
Theoretical and experimental study of energy transportation and
accumulation in femtosecond laser ablation on metals
TAN Xin-yu(谭新玉)1, 2,ZHANG Duan-ming(张端明)3, MAO Feng(毛 峰)1,
LI Zhi-hua(李智华)3, YI DI(易 迪)2, ZHANG Xiao-zhong(章晓中)2
1. School of Science, China Three Gorges University, Yichang 443002, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Advanced Materials, Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China;
3. School of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
Received 10 August 2009; accepted 15 September 2009
Abstract: The energy transportation and accumulation effect for femtosecond (fs) laser ablation on metal targets were studied using both theoretical and experimental methods. Using finite difference method, numerical simulation of energy transportation characteristics on copper target ablated by femtosecond laser was performed. Energy accumulation effects on metals of silver and copper ablated by an amplified Ti: sapphire femtosecond laser system were then studied experimentally. The simulated results show that the electrons and lattices have different temperature evolvement characteristics in the ablation stage. The electron temperature increases sharply and reaches the maximum in several femtoseconds while it needs thousands of femtoseconds for lattice to reach the maximum temperature. The experimental results show that uniform laser-induced periodic surface structures (PSS) can be formed with the appropriate pulsed numbers and laser energy density. Electron-phonon coupling coefficient plays an important role in PSS formation in different metals. Surface ripples of Cu are more pronounced than those of Au under the same laser energy density.
Key words: femtosecond laser ablation; energy transportation; energy accumulation; periodic surface structure
1 Introduction
Ultrashort pulsed laser processing of materials, especially on metals and dielectrics, has been studied extensively over the last few years for both fundamental researches and industrial applications[1-3]. With the development of ultrafast laser techniques, femtosecond lasers have become an advanced tool for materials processing[4-6]. It is commonly believed that one of the most important advantages of femtosecond laser ablation is that the energy deposited by ultrashort laser pulses does not have enough time to move into the interior of bulk sample. High-power short pulsed laser irradiation of materials involves many physical processes including electron and lattice energy absorbing and transportation, electron-phonon energy coupling and accumulation [6-9].
In this work, we applied femtosecond laser technique to studying surface periodic structures on Ag and Cu theoretically and experimentally. Firstly, the two- temperature model (TTM) is used to discuss the energy transportation in metal target, i.e. Cu, using finite difference method to solve heat flux equations. Then, study on the effect of laser energy accumulation on Cu and Ag is preformed experimentally. The corresponding theoretical analysis of the experimental results is given as well.
2 Effect of energy transportation in femto- second laser irradiation
Normally, pulsed laser beam irradiates on a target surface vertically. During the laser ablation, the energy transport processes can be simplified into a one- dimensional heat problem. Because the optical penetration depth is much shorter than the thermal diffusion depth, the thermal gradient parallel to the interface is less than that perpendicular to the interface by several orders[10]. A sketch of the laser-solid interaction is given in Fig.1.

Fig.1 Sketch of target subjected to femtosecond laser ablation(X refers to spatial coordinate in direction normal to target surface with origin located at surface)
In general, three energy transfer stages can be identified[11] during femtosecond laser irradiation of metals. In the first stage, the free electrons absorb the energy from the laser. This stage is characterized by a lack of thermal equilibrium among the electrons. In the second stage, the electrons reach thermal equilibrium and the density of states can now be represented by the Fermi distribution. However, the electrons and the lattice are still at two different temperatures. In the final stage, the electrons and the lattice reach thermal equilibrium and thermal diffusion carries the energy into the bulk. A two-temperature model, which predicts the non-equilibrium temperature distribution between electrons and lattice during femtosecond laser irradiation of metals[6-9], treats electrons and lattice as two separate subsystems with different temperatures governed by respective equations.
In the two-temperature model, the electron temperature Te and the lattice temperature Tl are subjected to two coupled one-dimensional governing equations:
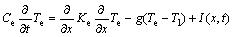 (1)
(1)
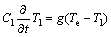 (2)
(2)
where Ce and Cl are the specific heat of electron and lattice, respectively; Ke is the thermal conductivity of electron; g is the electron-phonon coupling coefficient, which shows that the energy transfer from electrons to the lattice is proportional to their temperature difference; and I(x, t) is the laser heating source term which can be described by an exponential law[12]:
 (3)
(3)
where I0(t) is the intensity of the incident pulse (W/cm2); and R and b are the reflectance and the absorption coefficient of the target, respectively.
I0(t) has a nearly Gauss profile with time t in laboratory, so it can be described as[13]
 (4)
(4)
where τ is the pulse width of the laser beam.
Meanwhile, for Eqs.(1) and (2), the initial condition is
Te(x, 0)=Tl(x, 0)=T0 (5)
T(∞, t)=T0 (6)
At x=0, the boundary condition can be expressed as
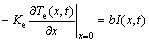 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
where T0=300 K is the initial temperature which is uniform across the target; and δ is the thermal diffusion depth. In low-fluence ablation case, the number density of the hot electrons is low enough so that the energy transfer occurs only within the area characterized by the skin depth δ=1/b[11].
Using Cu as an example, the two-temperature model Eqs.(1) and (2) are solved by the finite difference method. A time step of 1 fs and depth step of 10 nm were used in the simulation. The typical physical parameters of Cu[14] used for numerical simulation are given in Table 1.
Table 1 Typical thermal and optical properties of Cu

Under the initial conditions, Eqs.(5) and (6), and the boundary conditions, Eqs.(7) and (8), Eqs.(1) and (2) are numerically solved by a finite difference scheme.
Fig.2 shows the evolvement of temperatures of electron and lattice of the surface. The electron temperature firstly increases rapidly with the ablation time, and then decreases gradually when it reaches the maximum. In fact, when the electron reaches its maximum, it will remain the maximum for several femtoseconds (insert in Fig.2) because there is still laser energy injection in this period. Meanwhile, the temperature of lattice rises gradually, and subsequently it does not change evidently when it reaches the same value as the temperature of electron.

Fig.2 Time-dependence of electron and lattice temperature of surface for copper target (Insert: amplification of circle part of electron T-t curve during femtosecond laser irradiation)
Fig.3 shows the electron and lattice temperatures of the surface under different laser fluences. For higher fluence, the equilibrium temperatures of electron and lattice become higher accordingly. This reflects that the ultimate temperature of the target will be higher because it absorbs much more energy. Furthermore, the electron-phonon energy coupling time is relatively longer too. This is attributed to the greater kinetic energy of electron in higher laser energy fluence, resulting in more temperature difference between electron and lattice. The result of the evolvement of temperatures of electron and lattice is consistent with result reported in Refs.[15-16].

Fig.3 Time-dependence of electron and lattice temperature of surface for copper target irradiated by 60 fs, 800 nm pulse at different laser energy fluences
3 Experimental study on energy accumulation effect in femtosecond laser ablation
For surface texturing, we used an amplified Ti: sapphire laser system that generates 60 fs laser pulses at a repetition rate of 1 kHz with a central wavelength of 800 nm. The laser beam is focused at normal incidence onto a vertically standing copper sample in air under a pressure of 1.03×105 Pa. Commercial pure bulk copper (99.99%), bulk silver(99.999%) flat plates were used in this experiment. Both samples were polished and ultrasonically cleaned in ethanol before processing. The laser power is tuned by using a half-wave plate nearly at the ablation threshold which is determined as the onset of the surface modification and can be verified microscopically[6].
Fig.4 shows SEM micrographs of structural changes in copper surface induced by 0.8 mJ pulse corresponding to pulse number of 4, 17, 67 and 500, respectively. When N is 4, only nanoscale roughness and nanobranches are observed (Figs.4(a) and 4(a′)). However, when N is 17, apparent periodic surface pattern is observed. The surface ripples are most pronounced among four different values of N. While N is 500, the period ripples disappear and the surface structure is characterized by discontinuous island ripples.

Fig.4 Surface structural features induced by different train of pulses at 0.8 mJ pulse for Cu (N is number of pulse): (a), (a′) N=4; (b), (b′) N=17; (c), (c′) N=67; (d), (d′) N=500
The change in surface periodic structures with increasing pulse number can be attributed to laser energy accumulation effect. The spatial profile of the femtosecond laser beam is of nearly Gaussian type so that the energy density of the ablation center is significantly higher than that of the ablation edge. This leads to a faster transition of surface morphology in this region (Fig.4). In this experiment, multi-pulse irradiation is based on the metal of Cu. When the number of pulse increases to 17, uniformly periodic surface structures (PSS) emerge in the near center part of irradiation area. If more laser pulses are applied as shown in Fig.4(c) and 4(c′), because of redundant energy from latter pulses, periodic ripples closed to irradiation center become inapparent gradually and are preferable to be generated at the edge of ablation area. These results are in agreement with observations reported[17-18].
In order to study the effect of materials on surface configuration, bulk silver (99.999%) and copper sample (99.99%) are ablated under the same laser fluence and pulse. SEM images of surface patterns corresponding to N=17 (Fig.5) show that surface ripples in Cu are more pronounced than in Ag. And the periodic patterns observed on the surface of Cu occupy more space than on Ag.

Fig.5 Surface ripples induced by train of 17 femtosecond laser pulses at 0.8 mJ pulse for Ag (a) and Cu (b)
The difference in the observed surface ripples among different metals can be analyzed based on the two-temperature model[6]. It is known that electron-lattice energy coupling is determined by the electron-phonon coupling coefficient, g. For a larger g, electrons transfer more energy to the adjacent lattice and the overall thermalization between electrons and lattice will be reached sooner. For a weaker electron-phonon coupling with a smaller g, electron diffusion should play a more dominant role. In this case, the periodic electron temperature distribution may vanish before hot electrons transfer energy to the lattice. Therefore, a spatially nonuniform heat distribution should be more pronounced for a metal with a larger g. As the electron-phonon energy coupling coefficients for Cu and Ag are 1.0×1017 and 3.6×1016, respectively, surface ripples in Cu are expected to be more pronounced than in Au under the same laser energy density.
4 Conclusions
1) Using the finite difference method, numerical simulation of energy transportation characteristics of copper ablated by femtosecond laser is studied. It is found that electrons and lattices have different temperature evolvement characteristics in the ablation stage. The electron temperature increases sharply and reaches the maximum in several femtoseconds, while it needs thousands of femtoseconds for lattice to reach the maximal level. For higher fluence, the electron-phonon energy coupling time becomes longer.
2) Periodic surface structures are found in Cu and they are sensitively affected by pulsed number and laser energy density. When the pulse number is relatively lower (N=4), only nanoscale roughness and nanobranches are observed. However, when the N value is 17, apparent periodic surface pattern and the surface ripples are observed. While N=500, the period ripples disappear and the surface structure is characterized by discontinuous island ripples.
3) Spatially nonuniform heat distribution is more pronounced for Cu than Ag when the other conditions are the same, indicating that different metals exhibit different degrees of morphological clearness on their surface patterns. This different degree of morphological clearness can be attributed to the competition of electron-phonon energy coupling and hot electron diffusion mechanism.
References
[1] CHIMMALGI A, CHOI T Y, GRIGOROPOULOS C P. Femtosecond laser aperturless near-field nanomachining of metals assisted by scanning probe microscopy [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 82(8): 1146-1148.
[2] WANG J C, GUO C L. Numerical study of ultrafast dynamics of femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structure formation on noble metals [J]. J Appl Phy, 2007, 102: 0535221-0535227.
[3] MCDONALD J P, MA S W, POLLOCK TRESA M, YALISOVE STEVEN M, JOHNA N. Femtosecond pulsed laser ablation dynamics and ablation morphology of nickel based superalloy CMSX-4 [J]. J Appl Phys, 2008, 103: 093111-093117.
[4] KATSUYA O, YASUAKI O, TASASHI N. Dynamical study of femtosecond-laser-ablated liquid-aluminum nanoparticles using spatiotemporally resolved X-ray-absorption fine-structure spectroscopy [J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2007, 99: 165003-165005.
[5] POVARNITSYN M E, TINA T E, SENTIS M. Material decomposition mechanisms in femtosecond laser interactions with metals [J]. Phys Rev B, 2007, 75: 235414-235418.
[6] GUO C L. Thermal effects in femtosecond laser ablation of metals [J]. Proc of SPIE 2006, 6118: 61180801-61180814.
[7] GUO Z Y, QU S L, HAN Y H. Multi photon fabrication of two dimensional periodic structure by three interfered femtosecond laser pulses on the surface of the silica glass [J]. Opt Commu, 2007, 280: 23-26.
[8] VOROBYEV AY, GUO C L. Femtosecond laser structuring of titanium implantsp [J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2007, 30: 7272-7280.
[9] GUILLERMIN M, GARRELIE F, SANNER N. Single and multi pulse formation of surface structures under static femtosecond irradiation [J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2007, 253: 8075-8079.
[10] TAN X Y, ZHANG D M, LI Z H, GUAN L, LI L. Vaporization effect studying on high-power nanosecond pulsed laser deposition [J]. Physica B, 2005, 358: 86-92.
[11] LI L, ZHANG D M, LI Z H, GUAN L, TAN X Y. Metal absorptivity in femtosecond pulsed laser ablation [J]. Front Phys China, 2007, 2(3): 1-5.
[12] ZHANG D M, TAN X Y, LI Z H, GUAN L, LI L. Thermal regime and effect studying on the ablation process of thin films prepared by nanosecond pulsed laser [J]. Physica B, 2005, 357: 348-355.
[13] HASSAN A F, ElNICKLAWY M M, ElADAWI M K, HEMIDA A A. A general problem of pulse laser heating of a slab [J]. Opt Laser Technol, 1993, 25: 155-162.
[14] EESLEY G L. Generation of nonequilibrium electron and lattice temperature-sin copper by pocosecond laser pulses [J]. Phys Rev B, 1986, 33(4): 2144-2150.
[15] FANG Ran-ran, ZHANG duan-ming, WEI Hua, LI Zhi-hua, YANG Feng-xia, TAN Xin-yu. A unified thermal model of thermophysical effects with pulse width from nanosecond to femtosecond [J]. Eur Phys J Appl Phys, 2008, 42: 229-234.
[16] FANG R R, ZHANG D M, WEI H, LI Z H, YANG F X, TAN X Y. Effect of pulse width and fluence of femtosecond laser on the electron-phonon relaxation time [J]. Chin Phys Lett, 2008, 25(10): 3716-3718.
[17] RALPH W, JENS G. Subwavelength ripple formation induced by tightly focused femtosecond laser radiation [J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2006, 252: 8576-8579.
[18] GUILLERMIN M, GARRELIE F, SANNER N. Single and multi pulse formation of surface structures under static femtosecond irradiation [J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2007, 253: 8075-8079.
Foundation item: Project(10604017) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(Q20091303) supported by the Education Branch of Hubei Province, China
Corresponding author: TAN Xin-yu; Tel: +86-13811242919; E-mail: husttanxin@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60083-2
(Edited by YANG Bing)