裂隙在大型海底多金属硫化物矿体内流体运移中的作用
李怀明,陶春辉
(国家海洋局 第二海洋研究所,浙江 杭州,310012)
摘要:为了解裂隙在硫化物矿体内部流体运移过程中的作用,在三层结构多金属硫化物矿体模型的基础之上,构建发育有不同形态裂隙(横向和纵向裂隙)矿体模型,模拟不同渗透率情况下模型内部温度场和流场的分布特征,据此探讨不同形态裂隙在海底多金属硫化物矿体中的作用以及海底多金属硫化物矿体内部热场和流场分布的控制因素。结果表明:在具有单一热源的硫化物矿体内部,底部边界的热通量分布是控制硫化物矿体温度场和流场分布的主要因素;矿体内部的大型纵向裂隙可以是流体下渗的通道,也可以成为流体上升的通道,其通道作用会受到底部边界热通量分布、介质渗透率和矿体内裂隙性质等因素的限制。
关键词:多金属硫化物矿体;流体运移;裂隙;数值模拟
中图分类号:P736.3 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)S2-0049-07
Influence of fracture on hydrothermal circulation within large hydrothermal deposit
LI Huai-ming, TAO Chun-hui
(Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, Hangzhou 310012, China)
Abstract: Based on the three-layer model, the hydrothermal sulfide deposit model with different kinds of fractures was set up. The thermal and flow fields under different permeability conditions were simulated, while the functions of the fractures within the deposit were discussed. The results indicate that the thermal flux of the bottom boundary is the dominated factor that control the thermal and flow fields within the deposit model with single thermal source and the function of the fractures is constrained by some factors, such as the thermal flux of bottom boundary, the permeability and the characteristics of the fractures.
Key words: hydrothermal sulfide deposit; fluid flow; fracture; numerical simulation
目前全球已经发现的多金属硫化物储量超过百万吨级的大型海底多金属硫化物矿点已接近20处[1]。海底多金属硫化物被认为是继锰结核和富钴结壳之后又一具有重要开发潜力的矿产资源。同时,大型海底多金属硫化物矿体的形成过程不是简单的硫化物堆积,涉及到海水下渗、热液流体与海水的混合、矿物的沉淀/溶解等复杂动力学过程,具有重要的科学研究意义。大型海底多金属硫化物矿体大都经历了长时间、多阶段的生长过程,矿体内部组成结构和化学组成复杂,流体混合作用广泛,影响矿体形成过程的因素较多[2-17]。矿体内部多发育有不同性质裂隙,这些裂隙在海水的渗入和热液流体的上涌喷出等过程中发挥着重要作用,从而在很大程度上控制着硫化物矿体的内部结构。结合实测资料,构建符合多金属硫化物矿体实际情况的地质模型是了解海底多金属硫化物矿体形成过程的有效手段。已有的硫化物矿体模型[18-19]大都建立在均匀介质的基础之上,没有考虑到介质的不均一性对硫化物矿体的热场和流场的影响。因此,不同性质裂隙对大型海底多金属硫化物矿体内部温度场和流体运移的影响,裂隙在矿体中究竟是流体下渗还是上涌的通道以及其通道作用受到什么因素限制等都是值得深入探讨的问题。结合大西洋TAG热液活动区的大洋钻探(ODP)调查资料,李怀明等[20]曾经构建了一个具有三层结构的海底多金属硫化物矿体模型。本文作者基于此构建了发育有不同形态裂隙的硫化物矿体裂隙模型,并利用美国地质调查局开发并公开发布的地热体系模拟软件“HYDROTHERMAL”[21]对不同渗透率情况下裂隙模型内部温度场和流场的分布特征进行了模拟研究。
1 裂隙模型
1.1 数学模型简介和HYDROTHERMAL软件
裂缝模型的主要数学控制方程由建立在物质与能量守恒定律基础上的流体和热传输方程构成,利用控制方程,并结合达西定律和相关的限定方程可以对模型内流体的物理状态进行描述。通过有限元法对以上方程进行求解,采用Newton-Raphson迭代方法在每一时间步长内对每一个网格内的主要变量进行求解。
U.S. Geological Survey(美国地质调查局)开发了地下热水系统的模拟软件HYDROTHERMAL。该软件是一个能够模拟近临界或者超临界条件下地下水流动及热传输的三维有限差分模型,模拟实验条件为温度0~1 200 ℃,压力0.5~1 000 MPa[21]。本文采用该软件对海底硫化物矿体模型内部的流体运移过程进行 模拟。
1.2 几何模型
海底多金属硫化物矿体裂隙模型如图1所示。模型高度为150 m,横向长度为400 m,从顶部到底部共分3层,分别是块状硫化物层(20 m)、固结硫化物矿化层(60 m)和网脉状硫化物矿化层(70 m)。模型内部存在3种裂隙,分别为贯穿整个硫化物矿体的主裂隙,发育在局部层位的次级裂隙和横向裂隙。主裂隙和次级裂隙宽度为5 m,主裂隙贯穿整个硫化物矿体,长度为150 m,次级裂隙长度为60 m,横向裂隙横向长度为 150 m,纵向宽度为5 m。模型整体被划分为80×30的网格。

图1 多金属硫化物矿体的裂隙模型
Fig.1 Fracture model of sulfide deposit
1.3 边界和初始条件
模型的顶部边界设定为自由流动边界,即海水或者热液流体可以自由流入/流出。两侧边界条件分为2种情况,网脉状硫化物矿化层的侧边界为非自由流动边界,即在此边界上没有流体的流入/流出;块状硫化物层和固结硫化物矿化层部分的两侧边界同顶部边界条件相同,为自由流入边界,且温度和压力保持不变。底部边界设定为热传导边界,无流体进入,边界的热通量分布如图2所示。

图2 模型的底边界热通量分布(单位:mW/m2)
Fig.2 Distribution of model bottom heat flux
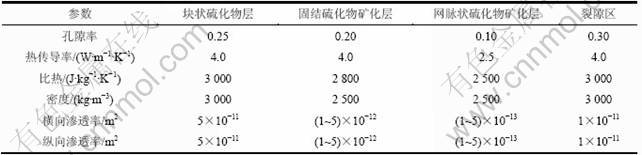
表1 裂隙模型的相关物理参数
Table 1 Related physical parameters of fracture model
模型内部为传导温度场,时间t=0时,模型内部流体为静止。顶部边界压力p为20 MPa,温度为30 ℃,从顶部边界到底部,温度以30 ℃/km的梯度增加。另外,该模型不考虑周围海水的运动对模型内流体运移的影响。
1.4 模型的物理参数
多金属硫化物矿体裂隙模型中各层以及裂隙区的介质物理参数(包括介质孔隙率、比热、密度和渗透率)来自于2方面资料:一方面是已有地质模型的相关参数,包括Dickson等[18-19]的硫化物矿体的模型参数和洋壳内部的热液循环模拟的相关结果[22-23];另一方面来自于ODP在Juan de Fuca区和TAG区的实测资料[4, 24]。表1给出了裂隙模型的相关物理参数。
2 模拟结果
渗透率是控制多孔介质中热场分布和流体运移的关键参数之一[25],本文将对3种不同渗透率情况下裂隙模型的温度场、流场和流体通量场的分布进行模拟计算,并对裂隙模型模拟结果同无裂隙存在的均质模型模拟结果进行对比[20]。其中,流场分布信息可以显示模型内每一个网格内的水流方向。流体通量可以表述为单位时间在单位面积内(即模拟区域的网格内)流过的流体质量,可用于描述该点的流体速度。模拟的地质时间为10 000 a。
2.1 横向渗透率与纵向渗透率一致条件下
设定模型内各层的介质渗透率如下:块状硫化物层渗透率为5×10-11 m2;固结硫化物矿化层内横向渗透率与纵向渗透率相同,为1×10-12 m2;网脉状硫化物矿化层内横向渗透率等于纵向渗透率,为1×10-13 m2。图3和图4所示分别为均质模型和裂隙模型内部温度场、流场和流体通量的分布图。
图3(a)表明:均质模型内温度场形态呈钟形,最高温度为140 ℃,位于模型底部的中央区域,对应于底部边界的热通量最大值。裂隙模型内,最高温度和温度场的分布特征与均质模型大体相似,只是在局部区域因为受到裂隙的影响发生改变(图4(a)),例如,钟形的温度场整体向左偏移,模型右侧区域的温度略高于左侧区域。由此可见,在横向渗透率与纵向渗透率相同的矿体模型内,不同形态裂隙的存在对于矿体温度场的整体分布影响不大。
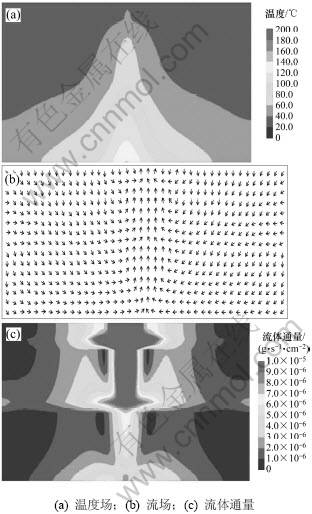
图3 均质模型模拟实验结果
Fig.3 Results of homogenous model

图4 裂隙模型模拟实验结果
Fig.4 Results of fracture model
图3(b)表明:在无裂隙均质模型内,海水从块状硫化物层和固结硫化物层的侧边界以及模型顶部进入矿体,模型顶部的中央区域为热液流体集中喷出区,在集中喷出区的两侧对称发育着2个形态相同的对流体。在裂隙模型内,主裂隙和次级裂隙都是流体的下渗通道,网脉状硫化物层中横向裂隙区的流体运移方向同周围介质中流体运移一致。海水从块状硫化物层和固结硫化物层的侧边界和模型顶部进入矿体。裂隙的存在使得集中喷出区的位置略向左移动,对称于集中喷出区发育的2个对流体规模并不相同,左侧对流体的规模略大于右侧(图4(b))。
对比图3(c)和图4(c)可以发现:裂隙区的介质渗透率较低造成裂隙区流体的运移速度明显高于其周围区域的流体运移速度。不同裂隙区内的流体运移速度并不相同,横向裂隙区的流体运移通量最大,大于1.0×10-5 g/(s·cm2),与集中喷出区的流体运移通量相当。主裂隙区内的流体运移通量在纵向上差别较大,其中,固结硫化物矿化层主裂隙区内的流体速度明显比块状硫化物层和网脉状硫化物矿化层的高,块状硫化物层内主裂隙区流体速度最小,与周围区域的流体运移通量相当。
由此可见:该情况下底部边界热通量分布应该是控制海底多金属硫化物矿体内温度场和流体运移模式的主要因素,裂隙对于矿体内的热场分布和流体运移影响不大。
2.2 横向渗透率为纵向渗透率的5倍条件下
设定模拟条件如下:块状硫化物层的渗透率为5×10-11 m2;固结硫化物矿化层内横向渗透率为5×10-12 m2,纵向渗透率为1×10-12 m2;网脉状硫化物矿化层内横向渗透率为5×10-13 m2,纵向渗透率为1×10-13 m2。图5和图6所示分别为该模拟条件下均质模型和裂隙模型内温度场、流场和流体通量的模拟结果。
图6(a)表明:裂隙模型内的最高温度为160 ℃,略高于前一种情况(140 ℃),等温线形态呈钟形,对应于底部边界的热通量的最大值,没有发生偏移。均质模型内最高温度和等温线的形态特征与裂隙模型相近(图5(a))。图5(b)表明:均质模型内的流体运移与前一种情况相同,海水从块状硫化物矿化层和固结硫化物矿化层两侧边界和模型的顶部边界进入模型,顶部边界的中央区域为热液流体的集中喷出区,集中喷出区两侧对称发育两个规模相同的对流体。在裂隙模型内,流体的运移没有发生改变,主裂隙和次级裂隙还是流体的下渗通道,流体集中喷出区两侧的对流体规模相差不大(图6(b))。对比图5(c)和图6(c)可以发现:裂隙区内的流体运移速度与前一种情况的模拟结果不同,主裂隙和次级裂隙区内的流体运移速度明显比横向裂隙区的高,固结硫化物矿化层和网脉状硫化物矿化层内主裂隙区的流体运移速度相差不大。

图5 均质模型模拟实验结果
Fig.5 Results of homogenous model

图6 裂隙模型模拟实验结果
Fig.6 Results of fracture model
因此,底部边界热通量分布还是控制矿体内温度场和流场分布的主要因素,横向渗透率的增加在一定程度上减小了裂隙对矿体内温度场和流场的影响。
2.3 纵向渗透率为横向渗透率的5倍条件下
模型内各层渗透率设定为:块状硫化物层的渗透率为5×10-11 m2;固结硫化物矿化层内横向渗透率为1×10-12 m2,纵向渗透率为5×10-12 m2;网脉状硫化物矿化层内横向渗透率为1×10-13 m2,纵向渗透率为5×10-13 m2。图7和图8所示分别为该情况下均质模型和裂隙模型内温度场、流场和流体通量的模拟结果。
图7(a)表明均质模型内温度场的形态同前两种情况相差较大,呈多峰式分布,且具有明显对称性,最高温度为120 ℃,位于模型底部的中央区域。在裂隙模型内,温度场形态类似于钟形,但并不对称,整体向左偏移,最高温度为100 ℃(图8(a)),等温线形态与纵向渗透率等于横向渗透率模型的模拟结果相近。
图7(b)和图7(c)表明:在均质模型内出现了3个流体的集中喷出区,其位置分别对应于温度场的3个峰。位于中央区域的流体喷出区规模最大,流体速度运移速度最快,左右两侧的流体喷出区对称发育,规模和流速都较小。图8(b)表明:在裂隙模型内的流体运移情况发生了较大变化,模型中央区域为流体的集中喷出区,但喷出区两侧并没有发育对流体。主裂隙区不再是流体的下渗通道,而成为流体的喷出通道。同时,主裂隙区内混合了2种流体,一是来自于深部高温流体,一是来自于左侧区域温度较低的流体,因此,主裂隙附近区域应该是重要的矿物沉淀区。次级裂隙区还是流体的下渗通道,横向裂隙区与周围区域的流体运移基本一致。图8(c)表明:该情况下横向裂隙区的流体运移速度要高于主裂隙和次级裂隙区。主裂隙和次级裂隙区内的流体运移通量分别为1.0×10-6 g/(s·cm2)和3.0×10-6 g/(s·cm2)。

图7 均质模型模拟实验结果
Fig.7 Results of homogenous model

图8 裂隙模型模拟实验结果
Fig.8 Results of fracture model
3 讨论
3.1 矿体温度场和流场分布的控制因素
模拟结果表明在具有单一集中热源的硫化物矿体内部,底部边界的热通量分布是控制矿体内温度场和流场的主要因素,但不是唯一的因素。介质渗透率分布和矿体内的裂隙也在很大程度上影响着矿体内温度场和流场分布。介质渗透率和裂隙对于矿体温度场和流场的作用不是独立的,而是相互联系。例如,模型横向渗透率的增加会在一定程度上减小纵向裂隙对模型的影响,而模型纵向渗透率又在很大程度上影响着裂隙在矿体内的作用。
3.2 裂隙的通道作用
多金属硫化物矿体内部的裂隙是流体运移的重要通道,但对于裂隙究竟是流体的下渗通道还是喷出通道这个问题还不是特别清楚。本文的模拟结果表明:发育在矿体内部的裂隙(排除裂隙位于流体集中喷发区的情况。因为即使没有裂隙,该区域也是流体的上升区),不仅可以作为流体下渗的通道,还能成为流体上升的通道,裂隙在硫化物矿体中的作用会受到多种因素的限制:
(1) 底部边界的热通量分布。来自于底部边界的热量是驱动矿体内流体运移的动力,同时是控制矿体内温度场和流场分布的最重要的因素。因此,热通量的分布特征是控制模型内裂隙作用的重要因素之一。
(2) 多孔介质的渗透率。模拟结果表明在纵向渗透率大于横向渗透率的情况下主裂隙成为流体上升的通道,而纵向渗透率小于或等于横向渗透率情况下主裂隙都是流体下渗的通道。因此,不仅底部边界热通量分布、介质的不均质性即渗透率分布也应该是影响矿体内纵向裂隙在矿体中通道作用的因素之一。
(3) 裂隙的性质。纵向渗透率大于横向渗透率的裂隙模型的模拟结果表明,主裂隙和次级裂隙虽然都是纵向裂隙,但二者的作用并不相同,主裂隙内流体向上运移,而次级裂隙内流体向下运移。同时,发育在次级裂隙下方的横向裂隙也应该是影响次级裂隙作用的一个因素。因此,裂隙本身的性质以及不同形态裂隙之间的相互限制也应该是影响纵向裂隙在矿体中通道作用的因素之一。
4 结论
(1) 在具有单一热源的硫化物矿体内部,底部边界的热通量分布是控制硫化物矿体温度场和流场分布的主要因素。
(2) 矿体内部的大型纵向裂隙可以是流体下渗的通道,也可以成为流体上升的通道,其通道作用会受到底部边界热通量分布、介质渗透率和矿体内裂隙性质等因素的限制。
致谢
美国地质调查局的Ken Kipp先生为本文提供了HYDROTHERMAL 软件,并在实验过程中给予了悉心指导,在此表示诚挚的谢意。
参考文献:
[1] Herizig P M, Petersen S, Hannington M D. Polymetallic massive sulphide deposits at the modern seafloor at the modern seafloor and their resource potential[R]. Kingston: International Seabed Authority, 2002: 8-35.
[2] Ohmoto H. Formation of volcanic-associated massive sulfide deposits: The Kuroko perspective[J]. Ore Geologica Review, 1996, 10: 135-177.
[3] Knott R, Fouquet Y, Honnorez Y, et al. Petrology of hydrothermal mineralization: A vertical section through the TAG mound[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1998, 139: 5-26.
[4] Gr?schel-Becke H M, Villinger H W, Konyukhov B A, et al. Seismic velocities of diabase and basalt from Middle Valley sills and flow, northern, Juan de Fuca Ridge[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1993, 139: 597-612.
[5] Tivey M K, Humphris S E, Thompson G, et al. Deducing patterns of fluid flow and mixing within the TAG active hydrothermal mound using mineralogical and geochemical data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1995, 100(B7): 12527-12555.
[6] Humphris S E, Alt J C, Teagle D A H, et al. Geochemical changes during hydrothermal alteration of basement in the stockwork beneath the active TAG hydrothermal mound[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1998, 139: 255-276.
[7] Mills R A, Damon A H, Tivey M K. Fluid mixing and anhydrite precipitation within the TAG mound[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1998, 158: 119-127.
[8] Fouquet Y, Henry K, Knott R, et al. Geochemical section of the TAG hydrothermal mound[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1998, 158: 363-387.
[9] Petersen S, Herzig P M, Hannington M D. Fluid inclusion studies as a guide to the temperature regime within the TAG hydrothermal mound, 26°N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1998, 158: 163-178.
[10] Binns R A, Barriga F J A S, Miller D J. Leg 193 synthesis: Anatomy of an active felsic-hosted hydrothermal system, Eastern Manus Basin, Papua New Guinea[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 2007, 193: 1-71.
[11] Fouquet Y, Knott R, Cambon P, et al. Formation of large sulfide mineral deposits along fast spreading ridges. Example from off-axial deposits at 12°43′N on the East Pacific Rise[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 144: 147-162.
[12] Peter J M, Goodfellow W D, Leybourne M I. Fluid inclusion petrography and microthermometry of the Middle Valley hydrothermal system, northern Juan de Fuca Ridge[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1994, 139: 412-428.
[13] Gemmell J B, Sharpe R. Detailed sulfur-isotope investigation of the TAG hydrothermal mound and stockwork zone, 26°N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1998, 158: 71-84.
[14] Münch U, Blum N, Halbach P. Mineralogical and geochemical features of sulfide chimneys from the MESO zone, Central Indian Ridge[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 155: 29-44.
[15] Glasby G P, Notsu. Submarine hydrothermal mineralization in the Okinawa Trough, SW of Japan: an overview[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2003, 23: 299-339.
[16] Binns R A. Data report: geochemistry of massive and semimassive sulfides from Site 1189, Ocean Drilling Program Leg 193[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 2006, 193: 1-22.
[17] Houghton J L, Shanks W C, Seyfried W E. Massive sulfide deposition and trace element remobilization in the Middle Valley sediment-hosted hydrothermal system, northern Juan de Fucan Ridge[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(13): 2863-2873.
[18] Dickson P, Schultz A, Woods A. Preliminary modeling of hydrothermal circulation within mid-ocean ridge sulphide structures, Hydrothermal Vents and Processes, Special Publication[J]. Geological Society of London, 1995, 87: 145-157.
[19] Pascoe A R, Cann J R. Modelling diffuse hydrothermal flow in black smoker vent fields, Hydrothermal Vents and Processes, Special Publication[J]. Geological Society of London, 1995, 87: 159-173.
[20] 李怀明, 翟世奎, 陶春辉, 等. 大型海底多金属硫化物矿体内部的流体过程[J]. 海洋学报, 2011, 33(4): 111-120.
LI Huai-ming, ZHAI Shi-kui, TAO Chun-hui, et al. A numerical study of hydrothermal circulation patterns within the large hydrothermal sulfide deposit[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2011, 33(4): 111-120.
[21] Jupp T, Schultz A. A thermodynamic explanation for black smoker temperatures[J]. Nature, 2000, 403: 880-883.
[22] Polyansky O P, Poort J. 2D modeling of fluid flow and heat transport during the evolution of the Baikal rift[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2000(69/70): 77-81.
[23] Wang K, He J, Davis E E. Influence of basement topography on hydrothermal circulation in sediment-buried igneous oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 146: 151-164.
[24] Ludwig R J, Iturrino G J, Rona P A. Seismic velocity-porosity relationship of sulfides, sulfate, and basalt samples from the TAG hydrothermal mound[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1998, 158: 313-327.
[25] 王兴涛, 翟世奎, 孟凡顺, 等. 渗透率对沉积物覆盖洋壳内热液循环的影响[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 2006, 36: 871-880.
WANG Xing-tao, ZHAI Shi-kui, MENG Fan-shun, et al. Influence of permeability on hydrothermal circulation in sediment-buried oceanic crust[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2006, 36: 871-880.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2011-06-15;修回日期:2011-07-15
基金项目:海洋二所基本科研业务费专项基金资助项目(JG0903);中国科学院海洋地质与环境重点实验室开放课题(MGE2009KG07)
通信作者:李怀明(1977-),男,山东聊城人,助理研究员,从事海底热液活动研究;电话:0571-81963233;E-mail: huaiming_lee@163.com