Zr对Mo-Zr合金力学性能与显微组织的影响
钱昭,范景莲,成会朝,田家敏
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:采用粉末冶金方法制备Mo-Zr合金,研究Zr对Mo-Zr合金相对密度、力学性能及其显微组织的影响。结果表明:合金经1 920 ℃烧结后接近全致密,相比纯Mo其室温抗拉强度明显提高,Zr添加量为3.0%(质量分数)时,合金抗拉强度最高,达603 MPa,较纯Mo提高了72.4%。显微组织分析发现,少量Zr原子固溶进入Mo基体中产生显著固溶强化作用,大部分Zr则与坯体中的氧结合,一方面净化了晶界氧,使晶界强度提高;另一方面形成二次相粒子弥散分布于晶界和晶粒内部,并阻碍合金烧结时的晶粒长大,有利于提高合金性能,但过多的氧化物粒子在晶界的富集将对合金强度产生不利影响。
关键词:Mo-Zr合金;固溶强化;二次相粒子
中图分类号:TG146.4 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)08-3146-05
Effect of Zr on property and microstructure of Mo-Zr alloy
QIAN Zhao, FAN Jinglian, CHENG Huichao, TIAN Jiamin
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Mo-Zr alloys were fabricated via powder metallurgy method. The effects of Zr on relative density microstructure and property of Mo-Zr alloy were studied. The results indicate that the relative density and tensile strength at room temperature of Mo-Zr alloy are effectively enhanced after adding Zr. The tensile strength achieves the highest value 603 MPa when the content of Zr is 3.0%(mass fraction), which is 72.4% higher than pure Mo. The microstructure analysis reveals that a part of Zr solves into the Mo matrix , which enhances the tensile strength of the alloys, while the other part of Zr forms oxide second phase particles. However, over-dose oxide particles would generate negative influence on the property of the alloy.
Key words: Mo-Zr alloy; solid solution; second phase particles
钼由于具有熔点高、强度大、硬度高、导电导热性好、热膨胀系数低,耐磨损和抗腐蚀性能强及良好的抗热震性能和耐热疲劳性能等特点,因而被广泛应用于钢铁工业、电子工业、航空航天、原子核能及金属压力加工等领域[1-3]。目前,制备钼制品的方法主要为熔炼法[4-6]和粉末冶金法。随着现代制品形状的不断复杂化,采用熔炼法制备的钼锭后续加工对材料浪费很大,而采用粉末冶金方法不仅可以制备形状复杂的零部件,而且后续加工少,材料利用率高。然而,由于氧、氮等杂质原子在晶界的富集及其本征脆性,钼及钼合金烧结后脆性非常明显[7-8],而采用粉末冶金方法制备的制品一般接近最终形状,难于再进行挤压、锻造、热扎等后续处理来改善脆性。因此,从材质上使钼的性能得以提高是扩大粉末冶金方法在钼制品中的研制与应用的关键。在钼中添加合金元素产生固溶强化及弥散强化是提高钼性能的有效方法[4, 9]。其中,Mo-Ti[10-11],Mo-Zr[12-13]及TZM[14]合金就是采用微量合金元素产生显著固溶强化的典型代表, 它们相比纯Mo在室温、高温力学性能上均取得较明显提高。Zr具有高的熔点,高温下能与钼产生固溶而低温下溶解度很小,能对钼起到显著的固溶强化及弥散强化效果,且Zr在加热时能大量吸收氧、氢、氮等元素,可能是改善烧结钼合金室温脆性的有效途径。前期研究证实[13],在Mo中添加微量元素Zr(0.06%~0.5%,质量分数)使合金室温抗拉强度得以显著提高,提高幅度最高达26%,说明Zr对钼合金的强化效果十分明显。但目前对于高Zr含量的Mo-Zr合金材料的研究,国内外尚无相关报道,并对合金烧结行为及强韧化机制尚缺乏系统的研究。为此,本文作者采用粉末冶金方法,制备了微量及高Zr含量Mo-Zr合金,研究Zr对合金室温力学性能与显微组织的影响。
1 实验
按照一定的成分配比,通过在Mo粉中直接添加纯Zr粉,采用高能球磨法分别制备出不同Zr含量的Mo-nZr混合粉末(n=0.1,0.3,0.5,1.0,1.5,2.0,3.0,5.0代表Zr的质量分数分别为0.1%,0.3%,0.5%,1.0%,1.5%,2.0%,3.0%和5.0%)。混合粉末在25 t油压机上采用刚模双向压制成3 mm×3 mm×14 mm的工字拉伸样坯,压制压力为350 MPa。压坯在氢气保护下进行预烧结,预烧温度为1 000 ℃,保温2 h。然后,预烧坯在氢气保护下进行高温烧结,烧结温度1 920 ℃,保温2 h。
采用阿基米德排水法测定烧结后样品密度,并根据合金理论密度计算其相对密度;采用LJ-3000A型机械式拉力实验机检测样品的室温拉伸性能;采用JSM-5600LV型扫描电镜观察断口形貌,并采用EDS能谱仪进行选区或定点成分分析;采用MeF3A型金相显微镜对样品进行显微组织观察。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 Zr对Mo-Zr合金相对密度的影响
图1所示为合金相对密度与元素Zr添加量的关系曲线。从图1可以看出:添加Zr的合金烧结后接近全致密,且随Zr含量的增加合金相对密度的变化可以分为2个区域:在Zr含量较低(<2.0%)的区域,随Zr含量的增加,合金相对密度逐渐降低;继续增加Zr含量(>2.0%),合金相对密度显著回升。
Zr原子的半径比Mo原子半径大且半径差较大,Zr的溶入必然造成Mo晶格点阵畸变严重,结构稳定性降低,因而Zr在Mo中的溶解度十分有限,在1 300 ℃以上才发生明显扩散[1]。高温烧结阶段,Zr开始缓慢进入Mo基体。虽然根据Mo-Zr合金相图,烧结温度下Zr在Mo中有足够的固溶度,但受扩散动力学的限制大部分Zr仍以液相存在,并逐渐吸附坯体中的氧在烧结后形成氧化物二次相粒子。后面的能谱分析证明了这一结论,即烧结后Zr在Mo中的溶解度很小且固溶成分分布不均匀,而二次相粒子中具有较高的氧含量。根据文献[15],烧结后合金晶界处的孔隙与预烧坯氧含量成正比,因而添加的Zr越多,聚集在晶界的氧化物粒子越多,烧结后的密度下降。另一方面,在烧结过程中,晶界可越过部分小的液相颗粒迁移,烧结后在晶粒内部形成弥散分布的二次相粒子,造成基体晶格膨胀;Zr添加量较少时,产生液相量较少,且部分Zr吸收坯体中氧在表面形成氧化物壳层,流动性变差,不足以完全填充固相颗粒间的空隙,因此,少量Zr的添加反而造成合金烧结后致密度小幅下降。
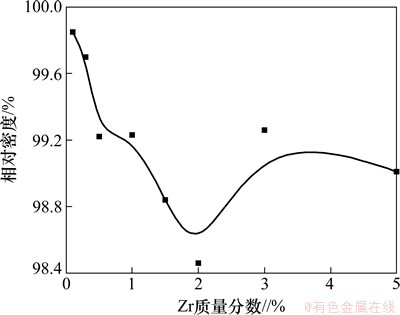
图1 Zr添加量对合金相对密度的影响
Fig. 1 Effect of addition amount of Zr on relative density of Mo-Zr alloy
然而,当合金中的Zr含量增加到一定程度后(>2.0%),高温烧结时产生的液相量大幅增多,液相烧结作用急剧上升,在颗粒间孔隙中液相所形成的毛细管力及液相本身的黏性流动和表面张力作用下,固相颗粒调整位置、重新分布以达到最紧密的排布。因此,添加高Zr含量的Mo-Zr合金的相对密度显著回升。
2.2 Zr对Mo-Zr合金室温力学性能的影响
图2所示为添加不同Zr含量的样品在1 920 ℃烧结1 200 ℃真空处理后的室温抗拉强度曲线。从图2可以看出:添加元素Zr后合金室温抗拉强度相比于纯Mo(350 MPa)显著提高。在Zr含量较少时,随Zr添加量的增加,合金强度先急剧升高而后下降,在高Zr含量区域(>2.0%),合金强度又急剧回升。Zr添加量为3.0%时,合金强度最高,达603 MPa,较纯Mo提高了72.4%。
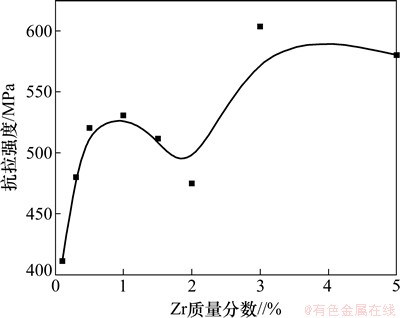
图2 Zr添加量对合金室温抗拉强度的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of addition amount of Zr on tensile strength of Mo-Zr alloy at room temperature
添加Zr使合金室温抗拉强度产生上述变化是Zr在合金中的固溶强化、形成二次相粒子产生弥散强化及晶粒细化等综合作用的结果。Zr添加量较低时,部分Zr原子固溶进入Mo基体中产生显著固溶强化效应,使合金强度急剧增强。然而,由于Zr在Mo中的溶解度很小,当Zr添加量超过一定程度时,烧结后在合金晶界处产生大量Zr的氧化物二次相粒子富集,使晶界脆化,强度下降。在高Zr含量区域,合金强度回升,则与二次相粒子阻碍合金烧结过程中的晶粒长大、晶粒细化效果显著有关。
2.3 Zr对Mo-Zr合金显微组织的影响
图3所示为不同Zr含量的合金金相显微组织。从图3可以看出:添加Zr后,在合金晶界和晶粒内部都出现了大量球形二次相粒子均匀弥散分布。对比发现,在Zr含量较少时(图3(a)),合金晶粒粗大且尺寸不均匀,部分晶粒长大,个别晶粒出现异常长大现象;随着Zr含量的增加,二次相粒子数量增多,合金晶粒尺寸不断减小,晶粒细化效果显著。
图4所示为Mo-0.1Zr(a)及Mo-5.0Zr(b)合金室温拉伸断口SEM像。合金室温拉伸主要为沿晶断裂机制,Zr含量较少的合金,二次相粒子数量较少,晶界平整光滑,个别晶粒出现穿晶断裂(图4(a));随Zr添加量的持续增加,二次相粒子和孔隙数量明显增多,晶粒趋于显著细化,合金室温拉伸为单一的沿晶断裂模式,没有出现穿晶断裂晶粒(图4(b))。
2.4 讨论
由图3和4可知:Zr在合金中主要以二次相粒子形式存在,并阻碍合金在高温烧结时的晶粒长大,从而合金的晶界强度得以显著提高。为了仔细研究Zr在合金中的存在形式及合金室温强韧化机制,对合金中的二次相粒子及Mo晶粒界面分别进行了EDS分析,结果如图5所示。结果显示二次相粒子组成元素为Zr,Mo和O,而Mo晶粒界面Zr元素谱线不明显,Zr添加量较少时部分Mo晶粒中甚至难以出现Zr的谱线;此外,二次相粒子中氧含量较高而在Mo晶粒界面氧含量甚微。由此可知:烧结过程中少量Zr原子扩散进入Mo基体中,产生固溶强化效应,在添加微量Zr含量区域,固溶强化效果表现最为显著,即合金室温抗拉强度随Zr含量增加急剧升高。同时,由于低温下Zr在Mo中的溶解度很小且固溶成分分布不均匀,烧结后部分固溶Zr原子脱溶析出,加之烧结过程中大部分Zr依旧以熔融液相存在并吸附坯体中的氧,烧结后便在合金晶界与晶粒内部形成弥散分布的氧化物二次相粒子,随添加的Zr含量增多,形成的二次相粒子数目也增多。根据Orowan机制,这些第二相粒子阻碍了位错线的运动,对提高合金强度有益。然而,从图4(b)可以看出:Zr含量较高时,尽管合金晶粒尺寸十分细小,但二次相粒子尺寸较粗大,这可能是由于高温烧结时熔融Zr液相发生表面氧化,便形成长大的二次相粒子,减弱其强化效果。作者前期已有研究表明,对于脆性材料,由于氧化物二次相粒子的大量生成,这些硬脆第二相粒子与Mo晶粒之间的界面容易成为微裂纹源,在两相界面形成显微空洞,反而会造成材料强度下降。因此,控制Mo-Zr合金中二次相粒子数目与尺寸,是提高合金室温力学性能的关键。
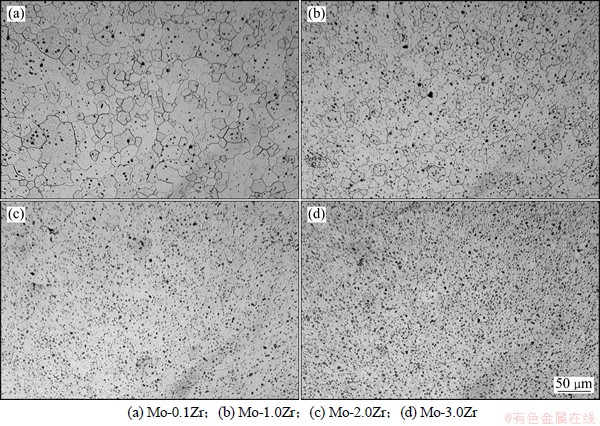
图3 部分合金的显微组织
Fig. 3 Microstructures of alloys
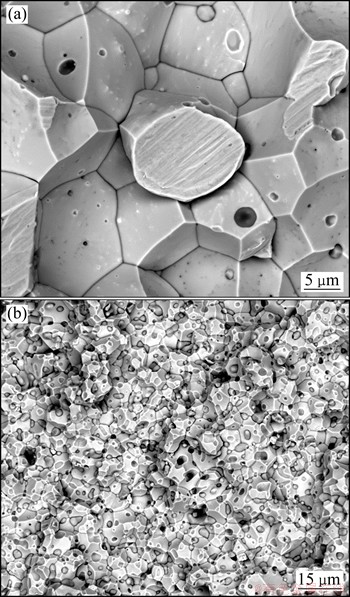
图4 Mo-0.1Zr(a)及Mo-5.0Zr(b)合金室温拉伸断口SEM像
Fig. 4 SEM images of Mo-0.1Zr alloy (a) and Mo-5.0Zr alloy (b)
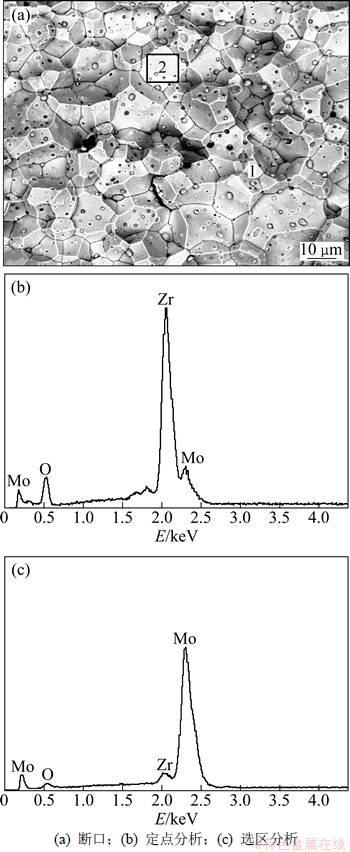
图5 Mo-1.0Zr合金断口能谱
Fig. 5 Fracture EDS patterns of Mo-1.0Zr alloy
在高Zr含量区域(>2.0%),合金强度显著回升,则与如下因素有关:一方面,由于Zr对氧的强的吸附性,减少了致脆元素氧在晶界的富集,晶界净化作用显著,Mo晶粒间的结合强度大大提高;另一方面,大量弥散分布的二次相粒子阻碍合金烧结过程中的晶粒长大,晶粒被显著细化,因而合金强度急剧回升。
3 结论
(1) 添加Zr的合金经1 920 ℃烧结后接近全致密,在低Zr含量区域,合金相对密度随Zr含量的增加逐渐降低;Zr含量超过2.0%(质量分数)后,合金相对密度又显著回升。
(2) 添加Zr后,合金室温抗拉强度相对于纯Mo显著提高。Zr添加量为3.0%时,合金抗拉强度最高,达603 MPa,较纯Mo提高了72.4%。
(3) 少量Zr原子固溶进入Mo基体中产生显著固溶强化作用,大部分Zr则与坯体中的氧结合,一方面净化了晶界氧,使晶界强度提高;另一方面形成二次相粒子弥散分布于晶界和晶粒内部,并阻碍合金烧结时的晶粒长大,有利于合金性能,但过多的氧化物粒子在晶界的富集将对合金强度产生不利影响。
参考文献:
[1] Moerkurova H H. 钼冶金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1984: 4-18.
Moerkurova H H. Molybdenum metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 1984: 4-18.
[2] 曹维成, 刘静, 任宜霞. 掺杂不同微量元素对钼材性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属快报, 2006, 25(8): 29-31.
CAO Weicheng, LIU Jing, REN Yixia. Influence of doping elements on the properties of molybdenum material[J]. Rare Metals Letters, 2006, 25(8): 29-31.
[3] 张久兴, 刘燕琴, 刘丹敏, 等. 微量La2O3 对钼的韧化作用. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(1): 13-17.
ZHANG Jiuxing, LIU Yanqin, LIU Danmin, et al. Toughness of La2O3-doped Mo alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(1): 13-17.
[4] Cockeram B V. Measuring the fracture toughness of molybdenum-0.5 pct titanium-0.1pct zirconium and oxide dispersion-strengthened molybdenum alloys using standard and subsized bend specimens[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33: 3685-3707.
[5] Sharma I G, Chakraborty S P, Suri A K. Preparation of TZM alloy by aluminothermic smelting and its characterization[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 393: 122-128.
[6] Cockeram B V. The mechanical properties and fracture mechanisms of wrought low carbon arc cast (LCAC), molybdenum-0.5pct titanium-0.1pct zirconium (TZM), and oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) molybdenum flat products[J]. Material Science and Engineering A. 2006, 418: 120-136.
[7] Mrotzek T, Hoffmann A, Martin U. Hardening mechanisms and recrystallization behaviour of several molybdenum alloys[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2006, 24: 298-305.
[8] 王德志, 刘心宇, 周美玲. Mo-La2O3 烧结坯间隙杂质的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2000, 29(14): 266-268.
WANG Dezhi, LIU Xinyu, ZHOU Meiling. Study of interstitial impurities in sintered Mo-La2O3 bars[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2000, 29(14): 266-268.
[9] Nagae M, Takemoto Y, Yoshio T, et al. Preparation of structurally controlled dilute molybdenum-titanium alloys through a novel multi-step inteenal nitriding technique and their mechanical properties[J]. Material Science and Engineering A, 2005, 406: 50-56.
[10] 卢明园, 范景莲, 成会朝, 等. Ti对Mo-Ti合金拉伸强度及显微组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(3): 409-413.
LU Mingyuan, FAN Jinglian, CHENG Huichao, et al. Effects of Ti on tensile strength and microstructure of Mo-Ti alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(3): 409-413.
[11] 成会朝, 范景莲, 卢明园, 等. 合金元素Ti对Mo合金性能及结构的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 40(2): 395-399.
CHENG Huichao, FAN Jinglian, LU Mingyuan, et al. Effect of alloyed element Ti on property and microstructure of Mo alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2009, 40(2): 395-399.
[12] 范景莲, 成会朝, 卢明园, 等. 微量合金元素 Ti、Zr对Mo合金性能和显微组织的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2008, 37(8): 1471-1474.
FAN Jinglian, CHENG Huichao, LU Mingyuan, et al. Effect of alloyed elements Ti, Zr on the properties and microstructure of mo alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2008, 37(8): 1471-1474.
[13] 范景莲, 成会朝, 卢明园, 等. 真空处理和Ti含量对Mo-0.1Zr合金性能与显微组织的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010, 39(2): 338-342.
FAN Jinglian, CHENG Huichao, LU Mingyuan, et al. Effect of vacuum treatment and Ti content on the properties and microstructure of Mo-0.1-Zr alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(2): 338-342.
[14] 成会朝, 范景莲, 刘涛, 等. TZM钼合金制备技术及研究进展[J]. 中国钼业, 2008, 32(6): 40-45.
CHENG Huichao, FAN Jinglian, LIU Tao, et al. Preparation and research development of TZM molybdenum alloys[J]. China Molybdenum Industry, 2008, 32(6): 40-45.
[15] Kadokura T, Hiraoka Y, Nakabayashi S, et al. Effects of sintering conditions on the properties of sintered molybdenum. Powder Metallurgy, 2006: 1153-1154.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2012-09-10;修回日期:2012-12-29
基金项目:国家杰出青年科学基金资助项目(50925416)
通信作者:范景莲(1967-),女,湖南澧县人,教授,博士生导师,从事难熔金属与硬质合金研究;电话:0731-88836652;E-mail:fjl@mail.csu.edu.cn