文章编号:1004-0609(2012)02-0388-06
TC4钛合金激光焊接接头力学行为的原位研究
赵锡龙,宋 旭,张建勋
(西安交通大学 金属材料强度国家重点实验室,西安 710049)
摘 要:采用扫描电镜(SEM)原位拉伸法观察TC4钛合金激光焊接接头各微区孔洞形核与成长、损伤与断裂行为,研究接头微观组织对其损伤和断裂行为的影响。结果表明:焊缝区裂纹形核于晶内孪晶、滑移线与晶界交汇处,主裂纹形成直至最终断裂;热影响区多裂纹起裂,单一裂纹扩展至最终断裂;母材区孔洞优先形核于相界面及晶界区域,缺口前端孔洞群相互贯穿直至最终断裂。当应变超过0.023时,母材区及热影响区靠近母材一侧从协调变形向以界面微孔洞的行核与聚合为主转化;焊缝区粗大晶粒内部网篮状马氏体存在且晶界面积较小,导致变形机制未发生改变,促使其力学性能低于焊缝的。
关键字:TC4钛合金;激光焊接接头;原位拉伸
中图分类号:TG 456.7 文献标志码:A
In-situ investigation on mechanical behavior of
laser-welded joint for TC4 titanium alloy
ZHAO Xi-long, SONG Xu, ZHANG Jian-xun
(State Key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior of Materials, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China)
Abstract:In order to investigate the effects of microstructures on damage evolution and fracture behavior in laser welded joint for Ti-6Al-4V alloy, the microvoids nucleation, growth, coalescence and crack were observed by in-situ tensile test. The results show that the crack in the weld metal grows rapidly when it nucleates at the twin boundary of the inner grain and the intersection of slip line and grain boundary. The multi-cracks in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) occur in front of the notch, one crack propagation leads to the final fracture. When the strain exceeds 0.023, the deformation mechanism in the base metal and HAZ near the base metal changes from compatible deformation to bluntness and expansion alternately when the microvoid is nucleated firstly along the grain boundary. The deformation mechanism in the welded metal does not change due to its coarse martensite and small grain boundary. Therefore, the tensile stress in the welded metal is higher than that in the other areas.
Key words: TC4 titanium alloy; laser welded joint; in-situ method
钛合金由于其具有良好的力学性能和耐蚀性能而被广泛地应用于航空航天和造船等领域[1]。对于钛合金及其焊接接头各微区的断裂行为,很多学者进行了大量研究。CHAN等[2]在研究TiAl合金时发现,等轴状γ合金的断裂方式为显微裂纹和主裂纹连接,然后扩展,最终导致断裂。CHEN等[3]在研究Ti-46.3AI-2V- 1Cr合金片层状结构时,发现断裂驱动力为拉伸应力。而在焊接过程中,随着加热方式与冷却速率不同,焊接接头各区域组织与晶粒尺寸也有所不同,这对接头力学性能、损伤及断裂行为影响很大。
张建勋等[4]和王蕊等[5]在研究TC4钛合金激光焊接接头时,考虑接头力学不均匀性,并结合均匀材料研究断裂力学思想给出其等效屈服应力和等效加工硬化指数。也有学者将焊接接头进行分区结合G-T-N模型来研究其力学不均匀性[6],但G-T-N损伤模型无法考虑晶粒大小及晶界对微孔洞的影响[7-8]。管欣和耿小亮[9]研究证明多晶体晶界对孔洞力学行为的影响,得出了孔洞易于从晶界处形核而扩展的结论,认为应该重视孔洞周围材料的力学不均匀性。
PATANKAR等[10]研究了两种不同晶粒尺寸的TC4钛合金超塑性变形时,提出晶粒细小的钛合金力学性能明显优异,其结论满足Hall-Petch关系。IRISARRI等[11]以及HU和LIU[12-13]研究TC4钛合金电子束焊接的工艺性能时,表明晶粒粗大焊缝金属的力学性能明显高于其他区域的,且焊后焊缝呈现较高的残余拉应力。CAO和IAHAZI[14]以及AKMAN等[15]采用Nd:YAG激光器研究TC4钛合金薄板时,同样发现晶粒粗大的焊缝金属力学性能优异。杨静等[16]研究TC4钛合金激光焊接接头的力学性能时,认为焊缝金属强度较高是由于粗大晶粒内部有大量的针状马氏体存在。
本文作者通过对TC4钛合金激光焊接接头各区域进行原位拉伸试验,从接头各微区起裂模式与断裂行为入手来深入阐述这个现象。
1 实验
实验所用材料为轧制态TC4钛合金,厚度为 mm,其成分如表1所列。利用CO2激光器焊接,激光功率为2 500 W,离焦量为0,焊接速度为1.5mm/min。在焊缝区域如图所示截取原位试样,试样厚度为0.4 mm。
表1 TC4钛合金化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of TC4 titanium alloy (mass fraction, %)


图1 原位拉伸取样位置及试样尺寸
Fig. 1 Notch location for in-situ tensile and specimen size (mm): (a) Notch in base metal; (b) Notch in welded metal; (c) Notch in HAZ
在Instron 1195型电子拉伸平台上进行拉伸实验,利用JSM-35C扫描电镜观察裂纹扩展过程,并进行断口形貌观察。试样所用腐蚀剂为3~5 mL HF,10 mL HNO3和85~87 mL H2O。
试验应力—应变曲线如图2所示。从表2列出的实验结果参数来看,焊缝的抗拉强度最高,热影响区的次之,母材的最低。
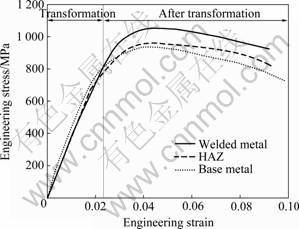
图2 原位拉伸试验工程应力—应变曲线
Fig. 2 In-situ tensile engineering stress—strain curves
表2 不同区域原位拉伸试样的实验数据
Table 2 Test data of in-situ tensile specimen in different areas

2 结果与分析
2.1 焊缝缺口拉伸原位观察
TC4钛合金激光焊接接头的焊缝区由马氏体相组成,平均晶粒尺寸约为200~300 μm。图3所示为缺口
位于焊缝金属时试样的断裂行为。由图3可见,当应力为538 MPa(见图3(a))不同晶粒内部皆出现孪晶,而孪晶密度由于取向不一致而有所不同;当应力为988 MPa时,如图3(b)所示箭头区域由于晶体取向与载荷方向夹角相对较大而孪晶明显较多。当应力为1 029 MPa时,从图3(c)中可以看出,主裂纹已形成,随着加载的继续,主裂纹贯穿前方孔洞,导致焊缝区域宏观断裂。图3(d)所示为断口形貌,可看出焊缝区域断口呈现准解理型与韧窝型同时存在。
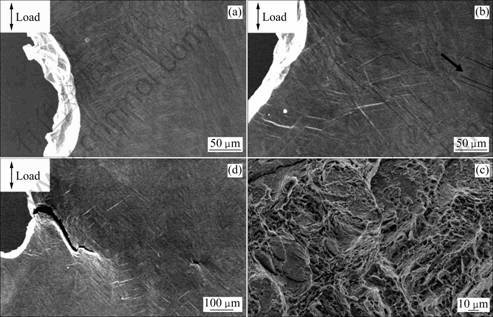
图3 缺口在焊缝区试样的原位拉伸过程
Fig. 3 In-situ tensile process of specimens with notch in welded zone: (a) Macro plastically deforming area at 538 MPa; (b) Change of notch tip at 988 MPa; (c) Change of notch tip at 1 029 MPa; (d) Fracture morphology
2.2 热影响区缺口拉伸原位观察
热影响区组织主要为马氏体相和α相,由于激光焊接热影响区域狭窄,靠近母材区域一侧存在β相。
由图4的原位拉伸结果可见,当应力为761 MPa时,如图4(a)所示,缺口前沿局部区域已出现微裂纹,长度约为2~5 μm,与该区域晶粒度大小相当,图中下部区域有较大微裂纹,沿晶界扩展,上部既有沿晶又有穿晶的较小微裂纹。可见,该区域低应力状态下,微裂纹多发生于相界或晶界面附近。当应力为910 MPa时,缺口前沿共出现3个裂纹源,且每个裂纹前方都有一定塑性区,如图4(b)和(c)所示。可以看出中部裂纹前方存在大量10~40 μm微裂纹,且微裂纹与微裂纹之间相差数个晶粒大小距离。结合图4(d)所示断口形貌可以推断最后断裂模式是微裂纹贯穿。

图4 缺口在热影响区试样的原位拉伸过程
Fig. 4 In-situ tensile process of specimens with notch in HAZ: (a) Local region of notch tip at 761 MPa; (b) Local region of notch tip at 910 MPa; (c) Local region of notch tip at 910 MPa; (d) Fracture morphology
2.3 母材缺口拉伸原位观察
TC4钛合金母材金属主要为α相和β相,α相易被腐蚀而凹陷呈深色,β相不易被腐蚀呈亮色,该区域晶粒尺寸约为1~3 μm,比热影响区的晶粒尺寸 略小。
由图5表示的原位观察结果可见,当应力为540 MPa时,缺口前沿晶粒有协调变形趋势。局部区域已出现孔洞(见图5(a)和(b)),且多形核于α和β 相界面处,其平均直径约为1~3 μm,PETERSON等[17]研究提出晶界区域的损伤行为主要是由于晶界滑移带来的剪切行为所致。当应力为840 MPa时,缺口前端孔洞群开始聚合,微裂纹已产生,如图5(c)所示。由此可见母材区域在高三向应力状态下,其前期损伤模式为缺口前端大量微孔洞的形核与聚合。

图5 缺口在母材区试样的原位拉伸过程
Fig. 5 In-situ tensile process of specimen with notch in base metal: (a) Macro area of notch tip at 540 MPa; (b) Local area of notch tip at 540 MPa; (c) Local area of notch tip at 840 MPa; (d) Fracture morphology
2.4 焊接接头不同区域对比分析与讨论
在应力为540 MPa时、应变约为0.019时,母材区α和β相界面及晶界区域出现大量孔洞,平均孔径0.5 μm(对比图3(a)和图5(b)),焊缝区表现为晶粒内部孪晶。从晶界面积角度考虑,母材区较大。对热影响区和母材而言,孔洞半径和晶界面积大小相当,因而强度相差不大。
从图2可以看出,当应变小于0.023时,晶粒细小的母材区所对应应力略微高于焊缝区的,以协调变形为主,伴生少量微孔洞出现于晶界区域。随着应力不断增加(应变超过0.023),缺口前端母材区相界及晶界区域微孔洞行核与聚合行为明显增加,界面损伤开始占据优势,如图5(c)所示。焊缝由于加热时生成粗大的β相晶体结构,冷却时冷却速度较快,原β相晶粒内部完全转变为马氏体,其室温强度较高且晶界区域小,变形机制未发生改变,表现为较高应力,也有学者研究表明其高温力学性能依然很好[18]。
应变超过0.023(所对应应力超过800 MPa,见图2)后,结合接头各区域原位实验结果,接头各微区变形机制如图6所示,焊缝区域依旧为晶内孪晶与滑移;母材区转变为相界及晶界面微孔洞行核与聚合;热影响区为两种变形机制的混合。从而对于整个TC4钛合金激光焊接接头,当应变达到一定值时,接头各区域变形机制发生转变,进而影响各区域的力学性能。
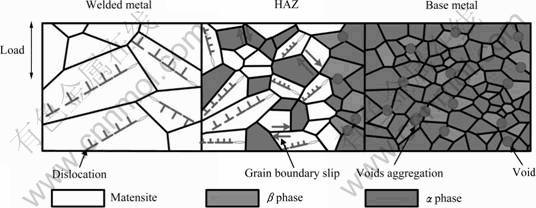
图6 应变超过0.023时TC4钛合金激光焊接接头各区域变形机制示意图
Fig. 6 Schematic diagram of deformation mechanism in TC4 titanium alloy welded joint for tensioning at strain exceeding of 0.023
由原位实验可以看出,焊缝区域、热影响区、母材区域的起裂模式及损伤行为各不相同。在焊缝区域,裂纹形核于晶内孪晶、滑移线与晶界交汇处,主裂纹形成直至最终断裂。在热影响区域,多裂纹起裂,单一裂纹扩展至最终断裂。而在母材区域,微孔洞优先形核于两相界面区域,缺口前端孔洞群相互贯穿直至断裂,如图7所示。

图7 起裂模式随所在焊接接头各区域变化
Fig. 7 Variation of crack initiation modes in different zones of welded joints distance from weld centerline
3 结论
1) 采用电镜拉伸原位观察法,通过研究TC4钛合金激光焊接接头各微区力学行为,来解释其力学不均匀性。TC4钛合金激光焊接接头的断裂强度表现为焊缝的最高,热影响区的次之,母材的最低。接头各区域起裂模式存在明显差异,焊缝区裂纹形核于晶粒内部孪晶、滑移线与晶界交汇处,主裂纹形成直至最终断裂;在低应力下,热影响区微裂纹多形核于晶界面(相界面)处,缺口前端以多裂纹起裂,单一裂纹扩展至最终断裂;母材区微孔洞优先形核于两相界面区域,缺口前端孔洞群相互贯穿直至最终断裂。
2) 拉伸断口形貌除焊缝区域有少量准解理型外,均为韧窝型。当应变超过0.023,母材以协调变形为主向以界面损伤为主转化;焊缝区由于粗大晶粒内部网篮状马氏体存在及晶界面积较小,变形机制未发生 改变。
REFERENCES
[1] 赵庆云, 徐 锋. 航空紧固件用钛合金的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): s1021-s1023.
ZHAO Qing-yun, XU feng. Research progress of titanium alloy for aerospace fasteners[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): s1021-s1023.
[2] CHAN K S, KIM Y S. Effects of lamellar spacing and colony size on the fracture resistance of a full-laminar TiAl alloy[J]. Acta Matall Mater, 1995, 43(2): 439-451.
[3] CHEN J H, CAO R, WANG G Z, ZHANG J. Study on notch fracture of TiAl alloys at room temperature[J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2004, 35(2): 439-456.
[4] 张建勋, 宋 旭, 董丽娜. 钛合金激光焊接接头塑性损伤行为分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2011, 32(5): 1-4.
ZHANG Jian-xun, SONG Xu, DONG Li-na. Analysis on plastic damage evolution of laser welded joint for a titanium alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2011, 32(5): 1-4.
[5] 王 蕊, 刘 川, 张建勋. 5A12铝合金有限宽薄板钨极惰性气体焊接的数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(3): 693-697.
WANG Rui, LIU Chuan, ZHANG Jian-xun. Numerical simulation of tungsten inert gas welding of 5A12 aluminum alloy limited size sheet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(3): 693-697.
[6] N?GRE P, STEGLICH D, BROCKS W. Crack extension at an interface: Prediction of fracture toughness and simulation of crack path deviation[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2005, 134(3/4): 209-229.
[7] 王万鹏, 岳珠峰, 杨治国. 含夹杂粉末冶金材料拉伸试件的损伤分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(4): 949-955.
WANG Wan-peng, YUE Zhu-feng, YANG Zhi-guo. Damage analysis of tensile specimens of powder metallurgy material including voids[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(4): 949-955.
[8] GURSON A L. Continuum theory of ductile rupture void nucleation and growth: Part 1—Yield criteria and flow rules for porous ductile media[J]. Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology, 1977, 99(1): 2-15.
[9] 管 欣, 耿小亮. 多晶体材料晶界孔洞应力场分析[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2004, 22(6): 726-729.
GUAN Xin, GENG Xiao-liang. Stress distribution near cavity on grain boundary[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2004, 22(6): 726-729.
[10] PATANKAR S N, ESCOBEDO J P, FIELD D P, SALISHEV G, GALEYEV R M, VALIAKHMETOV O R, FROES F H. Superior superplastic behavior in fine-grained Ti-6Al-4V sheet[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 345: 221-227.
[11] IRISARRI A M, BARREDA J L, AZPIROZ X. Influence of the filler metal on the properties of Ti-6Al-4V electron beam weldments. Part I: Welding procedures and microstructural characterization[J]. Vacuum, 2010, 84: 393-399.
[12] HU Mei-juan, LIU Jin-he. Effects of zonal heat treatment on residual stresses and mechanical properties of electron beam welded TC4 alloy plates[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(2): 324-329.
[13] 胡美娟, 刘金合. 12 mm厚钛合金平板电子束焊接的数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(7): 1622-1626.
HU Mei-juan, LIU Jin-he. Numerical Simulation for electron beam welding of 12 mm thickness titanium alloy plate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(7): 1622-1626.
[14] CAO X, JAHAZI M. Effect of welding speed on butt joint quality of Ti-6Al-4V alloy welded using a high-power Nd:YAG laser[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2009, 47: 1231-1241.
[15] AKMAN E, DEMIR A, CANEL T. Laser welding of Ti6Al4V titanium alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209: 3705-3713.
[16] 杨 静, 程东海, 黄继华. TC4钛合金激光焊接接头组织与性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(2): 259-263.
YANG Jing, CHEN Dong-hai, HUANG Ji-hua. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V Joints by laser beam welding[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(2): 259-262.
[17] PETERSON B, COLLINS P, FRASER H. On the use of a sub-scale thermomechanical simulator to obtain accurate tensile properties of (α+β) and β processed Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 513/514: 357-365.
[18] CHENG Dong-hai, HUANG Ji-hua, ZHAO Xing-ke. Microstructure and superplasticity of laser welded Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31: 620-623.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50875200);教育部博士点基金资助项目(20100201110065)
收稿日期:2011-03-09;修订日期:2011-12-20
通信作者:张建勋,教授,博士;电话:029-82668807;传真:029-82668807;E-mail: jxzhang@mail.xjtu.edu.cn