Microstructure and microhardness of directionally solidified and heat-treated Nb-Ti-Si based ultrahigh temperature alloy
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2011年第6期
论文作者:郭海生 郭喜平
文章页码:1283 - 1290
关键词:Nb-Ti-Si基超高温合金;均匀化处理;时效处理;组织变化;显微硬度
Key words:Nb-Ti-Si based ultrahigh temperature alloy; homogenizing treatment; aging treatment; microstructural evolution; microhardness
摘 要:对定向凝固Nb-Ti-Si基超高温合金分别进行(1 500 °C,50 h)的均匀化处理以及(1 500 °C,50 h + 1 100 °C,50 h)的均匀化+时效热处理。结果表明:热处理后合金组织更加均匀,大尺寸初生(Nb, X)5Si3(X 代表Ti和Hf元素)块逐渐溶解或破碎,并且定向凝固共晶团中的大部分片状铌基固溶体Nbss以及(Nb, X)5Si3变得短、粗;热处理能够有效消除定向凝固态合金中不同区域Nbss内存在的元素偏析,各元素偏析比在热处理后均趋向于1;热处理后,组织的显微硬度增加,最大值达到了HV1 404.57,较定向凝固态合金中共晶组织的显微硬度增加了72.8 %。
Abstract:
Directionally solidified (DS) specimens of Nb-Ti-Si based ultrahigh temperature alloy were heat-treated at (1 500 °C, 50 h) and (1 500 °C, 50 h) + (1 100 °C, 50 h), respectively. The results show that the microstructures become uniform, the long and big primary (Nb,X)5Si3 (X represents Ti and Hf elements) plates in the DS specimens are broken into small ones, and the eutectic cells lose their lamellar morphology and their interfaces become blurry after heat-treatment. Meanwhile, the (Nb,X)5Si3 slices in the eutectic cells of the DS specimens coarsen obviously after heat-treatment. Homogenizing and aging treatments could effectively eliminate elemental microsegregation, and the segregation ratios of all elements in niobium solid solution (Nbss) in different regions tend to 1. After heat-treatment, the microhardness of retained eutectic cells increases evidently, and the maximum value reaches HV1 404.57 for the specimen directionally solidified with a withdrawing rate of 100 μm/s and then heat-treated at (1 500 °C, 50 h) + (1 100 °C, 50 h), which is 72.8 % higher than that under DS condition.

GUO Hai-sheng, GUO Xi-ping
State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
Received 18 October 2010; accepted 16 December 2010
Abstract: Directionally solidified (DS) specimens of Nb-Ti-Si based ultrahigh temperature alloy were heat-treated at (1 500 °C, 50 h) and (1 500 °C, 50 h) + (1 100 °C, 50 h), respectively. The results show that the microstructures become uniform, the long and big primary (Nb,X)5Si3 (X represents Ti and Hf elements) plates in the DS specimens are broken into small ones, and the eutectic cells lose their lamellar morphology and their interfaces become blurry after heat-treatment. Meanwhile, the (Nb,X)5Si3 slices in the eutectic cells of the DS specimens coarsen obviously after heat-treatment. Homogenizing and aging treatments could effectively eliminate elemental microsegregation, and the segregation ratios of all elements in niobium solid solution (Nbss) in different regions tend to 1. After heat-treatment, the microhardness of retained eutectic cells increases evidently, and the maximum value reaches HV1 404.57 for the specimen directionally solidified with a withdrawing rate of 100 μm/s and then heat-treated at (1 500 °C, 50 h) + (1 100 °C, 50 h), which is 72.8 % higher than that under DS condition.
Key words: Nb-Ti-Si based ultrahigh temperature alloy; homogenizing treatment; aging treatment; microstructural evolution; microhardness
1 Introduction
Nb-Ti-Si based ultrahigh temperature alloys have been widely investigated as the candidates for the high-temperature structural applications, owing to their high melting temperature, low density, good elevated-temperature creep strength and acceptable room temperature fracture toughness [1-7]. Recently, several methods, such as arc melting [4], induction skull melting [7] and directional solidification [1, 8-12] were employed to prepare this kind of alloys. Among these processes, directional solidification could improve both room temperature ductility and high temperature strength of Nb-Ti-Si based ultrahigh temperature alloys [8-9]. However, solute segregation always exists in the directionally solidified (DS) specimens. It is well known that heat treatment has significant influences on the morphology, size, volume fraction and distribution of the strengthening phases, and thus a reasonable heat treatment procedure would improve the mechanical properties of the alloys [13]. QU et al [14] demonstrated that the metastable phase Nb3Si in the Nb-10Si (mole fraction, %) alloy could decompose into Nbss + Nb5Si3 completely through eutectoid reaction during heat-treatment at 1 500 °C for 100 h. ZELENITSAS and TSAKIROPOULOS [15] found that the high temperature stable phase β-Nb5Si3 could transform to a more stable phase α-Nb5Si3 according to the precipitation reaction β-Nb5Si3 → α-Nb5Si3 + (Nb,Ti)ss (here (Nb,Ti)ss denotes Nb and Ti solid solution), and the segregation of Ti in both (Nb,Ti)ss and (Nb,Ti)3Si was eliminated. In our previous study [16], the arc-melted Nb-Ti-Si based ultrahigh temperature alloy with the same composition as that in the present work was homogenized at 1 300, 1 400, 1 500 and 1 600 °C for 50 h, respectively, and then aged at 1 100 °C for 50 h. The results indicated that heat-treatment could eliminate both the metastable phases and solute segregation in the microstructure. The (Nb,X)5Si3 precipitates were distributed uniformly in the Nbss substrate and the microhardness values of both Nbss and (Nb,X)5Si3 (here Nbss denotes Nb solid solution, X represents Ti and Hf elements) reached the maxima after heat-treatment at (1 500 °C, 50 h) + (1 100 °C, 50 h). However, the influences of heat-treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the DS specimens have not yet been reported up to now.
To obtain homogenized microstructure and better mechanical properties, the DS specimens prepared with different withdrawing rates were heat-treated at (1 500 °C, 50 h) and (1 500 °C, 50 h + 1 100 °C, 50 h), respectively, and furthermore, the microstructure evolution upon heat-treatment and the corresponding change in microhardness were revealed in the present work.
2 Experimental
The alloy with a nominal composition of Nb-22Ti- 16Si-6Cr-4Hf-3Al-1.5B-0.06Y (mole fraction, %) was integrally directionally solidified at 2 000 °C in an ultrahigh temperature and high vacuum directional solidification furnace. The withdrawing rates (R) were 2.5, 10 and 100 ?m/s, respectively. Specimens with dimensions of 2.5 mm × 5 mm × 15 mm used for heat-treatment experiments were cut from the DS bars using electro discharge machining (EDM). Before these specimens were heat-treated, they were ground using 80–600# sand papers and then cleaned in an ultrasonic acetone bath. Two-step heat-treatment was employed, firstly homogenizing at 1 500 °C for 50 h and subsequently aging at 1 100 °C for 50 h. Heat-treatment was carried out in a high vacuum heat treatment furnace. After the vacuum level was higher than 1.0 × 10-3 Pa, the furnace chamber was heated up, and the temperature rise rate in the furnace chamber was about 20 °C/min. The molecular vacuum pump system did not stop until the temperature reached to 1 000 °C, and then high-purity argon (99.999%, mass fraction) as a protective atmosphere was filled into the furnace chamber. The temperature was further raised to the target temperature subsequently and then kept isothermally for 50 h. After heat-treatment, all specimens were furnace- cooled.
Microstructural analysis was performed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Supra 55) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, INCA Penta FETx3). EDS analysis data for the composition of each constituent phase were given in average values from three analysis sites. In order to reduce the influence of neighboring phases on the analyzing composition, the sampling points of EDS were chosen within phase areas of larger size (both the width and length of the analyzed phase were larger than 5 μm). The Vickers microhardness of the specimens was measured using an HXP-1000TM hardness machine with a load of 0.98 N. In all cases, the Vickers indenter was oriented parallel to the growth direction of the directionally solidified specimens. The microhardness values were the average of at least 10 indentations.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Directionally solidified microstructure
Figure 1 illustrates the microstructure of the Nb-Ti-Si based ultrahigh temperature alloy integrally directionally solidified (DS) with the withdrawing rate of 2.5, 10 and 100 μm/s, respectively. The DS microstructure was composed of gray primary (Nb,X)5Si3 blocks and Nbss + (Nb,X)5Si3 eutectic cells. From the transverse sections of the DS specimens (Figs. 1(a), (b) and (c)), it can be seen that most eutectic cells were nearly round and had an intrinsic lamellar morphology, which was resulted from a coupled growth of Nbss and (Nb,X)5Si3 slices during directional solidification. The interfaces between every two eutectic cells were distinct. In each eutectic cell, both Nbss and (Nb,X)5Si3 slices emanated radially from the cell interior and grew to the cell boundaries in a coupled manner; while in the exterior margin of some eutectic cells, Nbss dendrites became coarser (as shown by the circle in Fig. 1(b)), which might be caused by microsegregation. At the end of the eutectic solidification, the composition of the molten pool deflected the eutectic point, then the regular interfaces of the two phases in eutectic cells were destabilized, and Nbss dendrites became coarser.
From the longitudinal sections of the DS specimens (Figs. 1(a′), (b′), (c′)), it can be seen that both primary (Nb,X)5Si3 rods and Nbss + (Nb,X)5Si3 eutectic cells aligned erectly along the growth direction. The primary (Nb,X)5Si3 rods with regular morphology were very long (some were longer than 1 000 μm), and their side surfaces were usually sharp and straight, as shown by the arrow in Fig. 1(c′). In the center of each eutectic cell, Nbss and (Nb,X)5Si3 plates coupled grew regularly and formed well-aligned lamellar structure; while in the exterior margins of most eutectic cells, the eutectic possessed a continuous network morphology, as pointed out by the circle in Fig. 1(a′), which indicated that the coupled growth of Nbss and (Nb,X)5Si3 was weakened due to a relatively lower solidification rate there. In the intercellular regions, the eutectic was composed of Nbss dendrites and (Nb,X)5Si3 blocks, as shown by the circle in Fig. 1(b′), which indicated that the coupled growth of (Nb,X)5Si3 and Nbss was weakened further, and thus (Nb,X)5Si3 blocks distributed irregularly with coarser Nbss dendrites.
3.2 Microstructure after homogenizing treatment
Figure 2 shows the typical microstructure of the DS specimens after homogenizing treatment (HT) at 1 500 °C for 50 h. It can be seen that the (Nb,X)5Si3 blocks became coarser but distributed more uniformly after this homogenizing treatment. From the transverse sections (Figs. 2(a), (b), (c)) it can be seen that some eutectic cells lost their lamellar morphology after homogenizing treatment, and the interfaces between the retained eutectic cells became blurry, which can be attributed to the diffusion between the every two adjacent eutectic cells. After homogenizing treatment at 1 500 °C for 50 h, the previous emanative and couple-grown morphology of Nbss and (Nb,X)5Si3 slices in the eutectic cells in the DS specimens was weakened obviously, but (Nb,X)5Si3 rods distributed irregularly in the Nbss matrix instead (Fig. 2(c)). As shown in Fig. 2(a), many small aciform precipitates that were probably (Nb,X)5Si3 existed in the Nbss matrix. Some white and fine HfO2 particles appeared in the heat-treated specimens, as shown in Fig. 2, which indicated that some Hf atoms were oxidized during the long time heat-treatment.

Fig. 1 SEM images of both transverse ((a), (b, (c)) and longitudinal ((a′), (b′), (c′)) sections of Nb-Ti-Si based ultrahigh temperature alloy integrally directionally solidified at different withdrawing rates: (a), (a′) 2.5 μm/s; (b), (b′) 10 μm/s; (c), (c′) 100 μm/s
From the longitudinal sections of the DS + HT specimens (Figs. 2(a′), (b′), (c′)), it is seen that (Nb,X)5Si3 plates still distributed erectly along the growth direction for DS process. The width of (Nb,X)5Si3 plates increased but their length decreased obviously, and their side surfaces became smooth and blurry. Some original big (Nb,X)5Si3 blocks in the DS specimens dissolved partially or broke into small ones (as shown by the circle in Fig. 2(a′)), and therefore, the amount of very big (Nb,X)5Si3 blocks decreased, especially in the specimens with higher withdrawing rates after homogenizing treatment. The (Nb,X)5Si3 slices became shorter and wider after homogenizing treatment at 1 500 °C for 50 h, but distributed still regularly, just like unidirectional fibers reinforcing the Nbss matrix (as shown in Fig. 2(c′)). The former continuous network morphology in the exterior margins of eutectic cells in the DS specimens (Figs. 1(a′) and (b′)) was hardly observed after homogenizing treatment at 1 500 °C for 50 h, but (Nb,X)5Si3 slices distributed almost erectly along the growth direction for DS processes instead (Fig. 2(c′)), which suggested that the diffusion between Nbss and adjacent (Nb,X)5Si3 phases caused Ostwald ripening of (Nb,X)5Si3 plates. Furthermore, the former fine (Nb,X)5Si3 slices that did not align along the direction parallel to the growth direction for DS process also coarsened during the homogenizing treatment, as shown by the circle in Fig. 2(b′).
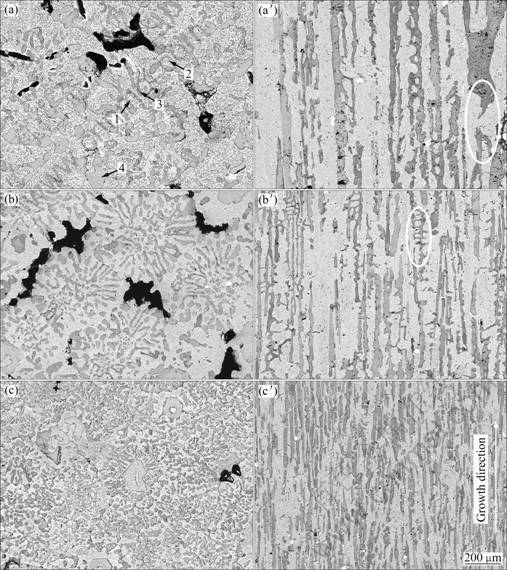
Fig. 2 SEM images of both transverse ((a), (b), (c)) and longitudinal ((a′), (b′), (c′)) sections of DS specimens with different withdrawing rates after homogenizing treatment at 1 500 °C for 50 h: (a), (a′) 2.5 μm/s; (b), (b′) 10 μm/s; (c), (c′) 100 μm/s
3.3 Microstructure after homogenizing and aging treatments
Figure 3 shows the microstructures of the DS specimens after homogenizing treatment at 1 500 °C for 50 h and then aging treatment at 1 100 °C for 50 h (HT + AT). It can be found that the microstructure became further coarser but more uniform after the compound heat-treatments. From the transverse sections of the DS + HT + AT specimens (Figs. 3(a), (b), (c)), it can be seen that a lot of eutectic cells in the DS specimens lost their lamellar morphologies, and the interfaces of eutectic cells were pretty blurry after aging treatment. In the retained eutectic cells, the former short and fine (Nb,X)5Si3 slices were spheroidized sufficiently, and distributed uniformly in the Nbss matrix (Fig. 3(c)). After heat-treatment at (1 500 °C, 50 h) + (1 100 °C, 50 h), more fine aciform precipitates distributed in the Nbss matrix, as shown in Figs. 3(a) and (b).
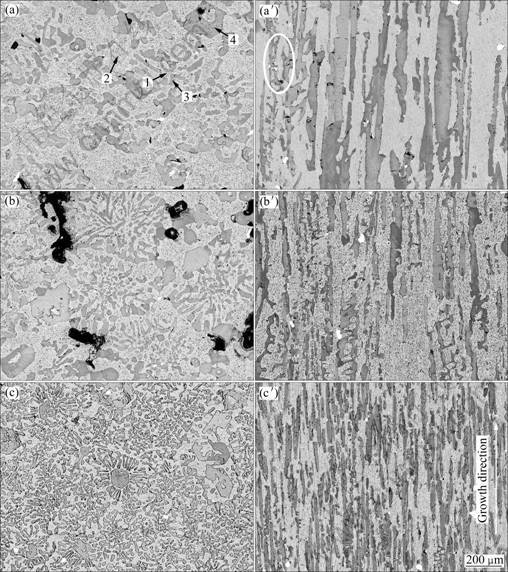
Fig. 3 SEM images of both transverse ((a), (b), (c)) and longitudinal ((a′), (b′), (c′)) sections of DS specimens with different withdrawing rates after homogenizing treatment at 1 500 °C for 50 h and then aging treatment at 1 100 °C for 50 h: (a), (a′) 2.5 μm/s; (b), (b′) 10 μm/s; (c), (c′) 100 μm/s
From the longitudinal sections of the DS + HT + AT specimens (Figs. 3(a′), (b′), (c′)), it can be found that the morphology of former primary (Nb,X)5Si3 blocks became more irregular, and their surfaces became more smooth and blurry after the aging treatment. Furthermore, more original big (Nb,X)5Si3 blocks broke into small ones, and therefore, the number of the typical long primary (Nb,X)5Si3 plates in the DS specimens decreased further after the two-step heat-treatment, as shown in Fig. 3. In the retained eutectic cells, (Nb,X)5Si3 slices coarsened further, but still aligned erectly along the growth direction for DS processes, as shown in Figs. 3(a′), (b′), (c′), thereby forming unidirectionally aligned short-fiber reinforced composite microstructure, as shown in Fig. 3(c′). The network-like eutectic morphology only retained in very limited regions of the specimens with a lower withdrawing rate after the compound heat- treatments, as shown by the circle in Fig. 3(a′).
3.4 Microsegregation in specimens after both homogenizing and aging treatment
From the SEM images of the DS specimens (Fig. 1), it can be noticed that the Nbss in the center of each eutectic cell was obviously brighter than that in the neighbouring intercellular region, which indicated that elemental microsegregation existed in these two regions. Because of relatively low solidification rates during directional solidification, the microstructure did not form simultaneously, but in a sequential order, their compositions and morphologies were obviously different. For example, high freezing temperature elements such as Nb solidified firstly from the melt, while low freezing temperature elements such as Ti and Cr were enriched in the retained melt. The intercellular region was the last crystallizing part during solidification, and therefore, the content of Nb in these regions was lower, while the contents of elements Ti and Cr were higher.
To determine the differences in the concentrations of Nb, Ti, Si, Cr, Hf and Al in Nbss located in the center of eutectic cells from those in intercellular regions, EDS analysis was conducted (see Table 1), and the segregation ratios (see Fig. 4), defined as the concentration of one element in Nbss in the center of a eutectic cell over that in Nbss located in the neighbouring intercellular region, were determined from the measured data. Figure 4 shows that only Nb exhibited positive segregation for its segregation ratio was over 1 and Ti, Si, Cr, Hf and Al showed negative segregation for their segregation ratios were less than 1 under the DS condition. After heat-treatment, the segregation ratio of Nb element had the tendency to decrease toward 1, while the segregation ratios of other elements had the tendency to increase toward 1, which indicated that the solute segregation in the DS specimen was weakened by the heat-treatments.
Table 1 also presents the compositions of both primary (Nb,X)5Si3 blocks and (Nb,X)5Si3 slices in the eutectic cells. It can be seen that the compositions of these two kinds of silicides were close to each other, even under the DS condition, which indicated that the microsegregation in (Nb,X)5Si3 was not so noticeable as that in Nbss. After homogenizing and aging treatments, the composition of (Nb,X)5Si3 in different regions did not change obviously, as shown in Table 1. In addition, as Hf atoms were extremely active at high temperatures, some Hf atoms had been oxidized during the heat-treatment, and therefore, the content of Hf in both Nbss and (Nb,X)5Si3 phases decreased evidently after heat- treatments.
Table 1 Compositions of constituent phases in Figs. 1(a), 2(a) and 3(a)
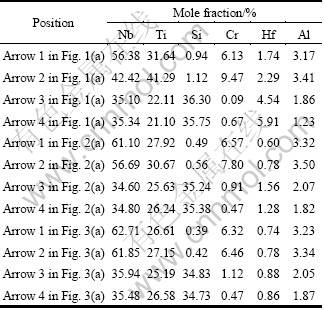
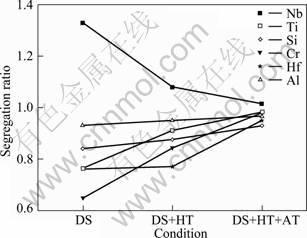
Fig. 4 Segregation ratios of different elements in Nbss in center of eutectic cells over that Nbss located in neighbouring intercellular region after DS, homogenizing and aging treatments respectively
3.5 Microhardness of specimens after homogenizing and aging treatments
Figure 5 shows the variation in microhardness of eutectic cells after homogenizing and aging treatments. It is worth noticing that the microhardness of still visible (Nbss + (Nb,X)5Si3) eutectics in all heat-treated specimens increased evidently. The maximum microhardness of retained eutectic reached HV 1 404.57 in the specimen with the withdrawing rate R = 100 μm/s after heat-treatment at (1 500 °C, 50 h) + (1 100 °C, 50 h), which was 72.8 % higher than that under DS condition. The main reason for the increase in microhardness of eutectic cells after heat-treatment is the microstructural evolution and improved solution strengthening effect in Nbss. After heat-treatment, (Nb,X)5Si3 plates distributed more regularly, and their width became more uniform, providing short fiber reinforcement. More importantly, the difference in compositions of Nbss located either in the center of each eutectic cell or neighbouring intercellular regions was almost eliminated, thereby guaranteeing the deserved solution strengthening effects in Nbss. These changes in the microstructure and composition resulted in increase in the microhardness of visible eutectic cells. In addition, the small and dense aciform precipitates separated out from the Nbss after the heat-treatment could also attribute to the increase in the microhardness of retained eutectic cells.
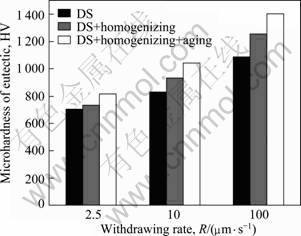
Fig. 5 Average microhardness of retained eutectic cells of DS specimens after homogenizing and aging heat-treatment
4 Conclusions
1) (Nb,X)5Si3 plates become coarser but more uniform after heat-treatment at (1 500 °C, 50 h) and especially (1 500 °C, 50 h + 1 100 °C, 50 h). Primary (Nb,X)5Si3 blocks after the DS specimens break into small ones, and the eutectic cells lose their lamellar morphology gradually in the heat-treatments. (Nb,X)5Si3 plates distribute, regularly along the original DS growth direction, forming short fiber reinforced composite microstructure. Furthermore, many small aciform precipitates form in the Nbss matrix after heat-treatment.
2) The elemental microsegregation in Nbss in the center of eutectic cells over that in the neighbouring intercellular regions is eliminated effectively, and the segregation ratio of each element in Nbss has the tendency to reach 1 after homogenizing and aging treatments.
3) The microhardness of visible retained eutectic cells increases obviously after heat-treatment.
References
[1] GUO Xi-ping, GUAN Ping, DING Xu, ZHANG Jun, KUSABIRAKI K, FU Heng-zhi. Unidirectional solidification of a Nbss/Nb5Si3 in-situ composite [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2005, 475–479: 745-748.
[2] PEREPEZKO J H. The hotter the engine, the better [J]. Science, 2009, 326: 1068–1069.
[3] YANG Ying, BEWLAY B P, CHEN Shuang-lin, CHANG Y A. Application of phase diagram calculations to development of new ultra-high temperature structural materials [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(6): 1396–1404.
[4] TIAN Y X, GUO J T, LIANG Y C, WU C L, ZHOU L Z, YE H Q. Effect of Ho additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb-22Ti-16Si-7Cr-3Al-3Ta-2Hf alloys [J]. International Journal of Material Research, 2007, 98(6): 511–515.
[5] GUO Hai-sheng, GUO Xi-ping, JIA Li-na, WU Xing-jun, DING Xu, GAO Li-mei, REN Jia-song. Effects of compositions and melting methods on the microstructure of multicomponent Nb-based ultrahigh temperature alloys [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2008, 37(7): 1299–1303.
[6] WEI Wen-qing, WANG Hong-wei, GAO Zeng-xin, WEI Zun-jie. Microstructure evolution of as-cast Nb-Ti-C alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(Z2): s440–s443.
[7] TEWARI R, SONG H J, CHATTERJEE A, VASUDEVAN V K. Microstructural characterization of multicomponent Nb-Ti-Si-Cr-Al-X alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006, 37(9): 2669–2682.
[8] BEWLAY B P, LIPSITT H A, JACKSON M R, REEDER W J, SUTLIFF J A. Solidification processing of high temperature intermetallic eutectic-based alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1995, 192-193(2): 534–543.
[9] SEKIDO N, KIMURA Y, MIURA S, WEI F G, MUSHIMA Y. Fracture toughness and high temperature strength of unidirectionally solidified Nb-Si binary and Nb-Ti-Si ternary alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 425(1–2): 223–229.
[10] GUO J T, TIAN Y X, CHENG G M, ZHOU L Z, HE L L, YE H Q. Microstructural characteristics and high temperature compressive properties at 1623 K of a directionally solidified Nb-silicides based in-situ composite [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 470(1–2): 606–609.
[11] SHA J B, HIRAI H, TABARU T, KITAHARA A, UENO H, HANADA S. Mechanical properties of as-cast and directionally solidified Nb-Mo-W-Ti-Si in-situ composites at high temperatures [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2003, 34(1): 85–94.
[12] RIOS C T, MILENKOVIC S, GAMA S, CARAM R. Influence of the growth rate on the microstructure of a Nb-Al-Ni ternary eutectic [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2002, 237–239(1): 90–94.
[13] XIA Peng-cheng, YU Jin-jiang, SUN Xiao-feng, GUAN Heng-rong, HU Zhuang-qi. Influence of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of DZ951 alloy [J]. Rare Metals, 2008, 27(2): 216–222.
[14] QU Shi-yu, HAN Ya-fang, SONG Li-guo. Microstructures and properties of refractory niobium-silicide-based composites [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2005, 475–479: 737–740.
[15] ZELENITSAS K, TSAKIROPOULOS P. Study of the role of Al and Cr additions in the microstructure of Nb-Ti-Si in situ composites [J]. Intermetallics, 2005, 13(2): 1079–1095.
[16] GUO Hai-sheng, GUO Xi-ping. Effects of homogenizing and aging treatments on the microstructure and microhardness of an Nb-silicide based ultrahigh temperature alloy [J]. International Journal of Materials Research, 2010, 101(7): 900–905.
郭海生, 郭喜平
西北工业大学 凝固技术国家重点实验室,西安 710072
摘 要:对定向凝固Nb-Ti-Si基超高温合金分别进行(1 500 °C,50 h)的均匀化处理以及(1 500 °C,50 h + 1 100 °C,50 h)的均匀化+时效热处理。结果表明:热处理后合金组织更加均匀,大尺寸初生(Nb, X)5Si3(X 代表Ti和Hf元素)块逐渐溶解或破碎,并且定向凝固共晶团中的大部分片状铌基固溶体Nbss以及(Nb, X)5Si3变得短、粗;热处理能够有效消除定向凝固态合金中不同区域Nbss内存在的元素偏析,各元素偏析比在热处理后均趋向于1;热处理后,组织的显微硬度增加,最大值达到了HV1 404.57,较定向凝固态合金中共晶组织的显微硬度增加了72.8 %。
关键词:Nb-Ti-Si基超高温合金;均匀化处理;时效处理;组织变化;显微硬度
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project (51071124) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (CX200605) supported by the Doctorate Foundation of Northwestern Polytechnical University, China; Project (20096102110012) supported by a Special Research Fund for Doctoral Disciplines in Colleges and Universities of the Ministry of Education, China
Corresponding author: GUO Xi-ping; Tel: +86-29-88494873; E-mail: xpguo@nwpu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60854-6

