基于Sigmoid二次型隶属度函数的改进LMS算法
徐洋,徐松涛,马健,杨永建,肖冰松,向建军
(空军工程大学 航空航天工程学院,陕西 西安, 710038)
摘要:基于Sigmoid函数变步长最小均方(LMS)算法优点是计算量小、收敛速度快且对时变系统的跟踪性能好,但存在些许不足之处,如当误差信号较小时,步长因子变化过快,对于未知系统辨识速度较慢且可控参量过少。为克服上述缺点,更优化该算法性能,通过建立Sigmoid二次型函数,提出一种新的变步长LMS算法,在收敛过程中动态渐进调整步长大小,在获得较小的稳态误差同时,能够更快达到收敛。研究结果表明:改进算法收敛速度要比其他基于S函数改进算法的快;对时变系统跟踪的性能要优于归一化类的LMS算法。本文算法可在增加少量计算量的前提下,较好地克服误差信号与步长因子之间的矛盾,加快收敛速度,并引入新的可控变量,使调控更加灵活。
关键词:Sigmoid二次型函数;最小均方算法;步长因子;系统跟踪;系统辨识
中图分类号:TN911 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)10-3470-07
Improved LMS algorithm based on Sigmoid quadratic membership function
XU Yang, XU Songtao, MA Jian, YANG Yongjian, XIAO Bingsong, XIANG Jianjun
(College of Aeronautics and Astronautics Engineering, Air Force Engineering University, Xi’an 710038, China)
Abstract: The least mean square (LMS) algorithm based on S-function some advantages such as has a small amount of calculation, high convergence rate and good tracking performance for time-varying systems. But when the signal’s error is small, the step factor changes too fast, and system identification is not quick enough and the controllable variables are few. To solve the above shortcomings, an algorithm based on the sigmoid quadratic membership function was put forward. The results show that convergence rate of the algorithm is superior to other improved algorithms based on the S-function, and the tracking performance of the time-varying system is better than the improved normalized LMS algorithms. The algorithm put forward in this paper not only overcomes the contradiction between the signal’s error and step factor, but also makes the algorithm more flexible by introducing new controllable variable.
Key words: Sigmoid quadratic membership function;LMS algorithm;variable step size;system tracking;system identification
自适应信号处理是研究一类结构可变或可调的系统,它通过自身与外界环境的接触来改善自身对信号处理的性能。自适应滤波具有很强的自学习、自跟踪能力且算法简单易于实现,目前广泛应用于通信系统的自适应均衡、系统辩识、噪声干扰的抵消和雷达阵列处理等方面[1-5]。最小均方(least mean square, LMS)算法[6]是一种对滤波器系数依据最小均方误差准则进行不断修正来实现的经典自适应滤波算法。衡量LMS算法优劣的3个重要指标分别为稳态失调、收敛速度以及对时变系统的跟踪能力[7]。普通LMS算法有着收敛速度和稳态误差二者不能同时达到最佳效果的缺 陷[8-9]。为克服该缺点,研究人员不断对变步长LMS算法进行改进,在算法不断收敛过程中动态改变步长[10-17]。在诸多动态改变步长的方法中,文献[13]提出了归一化LMS(NLMS)算法,并验证了其在收敛速度方面要好于传统LMS算法,但该算法存在对于未知系统辨识慢、可调参数少等缺点。文献[14]将误差向量的欧式平方范数作为NLMS调整步长的参数提出了NVSS算法,该算法在收敛速度方面要快于前者,但对于NLMS的缺点并未加以解决。文献[15]在文献[14]的基础上引入遗忘因子和修正系数,提出了λNVSS算法。该算法在系统辨识、收敛速度等方面的性能要好于其他归一化LMS类算法。但其可调变量少且计算量大,对于实时系统并不适合。覃景繁等[16]发现Sigmoid型隶属度函数对于步长因子良好的调节效果,并证明了迭代步长是误差向量的Sigmoid函数。该算法对系统辨识的性能有了很大提高,但在误差向量接近零时,迭代步长不具有缓慢变化的特性,可调参变量过少。文献[17]提出用相邻两项误差的乘积作为S函数的参数,该方法能够降低LMS算法对于噪声的敏感性,较大程度提高收敛速度,但仍未很好解决前一种方法的缺点。本文作者在此基础上提出了一种新的改进型算法,可有效解决上述缺点。该算法不仅在未知系统辨识方面有更快的辨识速度,在收敛速度方面与其他方法相比也更加迅速,并且在引入了1个新的变量后,使得算法的灵活性大大增加。
1 传统LMS算法
基本LMS算法横向滤波器如图1所示,输入信号x(n)经过m-1个延时单元z-1,在n时刻构成1个输入信号矢量X(n):
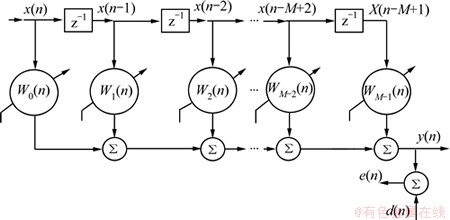
图1 横向自适应滤波器结构框图
Fig.1 Block structure of transversal adaptive filter
基于最速下降法的LMS(最小均方)算法迭代公式可总结如下。
自适应滤波器的输入向量为
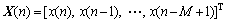 (1)
(1)
自适应滤波器权系数向量为
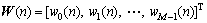 (2)
(2)
相应的滤波器输出信号为
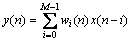 (3)
(3)
误差信号表示为
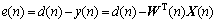 (4)
(4)
步长固定的LMS算法步长迭代方程为
 (5)
(5)
式中:μ是控制收敛速度和稳态误差的参量,即步长因子,此处为常数;e(n)为误差信号,等于输入信号X(n)经过系统后与期望信号d(n)的差值。为保证算法迭代后能够收敛,须满足0<μ<1/λmax;λmax为输入信号矢量X(n)的自相关矩阵Rxx中最大特征值[18]。
2 归一化LMS算法
在传统的LMS算法中,失调直接与抽头输入向量x(n)成正比。因此,当x(n)较大时,LMS滤波器会遇到梯度噪声放大问题。为了解决这个问题,可使用归一化LMS滤波器。
归一化LMS滤波器是最小化干扰原理的一种表现形式,约束条件为
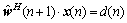 (6)
(6)
式中: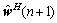 表示第n+1次迭代滤波更新的权向量;x(n)表示抽头输入向量;d(n)为期望信号。
表示第n+1次迭代滤波更新的权向量;x(n)表示抽头输入向量;d(n)为期望信号。
该算法的权系数的迭代公式是为
 (7)
(7)
式中:u(n)为步长参数,它决定着抽头权向量在每步迭代中的更新量,是影响算法收敛速度的关键参数[19-23]。
根据约束条件,得出最终的递归表达式为
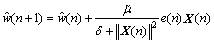 (8)
(8)
式中: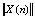 为输入向量的欧式平方范数;
为输入向量的欧式平方范数;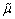 为自适应常数;δ为1个小的常数(为避免输入过小而引起的滤波发散现象)。
为自适应常数;δ为1个小的常数(为避免输入过小而引起的滤波发散现象)。
文献[14]在NLMS算法的基础上提出了NVSS算法,该算法用误差信号的欧式平方范数与自适应常数的乘积来代替式(8)中的输入信号矢量的欧式平方范数:
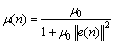 (9)
(9)
文献[15]将式(9)进行如下修改:
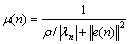 (10)
(10)
式中:ρ>0,为修正系数。λn为第n步迭代的误差系数:
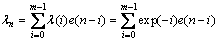 (11)
(11)
λNVSS算法通过引入遗忘因子λ(i),根据当前和过去共m个误差来产生误差系数λn,并通过λn和修正系数ρ来对下一步的迭代步长u(n)产生影响。该方法较之NVSS具有更快的收敛速度,对于时变系统的跟踪性能也更好。但由于该算法计算量过大,可调节参数过少,不适合于工程实践。
3 基于S函数的改进型LMS算法
基于归一化LMS算法在收敛速度、未知系统的辨识方面的不足,覃景繁等人提出了基于S型隶属度函数的变步长LMS(SVSLMS)算法,该算法中步长μ(n)是以误差e(n)为参数的Sigmoid函数(α和β为常数)
 (12)
(12)
由于SVSLMS算法对于噪声信号的过度敏感性,吕强等人又提出VSSLMS算法,该算法在式(12)的基础上进行如下修改:
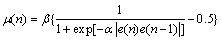 (13)
(13)
通过改进的VSSLMS算法,使得步长只与输入有用目标信号相关,与地杂波噪声信号无关,从而降低了变步长LMS算法对噪声的敏感性,并提高了收敛速度。
以上2种算法中,存在步长因子对于小误差信号变化过快的缺点,为此罗小东又在此基础上进行了改进,提出了改进型SVSLMS(GJSVSLMS)算法:
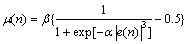 (14)
(14)
改进型SVSLMS算法在时变系统跟踪方面和未知系统辨识方面有明显的提高,但是在小误差时,步长因子变化随较前两者有所提高,但是仍然与理想要求差距很大。本文作者验证了基于e(n)四次方的S函数的性能,如图2所示。由图2可见:当e(n)趋近于零时,步长因子变化较之三次方要慢很多,但是当e(n)还未为零时,步长因子过早地等于零使得其将产生较大的稳态误差。
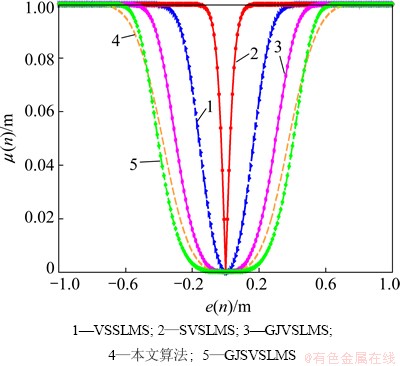
图2 基于S函数算法e(n)-μ(n)变换曲线对比 (α=40, β=0.2, α1=15)
Fig.2 Step size variations of several algorithms in stationary environment
为了克服e(n)-μ(n)之间存在的矛盾,解决算法参数过少而不利于控制的缺陷,本文提出了一种基于Sigmoid二次型隶属度函数的改进算法,其步长因子的表达式如下:
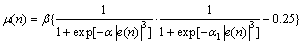 (15)
(15)
本文算法提出的基础:在现有基于S函数的变形LMS算法中,GJSVSLMS的性能要好于其他算法,并且通过文献[24]了解到Sigmoid型函数的乘积构造的隶属的函数的性能要优于一个的性能,为此,本文又引入了基于参数α1的S函数,使得算法在计算量较小时,性能提高。
通过图2对比本文算法与其算法的步长因子的变化特性可以得出:当e(n)较大时,本文算法中μ(n)也较大并且下降速度与GJSVSLMS的几乎相同;当算法进入收敛稳态时,μ(n)随着e(n)的变小而变小,当e(n)接近0时,μ(n)与其他算法相比具有更加缓慢变化的特性。而且本文提出的算法可控变量也比其他算法的多,使得算法更加灵活,易于控制。
4 仿真及性能分析
为了检验本文算法在收敛速度、未知系统的辨识和时变系统跟踪方面的性能,本文构建3种不同的仿真环境,并分别与归一化LMS、基于sigmoid函数改进型的LMS算法进行了对比,通过仿真说明本文算法的性能。
4.1 平稳环境中不同参数时本文算法收敛特性
为了取得最佳效果,本文先对影响算法性能的3个参数进行分析。
设滤波器阶数为2阶,其冲激响应的系数为[0.8, 0.5],输入x(n)是均值为0、方差为1的白噪声。v(n)是均值为0、方差为0.04的白噪声,x(n)与v(n)互不相关,仿真采样数500,均方误差曲线为独立进行1 000次试验取均值的结果。
在图3中,α1和β相同,α分别取2,8,15,30和50,由图3可见:随着α增大,收敛速度不断提高,在本文实验条件下最佳值为50。在图4中,α和α1相同,β分别取0.02,0.05,0.08,0.10和0.20,由图4可见:随着β增大,收敛速度不断提高,在本文实验条件下最佳值为0.20;在图5中,α和β相同,α1分别取30,50,200,300和500。由图3~5可见:随着α1增大,收敛速度不断提高,本文试验条件下取最佳值为500。
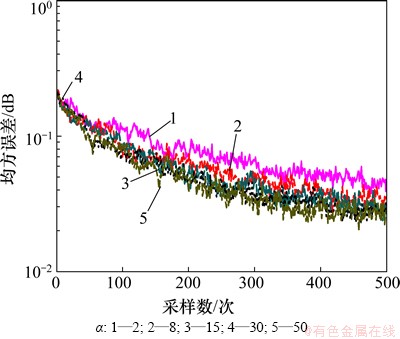
图3 α对均方误差的影响(β=0.3; α1=30)
Fig.3 Influence of α on MSE
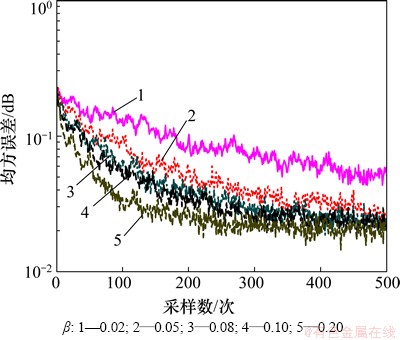
图4 β对均方误差的影响(α1=120; α=140)
Fig.4 Influence of β on MSE
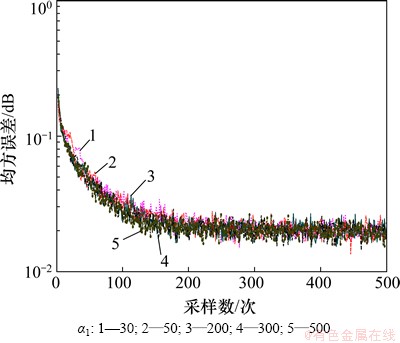
图5 α1对均方误差的影响(β=0.3; α=80)
Fig.5 Influence of α1 on MSE
由于归一化LMS算法的设计参数与基于S函数的LMS算法大不相同,所以,此处先只讨论4种基于S函数的LMS算法的收敛性能,对比各算法,S函数中的参数取为实验中的最佳值[11]。仿真参数设置:α=50,β=0.20,α1=500,采样数500,独立进行1 000次试验取均值。得出这4种算法的学习曲线对比如图6所示。由图6可见:与基于S函数的改进LMS算法相比,本文提出的算法收敛速度最快,收敛时间最短,表现出了本文算法的高效性。
4.2 未知系统参数辨识仿真
现设自适应滤波器阶数与未知系统的阶数均为三阶,它们共同的输入x(n)均值为0、方差为1的白噪声。设v(n)是均值为0、方差为0.02的白噪声,自适应滤波器的期望信号d(n)为x(n)通过冲激响应为[2, 1, -0.5]的系统后与v(n)的和[20]。通过文献[15]和[11]得出:在归一化LMS算法中λNVSS的性能要明显比NVSS和经典NLMS的好,在基于S函数的LMS算法中,GJSVSLMS算法的性能要比其他的基于S函数的改进LMS算法好,当取ρλNVSS=2.9,α=50,β=0.20时,λNVSS和GJSVSLMS算法的性能分别达到最佳。
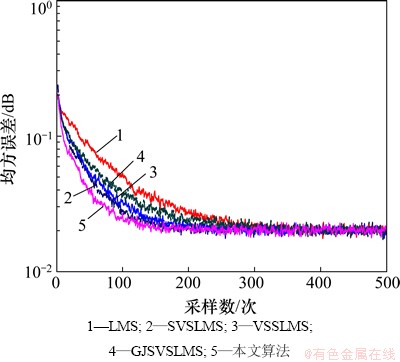
图6 基于S函数算法与本文算法学习曲线对比 (β=0.20; α=50; α1=500)
Fig. 6 MSE of several LMS algorithms based on S-Function in stationary environment
仿真参数设置:ρλNVSS=2.9,α=50,β=0.20,α1=500。采样点数为1 000,独立运行1 000次后取平均,结果如图7~9所示。
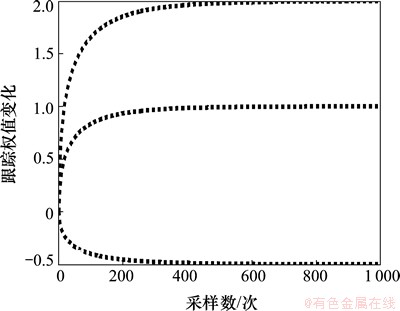
图7 λNVSS算法辨识结果
Fig.7 Simulation of λNVSS-LMS algorithm for system identification
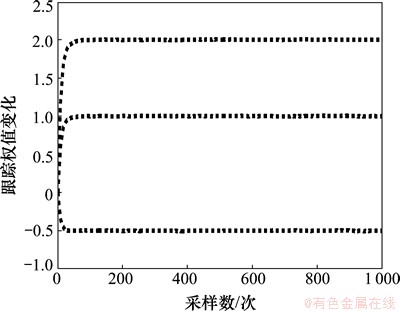
图8 GJSVSLMS算法辨识结果
Fig.8 Simulation of GJSVSLMS-LMS algorithm for system identification
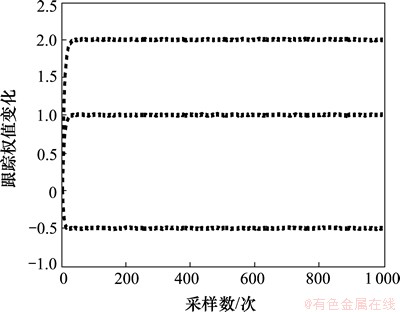
图9 本文算法系统参数辨识结果
Fig.9 Simulation of GJSVSLMS-LMS algorithm for system identification
判断算法的优劣就是看哪种算法辨识的结果最先与系统本身参数相同[25]。从图7~9可以看到:λNVSS算法在迭代接近400次时得出系统自身参数,GJSVSLMS算法在大约迭代60次时得出系统自身参数,而本文提出的基于S函数平方算法在迭代大约25次时就得出系统自身的参数。经对比可知:本文提出的算法在系统辨识方面要优于λNVSS算法和GJSVSLMS算法。本文算法对于权值的变化更加敏感,可以通过2个隶属度函数的乘积更加速修正与实际权向量的误差,使用较少的迭代次数辨识出系统参数。
4.3 跟踪多时变系统性能仿真
在跟踪多时变系统性能比较的仿真中,仍然使用均值为0、方差为1的白噪声信号x(n)作为多时变系统和自适应滤波器的共同输入,自适应滤波器的期望信号d(n)为x(n)经过多时变系统的输出与均值为0,方差为0.04的白噪声信号v(n)之和[11]。整个仿真采样数为1 800,多时变系统的初始冲激响应值为[0.8, 0.5],在第300个采样点时跳变为[0.4,0.2],之后分别在600,900,1 200和1 500点时,在上述2组冲激响应值之间来回跳变,分别采用NVSS算法、λNVSS算法、GJSVSLMS算法和本文所提出的算法进行跟踪性能比较。
仿真参数设置:μNVSS=0.037,ρλNVSS=2.9,α=50,β=0.20,α1=50,采样点数为1500,独立运行500次取平均值,结果如图10所示。
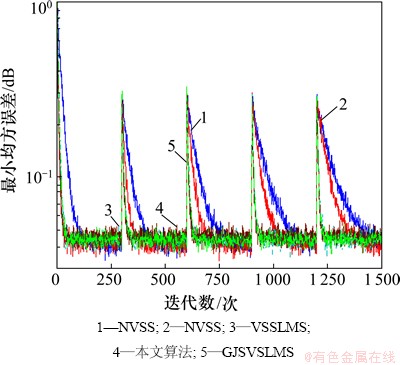
图10 各种算法对多时变系统跟踪性能的比较
Fig.10 Comparison of tracking performance of several algorithms for step change system
从图10可以看出:这5种算法在平稳环境中都有着较好的收敛性能(如0~200点),但在跳变系统中,尤其是多时变系统中,基于S函数的改进LMS算法整体都要好于归一化的LMS算法。
本文仿真中设有5个跳变点,NVSS和λNVSS算法(均属于归一化LMS算法)对于跳变系统有着较强的跟踪能力,但随着跳变次数的增加,其二者的跟踪速度会明显减慢,并且二者速度要明显落后于其他算法。可见,对于S型隶属度函数来说,其对于权值变化的敏感度要远比归一化算法的大。
对比3个基于S函数的改进LMS算法,其收敛速度大致相同,这也说明了Sigmoid函数对于权值变化的高度灵敏性和良好的鲁棒性。
5 结论
1) 提出了一种基于Sigmoid二次型隶属度函数的改进LMS算法,在分析了影响该算法的因子后,与归一化的LMS算法和其他基于S函数的改进LMS算法分别在平稳环境、时变系统环境下进行对比。仿真结果显示,本文算法在收敛速度、系统辨识方面性能都要优于其他基于S函数的改进LMS算法。
2) 在跳变系统下的跟踪性能好于归一化算法的LMS算法。本文算法还引入了1个可控参量,使得控制收敛速度更加灵活。
参考文献:
[1] Kwong R H, Johnston E W, Variable A. Step size LMS algorithm[J]. IEEE Trans on Signal Processing, 1992, 40(7): 1633-1642.
[2] Boulnasr T A, Mayyas K, Robust A. Variable step-size LMS type algorithm: Analysis and simulation[J]. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(3): 631-639.
[3] 魏武, 左天虎, 刘期烈, 等. 卫星通信中一种改进的变补偿LMS均衡算法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 26(1): 42-48.
WEI Wu, ZUO Tianhu, LIU Qilie, et al. A modified variable step size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm in satellite communication[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 26(1): 42-48.
[4] 龙戈农, 童宁宁, 李洪兵, 等. 改进的LMS算法及其在雷达干扰对消系统中的应用[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 11(5): 31-34.
LONG Genong, TONG Ningning, LI Hongbing, et al. A Refrained LMS algorithm and its application in radar jamming cancellation system[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 11(5): 31-34.
[5] Ang W P, Farhang-Boroujeny B. A new class of gradient adaptive step-size LMS algorithms[J]. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing, 2004, 49(4): 805-809.
[6] Bershad N J. Behavior of the ε-normalized LMS algorithm with Gaussian inputs[J]. IEEE Transaction on Acoustics Speech, and Signal Processing, 1987, 35(5): 636-644.
[7] 邹艳碧, 高鹰. 自适应滤波算法综述[J]. 广州大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 1(2): 44-49.
ZOU Yanbi, GAO Ying. Review for an adaptive filtering algorithm[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2003, 1(2): 44-49.
[8] Widrow B, Mccool J M, Larimoer M G, et al. Stationary and no stationary learning characteristics of the LMS adaptive filter[J]. Proc IEEE, 1976, 64(8): 1151-1162.
[9] Gelfand S B, Wei Y, Krogmeier J V. The stability of variable step-size LMS algorithms[J]. IEEE Trans on Signal Processing, 1999, 47(12): 3277-3288.
[10] 谷源涛, 唐昆, 崔慧娟, 等. 新的变步长归一化最小均方算法[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 42(1): 15-18.
GU Yuantao, TANG Kun, CUI Huijuan, et al. A new variable step size normalized LMS algorithm[J]. J Tsinghua Univ (Sci & Tech), 2002, 42(1): 15-18.
[11] 罗小东, 贾振红. 一种新的变步长LMS自适应滤波算法[J]. 电子学报, 2006, 34(6): 1123-1126.
LUO Xiaodong, JIA Zhenhong. A new variable step size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2006, 34(6): 1123-1126.
[12] 高鹰, 谢胜利. 一种变步长LMS自适应滤波算法及分析[J]. 电子学报, 2001, 29(8): 1094-1097.
GAO Ying, XIE Shengli. A variable step size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm and its analysis[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2001, 29(8): 1094-1097.
[13] 王敏强, 胡贵龙, 郑宝玉. 一种新的可变步长LMS自适应滤波算法[J]. 南京邮电学院学报(自然科学版), 2003, 23(4): 12-16.
WANG Minqing, HU Guilong, ZHENG Baoyu. A novel LMS adaptive filter algorithm with variable step size[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2003, 23(4): 12-16.
[14] Anderson P D. Ingram M A. The performance of the least mean squares algorithm combined with spatial smoothing[J]. IEEE Trans on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(4): 1005-1012.
[15] 杨金明, 王伟强. 一种可变步长LMS算法及其性能分析[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 34(3): 61-64.
YANG Jinming, WANG Weiqiang. A variable step size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm and Its analysis[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 34(3): 61-64.
[16] 覃景繁, 韦岗. 基于S型函数的变步长LMS自适应滤波算法[J]. 无线电工程, 1996, 26(4): 44-47.
TAN Jingfan, WEI Gang. A variable step size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm based on S-Function[J]. Radio Engineering, 1996, 26(4): 44-47.
[17] 张园, 王辉. 一种改进的变步长LMS自适应滤波算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2008, 30(7): 60-67.
ZHANG Yuan, WANG Hui. An improved variable step size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm[J]. Mordern Radar, 2008, 30(7): 60-67.
[18] 西蒙·赫金. 自适应滤波器原理[M]. 4版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2003: 183-187.
Haykin S. Adaptive filter theory fourth[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2003: 183-187.
[19] Kwong R H, Johnstone W. A variable step size LMS algorithm[J]. IEEE Trans Signal Processing, 1992, 40(7): 1636-1642.
[20] Gitlin R D, Weinstein S D. The effects of large interference on the tracking capability implemented echo cancellers[J]. IEEE Trans on COM, 1978, 30(6): 833-839.
[21] Tyseer A, Mayyas K. A robust variable step-size LMS type algorithm analysis and simulations[J]. IEEE Trans on Signal Proc, 1997, 45(7); 631-639.
[22] Pazaitls D I, Constantinides A G. A novel kurtosis driven variable step-size adaptive algorithm[J]. IEEE Trans. Signal Processing, 1999, 47(3): 864-872.
[23] Shin H C, Sayed A H, Song W J. Variable step-size NLMS and affine projection algorithms[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(2): 132-135.
[24] 吴晓莉, 林哲辉. MATLAB辅助模糊系统设计[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2002: 82-85.
WU Xiaoli, LIN Zhehui. Fuzzy system design based on MATL-AB[M]. Xi’an: Publishing House of XiDian University, 2002: 82-85.
[25] 李竹, 杨培林, 行小帅. 一种改进步长LMS算法及其在系统辨识中的应用[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2007, 28(7): 1340-1343.
LI Zhu, YANG Peilin, XING Xiaoshuai. An improved variable step size LMS algorithm and its application on system identification[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2007, 28(7): 1340-1343.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2013-09-28;修回日期:2013-12-18
基金项目(Foundation item):陕西省电子信息系统综合集成重点实验室基金资助项目(201107Y03)(Project (201107Y03) supported by Electronic Information System Meta-Synthetic Key Laboratory Project Fund of Shanxi Province)
通信作者:徐洋(1989-),男,吉林吉林人,硕士,从事目标跟踪研究;电话:15619262557;E-mail:mingze0108@126.com