文章编号:1004-0609(2012)09-2692-07
低温分离、富集冶金粉尘中的Zn
高金涛1,李士琦1,张延玲1,张颜庭1,陈培钰2,钱 刚3
(1. 北京科技大学 钢铁冶金新技术国家重点实验室,北京 100083;
2. 天津钢管集团股份有限公司,天津 300201;3. 湖北新冶钢有限公司,黄石 435001)
摘 要:系统地研究国内多家钢铁企业粉尘的基础特性,开发出一种低温分离、富集冶金粉尘中Zn等金属元素的新工艺。基于ZnO超细粉的还原挥发热力学分析和动力学实验,进行了粉尘的非熔态还原及Zn的回收、富集研究。结果表明:使用高纯度CO或H2为还原剂,在800~900 ℃可实现粉尘中ZnO(s)→Zn(g)的转变,气化脱Zn率可达99%;收集到的气态还原产物经水洗去除掉K、Cl 等元素后,富集成含Zn量可达90%的富Zn物料。同时,较低的温度使得粉尘于非熔融状态下还原,固态还原产物中Fe的金属化率可达90%,可直接经物理分离获得固态高纯铁。
关键词:冶金粉尘;非熔态还原;Zn富集
中图分类号:TF813 文献标志码:A
Separating and enriching zinc from metallurgical dust at
low temperature
GAO Jin-tao1, LI Shi-qi1, ZHANG Yan-ling1, ZHANG Yan-ting1, CHEN Pei-yu2, QIAN Gang3
(1. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy, University of Science and Technology Beijing,
Beijing 100083, China;
2. Tianjin Pipe Corporation, Tianjin 300201, China;
3. Hubei Xinyegang Steel Co. Ltd., Huangshi 435001, China)
Abstract: The characteristics of dust obtained from different steelmaking enterprises were systematically studied. A new process for separating and enriching zinc from metallurgical dust at low temperature was developed. Based on the volatilized thermodynamics analysis and dynamics reduction experiment of pure ultra-fine ZnO, the experimental study on non-molten reduction and recovery and enrichment of zinc in dusts was carried out. The results show that zinc oxide is reduced to metallic zinc, using high-purity CO or H2 as the reducing agent at 800-900 ℃, and the de-zincing rate is over 99%. The collected gaseous reduction products are washed to get rid of K, Cl and other elements, then the enrichment, called Zn-rich material, is obtained with the content of Zn up to 90%. At the same time, the dusts are reduced at the state of non-molten because of low temperature, and the metallization of Fe in product of solid-state reduction is as high as 90%. Furthermore, the solid-state high-purity iron can be directly separated physically.
Key words: metallurgical dust; reduction at non-molten state; enrichment of zinc
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目 (51074025);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(FRF-SD-12-009A)
收稿日期:2011-07-07;修订日期:2012-04-20
通信作者:张延玲,副教授;电话:13911891432;E-mail:zhangyanling@metall.ustb.edu.cn
我国钢铁厂每年产生大量冶金粉尘,主要包括高炉瓦斯灰、电炉粉尘、转炉二次粉尘等[1]。冶金粉尘作为钢铁工业的副产品,一般生成于高温环境,属于高温气溶胶组分,由于其中Zn等重金属含量高、铁品位低、粒度较细等问题[2-3],使得大部分粉尘未能得到有效利用,或露天堆放,或直接填埋,不仅危害人体健康,而且恶化生态环境。
目前,冶金粉尘的处理方法主要包括:安全填埋法,固化稳定化法,湿法提取工艺,火法处理工艺。安全填埋法[4]是将粉尘简单处理后,送安全填埋场填埋,土地成本高、处理能力有限,且无法实现重金属资源的循环利用;固化稳定化法[5]是使用水泥或化学药剂来降低有害元素浸出,使有害物质转变为低溶解性、低迁移性或低毒性物质,但未能实现重金属资源的回收利用;湿法提取工艺[6-10]是使用酸或碱对粉尘进行浸出,但锌、铅浸出率较低,难以作为钢厂原料循环使用,浸出剂消耗较多,成本较高,处理过程中会引入硫、氯,造成新的环境污染。以Waelz回转窑类处理和Inmetco环形炉类处理为代表的火法处理工 艺[11-15]是配入粘结剂、煤粉造球后,于1 300 ℃左右进行直接还原,虽能去除大部分Zn、Pb等重金属,但高温还原产物为金属铁和脉石紧密结合、互相嵌布的复相,一般α-Fe微粒常被包裹在玻璃体和焦炭颗粒中,还需破碎-细磨-再选处理后作为高炉原料使用。关于冶金粉尘处理方面的研究工作,主要集中在高温熔态火法处理和湿法提取工艺,从可获得的资料来 看,有关低温非熔态还原工艺的研究,尚未见到类似报道。
本文作者在系统研究国内多家钢铁企业粉尘基础特性的基础上,进行粉尘的非熔态还原及Zn的回收、富集研究,开发出一种低温分离、富集冶金粉尘中Zn等金属元素的新工艺。在非熔融状态下分离出粉尘中99%以上的Zn元素、并富集成含Zn量高达90%的富Zn物料,同时得到纯度较高的固态铁,实现了完全的“零排放”,为冶金粉尘的再资源化利用提供了新的途径。
1 实验
1.1 典型冶金粉尘的基础特性
本研究分别选取天津钢管集团股份有限公司的电炉粉尘(EAF dust1)、唐山钢铁集团有限责任公司的高炉粉尘(BF dust1)、湖北新冶钢有限公司的电炉粉尘(EAF dust2)和高炉粉尘(BF dust 2)进行实验研究,其化学成分见表1。
由表1可以看出:粉尘中Zn含量为10%左右、TFe含量为40%左右。4种粉尘的X射线衍射结果如图1所示。由图1可以看出:粉尘中Zn主要以ZnO形态存在,Fe主要以Fe2O3和Fe3O4形态存在。
冶金粉尘的粒度分布情况见图2。由图2可见,冶金粒尘的粒度分布区间较窄(300~9 000 nm)、中值为1 000~2 000 nm,如此细的粒度为冶金粉尘低温、非熔态还原提供了动力学保证。
表1 冶金粉尘化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of metallurgical dust

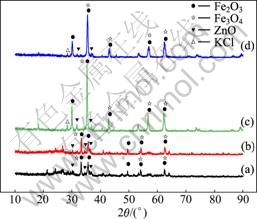
图1 冶金粉尘的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of metallurgical dusts: (a) BF dust1; (b) BF dust2; (c) EAF dust1; (d) EAF dust2
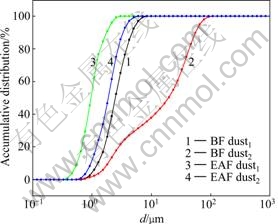
图2 冶金粉尘的粒度分布
Fig. 2 Size distribution of metallurgical dusts
综合典型钢铁企业4种粉尘的基础特性研究可知:冶金粉尘是富含Zn、Fe元素的超细固体废弃物。目前EAF dust1、EAF dust2的处理方式为直接外卖;BF dust1、BF dust2直接返回烧结工序。
1.2 实验方案
实验研究主要包括ZnO超细粉的还原动力学、粉尘的非熔态还原以及含Zn挥发物的提纯3个环节:
1) 首先使用分析纯ZnO超细粉进行非熔态还原试验,按L8(4×2)正交表安排试验,研究ZnO于还原气氛下的挥发动力学规律,实验目标变量Y为气化脱Zn率,其因素、水平见表2。
Y=1-[w(Zn)1×m1]/[w(Zn)0×m0] (1)
式中:m0、m1分别为试样还原前、后的质量;w(Zn)0、w(Zn)1分别为还原前、后Zn的质量分数。
表2 ZnO非熔态还原实验的因素和水平
Table 2 Factors and levels of non-molten reduction of ZnO

2) 进行4种粉尘的非熔态还原试验(试验的因素、水平见表3),按L32(4×4×2)正交表安排试验,研究还原温度、还原气氛以及粉尘粒度对气化脱Zn率和Fe金属化率的影响规律;并分别对气态和固态还原产物进行收集,采用XRD、XRF、化学分析等方法研究两类产物的组成、形态。
表3 冶金粉尘非熔态还原试验的因素和水平
Table 3 Factors and levels of non-molten reduction of metallurgical dusts

3) 对收集到的含Zn挥发物进行提纯试验,采用XRD、XRF、扫描电镜-能谱分析等方法研究所得富Zn物料的组成。
1.3 实验装置及方法
冶金粉尘的非熔态还原为气-固逆流反应过程[16],实验装置如图3所示。实验方法及参数如下。
1) 气源:N2为保护气体(流量为1 L/min);纯H2或CO为还原气体(流量为0.5 L/min),其中纯CO经CO2与重整装置中的C反应后过滤得到。
2) 物料:每次实验粉尘用量为10 g,将其平铺于坩埚内,置于管式电阻炉恒温区。
3) 升温:通入保护气体,将电阻炉升温至设定温度t,升温速率为20~35 ℃/min。
4) 还原:通入还原气体,于设定温度下恒温 1~2 h,对还原过程挥发物进行收集。
5) 冷却:停止还原气体,通入N2保护降温至室温。
6) 检测:对固态还原产物中Zn、TFe、MFe含量进行化学分析,计算气化脱Zn率Y以及Fe的金属化率R。
7) 提纯:对收集到的挥发物进行水洗处理,采用XRD和XRF等方法分析产物的组成。

图3 冶金粉尘的非熔态还原实验装置
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of non-molten reduction experimental apparatus of metallurgical dusts: 1—Nitrogen source; 2—Hydrogen source; 3—Carbon dioxide gas source; 4—Gas reforming unit; 5—Flow meters; 6—Gas mixing chamber; 7—Resistance furnace; 8—Control cabinet; 9—Crucible; 10—Dust removal device
2 结果与讨论
2.1 还原气氛中ZnO的挥发行为
使用Fact sage软件计算不同温度下CO或H2还原ZnO的平衡气相成分(如图4中曲线a和b所示),可以看出:温度高于907 ℃时,才可实现ZnO(s)→ Zn(g)的热力学转变;而由不同温度下Zn的饱和蒸气压曲线(见图4中曲线c)可以看出:Zn的饱和蒸气压曲线在700 ℃开始出现拐点,斜率增大,至907 ℃达到100 kPa;故在开放体系中,使用纯H2或CO为还原剂,在700~907 ℃下还原出Zn蒸气的分压小于该温度下的饱和蒸气压,为低温条件下Zn挥发行为的产生提供了热力学条件。
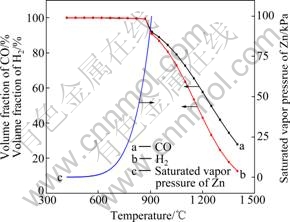
图4 不同温度下CO、H2还原ZnO的平衡气相成分
Fig. 4 Equilibrium gas composition of reduction of zinc oxide by H2 and CO at different temperatures
使用纯H2为还原剂,按表2进行分析纯ZnO超细粉(平均粒度为1.6 μm)的非熔态还原实验,结果如图5所示。
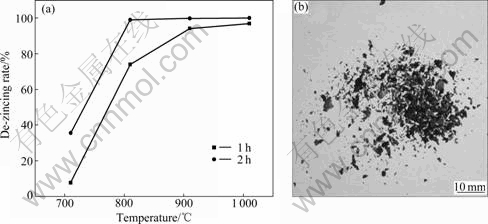
图5 纯ZnO超细粉的还原规律
Fig. 5 Reduction law of pure ultra-fine ZnO: (a) Effect of temperature on de-zincing rate; (b) Zn particle
由图5可以看出:使用纯H2为还原剂,在700 ℃即可开始实现ZnO(s)→Zn(g)的转变;温度达到800~900 ℃区间,可实现稳定的转变。
2.2 各因素对气化脱Zn率的影响
分别使用纯H2或CO为还原剂于800~900 ℃温度区间进行4种粉尘的非熔态还原试验,共32组试验,结果如图6所示。
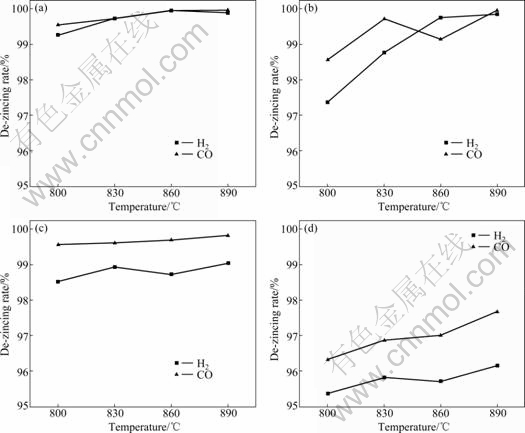
图6 冶金粉尘中Zn的还原特性
Fig. 6 Reduction property of zinc in metallurgical dusts: (a) EAF dust1; (b) BF dust1; (c) EAF dust2; (d) BF dust2
由图6可以看出:在800~900 ℃,使用纯H2或CO可实现粉尘中ZnO向Zn蒸气的转变,气化脱Zn率高达99%左右,还原产物中残Zn量小于1%。
同时,低至800~900 ℃的还原温度使得粉尘可于非熔融状态下实现FexOy向金属铁(MFe)的转变,Fe的金属化率达到90%以上;还原过程无烧结现象产生,C、P等杂质元素不会进入铁熔体,固态还原产物仍为粉状、分散度很高(其微观形貌如图7所示),仅经简易磁选分离即得到了TFe含量为92%的固态高纯铁。
1) 还原温度的影响
反应ZnO(s)+H2/CO(g)=Zn(g)+H2O/CO2(g)为吸热反应(见图4),随温度升高,反应活化分子增多,有效碰撞增加,还原反应平衡向正向进行,气化脱Zn率明显增加(图6中脱Zn率与温度呈正比)。
2) 还原气氛的影响
由图4可见,温度高于810 ℃时,H2的平衡气相分压低于CO的;而由于CO的密度较大,于卧式炉内与物料的接触条件明显优于H2,故图6中CO条件下的气化脱Zn率指标明显高于H2条件下的气化脱Zn率指标。
3) 粉尘粒度的影响
由气固未反应核模型可知,还原反应的限制环节主要为内扩散和界面反应,故物料的粒度对还原效果影响显著,由于BF dust2的粒度较其他3种粉尘的略大,故BF dust2的气化脱Zn率指标比其他3种粉尘的气化脱Zn率指标平均低3%左右。
2.3 Zn的富集
在冶金粉尘还原过程中,K、Cl等元素会伴随还原出的Zn蒸气一同挥发出,于收集装置中凝华。故对收集到的含Zn挥发物进行水洗处理,所得富Zn物料的主要成分如表4所列。
图7 固态还原产物的颗粒形貌
Fig. 7 Particle morphology of solid reduction products: (a) Particle morphology; (b) Energy spectrum diagram of Fe-rich particle; (c) Energy spectrum diagram of gangue particle

表4 富Zn物料的XRF分析结果
Table 4 XRF analysis results of zinc-rich material

图8所示为所得富Zn物料的XRD谱。综合表4和图8可以看出:冶金粉尘经前述分离、富集,可获得ZnO含量为90%,PbO含量为5%,伴随少量杂质元素的超细富Zn物料。

图8 富Zn物料的XRD谱
Fig. 8 XRD patterns of zinc-rich material: (a) BF dust1; (b) BF dust2; (c) EAF dust1; (d) EAF dust2
3 结论
1) ZnO超细粉的还原挥发热力学分析和动力学实验结果表明,温度低于900 ℃,即可实现ZnO(s)→ Zn(g)的转变;其中800~900 ℃为转变的稳定区间。
2) 冶金粉尘的非熔态还原实验结果表明,使用纯度较高的H2或CO为还原剂,在800~900 ℃可实现粉尘中ZnO(s)→Zn(g)的转变,气化脱Zn率达到99%;同时于非熔融状态下实现了FexOy→MFe的转变(金属化率为90%),可直接经物理分离获得固态高纯铁。
3) XRD、XRF、扫描电镜分析结果表明,粉尘非熔态还原过程产生的含Zn 挥发物经收集、水洗,可富集得到含Zn量高达90%的富Zn物料。
REFERENCES
[1] 王东彦, 王文忠, 陈伟庆, 周荣章. 转炉和含锌铅高炉尘泥的物性和物相分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1998, 8(1): 135-139.
WANG Dong-yan, WANG Wen-zhong, CHEN Wei-qing, ZHOU Rong-zhang. Analysis of intrinsic properties and phase condition on converter sludge and bearing Zn, Pb blast furnace sludge [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1998, 8(1): 135-139.
[2] TAHIR S, ALENKA R M, ?TEFICA C S, VJERA N R, MONIKA J, MLOE R. Characterization of steel mill electric arc furnace dust [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2004, 109(1/3): 59-70.
[3] NEGRO P, PETIT C, URVOY A, SERT D, PIERRET H. Characterization of the permeability of the blast furnace lower part [J]. Revue de Metallurgie-Cahiers D'Informations Techniques, 2001, 98(6): 521-532.
[4] WANG K S, CHIANG K Y, TSAI C C, SUN C J, TSAI C C, LIN K L. The effects of FeCl3 on the distribution of the heavy metals Cd, Cu, Cr, and Zn in a simulated multimetal incineration system [J]. Environmental International, 2001, 26(4): 257-263.
[5] HAFEZ A I, ELMANHARAWY M S, ABDEL FATTAH M A. Chemical treatment of the water used in the blast furnace gas cleaning cycle in the Egyptian iron and steel company [J]. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 2002, 18(4): 359-371.
[6] 黄志华, 伍喜庆, 彭冠兰. 高炉尘泥化学除锌[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(7): 1207-1212.
HUANG Zhi-hua, WU Xi-qing, PENG Guan-lan. Removal of zinc from blast furnace dust by chemical leaching [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(7): 1207-1212.
[7] DUTRA A J B, PAIVA P R P, TAVARES L M. Alkaline leaching of zinc from electric arc furnace steel dust [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2006, 19(5): 478-485.
[8] HERCK P V, VANDECASTEELE C, SWENNEN R, MORTIER R. Zinc and lead removal from blast furnace sludge with a hydrometallurgical process [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2000, 34(17): 3802-3808.
[9] PALENCIA I, ROMERO R, IGLESIAS N, CARRANZA F. Recycling EAF dust leaching residue to the furnace: A simulation study [J]. JOM—Journal of the Minerals Metals & Materials Society, 1999, 51(8): 28-32.
[10] RUIZ O, CLEMENTE C, ALONSO M, ALGUACIL F J. Recycling of an electric arc furnace flue dust to obtain high grade ZnO [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 141(1): 33-36.
[11] STROHMEIER G, BONESTELL J E. Steelworks residues and the Waelz kiln treatment of electric arc furnace dust [J]. Iron and Steel Engineer, 1996, 73(4): 87-90.
[12] 伍成波, 刁岳川, 杨 辉, 王朝东, 张丙怀. 含碳球团还原法处理含锌电炉粉尘的试验分析[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2007, 30(9): 51-55.
WU Cheng-bo, DIAO Yue-chuan, YANG Hui, WANG Chao-dong, ZHANG Bing-huai. Pilot-plant test of EAF dust treatment include zinc [J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2007, 30(9): 51-55.
[13] MAGER K, MEURER U, WIRLING J. Minimizing dioxin and furan emissions during zinc dust recycle by the Waelz process [J]. JOM—Journal of the Minerals Metals & Materials Society, 2003, 55(8): 20-25.
[14] MACHADO M F, REIS NETO J M, CUNHA C J. Mineral phases of weathered and recent electric arc furnace dust [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 154(1/3): 417-425.
[15] 王东彦, 王文忠, 陈伟庆, 周荣章, 林宗彩. 含锌铅粉尘配碳球团中铅挥发动力学[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1997, 7(4): 38-41.
WANG Dong-yan, WANG Wen-zhong, CHEN Wei-qing, ZHOU Rong-zhang, LIN Zong-cai. Evaporation kinetics of lead in carbon-containing pellets from Zn-Pb-bearing dusts [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1997, 7(4): 38-41.
[16] 李士琦, 李 瑾, 高金涛, 谷 林, 侯娜娜, 陈代明, 赵 传. 超细赤铁矿粉非熔态还原实验研究[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2010, 32(11): 1412-1417.
LI Shi-qi, LI Jin, GAO Jin-tao, GU Lin, HOU Na-na, CHEN Dai-ming, ZHAO Chuan. Experimental study on reduction of ultra-fine hematite powder at non-molten state [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2010, 32(11): 1412-1417.
(编辑 何学锋)