文章编号: 1004-0609(2005)05-0705-06
铸态及快淬态La-Mg-Ni系
(PuNi3型)贮氢合金的循环稳定性
张羊换1, 2, 董小平1, 王国清2, 郭世海2, 任江远1, 王新林2
(1. 内蒙古科技大学 材料学院, 包头 0140101;
2. 钢铁研究总院 功能材料研究所, 北京 100081)
摘 要: 用铸造及快淬工艺制备了La-Mg-Ni系(PuNi3型)La2Mg(Ni0.85Co0.15)9Bx (x=0~0.2)贮氢合金, 分析测试了铸态及快淬态合金的微观结构与循环稳定性, 研究了硼及快淬工艺对合金微观结构及电化学循环稳定性的影响。 结果表明, 铸态合金具有多相结构, 包括 (La, Mg)Ni3相和LaNi5相, 一定量的LaNi2相及微量的Ni2B相, 经大于15m/s淬速快淬处理后Ni2B相消失, 并且其它相的相对量随淬速的变化而变化。 硼的加入提高了铸态及快淬态合金的循环稳定性, 但其作用机理完全不同。 合金的循环寿命随淬速的增加而增加, 但快淬工艺对La-Mg-Ni系贮氢合金循环寿命的改善非常有限。
关键词: La-Mg-Ni系贮氢合金; 快淬工艺; 微观结构; 循环稳定性 中图分类号: TG139.7
文献标识码: A
Cycling stability of La-Mg-Ni system (PuNi3-type) hydrogen storage alloys prepared by casting and rapid quenching
ZHANG Yang-huan1, 2, DONG Xiao-ping1, WANG Guo-qing2,
GUO Shi-hai2, REN Jiang-yuan1, WANG Xin-lin2
(1. School of Materials, Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology,
Baotou 014010, China;
2. Department of Functional Materials Research, Central Iron and Steel Research Institute,
Beijing 100081, China)
Abstract: The La-Mg-Ni system (PuNi3-type) hydrogen storage alloys La2Mg(Ni0.85Co0.15)9Bx (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2) were prepared by casting and rapid quenching. The microstructures and electrochemical cycling stabilities of the as-cast and quenched alloys were determined and measured. The effects of boron content and quenching rate on the microstructures and electrochemical cycling stabilities of the alloys were investigated. The results show that the as-cast and quenched alloys are composed of the (La, Mg)Ni3 phase (PuNi3-type structure), the LaNi5 phase and the LaNi2 phase. A trace of the Ni2B phase exists in the as-cast alloys containing boron, and after the as-cast alloys are quenched when quenching rate is more than 15m/s, the Ni2B phase in the alloys nearly disappears. The relative amount of each phase in the alloys changes with the variety of the quenching rate. The addition of boron enhances the cycle stability of the as-cast and quenched alloys, but the mechanism is completely different. The cycle lives of the as-quenched alloys increase with the increasing quenching rate, but the improvement of the rapid quenching treatment on the cycling stability of La-Mg-Ni system hydrogen storage alloys is very limited.
Key words: La-Mg-Ni system electrode alloy; rapid quenching technology; microstructure; cycling stability
由于Ni-MH电池具有高的容量、 耐过充过放性能好、 优良的高倍率充放性能、 环境友好并可与Ni-Cd电池互换等优点, 其应用越来越广泛。 作为Ni-MH电池负极材料, 贮氢合金的研究成为拓宽Ni-MH电池应用领域的关键。 近年来, 人们已开发出一系列氢化物电极材料, 包括稀土基AB5型合金[1], AB2型Laves相合金[2], V基固溶体合金[3], Mg基合金[4]。 在上述合金中, AB5型合金的容量相对较低, AB2型Laves相合金和V基固溶体合金活化困难, Mg基合金的循环稳定性差[5-8]。 特别是AB5型合金的容量已经接近其理论值, 进一步提高其容量已相当困难[9]。 因此, 研究具有更高容量和更长寿命的新型电极合金对于提高Ni-MH电池在可充电电池领域的竞争力是至关重要的。 最近, 几种具有应用前景的新型电极合金已经被报道。 对于提高容量来说, 最具希望的合金之一是La-Mg-Ni系贮氢合金。 Kohno等[10]研究了La2MgNi9, La5Mg2Ni23和La3MgNi14合金的电化学性能, 发现La5Mg2Ni23型合金La0.7Mg0.3Ni2.8Co0.5的放电容量高达410mA·h/g, 并在30次充放电循环中有较好的循环稳定性。 Kadir等[11]研究了RMg2Ni9(R=La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Gd)合金的结构, 证明其具有PuNi3型结构。 PAN等[12]研究了La0.7Mg0.3(Ni0.85Co0.15)x(x=3.15~3.80)合金的电化学性能, 其最大放电容量可达398.4mA·h/g, 但其循环寿命需要进一步改进。
本文作者为了进一步提高La-Mg-Ni系(PuNi3型)合金La2Mg(Ni0.85Co0.15)9的循环稳定性, 在合金中加入微量硼, 并进行了真空快淬处理, 对硼及快淬工艺对合金循环稳定性及微观结构的影响作了较为全面的研究。
1 实验
1.1 合金的制备
实验合金成分为La2Mg(Ni0.85Co0.15)9Bx, x分别取0, 0.1, 0.2, 对应合金编号为B0, B1, B2。 制备合金所用La, Ni, Co, Mg, B等元素的纯度均高于99.7%, 用1kg真空中频感应电炉熔炼。 为了防止Mg在冶炼过程中的挥发, 用氩气加正压保护, 氩气的压力为0.1MPa。 熔炼后的合金经铜模浇铸获得母合金锭, 用真空快淬炉将铸态母合金重熔后, 进行单辊快淬处理, 获得不同淬速的快淬合金。 淬速以铜辊表面线速度表示, 本实验的淬速为15, 20, 25和30m/s。
1.2 显微结构分析
铸态合金样品直接研磨抛光, 用60% HF溶液浸蚀, 快淬样品用环氧树脂镶嵌后制样, 用扫描电镜(SEM)观察合金的形貌。 将合金研磨成粒度为75μm以下的粉末, 用X射线衍射仪(型号为D/max/2400) 测试合金的相组成及相结构, 射线源为CuKα1, 电流为160mA, 电压为40kV, 扫描速度为8(°)/min。 用无水酒精分散粉末合金试样, 通过透射电镜(TEM)观察试样的晶粒形貌并确定其晶态。 用扫描电镜观察了铸态及快淬态合金电化学循环前后的合金颗粒形貌, 分析合金的失效机理。
1.3 实验电极制备及电化学性能测试
铸态及快淬态合金经机械破碎后过孔径63μm筛, 将1g合金粉与1g镍粉和少量聚乙烯醇(PVA)充分混合, 在35MPa压力下制成直径为15mm的实验用电极片, 干燥4h后, 浸入6mol/L KOH溶液中, 经24h浸泡后, 用程控电池测试仪测试合金电极的电化学性能。 贮氢合金电极片作为实验电池的负极, 正极为Ni(OH)2/NiOOH, 参比电极为Hg/HgO, 电解液为6mol/L KOH水溶液, 负极与参比电极之间的电压为放电电压。 测试时充放电制度为: 100mA/g恒电流充电5h, 间隔15min后, 以100mA/g恒电流放电至-0.500V (vs Hg/HgO)。 测试环境温度保持在30℃。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 微观结构
2.1.1 微观组织形貌
铸态合金的SEM形貌如图1所示。 图中黑色的区域为LaNi5相, 灰白色的区域为(La, Mg)Ni3相, LaNi2相的量相对很少, 在结晶的过程中, LaNi2相依附于(La, Mg)Ni3相生长, 故难于辨别。 对于B2合金, 由于硼的加入, LaNi2相的量增加, 所以形成具有共晶形貌的(La, Mg)Ni3+LaNi2组织。 Ni2B由于量非常少, 扫描电镜难于辨别。
快淬态合金的TEM形貌及SAD分析结果见图2。 SAD分析结果表明, 快淬态B0和B1合金仍为多相结构, B0合金中出现了非晶化倾向, 而快淬B1合金已经出现了一定量的非晶相。 从快淬合金的形貌(图2(a), 2(c))可知, 快淬B0合金具有典型的微晶形貌, 而快淬B1合金中出现了非晶和纳米晶的混合结构。 这显然与硼的作用有关。 有关硼对非晶形成的作用及机理已经在文献[13, 14]中作过详细报道。

图1 铸态合金的SEM形貌
Fig.1 SEM morphologies of as-cast alloys

图2 快淬态合金的TEM形貌及选区衍射花样
Fig.2 TEM morphologies (a), (c) and corresponding SAD patterns (b), (d) of as-quenched alloys(30m/s)
2.1.2 相组成与相结构
用X射线衍射仪分析了铸态及快淬态La2Mg(Ni0.85Co0.15)9Bx(x = 0, 0.1, 0.2)贮氢电极合金的相组成及相结构, 结果如图3所示。 可以看出, 硼的加入及快淬处理对合金的相组成有明显影响。 铸态合金中均含有大量的LaNi3相(PuNi3结构), LaNi5相(CaCu5结构)以及少量的LaNi2相, 含硼合金中还有微量的Ni2B相, 且Ni2B相的量随着硼含量的增加而增加。 分析图3(a)可知, 随硼含量的增加, 铸态合金中的LaNi2相的量明显增加, 而LaNi5相和LaNi3相的量减少, 这可能是由于硼化物有利于LaNi2相的形成。 比较铸态及快淬态X射线衍射谱可以看出, 对于不含硼合金(B0), 快淬处理导致LaNi2相的量增加, 而对于含硼合金(B1和B2), 快淬导致LaNi2相的量减少。 这显然与硼化物的作用相关。 快淬和Ni2B均有促进LaNi2相形成的作用, 但Ni2B相的作用更强。 快淬处理使Ni2B相消失, Ni2B相促进LaNi2相形成的作用不复存在。 因此, 总的作用结果是快淬使含硼合金中的LaNi2相的量减少。
2.2 电化学循环稳定性
以100mA/g电流密度对合金恒流充放电, 当电化学容量下降到最大容量的60%时, 对应的循环次数被定义为合金的循环寿命。 铸态及快淬态合金的放电容量随循环次数的变化如图4所示。 从图4(a)可以看出, 随淬速的增加, B0合金的曲线斜率减小, 说明快淬对提高合金的电化学循环稳定性有利。 从图4(b)可以看出, 在相同的淬速下, 随硼含量的增加, 曲线的斜率减小, 说明硼的加入对合金的循环稳定性有利。 为了更清楚地表达淬速对合金循环寿命的影响, 得到淬速与循环寿命之间的关系, 如图5所示。 由图5可见, 铸态合金的循环寿命随硼含量的增加而增加, 当硼含量从0增加到0.2时, 合金的循环寿命从72次增加到94次。 对于快淬态合金, 随淬速的增加, 循环寿命提高。 对B0, B1, B2合金, 当淬速从0 (铸态被定义为淬速等于0m/s) 增加到30m/s时, 循环寿命分别从72, 86, 94次增加到100, 106, 110次。 贮氢合金的循环稳定性是Ni-MH电池寿命的决定因素, 电池失效的根本原因在负极而不在正极。 电池失效表现为在高倍率放电循环过程中容量减少, 放电电压降低, 结果使电池贮存的能量下降。 文献[15, 16]的研究结果证实, 导致贮氢合金容量衰减的主要原因是合金在充放电过程中的氧化和粉化。 贮氢合金吸氢时必然导致体积膨胀而产生晶格内应力, 这是导致贮氢合金粉化的内在驱动力。 硼对铸态合金循环寿命的作用包括两方面, Ni2B相的形成增加了相界面积, 在相界处可能成为吸放氢时应力释放的缓冲区, 从而提高合金的抗粉化能力。 此外, 硼促进LaNi2相的形成。 在电化学循环的过程中, LaNi2中的La会被电解液腐蚀, 使LaNi2中的Ni含量升高, 从而提高了LaNi2相的催化活性, 使合金的可逆吸放氢能力增加, 部分抵消了合金在循环过程中的容量下降。 快淬处理后, Ni2B相消失。 快淬使含硼合金循环寿命提高的主要原因是快淬导致的晶粒细化和非晶相的形成。 由于晶粒细化和非晶相的存在能显著提高合金的抗粉化能力。 快淬对含硼合金循环寿命的作用很有限, 可能是由于导致合金失效的主要原因是电化学循环过程中的腐蚀和氧化。 快淬显著提高不含硼合金循环寿命的主要原因是快淬促进LaNi2相的形成, 同时, 合金的晶粒细化也有一定的作用。 用铸态及快淬态B0合金电化学循环前和100次循环后的形貌变化如图6所示。 从图6可看出, 铸态及快淬态B0合金电化学循环前均为带有尖角的不规则颗粒状, 颗粒直径相差较大。 经100次循环以后, 颗粒形貌发生了较大变化。 主要表现为颗粒的棱角消失, 颗粒直径变小。 这说明导致合金容量衰减的原因与合金在循环过程中的粉化有关。 用SEM能谱分析合金颗粒表面的成分, 发现其表面有腐蚀氧化产物。 从合金循环以后的颗粒形貌中, 也可以看到明显的腐蚀氧化痕迹, 说明腐蚀氧化是合金失效的重要原因。

图3 铸态及快淬态合金的X射线衍射谱
Fig.3 XRD patterns of as-cast and quenched alloys
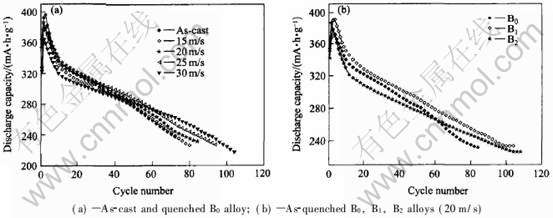
图4 铸态及快淬态合金循环次数与容量的关系
Fig.4 Relationships between cycle life and discharge capacity of alloys

图5 淬速与合金循环寿命的关系
Fig.5 Relationships between
quenching rate and cycle life of alloys

图6 铸态及快淬态B0合金电化学循环前后颗粒的SEM形貌
Fig.6 SEM granular morphologies of as-quenched alloys (20m/s) before((a), (b)) and after electrochemical cycle((c), (d))
3 结论
1) 铸态及快淬态La2Mg(Ni0.85Co0.15)9Bx (x=0~0.2)贮氢合金由多相组成, 包括(La, Mg)Ni3相、 LaNi5相以及少量LaNi2相。 铸态含硼合金中含有微量的Ni2B相。 合金中各相的相对量与合金的成分相关, 硼的加入有利于铸态合金中LaNi2相的形成, 这是硼提高铸态合金电化学循环稳定性的主要原因。
2) 快淬使合金的循环稳定性提高, 快淬导致不含硼合金中的LaNi2相增加是其寿命提高的主要原因, 而含硼合金的循环寿命随淬速的增加而增加是由于晶粒细化和非晶相的形成。
3) La-Mg-Ni系贮氢合金的失效原因主要是由于在电化学循环过程中的粉化和电极在腐蚀性电解液中的腐蚀氧化造成的。 快淬导致的晶粒细化和非晶相的形成对提高合金的抗粉化能力有利。 但用快淬的方法使La-Mg-Ni系合金中形成较多的非晶相是很困难的, 因此, 快淬工艺对La-Mg-Ni系贮氢合金循环寿命的改善非常有限。
REFERENCES
[1]Meli F, Sakai T, Züttel A, et al. Passivation behavior of AB5-type hydrogen storage alloys for battery electrode application[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1995, 221: 284-290.
[2]Hsu Y S, Perng T P. Hydrogenation of multicomponent Zr-base C15 type alloys[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1995, 227: 180-185.
[3]Tsukahara M, Kamiya T, Takahashi K, et al. Hydrogen storage and electrode properties of V-based solid solution type alloys prepared by a thermic process[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2000, 147: 2941-2944.
[4]Sun D, Enoki H, Gingl F, et al. New approach for synthesizing Mg-based alloys[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1999, 285: 279-283.
[5]Huot J, Pelletier J F, Lurio L B, et al. Investigation of dehydrogenation mechanism of MgH2-Nb nanocomposites[J]. J Alloys Comp, 2003, 348: 319-324.
[6]Shang C X, Bououdina M, Guo Z X. Structural stability of mechanically alloyed (Mg+10Nb) and (MgH2+10Nb) powder mixtures[J]. J Alloys Comp, 2003, 349: 217-223.
[7]Spassov T, Solsona P, Suriach S, et al. Optimisation of the ball-milling and heat treatment parameters for synthesis of amorphous and nanocrystalline Mg2Ni-based alloys[J]. J Alloys Comp, 2003, 349: 242-254.
[8]房文斌, 张文丛, 于振兴, 等. 镁基储氢材料的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002,12(5): 853-860.
FANG Wen-bin, ZHANG Wen-cong, YU Zheng-xing, et al. Recent development of Mg-based hydrogen storage material[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(5): 853-862.
[9]张羊换, 陈梅艳, 王新林, 等. 硼对稀土系AB5型贮氢合金微观结构及电化学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(4): 580-586.
ZHANG Yang-huan, CHEN Mei-yan, WANG Xin-lin, et al. Effect of boron additive on microstructures and electrochemical properties of rare earth-based AB5 hydrogen storage alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(4): 580-586.
[10]Kohno T, Yoshida H, Kawashima F, et al. Hydrogen storage properties of new ternary system alloys: La2MgNi9, La5Mg2Ni23, La3MgNi14[J]. J Alloys Comp, 2000, 311: L5-L7.
[11]Kadir K, Uehara I, Sakai T. Synthesis and structure determination of a new series of hydrogen storage alloys: RMg2Ni9 (R=La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm and Gd) built from MgNi2 Laves-type layers alternating with AB5 layers[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1997, 257: 115-121.
[12]PAN Hong-ge, LIU Yong-feng, GAO Ming-xia, et al. An investigation on the structural and electrochemical properties of La0.7Mg0.3(Ni0.85Co0.15)x (x=3.15-3.80) hydrogen storage electrode alloys[J]. J Alloys and Comp, 2003(351): 228-232.
[13]ZHANG Yang-huan, CHEN Mei-yan, WANG Xin-lin, et al. Effect of boron additive on the cycle life of low-Co AB5-type electrode consisting of alloy prepared by cast and rapid quenching[J]. J Power Sources, 2004, 125: 273-279.
[14]ZHANG Yang-huan, CHEN Mei-yan, WANG Xin-lin, et al. Microstructure and electrochemical characteristics of Mm(Ni,Co,Mn,Al)5Bx (x=0-0.4) hydrogen storage alloys prepared by cast and rapid quenching[J]. J Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 49: 1161-1168.
[15]Li Y, Cheng Y T. Amorphous La-Ni thin film electrodes[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1995, 223: 6-12.
[16]Chartouni D, Meli F, Zuttel A, et al. The influence of cobalt on the electrochemical cycling stability of LaNi5-based hydride forming alloys[J]. J Alloys and Comp, 1996, 241: 160-166.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(50131040)
收稿日期: 2004-09-11; 修订日期: 2005-01-20
作者简介: 张羊换(1959-), 男, 教授, 博士.
通讯作者: 张羊换, 教授; 电话: 010-62187570; E-mail: zhangyh59@163.com
(编辑陈爱华)