J. Cent. South Univ. (2017) 24: 1537-1543
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-017-3558-x
Optimization on selenium and arsenic conversion from copper anode slime by low-temperature alkali fusion process
GUO Xue-yi(郭学益)1, 2, XU Zhi-peng(许志鹏)1, TIAN Qing-hua(田庆华)1, 2, LI Dong(李栋)1, 2
1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China; 2. Hunan Engineering Research Center of Nonferrous Metals Resource Recycling, Changsha 410083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2017
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2017
Abstract: A process was proposed to convert and separate selenium and arsenic in copper anode slime (CAS) by low-temperature alkali fusion process. Central composite design was employed to optimize the effective parameters, in which NaOH/CAS mass ratio, fusion temperature and fusion time were selected as variables, and the conversion ratio of selenium and arsenic as responses. Second-order polynomial models of high significance and 3D response surface plots were constructed to show the relationship between the responses and the variables. Optimum area of >90% selenium conversion ratio and >90% arsenic conversion ratio was obtained by the overlaid contours at NaOH/CAS mass ratio of 0.65-0.75, fusion temperature of 803-823 K and fusion time of 20- 30 min. The models are validated by experiments in the optimum area, and the results demonstrate that these models are reliable and accurate in predicting the fusion process.
Key words: optimization; low-temperature alkali fusion; copper anode slime; selenium; arsenic; central composite design
1 Introduction
Copper anode slime (CAS) is a byproduct of electrolytic refining of blister copper, which contains many valuable metals such as Au, Ag, Cu, Pb, Se, Te, As, Sb, Bi and platinum group metals (PGMs) [1, 2]]. It is certainly one of the important materials for recovery of precious metals [3].
Generally, the conventional process of CAS includes the following three steps: pretreatment, concentration and refining. In such process, CAS is firstly pretreated with different methods to remove base metals which are harmful to the subsequent procedure, then followed by smelting or selective dissolution for further enrichment of precious metals, and finally the products of precious metals are produced through refining [4]. Relatively, pretreatment is the most crucial link in the whole process of CAS [5]. Some pretreatment technologies such as sulfation roasting-leaching, oxidative sulfuric acid leaching and chlorination leaching are developed for the primary recovery of metals like Cu, Ni, Se and Te from anode slimes [6-9]. Similar to acid based processes, CAS can also be treated in alkaline route. LI et al [10] fused CAS with NaOH and NaNO3 as oxidizing agent, with selenium, arsenic, tin and lead extracted and tellurium, silver, gold and PGM enriched in the residue. LIU et al [11] pretreated CAS with alkaline pressure oxidative leaching, with slimes completely oxidized and dissolved into alkaline solution; however, copper, tellurium and other metals oxidized and remained in residue. LU et al [12] used soda roasting-alkaline leaching-acid leaching to pretreat CAS, with selenium, tellurium and copper removed sequentially. Compared to acid based processes, alkaline based processes have a greater advantage in separation of base metals and enrichment of noble metals.
CAS was pretreated by low temperature alkali fusion (LTAF) process in this work, which is an efficient method in nonferrous metallurgy especially for resources bearing amphoteric metals. LTAF has been used to extract metals from low grade ores and to selectively recover metals from secondary resources [13-16]. The objective of this work is to model the LTAF process and obtain the optimum area by central composite design (CCD) [17, 18]].
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
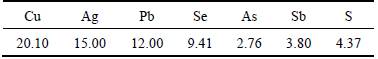
A single batch of CAS used in all the experiments was collected from Daye Nonferrous Metal Co., Ltd.,Hubei Province, China. It is typical of high lead and low nickel content, ground to <150 μm mesh after drying at 110 °C for 24 h. Table 1 shows the chemical composition of the sample. All of the reagents are of analytical grade.
Table 1 Main chemical composition of CAS (mass fraction, %)
2.2 Procedure
The experiments were carried out at a laboratory scale. CAS mixed with sodium hydroxide in a 200 mL stainless steel crucible was fused in a muffle furnace at a certain temperature for a certain time. The fused mass was then cooled to room temperature and leached with water at 343 K for 60 min at a liquid to solid ratio of 12.5 mL/g. The sludge was filtered and residue was washed thoroughly several times with distilled water.
The concentrations of metal ions in aqueous solution were analyzed by ICP-AES, and conversion ratio was calculated by Eq. (1) to evaluate the effects of variables:
 (1)
(1)
where Ri (%) is the conversion ratio of metal i, c (mg/L) is the concentration of metal i in the leaching solution, V (L) is the volume of solution, m (g) is the mass of CAS, and ω (%) is the mass fraction of metal i in CAS.
Theoretically, only selenium and arsenic react with alkali, converting into soluble sodium salts (Eqs. (2)-(5)). However, trace amount of copper and lead will also be converted in the alkaline melt at high concentration of alkali (Eqs. (6)-(8)):
2Ag2Se+4NaOH+3O2=2Ag2O+2Na2SeO3+2H2O (2)
2Ag2O=4Ag+O2↑ (3)
Cu2Se+2O2+2NaOH=Na2SeO3+2CuO+H2O (4)
As2O3+2NaOH=2NaAsO2+H2O (5)
PbSO4+2NaOH=PbO+Na2SO4+H2O (6)
PbO+2NaOH=Na2PbO2+H2O (7)
CuO+H2O+2NaOH=Na2Cu(OH)4 (8)
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Central composite design
CCD, originally developed by BOX [19] and WILSON and improved upon by BOX and HUNTER [20], is an experiment technique applied in the progression of an appropriate functional relationship between the response and the related input variables. The relationship of the response and the related input variables can be approximated by low-order polynomials (the most common ones are first- and second-degree polynomial models) [21]. This technique helps to determine the most important parameters and its main quadratic effect or interactions which influence the response. CCD gives almost as much information as a multilevel factorial, requires much fewer experiments than a full factorial and has been shown to be sufficient to describe the majority of steady-state process responses [22, 23].
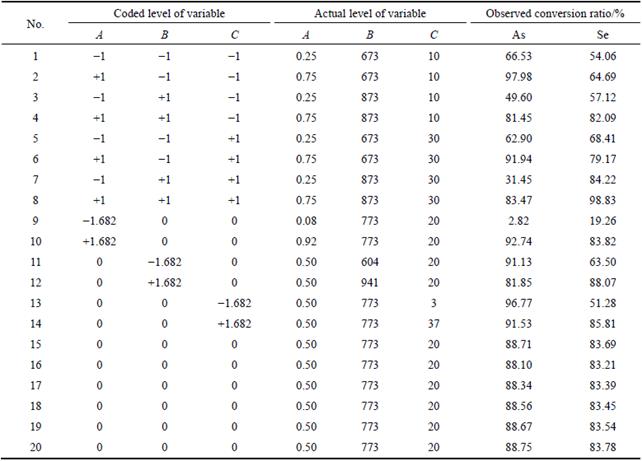
In this work, the NaOH/CAS mass ratio (A), fusion temperature (B) and fusion time (C) were selected as the variables, and the codes were calculated as functions of the range of interest of each variable, as shown in Table 2. According to the design matrix, 20 tests were conducted by running in order of the sequence defined by Minitab 15 software. Responses of selenium and arsenic conversion ratio were evaluated, and the design matrix of the variables in actual units along with the results is presented in Table 3.
15 software. Responses of selenium and arsenic conversion ratio were evaluated, and the design matrix of the variables in actual units along with the results is presented in Table 3.
3.2 Combined effect of variables on metals conversion ratio
3.2.1 Model construction for selenium conversion ratio
The experimental results in Table 3 are fitted to a model equation by applying multiple regression analysis for selenium conversion ratio (using the Minitab 15 software). The model equation representing the selenium conversion ratio (YSe) is expressed as a function of NaOH/CAS mass ratio (A), fusion temperature (B), and fusion time (C) as below:
15 software). The model equation representing the selenium conversion ratio (YSe) is expressed as a function of NaOH/CAS mass ratio (A), fusion temperature (B), and fusion time (C) as below:
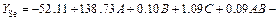
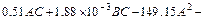
 (9)
(9)
Table 2 Independent variables and levels for CCD

Table 3 Coded and actual levels of variables with experimental results
The precision of models developed by regression of Eq. (9) is proved by determination of the coefficient R2, which is a measure of the total amount of variation around the mean value. The value of R2 is 0.88, which means that the model could explain approximately 88% of the total variations in the system. The p-value of the analysis of variance (ANOVA) is less than 0.05, indicating that this model is significant at a high confidence level (95%) [24]. The plot of the graph which depicts the predicted values obtained from Eq. (9) versus observed values for selenium conversion ratio is shown in Fig. 1.
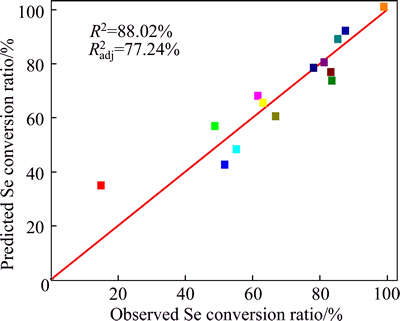
Fig. 1 Relation between observed and predicted selenium conversion ratio In order to obtain a better understanding of the interaction effects of variables on Yse, three-dimensional (3D) plots for the measured responses are formed based on the model equation (Eq. (9)). Also the relationship between the variables and responses can be further understood by these plots. In such plots, two variables vary while keeping the other variable constant at the center level. As shown in Figs. 2(a)-(c), increasing NaOH/CAS mass ratio or fusion temperature or fusion time leads to an increase in Yse. More curved surface and more intensive contour lines are shown by varying NaOH/CAS mass ratio, meaning that it has a more significant effect on Yse than the other operating parameters, fusion temperature and fusion time.
3.2.2 Model construction for arsenic conversion ratio
The model equation of arsenic conversion ratio (YAs) is given by

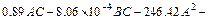
 (10)
(10)
The coefficient of multiple determinations R2 in Fig. 3 is 0.95, indicating the equation is capable to represent 95% of the system in the given experimental range.
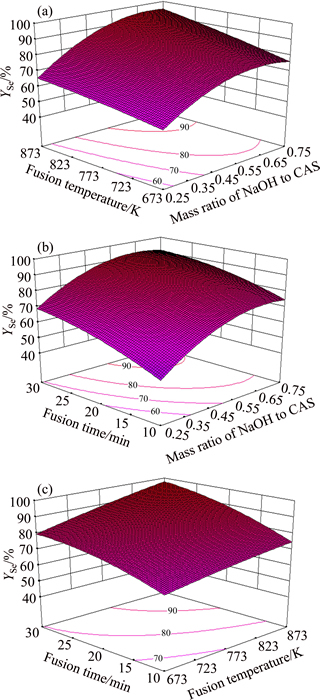
Fig. 2 Response surface plots of effects of variables on selenium conversion ratio
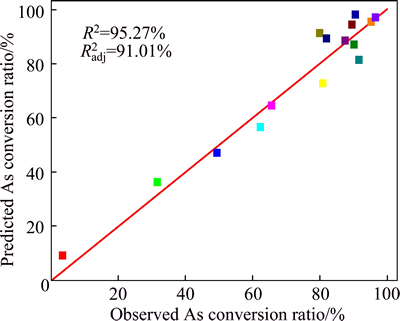
Fig. 3 Relation between observed and predicted arsenic conversion ratio
Three-dimensional plots are utilized to study the interaction between factors on response YAs. In such plots, two factors vary while keeping the other one constant at the middle of the variable’s range. It is observed in Fig. 4 that the conversion ratio of arsenic increases with the increase of the NaOH/CAS mass ratio, however, high fusion temperature and long fusion period are disadvantageous for arsenic conversion ratio.
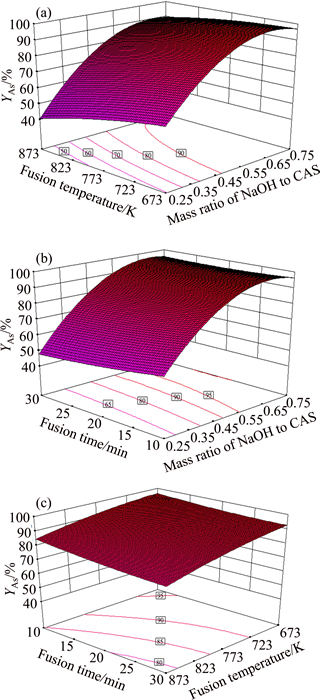
Fig. 4 Response surface plots of effects of variables on arsenic conversion ratio
3.3 Overlaid contour plots of metals conversion ratio
In the above sections, combined effects of variables including NaOH/CAS mass ratio, fusion temperature and fusion time on selenium and arsenic conversion ratio are presented separately. Meanwhile, it is necessary to determine a region where selenium and arsenic conversion ratio simultaneously meet the critical criterion. The best compromise can visually be searched by an overlaid contour plot that displays the area of feasible response. It shows that the overlaid contour plots of selenium and arsenic conversion ratio are affected by NaOH/CAS mass ratio and fusion temperature in Fig. 5, keeping the fusion time fixed at 10, 20 and 30 min, respectively. The most anticipated field of selenium and arsenic conversion ratio over 90% is determined as area A.
As can be seen from Fig. 5(a), it is impossible to get an area A in the studied ranges and the feasible way is to increase the fusion time by keeping the NaOH to CAS mass ratio around 0.65. In Fig. 5(b), a small area A is obtained. Figure 5(c) indicates that the increase of fusion time results in the increase of area A. Given the consideration to the energy consumption, material cost and metal conversion ratio, the optimum area is determined as NaOH/CAS mass ratio of 0.65-0.75, fusion temperature of 803-823 K, and fusion time of 20-30 min.
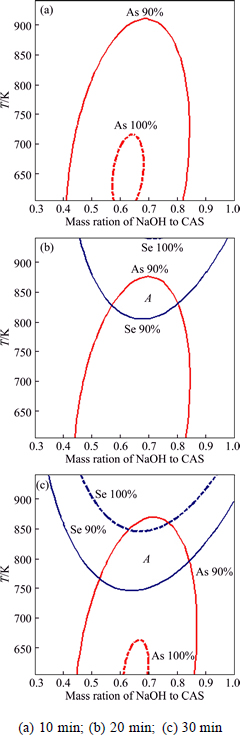
Fig. 5 Overlaid contour plots of selenium and arsenic conversion ratio affected by NaOH/CAS mass ratio and fusion temperature with different fusion time
A series of verification experiments are conducted to verify the accuracy of the models. The results presented in Table 4 strongly demonstrate the accuracy of the models. The results indicate that >90% selenium conversation and >90% arsenic conversation are achieved under the conditions in the optimum area, which shows good agreement with the value predicted from the models. It implies that the strategy to optimize the LTAF process and to obtain the suitable metal conversations by response surface methodology is successful.
Table 4 Conditions and results of verification experiments
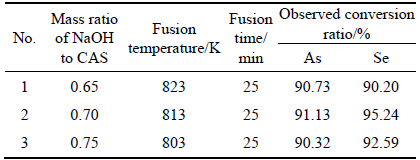
Figure 6 shows the XRD pattern of the water leaching residue produced in verification experiments, in which Ag, Cu and Pb are enriched in residue as Ag, CuO and PbO. The experimental results indicate that the metals in CAS can be simply and effectively separated into two groups (leachate and residue) by low- temperature alkali fusion process. Combined with downstream treatments such as sulfuric acid leaching and replacement by active copper powder, the flow sheet for comprehensive recovering metal values from CAS is proposed and shown in Fig. 7.
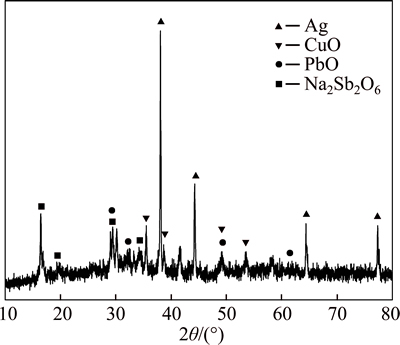
Fig. 6 XRD pattern of leaching residue obtained in verification experiments
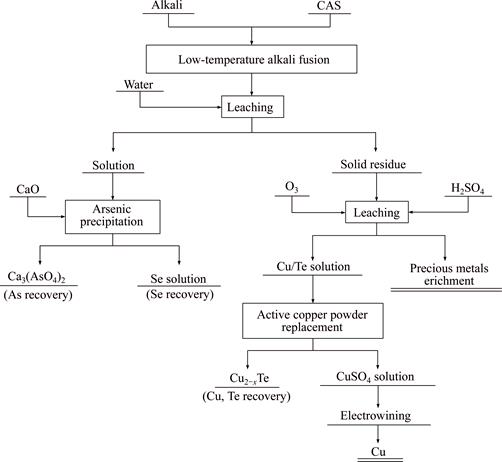
Fig. 7 Proposed flow sheet for comprehensive recovery of metal values from CAS
4 Conclusions
1) The present studies are carried out to optimize the selenium and arsenic conversion from CAS. The experiments are designed using CCD technique, to carry out a systematic and optimized approach to experimentation.
2) Interaction effects of NaOH/CAS mass ratio, fusion temperature and fusion time on the conversion ratio of selenium and arsenic are presented in response surface plots based on the modeling of experimental results. Optimum area of >90% selenium conversation ratio and >90% arsenic conversation ratio are obtained by the overlaid contours.
3) Taking into account the energy consumption, material cost and metal conversion ratio, the optimum area is determined as NaOH/CAS mass ratio of 0.65-0.75, fusion temperature of 803-823K, fusion time of 20-30 min. Verification experiments in the optimum areas are conducted and the results are in good agreement with the predicted values obtained from the models.
References
[1] HUANG Wang-yin, SU Qing-ping. The situation and development of copper hydrometallurgy [J]. Anhui Chemical, 2011, 37(2): 13-14. (in Chinese)
[2] CHEN Guo-bao, YANG Hong-ying, GUO Jun, LI Xue-jiao. The rougher flotation process of copper anode slime for collecting gold and silver [J]. Precious Metals, 2013, 34(3): 32-33. (in Chinese)
[3] LI Xue-jiao, YANG Hong-ying, TONG Lin-lin, CHEN Guo-bao. Technological mineralogy of copper anode slime [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2013, 34(4): 560-561. (in Chinese)
[4] LIU Wei-feng. Study on copper/lead anode slimes treated by alkaline oxidative leaching [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2011: 120-128. (in Chinese)
[5] GUO Xue-yi, XIAO Cai-mei, ZHONG Ju-ya, TIAN Qing-hua. Behaviors of precious metals in process of copper anode slime treatment [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(5): 990-998. (in Chinese)
[6] COOPER W C. The treatment of copper refinery anode slimes [J]. JOM, 1990, 42(8): 45-49.
[7] YASIN K, GULDEM K, SERVET T. An investigation of copper and selenium recovery from copper anode slimes [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2013, 124: 75-82.
[8] HOFFMANN J E. Recovering selenium and tellurium from copper refinery slimes [J]. Journal of the Minerals Metals Materials Society, 1989, 41(7): 33-38.
[9] SYED S. Recovery of gold from secondary sources—A review [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 115: 30-51.
[10] LI Dong, GUO Xue-yi, XU Zhi-peng, TIAN Qing-hua, FENG Qi-ming. Leaching behavior of metals from copper anode slime using an alkali fusion-leaching process [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 157: 9-12.
[11] LIU Wei-feng, YANG Tian-zu, ZHANG Du-chao, CHEN Lin, LIU You-nian. Pretreatment of copper anode slime with alkaline pressure oxidative leaching [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2014, 128: 48-54.
[12] LU Dian-kun, CHANG Yong-feng, YANG Hong-ying, XIE Feng. Sequential removal of selenium and tellurium from copper anode slime with high nickel content [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(4): 1307-1314.
[13] TANG Mo-tang, TANG Chao-bo, CHEN Yong-ming, YANG Jian-guang, YANG Sheng-hai, HE Jing, OU Zhao. A promising low carbon clean metallurgical method: low-temperature molten salt metallurgy of heavy metal [J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2010, (4): 49-53. (in Chinese)
[14] HU Yu-jie, TANG Chao-bo, TANG Mo-tang, YANG Jian-guang, CHEN Yong-ming, YANG Sheng-hai, HE Jing. A clean and green process of low-temperature for smelting of secondary lead [J]. Nonferrous Metals(Extractive Metallurgy)2013(8): 1-4. (in Chinese)
[15] GUO Xue-yi, LIU Jing-xin, TIAN Qing-hua. Elemental behavior of multi-component metal powders from waste printed circuit board during low-temperature alkaline smelting [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(6): 1757-1763. (in Chinese)
[16] LIU Jing-xin, GUO Xue-yi, TIAN Qing-hua, LI Dong. Separation and extraction of amphoteric metals from waste printed circuit board powders by low-temperature alkaline smelting [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2014, 36(7): 875-879. (in Chinese)
[17] PODSTAWCZYK D, WITEK-KROWIAK A, DAWIEC A, BHATNAGAR A. Biosorption of copper (II) ions by flax meal: Empirical modeling and process optimization by response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) simulation [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2015, 83: 364-379.
[18] AKALIN M K, TEKIN K, AKYUZ M, KARAGOZ S. Sage oil extraction and optimization by response surface methodology [J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2015, 76: 829-835.
[19] BOX G E P, WILSON K B. On the experimental attainment of optimum conditions [J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B (Methodological), 1951, 13(1): 1-45.
[20] BOX G E P, HUNTER J S. Multi-factor experimental designs for exploring response surfaces [J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1957, 28(1): 195-241.
[21] KHURI A I, MUKHOPADHYAY S. Response surface methodology [J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics, 2010, 2(2): 128-149.
[22] ZHANG Xian, WANG Ri-jie, YANG Xiao-xia, YU Jin-gang. Central composite experimental design applied to the catalytic aromatization of isophorone to 3, 5-xylenol [J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2007, 89(1): 45-47.
[23] LIN Y C, TSAO C C, HSU C Y, HUNG S K, WEN D C. Evaluation of the characteristics of the microelectrical discharge machining process using response surface methodology based on the central composite design [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2012, 62(9-12): 1013-1014.
[24] OBENG D P, MORREL S, NAPIER-MUNN T J. Application of central composite rotatable design to modelling the effect of some operating variables on the performance of the three-product cyclone [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2005, 76(3): 181- 192.
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Cite this article as: GUO Xue-yi, XU Zhi-peng, TIAN Qing-hua, LI Dong. Optimization on selenium and arsenic conversion from copper anode slime by low-temperature alkali fusion process [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(7): 1537-1543. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-017-3558-x.
Foundation item: Project(51234009) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2014DFA90520) supported by International Cooperation Program of Ministry of Science of China; Project(2013A100003) supported by the Production, Teaching and Research Program of Guangdong Province, China
Received date: 2016-01-27; Accepted date: 2016-05-11
Corresponding author: LI Dong, PhD; Tel/Fax: +86-731-88876255; E-mail: yejin013_18@163.com