Corrosion behavior and electrochemical property of Q235A steel in treated water containing halide ions (F-, Cl-) from nonferrous industry
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2020年第4期
论文作者:徐慧 王云燕 罗永健 肖海娟
文章页码:1224 - 1234
Key words:simulated water; halide anions (F-, Cl-); Q235A steel; corrosion behavior; electrochemical property
Abstract: The corrosion behaviors and electrochemical properties of Q235A steel in the treated water containing corrosive halide anions (F-, Cl-) have been investigated with corrosion tests of static coupon and dynamic coupon testing, electrochemical measurement of open-circuit potential and linear sweep voltammetry. The results reveal that the existence of F- and Cl- ions in the simulated treated water accelerate the corrosion rate of Q235A steel. The corrosion rate reaches maximum with F- concentration of 50 mg/L, Cl- concentration of 200 mg/L, respectively. However, Q235A steel would passivate when an applied potential is added to the system. Meanwhile, the initiating passive potential becomes positive with F-, Cl- concentration increasing. There is a little influence of F-, Cl- concentration on the initiating passivation current density. Therefore, it is necessary to control F-, Cl- concentration in the treated water when it is recycled by the pipelines made of Q235A steel.
Cite this article as: WANG Yun-yan, LUO Yong-jian, XU Hui, XIAO Hai-juan. Corrosion behavior and electrochemical property of Q235A steel in treated water containing halide ions (F-, Cl-) from nonferrous industry [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(4): 1224-1234. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4362-6.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2020) 27: 1224-1234
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4362-6

WANG Yun-yan(王云燕)1, 2, LUO Yong-jian(罗永健)1, XU Hui(徐慧)1, XIAO Hai-juan(肖海娟)1
1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Control & Treatment of Heavy Metal Pollution, Changsha 410083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Abstract: The corrosion behaviors and electrochemical properties of Q235A steel in the treated water containing corrosive halide anions (F-, Cl-) have been investigated with corrosion tests of static coupon and dynamic coupon testing, electrochemical measurement of open-circuit potential and linear sweep voltammetry. The results reveal that the existence of F- and Cl- ions in the simulated treated water accelerate the corrosion rate of Q235A steel. The corrosion rate reaches maximum with F- concentration of 50 mg/L, Cl- concentration of 200 mg/L, respectively. However, Q235A steel would passivate when an applied potential is added to the system. Meanwhile, the initiating passive potential becomes positive with F-, Cl- concentration increasing. There is a little influence of F-, Cl- concentration on the initiating passivation current density. Therefore, it is necessary to control F-, Cl- concentration in the treated water when it is recycled by the pipelines made of Q235A steel.
Key words: simulated water; halide anions (F-, Cl-); Q235A steel; corrosion behavior; electrochemical property
Cite this article as: WANG Yun-yan, LUO Yong-jian, XU Hui, XIAO Hai-juan. Corrosion behavior and electrochemical property of Q235A steel in treated water containing halide ions (F-, Cl-) from nonferrous industry [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(4): 1224-1234. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4362-6.
1 Introduction
Water resource scarcity is a worldwide problem. Demands for rational use of water impel an emphasis on industrial water reuse. However, application of multiple industrial water such as cooling water, smelting wastewater and boiler water is limited because of chloride and/or fluoride ions which will make a risk of equipment corrosion with the increase of cycle length of circulating water [1, 2]. Hence, chloride and/or fluoride ions have been the major constraints for water reuse [3-5].
Although there has been a great success of non-ferrous metal industry in China, the further development will be limited by water resources shortage [6, 7] and the discharge of heavy metal-containing wastewater [8-10]. For sustainable development of the non-ferrous metal industry in China, it is of critical significance to solve the problem of water resource waste and environment pollution. At present, the only way to solve the problem is to improve the recycling ratio of the treated water [11-14]. To do this, the treated water needs to be transmitted by the dedicated pipelines firstly.
Many industrial processes, especially in the mining and metallurgical processing industry, discharge the acidic effluents containing significant amounts of metals such as copper, nickel, zinc, lead and arsenic. Due to the toxicity and the tendency to bioaccumulate, strict environmental regulations have been implemented on the release of heavy metals [15-18]. In China, the stringent environmental regulations of the Emission Standard of Pollutants from Lead and Zink Industry (GB 25466—2010) and/or Copper, Nickel and Cobalt Industry (GB 25467—2010) have been promulgated [19]. For heavy metal removal from wastewater, many different methods, such as adsorption, precipitation, ion exchange, have been developed, and only metal sulfurization and hydroxide precipitation are used commercially at present [20-24]. However, the purified water treated by sulfurization and/or precipitation is not facilitated to reuse because of the higher concentration of non-metal ions (Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42-, F-, Cl-). To meet the strict standard levels, the novel technology for treatment of the acidic wastewater containing heavy metals from non-ferrous metal smelter by biologics has been proposed, developed and extensively applied in China [25]. Commercially heavy metals concentrations of the treated water are much lower than the limits of the standard. However, there are still some F-, Cl-, and SO42- ions which are all aggressive corrosion ions for the pipelines. It is therefore expected that corrosion due to the treated water can mainly affect the pipelines used to transport it. Corrosion problems are usually connected with operating problems and equipment maintenance, leading to recurrent partial and even total process shutdown, resulting in severe economic losses [26-28]. Pipeline corrosion is the deterioration of pipe material and related systems due to their interaction with the service environment.
Almost always carbon steel is the best choice for pipeline material because of the low cost and good mechanical property. Due to carbon steel’s susceptibility to corrosion, sooner or later a carbon steel pipeline will be corroded. Internal corrosion occurs due to the presence of water in the transported fluid [29]. Some significant progresses have been made on the adsorption of Cl- on surface of metals, growth mechanisms, and several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the passivity breakdown [30]. For pipelines made by high strength steel, most studies on corrosion in water pollution have focused on corrosion impacted by the pollution of water bodies, corrosion laws and mechanism of alloy in polluted seawater, and so on [31-34]. Corrosion of pipelines occurs due to an electrochemical reaction in the presence of an electrolyte in the aqueous media, usually fractions of the products they transport. Electron transfer is a very important component of the corrosion process.
Steel corrosion is largely determined by the water composition [35]. It is well known that the presence of some anions such as F-, Cl-, and SO42- has a significant effect on the extent and growth of localized corrosion [36-38]. Among of them, chloride and/or fluoride ions acting as the aggressive ions, play a remarkable role in the metal corrosion process [39-44]. Thus, corrosion behaviors of the Q235A steel pipeline by fluoride and chloride ions in the treated water are worth investigating from the viewpoint of electrochemistry. Q235A steel as the anode material was used as the object, the weight-loss analysis and electrochemical polarization were employed to investigate the corrosion behaviors of Q235A steel in the simulated treated water with different fluoride, chloride ions.
2 Materials and experimental methods
2.1 Q235A steel specimen
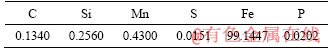
Chemical compositions of Q235A steel specimen, a kind of carbon structural steel, used in this study were shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of Q235A steel (mass fraction, %)
2.2 Corrosion media
The treated water [11-13] was simulated as the corrosion media. It consisted of 1.74 g/L SO42-, 0.833 g/L Na+, 60 mg/L Ca2+, 0.05 mg/L Cd2+,0.2 mg/L Cu2+ and 1.0 mg/L Zn2+. The pH value of the solution was adjusted to 10 with the dilute NaOH solution. The concentrations of Cl-, F- ions were altered based on the above simulated treated water. All solutions in the experiment were prepared from analytical grade chemicals and redistilled water. All experiments were performed at 40 °C.
2.3 Experiments
2.3.1 Coupon testing
Weight loss analysis is regarded as the simplest and longest-established method of estimating corrosion loss. A weighed sample (coupon) of the metal under consideration was introduced into the process, and removed later after a reasonable time interval. Corrosion weight loss was measured by means of the static and dynamic coupon tests. The specimens were polished using rough and fine emery papers, washed thoroughly with the double distilled water, and then degreased with acetone and absolute ethyl alcohol, finally dried at room temperature. The pretreated specimens were immersed into the prepared solution. The electrode potentials were measured every 24 h. After immersion, the corrosion products on the surface of the specimens were cleaned with membrane removing agent. The specimens were washed thoroughly and dried to a constant weight.
For the static coupon tests, the specimen was completely immersed into the solution in a 500 mL flask. The tests were continuously performed in the unstirred solutions for 18 d. While for the dynamic coupon tests, the specimens were fixed in a 1000 mL flask. The tests were continuously running with a stirring speed of 91 r/min for 7 d. The coupon was then cleaned all corrosion product off and was reweighed. The weight loss is converted to a corrosion rate.
2.3.2 Electrochemical experiments
In the experiments, a conventional three-electrode configuration with a piece of platinum counter electrode with the size of 2 cm×2 cm and a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) reference electrode, connected with the electrolyte through a salt bridge positioned close to the working electrode surface to minimize ohmic potential drop. The working electrode was made from Q235A steel with the size of 4 mm×4 mm collected from a smelter. The experimental specimens were machined from steel plate, soldered to copper conducting wires at its back side, inserted into a glass tube, then mounted with epoxy resin leaving a working area of 0.16 cm2. And then the prepared working electrode was polished with a 300 mesh and a 1000 mesh emery paper separately to remove the oxides on the electrode surface. Then it was washed successively with the acetone and ethanol three times before it was rinsed with the redistilled water to remove grease from the surface. Finally, the working electrode was dried with a drier prior to use. All the electrodes and probes were fixed in a 1000 mL flask with an open mouth connecting the electrolyte with the atmosphere. The electrolyte comprised de-ionized water with different concentrations of F-, Cl- ions.
The corrosion behaviors described by open circuit potential curves, polarization curves, and Tafel polarization fitting curves were conducted with an electrochemical workstation (Multi Autolab M204). To achieve quasi-stationary condition, the polarization curves were potential-dynamically measured with a potential scan rate of 1 mV/s, the cathodic polarization curve was obtained by polarizing from the corrosion potential toward the cathodic direction. Prior to electrochemical measurement, a stabilization period is allowed to attain a stable value of corrosion potential.
The electrochemical experiments were carried out in different electrolytes without stirring at 40 °C. Active dissolution stage of the polarization curves was measured with the above electrochemical apparatus for analyzing the corrosion behaviors, and instantaneous corrosion rate of the electrode was calculated using the polarization curve extrapolation. Open circuit potential-time curves of the corrosion system were recorded by the potentiostatic technique, and polarization measurements were performed when the corrosion system reached stability.
3 Corrosion behaviors of Q235A steel in simulated treated water
3.1 Corrosion weight loss
The Q235A steel specimens were immersed in the simulated solutions with different concentrations of F-, Cl-, the results of the static and dynamic coupon testing were shown in Figure 1, Tables 2 and 3.
The corrosion rate (CR) can be defined as
CR=(Mend-Minitial)/S·t (1)
where CR is the corrosion rate with the unit of mg/(dm2·d); Minitial, Mend represent the initial mass, the ending mass of the specimen, respectively, g; S is the surface area of the specimen, cm2; and t is corrosion time, day. In addition, CF- and CCl- stand for the concentrations of F-, Cl-, mg/L, respectively.
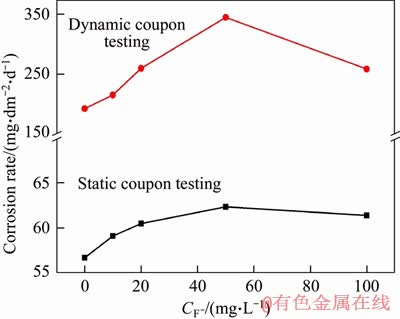
Figure 1 Effect of concentration of F- ion on corrosion rate
Table 2 Results of static coupon testing for Q235A steel specimen

Table 3 Results of dynamic coupon testing for Q235A steel specimen
For static coupon testing, the CR of Q235A steel increases from 56.67 to 62.36 mg/(dm2·d) with the concentration of F- increasing from 0 to 50 mg/L, while for dynamic coupon testing, it increases from 192.19 to 345.22 mg/(dm2·d), the latter CR is 4 times that of the former. The maximum CR is obtained at the concentration of 50 mg/L. Further increasing the concentration of F- ion more than 50 mg/L, CRs decrease a little. For both static and dynamic coupon testing, CR changing tendency over the concentration of F- is same. There is a maximum value at 50 mg/L of F- in the simulated water. Because of the presence of the Ca2+, Cu2+ in the treated water, insoluble metal fluorides (CaF2, CuF2) may form simultaneously with F- concentration increasing, which results in a slight decrease of the corrosion rate.
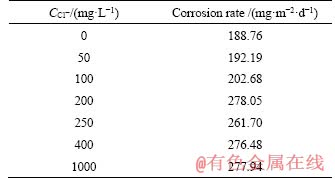
For static coupon testing, CR of Q235A steel increases from 58.19 to 68.93 mg/(dm2·d) with Cl- concentration increasing from 0 to 200 mg/L, while for dynamic coupon testing, CR increases from 188.76 to 278.05 mg/(dm2·d), and then it becomes smaller. The corrosion types of F- and Cl- ions are different due to their distinction in nature. The former tends to cause general corrosion, and the latter is prone to initiate pitting corrosion. CRs tend to stabilize and slightly fluctuate within 60.69 to 64.83 mg/L, 261.70 to 277.94 mg/L, respectively, with increasing Cl- concentration in the simulated media from 250 to 1000 mg/L. The maximum CRs of 68.93 and 278.05 mg/(dm2·d) are achieved at Cl- concentration of 200 mg/L, respectively. The average CR of dynamic coupon testing is about 4 times than that of static coupon testing.
Chloride ions may preferentially be adsorbed onto the steel surface in competition with other species. When the chloride ion is added to the solution, OH- ions must be competed with Cl- for surface sites. The adsorbed chloride ions would break down passivity of the steel and thus increase the corrosion rate. The acceleration effect due to chloride on the steel dissolution by forming an intermediate bridge structure is usually described as the “catalytic mechanism” [30, 45, 46].
Open-circuit potential (OCP)-time curves with different F-, Cl- concentrations over time were shown in Figure 2. There is an obviously negative movement of the OCP in the beginning, and then it tends to be steady with the increase of the immersion time. The reason is that the oxide film formed in air initially covers the steel surface. When the steel coupon is immersed, this native oxide film tends to dissolve which leads to a decrease of the OCP.
For static coupon testing, OCP of the Q235A steel specimen decreases rapidly before 1.5 d, and then fluctuates slightly with the time prolonging, the corrosion processes become stable. For dynamic coupon testing, OCP decreases sharply before 1.5 d, and then increases gradually.
3.2 Polarization behaviors
Acceleration of corrosion is due to the enhancement of the electrode process. The initial stages of the corrosion have been studied via the open circuit potentials-time curves and anodic polarization curves of Q235A steel specimen in the aggressive solution with different concentrations of F-, Cl-, and the results were shown in Figures 3 and 4. The OCPs become positive apparently when F-, Cl- ions are added to the system. The OCP is more positive with F- concentration increasing, and for Cl- ions, it tends to be stable and maintains constant with the time going. The fitted values of corresponding kinetic parameters such as corrosion potential Ecorr and corrosion current densities icorr were obtained. Ecorr moves positively and icorr increases gradually as the concentrations of F-, Cl- increasing. icorr of 1.2594 A/m2 is maximum at F- concentration of 48 mg/L, Ecorr of -0.770 V is maximum at Cl- concentration of 200 mg/L, which consists with the results of corrosion mass loss. Q235A steel passivation becomes more stable in the weak alkaline solution containing Cl- ions, and in the process of the active dissolution Ecorr moves positively and icorr increases gradually.
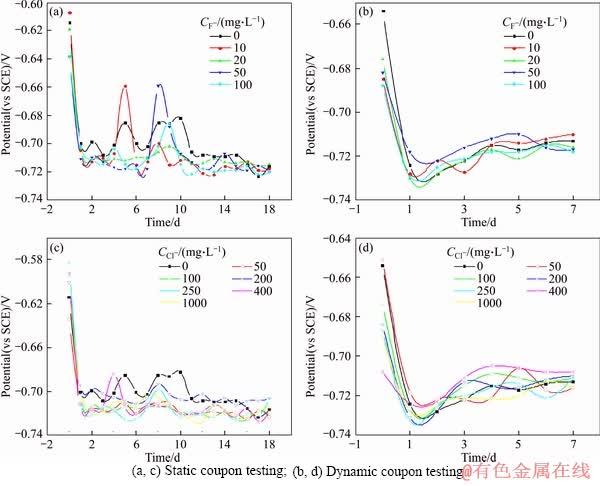
Figure 2 Self corrosion potential-time curves with different concentrations of F-, Cl- ions:
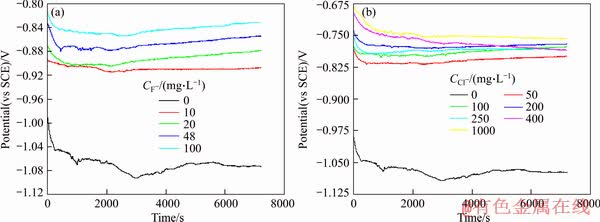
Figure 3 Open circuit potentials-time curves for different concentrations of F- (a) and Cl- (b)

Figure 4 Anodic polarization curves for different concentrations of F- (a) and Cl- (b)
In addition, Figure 4 illustrates that the existence of F-, Cl- contributes to the corrosion process, the anodic current becomes constant at high anodic potentials. It is obvious that the addition of F-, Cl- ions to the simulated treated water increases the limited current density.
The lines obtained from the active dissolving part of anodic polarization curves via Tafel transformation were shown in Figures 5 and 6, the correlated parameters including free corrosion potential Ecorr and corrosion current icorr through Tafel extrapolation were listed in Tables 4 and 5.
In the whole process, the initiating passive potential and current density increase mainly with the concentration of F- increasing. The reason is that F- has the properties of stronger electron affinity and permeability owning to its less atomic number, and then when F- increases to a certain concentration it could penetrate the adsorption layer and activate specimen’s surface leading to the acceleration of Q235A steel corrosion speed. In addition, stable complex ions formed between F- and Fe3+ [47] will accelerate the dissolution of passivation layer on the specimen’s surface.
Fe·H2O+F-→(MFOH-)ads+H++e (2)
(MFOH-)ads→(MFOH-)com+e (3)
(MFOH-)com+H+→M2++F-+H2O (4)
Passivation of the steel is typically due to a protective metal oxide film being applied to or forming naturally on the surface of the steel as a protection against corrosion. It is commonly accepted that chloride ions can affect the passivity of the substance by penetrating the passive film.
The corrosion of pipeline steel is due to chloride ion reactions, and accordingly the role of chloride ions in steel pipeline corrosion has been investigated extensively. The early studies have revealed that chloride ions affect corrosion in several ways, including catalytic processed (adsorption theory), oxide film effect, or dissolved gas effect [48].
The active dissolution process includes dissolution mechanism by OH- and by Cl- when corrosion occurs of Fe in the weak alkaline solution containing Cl- ion. Fe dissolution is accelerated via the following processes.
Dissolution mechanism by OH-,
Fe+OH-→FeOH+e (5)
FeOH→FeOH++e (6)
FeOH+→Fe2++OH- (7)
Dissolution mechanism by Cl-,
Fe+Cl-→FeCl+e (8)
FeCl→FeCl++e (9)
FeCl+→Fe2++Cl- (10)
The above mechanisms compete, dissolution mechanism by OH- is dominant at lower Cl- concentration, while dissolution mechanism by Cl- plays a significant role at the higher concentration of Cl-, and corrosion rate increases gradually with the increasing concentration of Cl-.
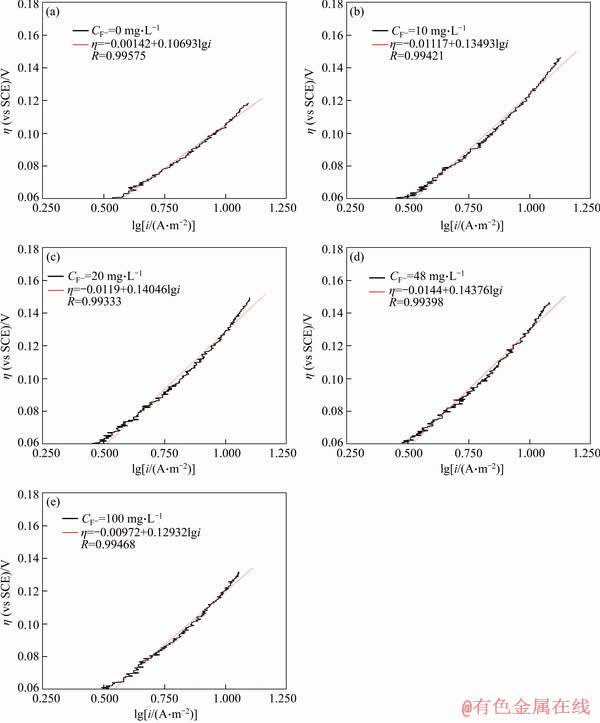
Figure 5 Tafel beelines for different F- concentrations
Q235A steel surface transforms to passivation state through the formation of hydrated ferrous hydroxide film. The addition of Cl- does not change the basic process of the passivation. The increase of icorr is due to the different structure of the passivation film at the presence of Cl- ion. The acceleration of the dissolution rate of the passivation film by Cl- ion leads to the increase of Ecorr and icorr. On the other hand, the addition of Cl- ion changes the dissolution mechanism of passivation film through complexation between Cl- ion and passivation surface. The presence of Cl- ions increases the probability of passivity layer breakdown and inclusion dissolution, which allows for the stable growth of pits over time.
4 Conclusions
The existence of F-, Cl- in the treated water from the non-ferrous metallurgical industry would accelerate the Q235A steel corrosion rate. CR is maximum at the concentration of F-, Cl- with 50 and 200 mg/L, respectively. The corrosion process takes place mainly in the beginning stage when the Q235A steel is immersed in the simulated solution.
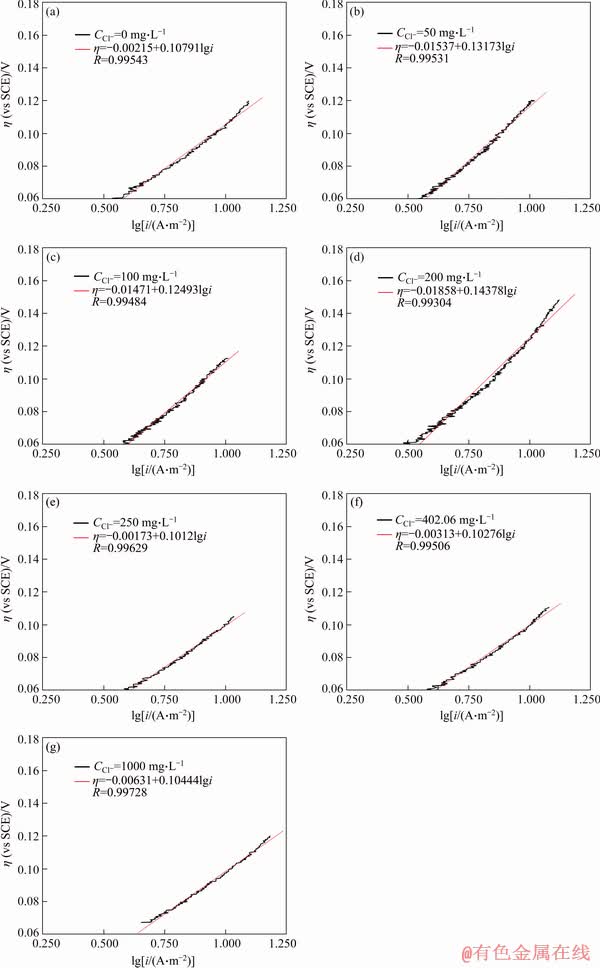
Figure 6 Tafel beelines for different Cl- concentrations
Table 4 Ecorr, icorr, Ep and Imax of Q235A steel at different F- concentrations

Table 5 Ecorr, icorr, Ep and Imax of Q235A steel for different Cl- concentrations

Corrosion current is maximum at the concentration of Cl- with 48 mg/L, which consists with the results of corrosion weight loss. The existence of F-, Cl- contributes to the corrosion process and becomes stable quickly. The initiating passive potential moves positively with the concentrations of F-, Cl- increasing. There is a little effluence of the concentrations of F-, Cl- on the initiating passive current. Therefore, it is necessary to control F-, Cl- concentration in the treated water when it is recycled by the pipelines made of Q235A steel.
References
[1] LIU Zhi-yong, ZHAO Tian-liang, LIU Ran-ke, JIA Jing-huan, DU Cui-wei, LI Xiao-gang. Influence factors on stress corrosion cracking of P110 tubing steel under CO2 injection well annulus environment [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23: 757-764. DOI: 10.1007/ s11771-016-3121-1.
[2] LIU Xia, YUAN Yi-zhi, WU Zhu-ying, TIAN Gao-deng, ZHENG Yu-gui. Synergistic corrosion inhibition behavior of rare-earth cerium ions and serine on carbon steel in 3% NaCl solutions [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25: 1914-1919. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-018-3881-x.
[3] FINSGAR M, JACKSON J. Application of corrosion inhibitors for steels in acidic media for the oil and gas industry: A review [J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 86: 17-41. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2014.04.044.
[4] KEAR G, BARKER B D, WALSH F C. Electrochemical corrosion of unalloyed copper in chloride media––A critical review [J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46(1): 109-135. DOI: 10.1016/S0010-938X(02)00257-3.
[5] MOSKVICHEVA E V, SIDYAKINB P A, SHITOV D V. Method of corrosion prevention in steel pressure pipelines in sewerage systems [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 150: 2381-2386. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.07.317.
[6] CHAI Li-yuan, MIN Xiao-bo, TANG Ning, WANG Yun-yan. Mechanism and kinetics of Zn(II) removal from wastewater by immobilized beads of SRB sludge [J]. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 2009, 37(1): 20-33. DOI: 10.1504/ijep.2009.024468.
[7] CHAI Li-yuan, WANG Qing-wei, LI Qing-zhu, YANG Zhi-hui, WANG Yun-yan. Enhanced removal of Hg(II) from acidic aqueous solution using thiol-functionalized biomass [J]. Water Science & Technology, 2010, 62(9): 2157-2166. DOI: 10.2166/wst.2010.385.
[8] WANG Qing-wei, QIN Wen-qing, CHAI Li-yuan, LI Qing-zhu. Understanding the formation of colloidal mercury in acidic wastewater with high concentration of chloride ions by electrocapillary curves [J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2014, 21: 3866-3872. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-013-2379-1.
[9] CHAI Li-yuan, YAN Xu, LI Qing-zhu, YANG Ben-tao, WANG Qing-wei.A comparative study of abiological granular sludge (ABGS) formation in different processes for zinc removal from wastewater [J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2014, 21: 12436-12444. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-014-3184-1.
[10] YAN Xu, LI Qing-zhu, CHAI Li-yuan, YANG Ben-tao, WANG Qing-wei. Formation of abiological granular sludge– A facile and bioinspired proposal for improving sludge settling performance during heavy metal wastewater treatment [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 113: 36-41. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.038.
[11] CHAI Li-yuan, XIAO Hai-juan, WANG Yun-yan, PEI Fei, SHU Yu-de, ZHANG Jin-long.Establishment of water quality index (Na+, Ca2+) for purified water reused to zinc electrolysis process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(2): 484-488. DOI: 10.1016/ S1003-6326(08)60300-3.
[12] LIU Hui, WANG Yun-yan, CHAI Li-yuan, XIAO Hai-juan, PEI Fei, SHU Yu-de.Effect of impurities in recycling water on Pb-Ag anode passivation in zinc electrowinning process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(7): 1665-1672. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11) 60912-6.
[13] WANG Yun-yan, PENG Xiao-yu, CHAI Li-yuan, SHU Yu-de.Corrosion mechanism of A3 steel induced by chloride ions in the purified water [C]// TMS 2009 Annual Meeting and Exhibition. TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2009. EPD Congress : 73-80.
[14] WANG Yun-yan, PENG Xiao-yu, CHAI Li-yuan, SHU Yu-de.Phase equilibrium of CaSO4-Ca(OH)2-H2O system [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(6): 1478-1485. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11) 61344-7.
[15] CHAI Li-yuan, WANG Zhen-xing, WANG Yun-yan, YANG Zhi-hui, WANG Hai-ying, WU Xie.Ingestion risks of metals in groundwater based on TIN model and dose-response assessment—A case study in the Xiangjiang watershed, central-south China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 8: 3118-3124. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.04.030.
[16] WANG Zhen-xing, CHAI Li-yuan, WANG Yun-yan, YANG Zhi-hui, WANG Hai-ying, WU Xie. Potential health risk of arsenic and cadmium in groundwater near Xiangjiang River, China: A case study for risk assessment and management of toxic substances [J]. Environ Monit Assess, 2011, 175: 167-173. DOI: 10.1007/s10661- 010-1503-7.
[17] HUANG Xiao, HE Li-ping, LI Jun, YANG Fei, TAN Hong-zhuan. Different choices of drinking water source and different health risks in a rural population living near a lead/zinc mine in Chenzhou city, southern China [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2015, 12(11): 14364-14381. DOI: 10.3390/ ijerph121114364.
[18] ZENG Fan-fu, WEI Wei, LI Man-sha, HUANG Rui-xue, YANG Fei, DUAN Yan-ying.Heavy metal contamination in rice-producing soils of hunan province, china and potential health risks [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2015, 12(12): 15584-15593. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph121215005.
[19] CHEN Run-hua, CHAI Li-yuan, LI Qin-zhu, SHI Yan, WANG Yang-yang, MOHAMMAD A. Preparation and characterization of magnetic Fe3O4/CNT nanoparticles by RPO method to enhance the efficient removal of Cr(VI) [J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research International, 2013, 20(10): 7175-7185. DOI:10.1007/s11356-013-1671-4.
[20] WANG Yang-yang, PENG Bing, YANG Zhi-hui, TANG Chong-jian, CHEN Yue-hui, LIAO Qi, LIAO Ying-ping. Treatment of Cr(VI) contaminated water with Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 71(10): 4333-4339. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-013-2827-8.
[21] ZHANG Q L, GAO N Y, LIN Y C, XU B, LE L S. Removal of arsenic(V) from aqueous solutions using iron-oxide- coated modified activated carbon [J]. Water Environment Research, 2007, 79(8): 931-937. DOI: 10.2175/ 106143007X156727.
[22] ZENG Jian-xian, YE Hong-qi, HUANG Nian-dong, LIU Jun-feng, ZHENG Li-feng. Selective separation of Hg(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by complexation– ultrafiltration process [J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 76(5): 706-715. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.05.019.
[23] CHEN Yong-gui, YE Wei-min, YANG Xiao-min, DENG Fei-yue, HE Yong. Effect of contact time, pH and ionic strength on Cd(II) adsorption from aqueous solution onto bentonite from Gaomiaozi, China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 64(2): 329-336. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-010- 0850-6.
[24] DAI Jun, REN Feng-lian, TAO Chun-yuan. Adsorption of Cr(VI) and speciation of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) in aqueous solutions using chemically modified chitosan [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health, 2012, 9(5): 1757-1770. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph905 1757.
[25] YAN Xu, CHAI Li-yuan, LI Qing-zhu, YE Li-jun, YANG Ben-tao, WANG Qing-wei. Abiological granular sludge formation benefit for heavy metal wastewater treatment using sulfide precipitation [J]. CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water, 2017, 45(4): 1500730-1500737. DOI: 10.1002/clen.201500730.
[26] LIU Jian-guo, LI Yan-tao, HOU Bao-rong. Corrosion behavior of Q235A steel under wet-dry cyclic condition [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 557-559: 139-142. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.557-559.139.
[27] KHAN M U, AHMAD S, AL-GAHTANI H J. Chloride- induced corrosion of steel in concrete: An overview on chloride diffusion and prediction of corrosion initiation time [J]. International Journal of Corrosion, 2017: 5819202. DOI: 10.1155/2017/5819202.
[28] KHAMIS A, SALEH M M, AWAD M I. Synergistic inhibitor effect of cetylpyridinium chloride and other halides on the corrosion of mild steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 [J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 66: 343-349. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2012.09. 040.
[29] ADILSON C B, JOSE L F F, RONALDO D V, DIVINO J S. Interaction of corrosion defects in pipelines—Part 1: Fundamentals [J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2016, 144: 56-62. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpvp.2016. 05.007.
[30] SAADI S A, YI Yong-sun, CHO Pyung-yeon, JANG Chang-heui, BEELEY P. Passivity breakdown of 316L stainless steel during potentiodynamic polarization in NaCl solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 111: 720-727. DOI: 10.1016/ j.corsci.2016.06.011.
[31] ANADEBEA V C, ONUKWULIB O D, OMOTIOMAC M, OKAFOR, N A. Optimization and electrochemical study on the control of mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid solution with bitter kola leaf extract as inhibitor [J]. South African Journal of Chemistry (Suid Afrikaanse Tydskrif Vir Chemie), 2018, 71: 51-61. DOI: 10.17159/0379-4350/2018/ v71a7.
[32] MORENO M, MORRIS W, ALVAREZ M G, DUFFO G S. Corrosion of reinforcing steel in simulated concrete pore solutions-effect of carbonation and chloride content [J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46(11): 2681-2699. DOI: 10.1016/ j.corsci.2004.03.013.
[33] WANG Hai-bo, LI Yun, CHENG Guang-xu, WU Wei, ZHANG Yao-heng. A study on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel exposed to a H2S-containing NH4Cl medium [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2018, 27(2). DOI: 10.1007/s11665-018-3355-1.
[34] YANG Lu-jia, XU Yun-ze, ZHU Ye-sen, LIU Liang, WANG Xiao-na, HUANG Yi. Evaluation of interaction effect of sulfate and chloride ions on reinforcements in simulated marine environment using electrochemical methods [J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2016, 11: 6943-6958. DOI: 10.20964/2016.08.51.
[35] HU Jia-yuan, CAO Shu-nan, YIN Li, LIANG Qin-qin, XIE Jian-li. Study on the corrosion behavior of Q235A carbon steel in RO product water of seawater [J]. Anti-Corrosion Methods and Materials, 2012, 59(6): 305-310. DOI: 10.1108/00035591211274424.
[36] ZHANG Zhi-guo, WU Ming, CHEN Xu. Effect of aggressive anions on corrosion behavior on A3 steel [J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2011, 32(8): 9-12. (in Chinese)
[37] LI M C, ZENG C L, LIN H C, GAO C N. Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of type 316 stainless steel in acid media containing fluoride ions [J]. British Corrosion Journal, 2001, 36(3): 179-183. DOI: 10.1179/bcj.2001.36.3.179.
[38] CHEN Gang, SU Hui-jun, SONG Ying-pan, GAO Yu, ZHANG Jie, HAO Xiao-jiang, ZHAO Jing-rui. Synthesis and evaluation of isatin derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for Q235A steel in highly concentrated HCl [J]. Res Chem Intermed, 2013, 39: 3669-3678. DOI: 10.1007/s11164-012- 0870-9.
[39] SEKINE I, USUI H, KITAGAWA S, YUASA M, SILAO L. The effect of fluoride ions on the corrosion of steel materials in H2SO4 and CH3COOH solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 1994, 36(8): 1411-1424. DOI: 10.1016/0010-938x(94) 90189-9.
[40] MACIAS A, ESCUDERO M L. The effect of fluoride on corrosion of reinforcing steel in alkaline solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 1994, 36(12): 2169-2180. DOI: 10.1016/ 0010-938x(94)90015-9.
[41] LE D P, YOO Y H, KIM J G, CHO S M, SON Y K. Corrosion characteristics of polyaniline-coated 316L stainless steel in sulphuric acid containing fluoride [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(2): 330-338. DOI: 10.1016/ j.corsci.2008.10.028.
[42] PAHLAVAN S, MOAZEN S, TAJI I, SAFFAR K, HAMRAH M, MOAYED M H, BEIDOKHTI S M. Pitting corrosion of martensitic stainless steel in halide bearing solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 112(11): 233-240. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2016.07.008.
[43] NIU Lin-qing, GUO Rui-guang, TANG Chang-bing, GUO Hong-tao, CHEN Jie. Surface characterization and corrosion resistance of fluoferrite conversion coating on carbon steel [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2016, 300(8): 110- 117. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.05.023.
[44] HU Jia-yuan, CAO Shun-an, YIN Li, GAO Yang. Electrochemical study on the corrosion of rusted carbon steel in dilute NaCl solutions [J]. Anti-corrosion Methods and Materials, 2014, 61(3): 139-145. DOI: 10.1108/ACMM- 05-2013-1261.
[45] WANG Z B, HU H X, ZHENG Y G. Synergistic effects of fluoride and chloride on general corrosion behavior of AISI 316 stainless steel and pure titanium in H2SO4 solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 130: 203-217. DOI: 10.1016/ j.corsci.2017.10.028.
[46] FENG H, JIANG Z, LI H, LU P, ZHANG S, ZHU H, ZHANG B, ZHANG T, XU D, CHEN Z. Influence of nitrogen on corrosion behaviour of high nitrogen martensitic stainless steels manufactured by pressurized metallurgy [J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 144: 288-300. DOI: 10.1016/ j.corsci.2018.09.002.
[47] LI Mou-cheng, ZENG Chao-liu, LIN Hai-chao, CAO Chu-nan. Effect of fluoride ions on passive performance of 316 stainless steel in acid media [J]. ACTA Metallurgical Sinica, 2001, 37(10): 1083-1086. DOI: 10.1016/S0925- 8388(01)01318-4. (in Chinese)
[48] WANG Ya-fei, CHENG Guang-xu, WU Wei, QIAO Qiao, LI Yun, LI Xiu-feng. Effect of pH and chloride on the micro-mechanism of pitting corrosion for high strength pipeline steel in aerated NaCl solutions [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 349: 746-756 DOI: 10.1016/ j.apsusc.2015. 05.053.
(Edited by HE Yun-bin)
中文导读
Q235A钢在有色工业含氟氯净化水中的腐蚀行为及电化学性质
摘要:采用静态挂片及动态挂片腐蚀试验,开路电势及线性扫描伏安法电化学实验研究了Q235A钢材在有色工业含氟氯净化水中的腐蚀行为及电化学性质。结果表明,模拟净化水中的F-、Cl-离子加快了Q235A钢材的腐蚀速率。F-、Cl-离子浓度分别为50 mg/L,200 mg/L时,腐蚀速率达到最大值。但是当外加电势于体系时,Q235A钢材会钝化。然而随着F-、Cl-离子浓度的增加,起始钝化电势正移。F-、Cl-离子浓度对起始钝化电流密度影响不大。因此,当净化水经由Q235A钢材制成的管道中回用时有必要控制F-、Cl-离子的浓度。
关键词:模拟水;卤素阴离子(F-, Cl-);Q235A钢材;腐蚀行为;电化学性质
Foundation item: Project(2018YFC1900304) supported by the National Key R&D Program of China; Project(2018SK2026) supported by the Key R&D Program of Hunan Province, China; Project(2017SK2420) supported by the Science and Technology of Hunan Province, China
Received date: 2019-12-21; Accepted date: 2020-03-26
Corresponding author: XU Hui, PhD Candidate; Tel: +86-731-88830511; E-mail: xuhuiyh@csu.edu.cn; ORCID: 0000-0002-5801-0987

