J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (2008) 15(s1): 098-101
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-008-323-1
Wall slip behavior of polymer melts on capillary rheometer
LIAO Hua-yong(廖华勇)1, TAN Zhong-xin(谭中欣)2, ZOU Guo-xiang(邹国享)1,
DING Yong-hong(丁永红)1, TAO Guo-liang(陶国良)1
(1. Polymer Materials Key Laboratory of Changzhou City, Jiangsu Polytechnic University, Changzhou 213164, China;
(2. Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510640, China)
Abstract: Wall slip behavior of three commercial polymer melts polypropylene(iPP), low-density polyethylene (LDPE)(branched chains) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE)(linear chains) were studied by using a capillary rheometer with twin bores at different temperatures. The results show that a sudden first-stick-then-slip transition was observed for HDPE and a first-slip-then-stick transition was observed for LDPE and iPP as the shear rate sweep was done in an increased order, which shows that the chain structure has an obvious effect on the wall slip behavior of polymers. The critical shear stress for the onset of stick-slip transition increases linearly with temperature for HDPE, which accords with the disentanglement mechanism proposed by Brochard and de Gennes. While the extrapolation length used to quantify the magnitude of the transition remains about 0.05-0.09 mm for HDPE at 150-230 ℃. Also the relationship between the critical shear stress for the onset of wall slip and the molecular mass for polymer samples agrees with the disentanglement model of Brochard and de Gennes. The onset of slip-stick transition for LDPE and iPP at a critical shear stress may be interpreted as the shear thinning of the polymer chains at high shear rates, preventing further development of wall slip behavior.
Key words: polymer; wall slip; critical shear stress; capillary rheometer; temperature dependence
1 Introduction
Wall slip, a common phenomenon occurred on the polymer/wall interface, has attracted great attention for decades of years since Mooney’s work in 1931[1]. BROCHARD and GENNES[2] originally put forward the well-known disentanglement model based on a coil stretch transition undergone by the grafted chains onto a solid surface above a certain critical shear stress (τc) which is proportional to temperature. Disentanglement mechanism is mainly for slip of polymers on wall surface with high adhesive energy[3], while another mechanism is the debonding slip for polymer chains on solid surface with low adhesive energy such as an organic wall[4]. WANG and DRDA[5] first found the break of shear stress-shear rate curve for HDPE melts in capillary rheometer, which they interpreted as an interfacial stick-slip transition of the HDPE/wall. And they found that the critical shear stress on the transition almost increased linearly with temperature, which agrees with the disentanglement model proposed by BROCHARD and de GENNES[2]. JOSHI et al[3] confirmed the temperature dependence for the debonding slip mechanism both through an unified model and the shear rate sweep experiment for a linear low density polyethylene(LLDPE) on bare/fluoroelastomer coated cone-and-plate viscometry.
LIAO and FAN[6] studied wall slip for a HDPE 5306J by investigating the gap-dependence of the shear stress versus shear rate 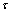 —
—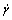 curve on the rotary rheometer with parallel plates fixtures, and found that the
curve on the rotary rheometer with parallel plates fixtures, and found that the 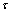 —
—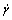 curve overlapped well for three gaps during the stress range 100-5 000 Pa at 150 ℃, indicating no obvious slip occurred probably because the shear stress was far below the so-called critical stress for the onset of wall slip. So a further work needs to be done to give a more relatively complete result. An outstanding advantage of the capillary rheometer is that its shear rates are much higher than that of the rotary rheometer. In this work, the wall slip behavior of several polymer melts with different chain structures was studied by using a twin-bore capillary rheometer; our experimental results for a linear HDPE sample were compared with that done by WANG and DRDA[5]; and the slip characteristics of an iPP and a brached LDPE was explored by investigating both the continuity and capillary diameter-dependence of the
curve overlapped well for three gaps during the stress range 100-5 000 Pa at 150 ℃, indicating no obvious slip occurred probably because the shear stress was far below the so-called critical stress for the onset of wall slip. So a further work needs to be done to give a more relatively complete result. An outstanding advantage of the capillary rheometer is that its shear rates are much higher than that of the rotary rheometer. In this work, the wall slip behavior of several polymer melts with different chain structures was studied by using a twin-bore capillary rheometer; our experimental results for a linear HDPE sample were compared with that done by WANG and DRDA[5]; and the slip characteristics of an iPP and a brached LDPE was explored by investigating both the continuity and capillary diameter-dependence of the 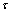 —
—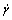 curve. The wall slip behavior of iPP and a brached LDPE were very different from that of HDPE. The related slip mechanisms were also discussed.
curve. The wall slip behavior of iPP and a brached LDPE were very different from that of HDPE. The related slip mechanisms were also discussed.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
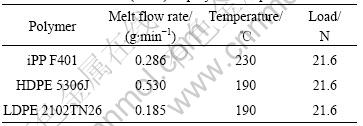
The polymer samples under investigation were a polypropylene (iPP F401), a high density polyethylene (HDPE 5306J), both manufactured by Yangzi Petro. Co. Ltd., China, and a low-density polyethylene (LDPE) manufactured by Qilu Petro. Co. Ltd., China, Table 1 lists the melt flow rate (MFR) measured by using MFR tester made in New San-Si Material Test Co. Ltd., Shenzhen, China. All the samples are dried articles before being added fully into the twin bores of the rheometer.
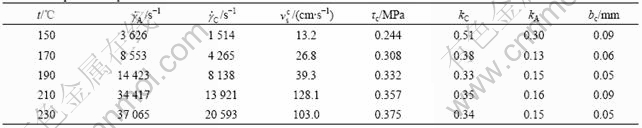
Table 1 Melt flow rate(MFR) of polymer samples
2.2 Rheometry
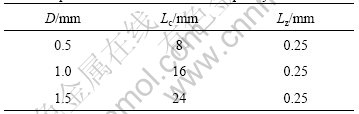
The experiments were done on a controlled-piston speed RH2000 capillary rheometer manufactured by Bohlin Instruments Comp. The rheometer is equipped with twin bores, i.e., a common capillary die and a zero length capillary die. Table 2 lists the specifications of three sets dies used in this study. Lc and Lz represent the length of the common capillary and zero length capillary, respectively. D is the diameter for both the capillaries. Before experiment the bores were cleaned carefully with liquid paraffin to eliminate possible contaminant or residual polymer chains. The shear stress data are dealt with Bagley correction.
Table 2 Specifications of three sets of capillary dies
2.3 Temperature control
The experimental temperatures were 150, 170, 190, 210 and 230 ℃ for the iPP, HDPE and LDPE samples, respectively. Before rheological measurement the samples in the twin bores were pressed at 0.5 MPa and 0.2 MPa with a speed of 2 mm/min respectively twice and after each pressure 2, 4 min were lasted respectively when the samples were firstly melted in the rheometer at required temperatures in order to remove the thermal and strain history and possible air bubbles. During the experiments, the temperature fluctuation did not exceed ± 0.2 ℃.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Wall slip of iPP and LDPE
Shear rate sweep was done for iPP at 190, 210 and 230 ℃ with capillaries diameter of 1.0 mm, the shear stress versus shear rate curves is shown in Fig.1(a). It can be seen from Fig.1(a) that the 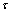 —
—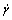 curves are continuous without any obvious sudden break, which means that no obvious stick-slip transition occurs. So it cannot be concluded arbitrarily that no slippage happens during the extrusion flow of the iPP melt from the capillaries. From the rheological knowledge it can be concluded that slip occurs on the interface of the polymer/wall if the
curves are continuous without any obvious sudden break, which means that no obvious stick-slip transition occurs. So it cannot be concluded arbitrarily that no slippage happens during the extrusion flow of the iPP melt from the capillaries. From the rheological knowledge it can be concluded that slip occurs on the interface of the polymer/wall if the 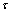 —
—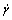 curve depends on the diameter of the capillary die.
curve depends on the diameter of the capillary die.
In order to check it, two sets of capillary dies with different diameters, i.e. 1.0 mm and 1.5 mm were used in the shear rate sweep experiment at 210 ℃. The results are shown in Fig.1(b), which indicates that the 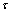 —
—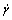 curves are dependent on the diameter of the capillaries at relatively low shear rate. This means that slip exists. And the
curves are dependent on the diameter of the capillaries at relatively low shear rate. This means that slip exists. And the 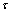 —
—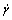 curves overlapped well at and beyond a certain critical shear stress
curves overlapped well at and beyond a certain critical shear stress 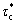 of about 0.06 MPa, which means that the slip disappears gradually and the polymer/wall is in a stage of stick. Thus the polymer/wall is in slip state when the shear stress is below
of about 0.06 MPa, which means that the slip disappears gradually and the polymer/wall is in a stage of stick. Thus the polymer/wall is in slip state when the shear stress is below 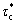 , and in stick state when at and beyond
, and in stick state when at and beyond 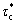 . And it is not an occasional phenomenon. Similar first-slip-then-stick transition is observed at about 0.04-0.05 MPa for a LDPE 2102TN26 at 190 and 210 ℃ by using two sets of capillary dies with different diameters (1.0 mm and 1.5 mm). Detailed description is omitted here for the sake of simplicity.
. And it is not an occasional phenomenon. Similar first-slip-then-stick transition is observed at about 0.04-0.05 MPa for a LDPE 2102TN26 at 190 and 210 ℃ by using two sets of capillary dies with different diameters (1.0 mm and 1.5 mm). Detailed description is omitted here for the sake of simplicity.
The interpretation for this may be as follows[7]: at high shear rates the molecular chains are oriented thus the configuration changes, part of the polymer chains are disentangled, the entanglement density declines, thus it results in the weakening even vanishment of the wall slip behavior.
In as much the polymer/wall was in a first-slip- then-stick state for polymers such as iPP and LDPE, one may ask another interesting question: whether wall slip always happens only if the shear stress was always below the critical value 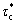 ? LIAO and FAN[8] studied the dynamic wall slip for some polymer melts including iPP and found a dimensionless elastic shear stress
? LIAO and FAN[8] studied the dynamic wall slip for some polymer melts including iPP and found a dimensionless elastic shear stress 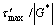 (
(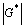 is the absolute value of the linear complex modulus), below which iPP/wall is in a stick state. Thus we speculate that when the shear rate increases gradually from very low values to high ones, iPP and LDPE stick on the wall below a critical stress
is the absolute value of the linear complex modulus), below which iPP/wall is in a stick state. Thus we speculate that when the shear rate increases gradually from very low values to high ones, iPP and LDPE stick on the wall below a critical stress 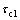 , and slip on the wall between
, and slip on the wall between 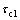 and
and 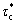 , and returns to stick on the wall beyond
, and returns to stick on the wall beyond 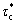 . More systematic work is needed to give a satisfying answer.
. More systematic work is needed to give a satisfying answer.
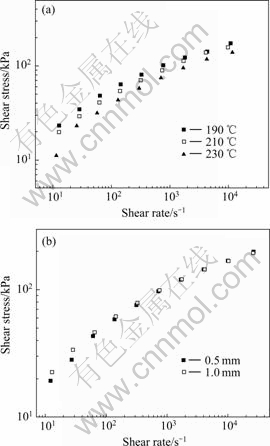
Fig.1 Shear stress versus shear rate for iPP: (a) With 1.0 mm diameter capillary dies at 190, 210 and 230 ℃, respectively; (b) With 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm diameter capillary dies respectively at 210 ℃
3.2 Wall slip of HDPE
Shear rate sweep was done for HDPE at five temperatures 150, 170, 190, 210 and 230 ℃ by using twin capillary dies with a diameter of 0.5 mm. The 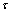 —
—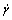 curve shown in Fig.2(a) exhibits obvious discontinuities at all the temperatures, the magnification curve at the transition is shown in Fig.2(b). It clearly indicates that a first-stick-then-slip transition occurs on the polymer/wall interface. The various rheological parameters at the transition are tabulated in Table 3. The
curve shown in Fig.2(a) exhibits obvious discontinuities at all the temperatures, the magnification curve at the transition is shown in Fig.2(b). It clearly indicates that a first-stick-then-slip transition occurs on the polymer/wall interface. The various rheological parameters at the transition are tabulated in Table 3. The
shear rate and slope just before the transition are denoted as 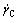 and kC, respectively, and the shear rate and slope just over the transition are denoted as
and kC, respectively, and the shear rate and slope just over the transition are denoted as 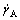 and kA, respectively. The critical shear stress was denoted as
and kA, respectively. The critical shear stress was denoted as  . In general the level of the wall slip can be characterized by the extrapolation length
. In general the level of the wall slip can be characterized by the extrapolation length 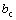 .When the pressure is at and beyond the critical value Pc, the volumetric flow rate Q jumps from QC to QA, where QC and QA represent the one for the stick and slip hydrodynamic boundary condition respectively, and accordingly the wall shear rate
.When the pressure is at and beyond the critical value Pc, the volumetric flow rate Q jumps from QC to QA, where QC and QA represent the one for the stick and slip hydrodynamic boundary condition respectively, and accordingly the wall shear rate 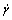 jumps from
jumps from 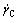 to
to 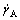 , the relationship between them are as follows:
, the relationship between them are as follows:
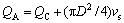 (1)
(1)
where vs is the wall slip velocity, D is the capillary diameter, and 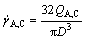 . Thus Eqn.(1) can be rewritten in the Mooney form[5] as
. Thus Eqn.(1) can be rewritten in the Mooney form[5] as
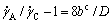 (2)
(2)
The slip velocity  can be computed based on the definition of the extrapolation length
can be computed based on the definition of the extrapolation length 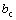 :
:
 (3)
(3)
It can be seen from Table 3 that  increases nearly with the temperature, but bc is in the range of 0.05-0.09 mm, is almost a constant. This result agrees well with the work done with HDPE (MW=316 600) by WANG and DRDA[5]. After a simple computation from Table 3, it can be found that the ratio of the critical shear stress τc to the temperature lays in a narrow range 1.6-1.8 kPa/℃, which means τc increases linearly with temperature. The stick-slip transition and τc—t relationship is also found experimentally for other two HDPE samples (5000S and 2300J) and a linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE 7042). This suggests that the stick-slip transition arises very likely from the entanglement-disentanglement transition between the absorbed chains on the wall and the bulk chains, a slip mechanism proposed by BROCHARD and de GENNES[2]. The capillaries used in this study were made by steel, whose high adhesive energy surface makes it possible for slip to occur by disentanglement[3]. The dis-
increases nearly with the temperature, but bc is in the range of 0.05-0.09 mm, is almost a constant. This result agrees well with the work done with HDPE (MW=316 600) by WANG and DRDA[5]. After a simple computation from Table 3, it can be found that the ratio of the critical shear stress τc to the temperature lays in a narrow range 1.6-1.8 kPa/℃, which means τc increases linearly with temperature. The stick-slip transition and τc—t relationship is also found experimentally for other two HDPE samples (5000S and 2300J) and a linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE 7042). This suggests that the stick-slip transition arises very likely from the entanglement-disentanglement transition between the absorbed chains on the wall and the bulk chains, a slip mechanism proposed by BROCHARD and de GENNES[2]. The capillaries used in this study were made by steel, whose high adhesive energy surface makes it possible for slip to occur by disentanglement[3]. The dis-
Table 3 Temperature dependence for HDPE 5306J
entanglement model[2-3] predicts the τc—T relationship as follows:
 (4)
(4)
where  and
and  are the number of chains per unit area and the absolute temperature respectively. From Table 3 and Eqn.(4) one can conclude that increasing temperature properly is a method to postpone wall slip caused by disentanglement mechanism.
are the number of chains per unit area and the absolute temperature respectively. From Table 3 and Eqn.(4) one can conclude that increasing temperature properly is a method to postpone wall slip caused by disentanglement mechanism.
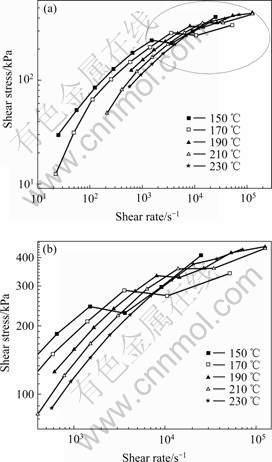
Fig.2 Shear stress versus shear rate for HDPE with 0.5 mm diameter capillaries at different temperatures ((b) is enlarged curve for part marked in (a))
From Table 1 it can be seen that the melt flow rate of HDPE is higher than that of iPP and LDPE, which means that the relative molecular mass of HDPE is lower than that of iPP and LDPE. The critical stress for the onset of slip for HDPE at 170 and 210 ℃ is 0.308 and 0.357 MPa, respectively, higher than that (0.05 MPa) of LDPE at 170 ℃ and that (0.06 MPa) of iPP at 210 ℃, which is in accord with Eqn.(4), because 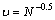 , where N is the average number of the chains, which is proportional to the molecular mass[7]. So the molecular mass and chain structure of polymers affect the wall slip behavior greatly.
, where N is the average number of the chains, which is proportional to the molecular mass[7]. So the molecular mass and chain structure of polymers affect the wall slip behavior greatly.
The slopes kC and kA were investigated. From Table 3, it can be seen that kC lays in the range of 0.33-0.51, thus the slope of 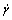 —
—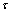 curve on the stick stage is 2-3, kA in the range 0.13-0.16, thus the slope of
curve on the stick stage is 2-3, kA in the range 0.13-0.16, thus the slope of 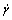 —
—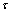 curve on the slip stage is 6.3-7.7 (the slope of the stick stage and slip stage is about 3.0 and 2.0 respectively in Ref.[8]), indicating that the
curve on the slip stage is 6.3-7.7 (the slope of the stick stage and slip stage is about 3.0 and 2.0 respectively in Ref.[8]), indicating that the 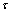 —
—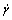 curve’s slope changed suddenly when stick-slip transition occurred.
curve’s slope changed suddenly when stick-slip transition occurred.
4 Conclusions
1) As the shear rate increases a first-stick-then-slip transition occurs at a critical shear stress for linear polymers, such as HDPE and LLDPE. The mechanism is very likely the disentanglement between the chains absorbed on the wall and the bulk chains.
2) For iPP and branched polymers, such as LDPE, a first-stick-then-slip transition occurs at some critical shear stress, the possible reason may be that the wall slip is retarded by the shear thinning at high shear rates. Although iPP is a polymer with linear chains, the helical structure of iPP whose methyl radicals lie in the same side of the backbone possibly makes its slip behavior quite different from that of linear polyethylene.
3) The molecular mass and chain structure have an important effect on the wall slip behavior.
References
[1] MOONEY M. Explicit formulas for slip and fluidity [J]. J Rheol, 1931, 2(2): 210-223.
[2] BROCHARD F, de GENNES P G. Shear-dependant slippage at a polymer/solid interface [J]. Langmuir, 1992, 8(12): 3033-3037.
[3] JOSHI Y M, TAPADIA P S, LELE A K, MASHELKAR R A. Temperature dependence of critical stress for wall slip by debonding [J]. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech, 2000, 94(2): 151-157.
[4] BARONE J R, WANG S Q. Adhesive wall slip on organic surfaces [J]. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech, 2000, 91(1): 31-36.
[5] WANG S Q, DRDA P A. Superfluid-like stick-slip transition in capillary flow of linear polyethylene melts. Ⅰ: General features [J]. Macromolecules, 1996, 29(6): 2627-2632.
[6] LIAO Hua-yong, FAN Yu-run. Rheological characterization and wall slip of a polymethylvinylsiloxane and a high density polyethylene [J]. J Cent South Univ Technol, 2007, 14(s1): 170-173.
[7] WU Qi-ye, WU Jing-an. Polymer rheology [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2005: 306-311. (in Chinese)
[8] LIAO Hua-yong, FAN Yu-run. A rheological study on wall slip of polymer melts [J]. Chem J Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(9): 1755-1761. (in Chinese)
(Edited by LONG Huai-zhong)
Foundation item: Projects(ZMF07020038) supported by the Young Teacher’s Scientific Research Fund of Jiangsu Polytechnic University, China
Received date: 2008-06-25; Accepted date: 2008-08-05
Corresponding author: LIAO Hua-yong, PhD; Tel: +86-519-86330097; E-mail: lhy01@jpu.edu.cn