝化膜内部则主要是由Ni、Cr 的氧化物构成(见图6(a))。在10 g/L元素S条件下腐蚀后,钝化膜中元素含量变化与没有元素S条件下腐蚀后的结果类似,钝化膜中氧含量仍然较高,在表层出现很少量的S,但这并不影响其钝化膜的完整性。XPS 的分析结果显示,钝化膜表层主要由Ni、Cr 的氢氧化物构成,而钝化膜内层则主要由Ni、Cr的氧化物构成(见图7(b))。在前两种条件下形成的钝化膜元素分布图中,Cr元素的含量均在表面富集,其原因可能是Ni的氢氧化物(Ni(OH)2的溶度积(5.48×10-16)高于Cr的氢氧化物Cr(OH)3(6.3×10-31)的溶度积[23],Ni的氢氧化物比Cr的氢氧化物更易溶解于水相关。镍基合金G3在100 g/L元素S条件下腐蚀后,钝化膜结构发生了明显的变化,表层主要由Ni和Cr的硫化物组成,而内层则主要是由Ni、Cr 的氧化物构成。在硫化物层,Ni 的含量高于Cr,其原因可能与NiS以及Cr2S3在水中的水解能力有关。NiS难溶于水,β-NiS的溶度积为1×10-24,而Cr2S3水解能力强,在水中容易分解[23],这可能导致钝化膜表层中Ni含量高于Cr的。
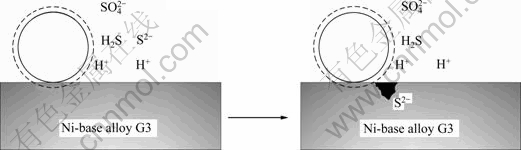
图5 硫在镍基合金G3表面沉积产生局部酸化过程示意图
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of localized acidification caused by sulfur deposition on nickel-base alloy G3
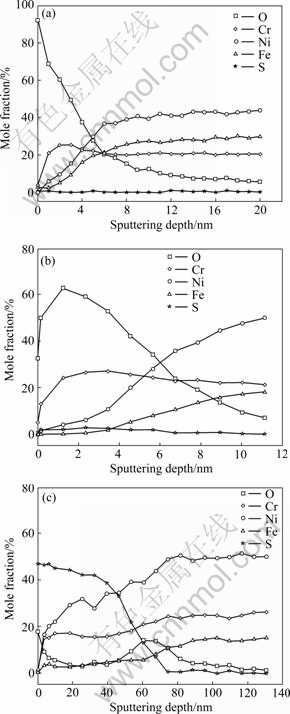
图6 镍基合金G3在不同条件下腐蚀后钝化膜的元素含量随溅射深度的变化曲线
Fig. 6 Change of mole fraction with sputtering depth in passive films formed on surface of nickel-base alloy G3 under different conditions: (a) 0 S; (b) 10 g/L S; (c) 100 g/L S
2.4 腐蚀机理分析
由以上分析结果得知,环境温度为130 ℃、H2S和CO2分压分别为10 MPa和6 MPa时,镍基合金G3在元素S含量为0、1、10 g/L条件下,平均腐蚀速率变化不大,而当元素S含量达到100 g/L条件时,腐蚀速率显著地增大了5倍左右。镍基合金表面形成的钝化膜对其耐蚀性能有决定性影响,从XPS的分析结果来看,在前3种条件下,钝化膜主要由氢氧化物和氧化物组成,按照SATO[24]的双极性钝化膜理论,外层氢氧化物膜能够阻碍阴离子向钝化膜内层扩散,内层氧化物膜能阻碍阳离子向钝化膜外扩散,从而对基体金属产生保护。当腐蚀环境中的元素S含量增加到100 g/L时,镍基合金G3的腐蚀速率成倍的增加,发生了突变,表明在该条件下,钝化膜明显遭到介质侵蚀,钝化膜外层形成硫化物层,这种腐蚀产物往往不致密,但钝化膜中间层仍然是氢氧化物层,内层是氧化物层,仍然具有双极性的特征,所以对基体仍然具有一定的保护作用,即使钝化膜表面遭到破坏,钝化膜的双极性结构仍然存在,说明钝化膜存在自修复能力,钝化膜的形成机制如图8所示。
在元素S含量相对较大的情况下,通过反应(1),能够产生大量的S2-和HS-。CHEN等[10]认为,如果溶液中存在大量S2-、HS-,依照MACDONALD[25]提出的PDM、SVIM模型,钝化膜中的氧空位迁移至钝化膜/溶液界面处,通过Schottky空位对反应,导致膜表面金属阳离子溶解,与OH-形成金属氧化物沉淀。S2-的极性高于Cl-以及OH-的,这样溶液中的S2-就有可能与Cl-以及OH-竞争吸附于部分氧空位,且逐渐在钝化膜表层形成金属硫化物,进一步反应,膜中的S2-借助空位迁移扩散到钝化膜内层。这种金属氧化物钝化膜向金属硫化物钝化膜的转变过程有可能是耐蚀合金高温高压H2S/CO2钝化膜形成及破坏机制之一,进而导致镍基合金G3在元素S含量相对较大的情况下腐蚀速率迅速升高。
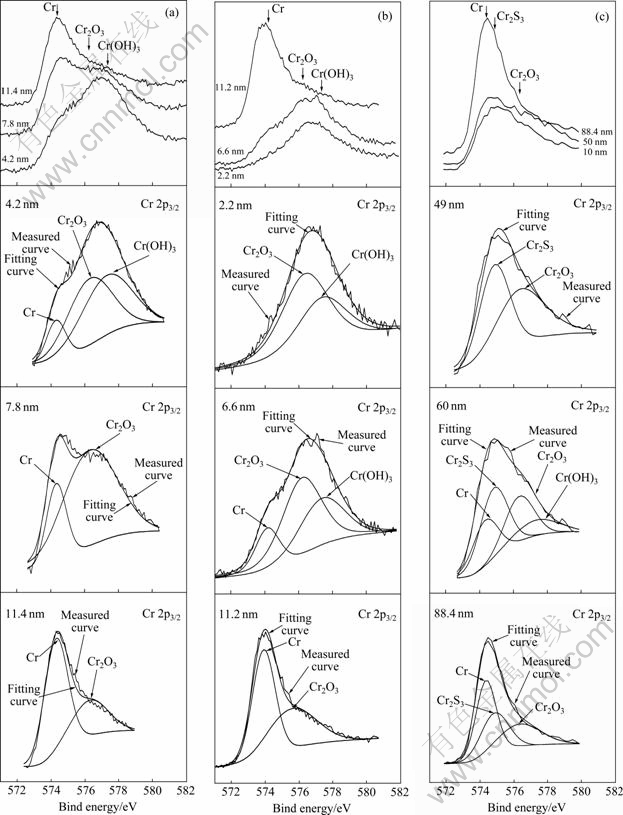
图7 镍基合金G3在不同条件下腐蚀后钝化膜中Cr元素的价态分析及XPS拟合曲线
Fig. 7 Valence state analysis and XPS fitting curves of element Cr in passive films formed on surface of nickel base alloy G3 under different conditions: (a) 0 S; (b) 10 g/L S; (c) 100 g/L S

图8 钝化膜形成机制示意图(其中V2-为阴离子空位)
Fig. 8 Schematic diagram of formation mechanism of passive film (V2- is anion vacancy)
3 结论
1) 在元素S含量为0、1、10 g/L条件下,镍基合金G3经高温高压H2S/CO2腐蚀后,试样表面完好,几乎没有腐蚀。当元素S含量达到100 g/L时,其腐蚀速率急剧增加,达到25.4 μm/a,但也只属于轻度腐蚀范畴,表明镍基合金G3在高含硫条件下仍具有非常好的耐蚀性。
2) 镍基合金G3经高温高压H2S/CO2及元素S腐蚀后,容易产生轻微的点蚀,点蚀以沿晶为主,穿晶为辅,这与晶界处Si、Al杂质含量较高导致活性较大以及出现贫Cr 区有关。
3) 镍基合金G3在元素S含量为0、1、10 g/L条件下经高温高压H2S/CO2腐蚀后,钝化膜厚度变化不大,均约为11 nm,钝化膜的结构由外层Cr、Ni的氧化物及氢氧化物和内层Cr、Ni的氧化物组成;当元素S含量为100 g/L腐蚀后,钝化膜的厚度增大到90 nm左右,其结构转变为外层以硫化物为主,内层以氧化物为主。钝化膜结构的转变可能是导致镍基合金G3耐蚀性能降低的最主要原因。
REFERENCES
[1] 赵新伟, 罗金恒, 郑茂盛, 李鹤林, 张 华. 弥散型腐蚀损伤管道剩余寿命预测方法[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(1): 119-123.
ZHAO Xin-wei, LUO Jin-heng, ZHENG Mao-sheng, LI He-lin, ZHANG Hua. A method for predicting remaining life of pipeline with dispersion-type corrosion damage[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(1): 119-123.
[2] 顾春元, 狄勤丰, 王掌洪. N80钢在地层水中的应力腐蚀行为研究[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(2): 141-144.
GU Chun-yuan, DI Qin-feng, WANG Zhang-hong. Stress corrosion performance of N80 steel in formation water[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(2): 141-144.
[3] LAMIC A F, DAUDIN A, BRUNET S, LEGENS C, BOUCHY C, DEVERS E. Effect of H2S partial pressure on the transformation of a model FCC gasoline olefin over unsupported molybdenum sulfide-based catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2008, 344(1): 198-204.
[4] YIN Z F, ZHAOA W Z, BAI Z Q, FENG Y R, ZHOU W J. Corrosion behavior of SM 80SS tube steel in stimulant solution containing H2S and CO2[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53(10): 3690-3700.
[5] BANA?S J, BORKOWSKA U L, MAZURKIEWICZ B, SOLARSKI W. Effect of CO2 and H2S on the composition and stability of passive film on iron alloys in geothermal water[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 52(18): 5704-5714.
[6] SHAIKH H, ANITA T, POONGUZHALI A, AMIRTHALINGAM R, KHATAK H. Effect of high temperature aging on the corrosion behavior of nitrogen-added AISI type 316L stainless steel[J]. Trans Ind Inst Met, 2006, 59(6): 271- 282.
[7] MUDALI U, SHANKAR P, NINGSHEN S, DAYAL R, KHATAK H. On the pitting corrosion resistance of nitrogen alloyed cold worked austenitic stainless steels[J]. Corrosion Science, 2002, 44(10): 2183-2198.
[8] SATO N. Passivity of metals[M]. New Jersey: The Electrochemical Society, 1978: 479.
[9] 陈长风, 范成武, 郑树启, 张国安, 戈 磊, 陈立强. 高温高压H2SO4/CO2 G3镍基合金表面的XPS分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(11): 2050-2055.
CHEN Chang-feng, FAN Cheng-wu, ZHENG Shu-qi, ZHANG Guo-an, GE Lei, CHEN Li-qiang. XPS analysis of surface of G3 nickel base alloy under high H2S and CO2 partial pressure[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(11): 2050- 2055.
[10] CHEN Chang-feng, JIANG Rui-jing, ZHANG Guo-an, ZHENG Shu-qi, GE Lei. Study on local corrosion of nickel-base alloy tube in the environment of high temperature and high pressure H2S/CO2[J]. Rear Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(3): 427-432.
[11] KOPLIKU A, SCOPPIO L. Selecting materials for an offshore development characterized by sour and high salinity environment [C]//Corrosion. Houston: NACE, 2003: 03128.
[12] HIBNER E L, PUCKETT B C, PATCHELL J K. Comparison of corrosion resistance of nickel-base alloys for OCTG’S and mechanical tubing in severe sour service conditions [C]//Corrosion. Houston: NACE, 2004: 04110.
[13] TABINOR M, BAILEY B, CHELDI T, NICE P I, TORELLA R, BUFALINI A, FRANCI S. Corrosion and environmental cracking behavior of three corrosion resistant alloys at various expansion ratios [C]//Corrosion. Houston: NACE, 2006: 06152.
[14] WANG H, FANG D M, CHUANG K T. A sulfur removal and disposal process through H2S adsorption and regeneration: Ammonia leaching regeneration[J]. Process Safety and Environment Protection, 2008, 86(4): 296-302.
[15] AZEVEDO C R F. Failure analysis of a crude oil pipeline[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2007, 14(6): 978-994.
[16] TANG J Q, GONG J M, ZHANG X C, TU S T. Comparison on the cracking susceptibility of different low alloy steel weldments exposed to the environment containing wet H2S[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2006, 13(7): 1057-1064.
[17] BARBUCCI A, CERISOLA G, CABOT P L. Effect of cold-working in the passive behavior of 304 stainless steel in sulfate media[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2002, 149(12): B534- B542.
[18] STEFANOV P, STOYCHEV D, STOYCHEVA M, MARINOVA T. XPS and SEM studies of chromium oxide films chemically formed on stainless steel 316L[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2000, 65(2): 212-215.
[19] KAMACHI-MUDALI U, REYNDERS B, STRATMANN M. Localized corrosion behavior of Fe-N model alloys[J]. Corros Sci, 1999, 41(1): 179-189.
[20] DEAN M H, STIMMING U. The electronic properties of disordered passive films[J]. Corros Sci, 1989, 29(2/3): 199-211.
[21] PAN Y M, DUNN D S, CRAGNLOLINO G A, SRIDHAR N. Grain boundary chemistry and inter granular corrosion in alloy 825[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2000, 31(4): 1163-1173.
[22] ZHANG De-kang. Localized corrosion of stainless steels[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1982: 42.
[23] LIDE D R. CRC handbook of chemistry and physics[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press Inc, 2006.
[24] SATO N. Toward amore fundamental understanding of corrosion processes[J]. Corrosion, 1989, 45(5): 354-368.
[25] MACDONALD D D, URQUIDI-MACDONALD M. Theory of steady-state passing films[J]. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 1990, 137(8): 2395.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50871122)
收稿日期:2011-07-28;修订日期:2012-02-20
通信作者:陈长风,教授,博士;电话:010-89733200;E-mail: chen _c_f@163.com